CARBON MONOXIDE Flashcard
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and details about carbon monoxide and its effects on the human body, as discussed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are the physical properties of carbon monoxide that render it difficult for humans to detect?
It is a non-irritating, colorless, odorless gas with no physiological trigger for excess.
How is exogenous carbon monoxide formed?
Exogenous carbon monoxide is formed
during incomplete combustion of carbon (fossil) fuels.
Where might carbon monoxide poisoning occur?
In car exhaust in a confined garage,
older properties with unmaintained heating systems,
blocked chimneys above gas or wood fires,
heating systems after significant storms, and in the presence of other toxins.
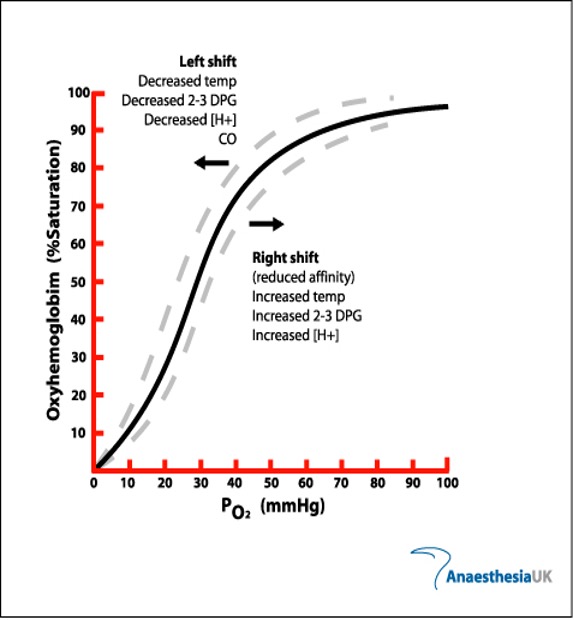
How does CO poisoning cause tissue hypoxia?
CO binds to hemoglobin,
reducing arterial O2 content
and
shifting the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
to the left, preventing oxygen delivery to tissues.
List 4 symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Headache,
dizziness
and nausea,
vomiting,
tiredness
and confusion.
What gives the cherry red appearance to the skin of a CO poisoned individual?
Formation of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)
seen post mortem.
What organs are particularly sensitive to carbon monoxide poisoning?
The heart and brain, as they are oxygen-hungry organs.
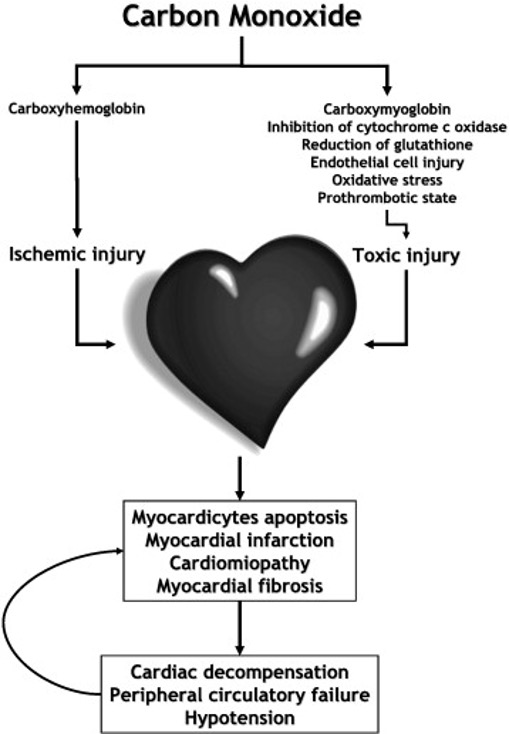
What is the mechanism of toxicity in the heart due to CO?
CO binds to myoglobin,
reducing oxygen supply to mitochondria,
affecting oxidative phosphorylation
and
energy source to myocardium.
What are effects of carbon monoxide poisoning on the heart?
Carboxyhemoglobin formation,
inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase,
endothelial cell injury,
ischemic injury, and myocardial infarction.
Describe the pathophysiology of CO poisoning on the brain.
CO binds to cytochrome oxidase causing dysfunction,
releases NO leading to free radical production
damaging the endothelium,
resulting in oxidative stress.
What diagnostic test confirms carbon monoxide poisoning?
Spectrophotometric analysis of arterial blood for COHb.
Other tests:
PO2
Lactate levels
Kunkel’s test
Why is carbon monoxide poisoning underreported?
Symptoms mimic other conditions
and those susceptible might already
have other health conditions.
What is the normal treatment following suspected/confirmed CO poisoning?
•Atmospheric O2 concentration – COHb half life 250 minutes
•100% oxygen given through a non-rebreather mask (NRM)
at normal atmospheric pressure
– COHb half life 50 minutes
What further treatment improves recovery from CO poisoning?
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment
which reduces COHb half life to 22 minutes
and
increases dissolved oxygen in plasma.
List 3 individuals for whom hyperbaric treatment might be required.
Pregnant individuals,
those with pre-existing heart conditions,
and
individuals who have lost consciousness.
Why might CO poisoning be particularly detrimental to the fetus?
Fetuses have greater sensitivity to CO,
and
CO levels in the fetus exceed those in adults,
which exacerbates tissue hypoxia.
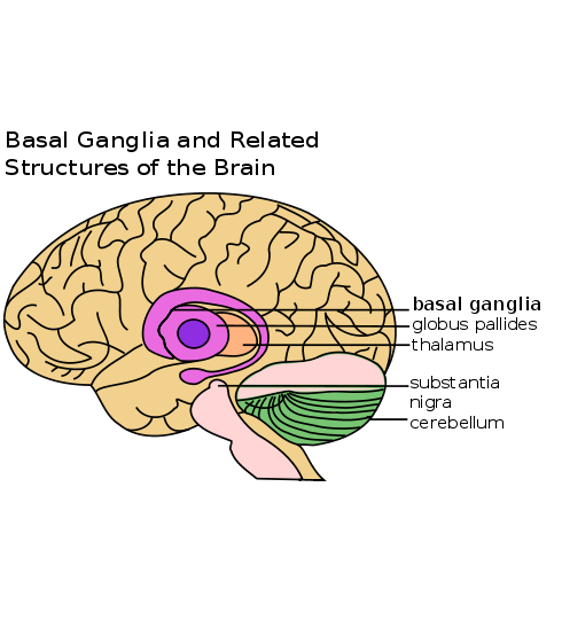
What causes delayed development of neurological symptoms after CO poisoning?
- Damage occurs in brain regions like the basal ganglia, cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, and substantia nigra.
- Nitric oxide prevents white blood cell (leucocyte)
- Reperfusion leads to leucocyte adhesion
What is the carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) in the body during CO poisoning?
A the complex formed
when carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin,
impairing oxygen transport.
How long can carboxyhemoglobin remain in the body after CO exposure ceases?
COHb levels
fall slower in the fetus than in adults after CO exposure.