16 Kinetics II
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the order of reaction of a reactant?
How the reactants concentration affects the rate.
What are the orders of these reactants?
When [X] doubles, the rate is multiplied by 4.
When [X] doubles, the rate is doubled.
When [X] doubles, the rate stays the same.
When [X] triples, the rate is multiplied by 9
1) second order
2) first order
3) zero order
4) second order
What is the overall order of reaction?
The overall sum of all of the orders of the reactants.
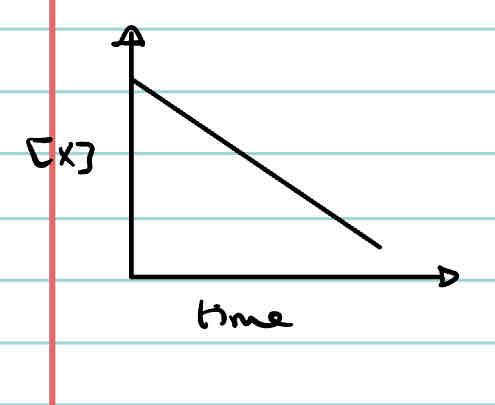
What is the concentration- time graph of a 0 order reaction?
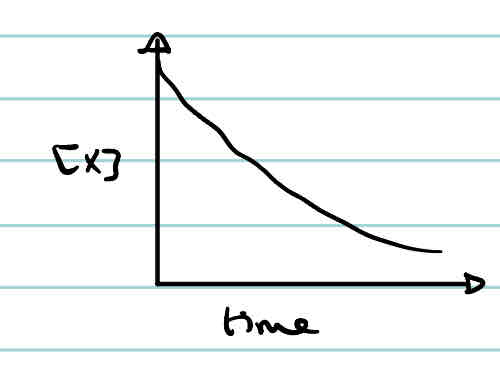
What is the concentration-time graph of a first order reaction?
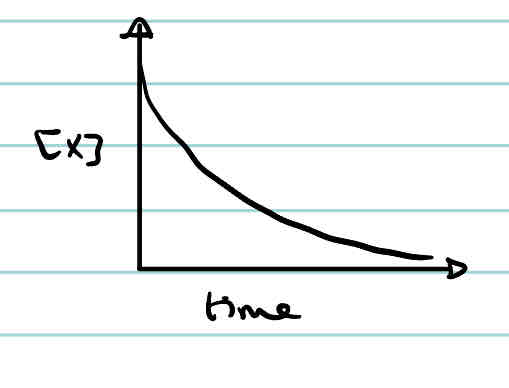
What is the concentration-time graph of a third order reactant?
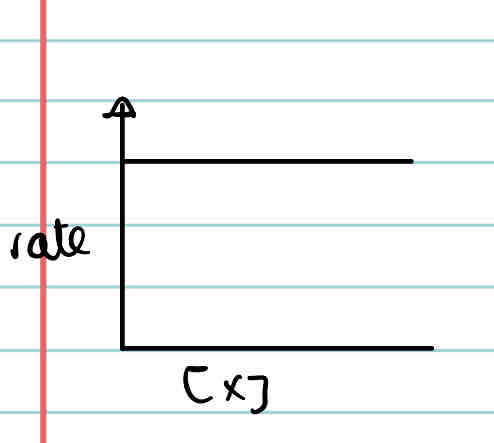
What is the rate-concentration graph of a 0 order reaction?
What is the rate-concentration graph of a first order reactant?
