Understanding Disordered Eating and Eating Disorders (lecture 23)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the difference between disordered eating and an eating disorder?
Disordered eating refers to a variety of abnormal or atypical eating behaviors used to reduce weight, while an eating disorder is a psychiatric condition involving extreme body dissatisfaction and long-term harmful eating patterns.
What are some examples of disordered eating behaviors?
Chronic overeating, chronic dieting, food restriction, purging, binge eating, excessive or rigid exercise routines, obsessive calorie counting, and anxiety about certain foods.
What is anorexia nervosa?
An eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight and a distorted body image, leading to severe food restriction.
What is bulimia nervosa?
An eating disorder marked by cycles of binge eating followed by purging to prevent weight gain.
What is binge eating disorder?
An eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food, often quickly and to the point of discomfort.
What is the Female Athlete Triad?
A condition in female athletes that includes disordered eating, amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), and osteoporosis.
What is seasonal affective disorder in relation to eating?
A type of depression that occurs at a specific time of year, which can influence eating habits and behaviors.
What are cognitive factors that influence food intake?
Conscious control, conditioning, and beliefs.
What brain mechanisms are involved in eating?
Signal sensory modulation and reward and appetite systems.
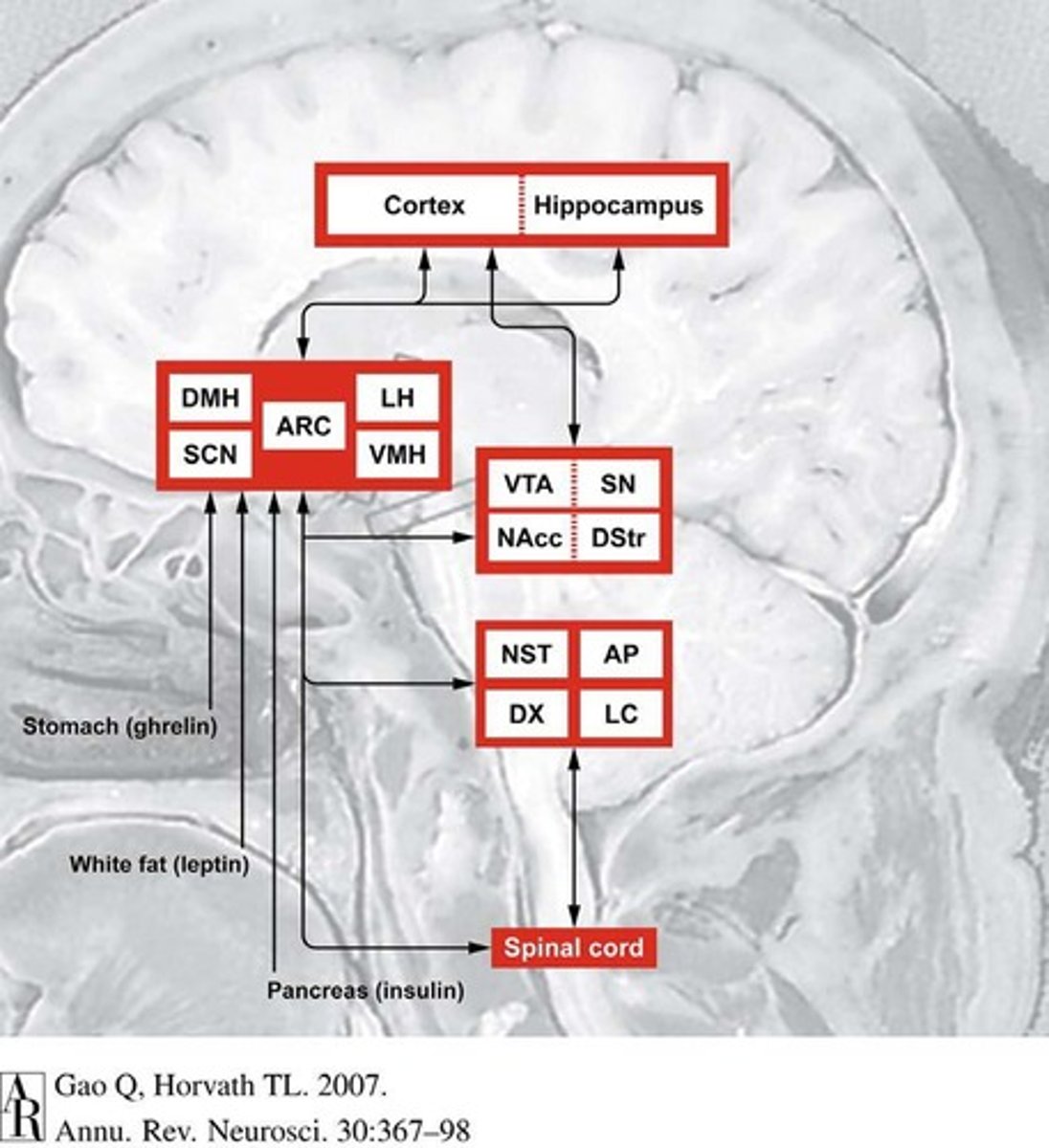
What sensory factors affect food intake?