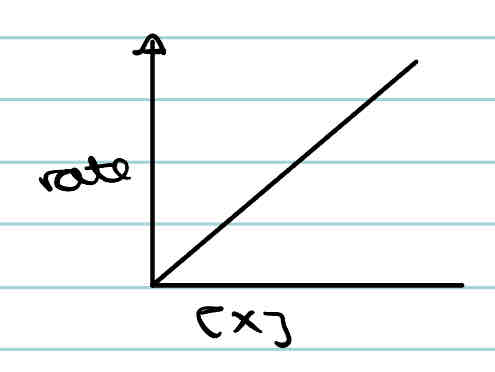
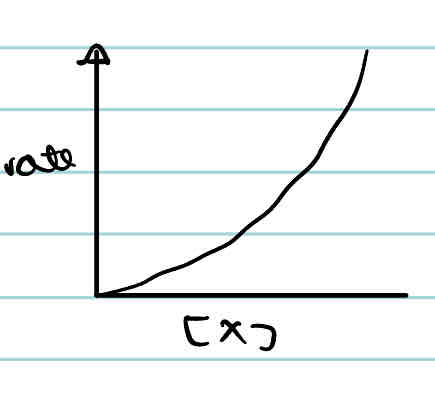
What is the rate-concentration graph of a second order reactant?
How can half lives be used to find if a reactant is first order?
Draw lines on a concentration-time graph where the concentration is halved repeatedly, eg, at 4moldm, 2moldm and 1moldm. If it is a first order reactant, the time will be constant.
What is the rate equation for general equation A + B → C + D
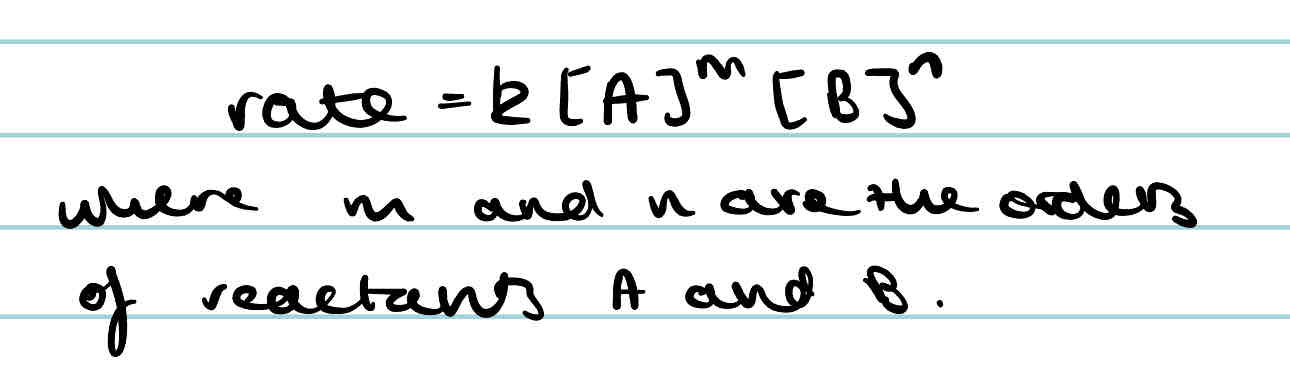
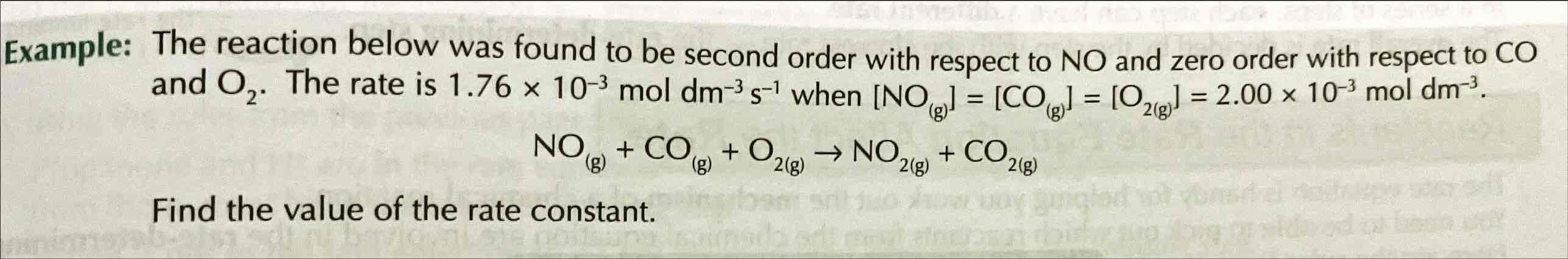
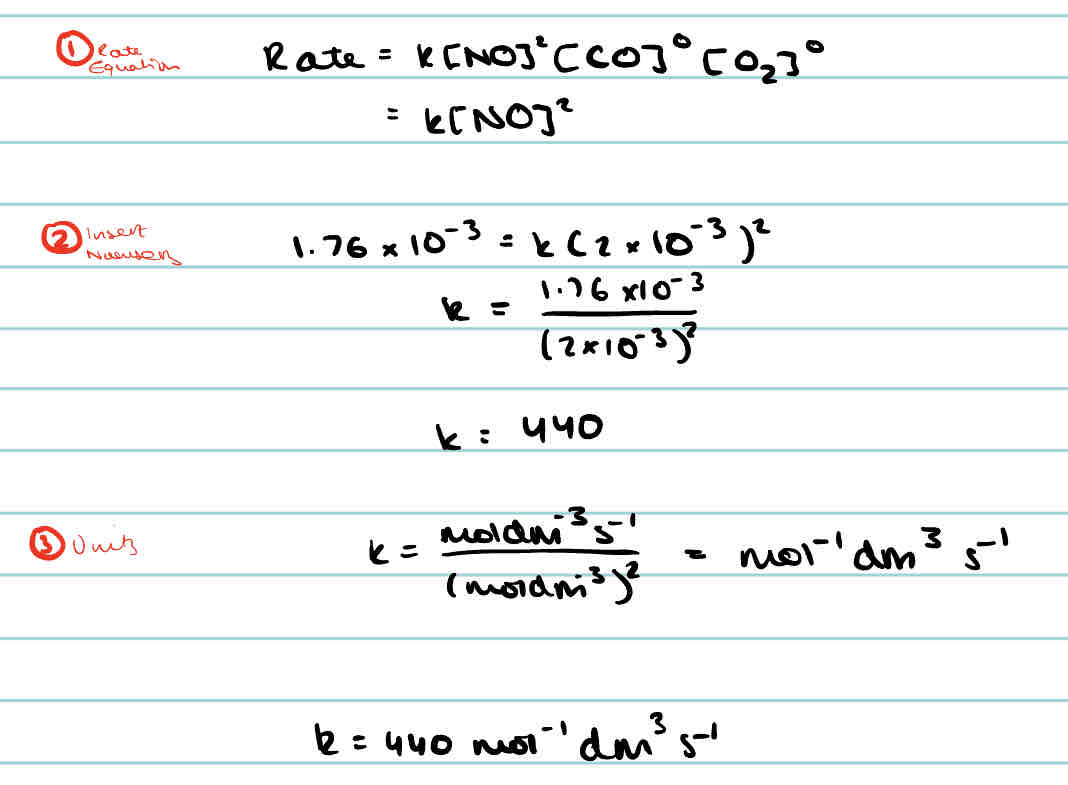
What will change the rate constant of a reaction?
Changing the temperature that the reaction occurs at.
What is the rate-determining step?
The slowest step of a multi-step reaction.
How can the rate equation be predicted from the rate-determining step?
The order of a reaction with respect to a reactant shows the number of molecules of that reactant involved in the rate-determining step.
What will the rate equation for an Sn2 reaction be like?
It will include both reactants, eg. In the nucleophilic substitution reaction between bromoethane and hydroxide ions, the rate equation will have both bromoethane and hydroxide ions.
How does the rate equation show that tertiary halogenoalkanes use Sn1?
The rate is only dependent on the concentration of the haloalkane as only the haloalkane is involved in the rds - the formation of the carbocation.

Here is the Arrhenius equation. What are the variables?
k= rate constant
A= another constant
Ea= activation energy
T = temperature (K)
R = gas constant (8.31)
What are the axes of an Arrhenius plot?
1/T and lnK
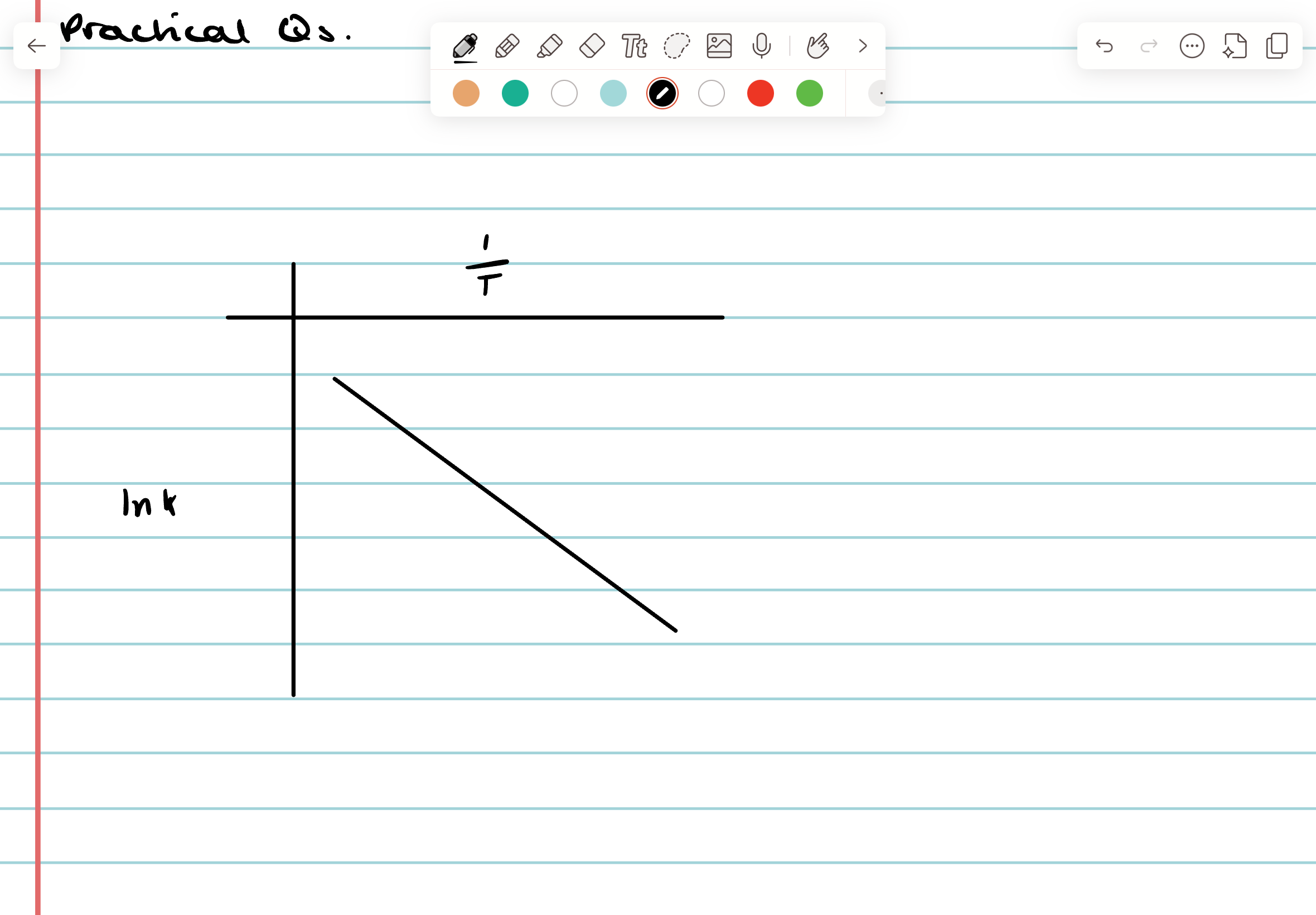
How can an Arrhenius plot be used?
Its gradient is equal to -Ea/R (where R is the gas constant 8.31).
Why can ln1/t be used instead of lnk in an Arrhenius plot?
Rate is proportional to 1/time.
How can heterogenous catalysts be poisoned?
A poison is a substance that clings to the catalyst surface more strongly than the reactants. This prevents the catalyst from being involved in the reaction.