Taste, smell, texture, and sight.
What are some effects of sensory factors on eating?
Palatability, concentration, availability, and aversion.
What signals are associated with satiety and hunger?
Adipose tissue, gut hormones/nerves, distension, and sensors.
How does portion size affect food intake?
The more food placed on a person's plate, the more they tend to eat.
What is a common misconception about body image in disordered eating?
Individuals may feel overweight even if they fall within a healthy weight range.
What role does community play in healthy nutrition?
Healthy nutrition is supported by having a community.
What is the DSM-5's definition of eating disorders?
A group of disorders involving disturbed body image and eating/weight loss behaviors that cause severe distress and impairment to quality of life.
What distinguishes disordered eating from an eating disorder?
The degree of severity and the impact on the individual's quality of life.
What is a rigid approach to eating?
Only eating certain foods, having inflexible meal times, or refusing to eat in restaurants or outside one's home.
What is the significance of self-worth in disordered eating?
Self-worth or self-esteem may be based highly or exclusively on body shape and weight.
What are common symptoms of chronic dieting?
Preoccupation with food, weight, and calories; strict dieting; excessive exercise; loss of concentration; mood swings; increased criticism of body shape.
What health risks are associated with chronic dieting?
Poor nutrient and energy intakes; low vitamin and mineral intake; decreased energy expenditure due to a reduced basal metabolic rate (BMR); decreased ability to exercise; increased risk of eating disorders.
What factors contribute to the development of eating disorders?
Family environment; unrealistic media images; sociocultural values; personality traits; genetic and biological factors.
What are some types of eating disorders?
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and eating disorders not otherwise specified.
Why are eating disorders considered chronic psychiatric disorders?
They are believed to be multifactorial disorders or of unknown etiology.
What is necessary to determine if someone has an eating disorder?
A definition for 'normal' eating is required.
What percentage of high school women diet regularly?
90%.
What is the mortality rate of anorexia compared to other psychiatric diagnoses?
Anorexia has the highest mortality rate of any psychiatric diagnosis.
What percentage of college students in the U.S. are suffering from an eating disorder?
17-30%.
What are the symptoms of binge eating disorder?
Often overweight; a sense of lack of control during binging; chaotic eating behaviors; negative self-esteem; often associated with depression, substance abuse, and anxiety disorders.
What health risks are associated with binge eating disorder?
Increased risk of overweight or obesity; foods eaten during binging are often high in fat and sugar; stress leads to psychological effects.
What role does physiological and environmental stress play in binge eating?
It plays a crucial role in animal models of binge eating.
What is seasonal affective disorder (SAD)?
A mood disorder characterized by predictable onset of depression in fall/winter with spontaneous remissions in spring/summer.
What typical symptoms do patients with SAD exhibit?
Marked craving for high-carbohydrate/high-fat foods and significant weight gain during winter depressive episodes.
How is SAD related to obesity?
SAD has been described as a naturally reversible form of obesity.
What are the three components of the Female Athlete Triad?
1) Disordered eating, 2) Amenorrhea, 3) Osteoporosis.
Which sports are young female athletes particularly at risk for developing the Female Athlete Triad?
Gymnastics, ballet, figure skating, distance running, and other similar sports.
What is the major difference between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa?
Anorexia nervosa patients are underweight, while bulimia nervosa patients are typically of normal weight.
What characterizes bulimia nervosa?
Binge eating followed by purging.
What is binge eating?
Eating a large amount of food in a short period of time.
What are some methods of purging in bulimia nervosa?
Vomiting, laxatives, fasting, excessive exercise, or other means.
What percentage of women are affected by bulimia nervosa?
1 to 4%.
What is the male-female ratio for bulimia nervosa?
Between 1:6 and 1:10.
What is the mortality rate of bulimia patients within 10 years of diagnosis?
1% die from complications.
What are the symptoms of bulimia nervosa?
Recurrent binge eating, inappropriate compensatory behaviors, binge eating at least twice a week for three months, and negative body image.
What defines anorexia nervosa?
A medical disorder where unhealthful behaviors are used to maintain a body weight less than 85% of expected weight.
What are the symptoms of anorexia nervosa?
Restrictive eating practices, self-starvation, intense fear of weight gain, amenorrhea, and unhealthful body image.
What are some health risks associated with anorexia nervosa?
Electrolyte imbalance, cardiovascular problems, gastrointestinal problems, bone problems, hypothermia, and sleep disturbances.
What health risks are associated with bulimia nervosa?
Electrolyte imbalance, gastrointestinal problems, dental problems, calluses on hands, and swelling of cheeks or jaw.
What is a key component of successful treatment for eating disorders?
A team approach involving the patient, physician, nutritional counselors, and psychiatric counselors.
What constitutes a healthy diet?
The right amount of energy to maintain weight, proper balance of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, plenty of water, and sufficient vitamins and minerals.