4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Cell Signaling and Communication | AP Biology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Signaling pathways can provide which list?
What proteins/enzymes/molecules are activators and which are inhibitors in the pathway. They also indicate if a gene transcription is repressed or induced. The molecules that act as second messengers (like cAMP) are also defined.
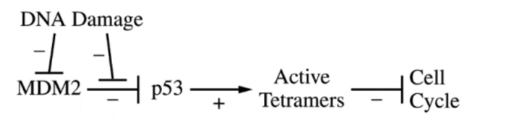
What do the - signs mean? How about the + signs?
- is inhibition, + is activation of molecule/cellular process.
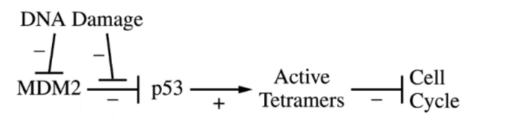
What happens if DNA Damage doesn’t occur?
DNA Damage inhibits MDM2, but since it isn’t present, MDM2 isn’t inhibited, and p53 cannot form
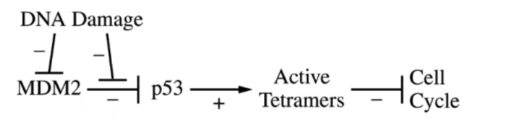
What happens if MDM2 was inhibited?
DNA Damage inhibits MDM2, allowing p53 to activate. P53 activates active tetramers, which inhibits the cell cycle.
Signaling usually requires secretion of ____
ligand (chemical signal) from initiating cell that travels to target cell
Only cell with correct receptor protein will ___
react to the signal molecule. The ligand and the receptor have complementary shape.
What happens in Reception of the cell signaling pathway?
The ligand binds to the receptor. Receptor undergoes conformational change, which transmits signal inside of cell.
What happens in Transduction of the cell signaling pathway?
Signal moves through cell membrane, to nucleus using phosphorylation of a series of proteins. Signal is transferred and amplified.
What is phosphorylation?
Adding a phosphate
Define Cell to Cell contact.
Cells make physical/direct contact between signal and receptor proteins embedded on the cell membranes of the cells to transmit signals and initiate cell response.
Define Paracrine Signaling
Ligands (released by communicating cells) travel short distances through diffusion/bloodstream to get to the target.
Advantage of Cell to cell contact?
Fastest at transmitting signal
Describe traditional cell to cell contact.
The originating cell expresses a ligand on the cell membrane, and the target cell expresses a receptor protein on the cell membrane.
An example of a ligand.
Remember the Bioluminescence TedTalk? An autoinducer is a ligand.
Define Gap Junctions.
In animal cells, cell membranes fuse between cells to allow signals to quickly diffuse and initiate cell response. Juxtacrine.
Define Plasmodesmata.
In plant cells, pores open between the two cells’ membranes, allowing signals to quickly diffuse and initiate cell response. Juxtacrine.
Define Membrane-bound/transmembrane receptors
Hydrophilic (polar, water-soluble, charged) ligands bind to membrane-embedded receptors. Ligand can NOT cross membrane. The signal is amplified and moved from membrane to nucleus using transduction.
Process of Signal transduction?
Ligand binds to the membrane-bound receptor, causing shape change, which transmits the signal into the cell. A second messenger (like cAMP) is activated, phosphorylates the next protein in the chain to activate it. Process cycles until last protein in pathway (transcription factor) enters nucleus and initiates cell response.
How does the cell respond to signal transduction?
Transduction pathways initiate gene transcription, synthesizing proteins that cause the cell to respond to the signal.
Which of the following lists are an example of cellular responses?
All of the following
“Auto” in autocrine means what?
self
“Juxta” in juxtacrine means what?
beside, next to, touching
“Para” in paracrine means what?
nearby
“Endo” in endocrine means what?
within
Plasmodesmata (and Gap Junctions) is an example of which type of cell communication?
Juxtacrine
Cancer cells releasing their own growth hormone is an example of what type of cell communication?
Autocrine
Quorum sensing bacteria is an example of which type of cell communication?
Paracrine
Pancreas releases insulin when blood sugar increases. Insulin signals liver cells to absorb glucose to be converted into glycogen. This is an example of what type of cell communication?
Endocrine
What is a ligand?
Signaling Molecules that activate receptors
A cell is infected by a virus, and signals itself to do apoptosis (planned cell death), in order to kill the cell and the virus.
Autocrine
Growth factors secreted by nearby cells to signal each other to grow.
Paracrine
What is quorum sensing?
When bacteria determine population size to perform a collective action (glowing, attacking something).
What is synaptic signaling?
Nerve cells in animals use paracrine communication: Electrical impulse in nerve cell signals to release neurotransmitters into a gap between neurons (synapse), which stimulates the target cell.
Define endocrine communication.
Cells communicate with far away cells by secreting ligands into bodily fluids like blood so they can be carried throughout the body.
Hormones like insulin (large protein secreted by pancreas cells to regulate blood sugar) and ethylene (small gas secreted by plants to ripen fruit) are used for long distance communication.
Endocrine
Define Intracellular receptors.
Found in cytoplasm or nucleus: Complex travels directly to nucleus, bypassing transduction. Lipid soluble ligand (hydrophobic, nonpolar, small, fat-soluble) such as hormones (testosterone, estrogen) diffuse across the membrane and bind to the receptor inside the cell.
What happens in cell Response of signal pathway?
Signal triggers response in cell.
Type of receptor?:
G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) works with G protein.
Ligand binds to GPCR, GPCR uses GTP (energy molecule) to activate G protein inside of cell
Activate another protein, leads to cellular response
Transmembrane/Membrane-bound
Type of receptor?:
Ligand-gated ion channels are gated receptors, only correct ligand opens them.
Na+ or Ca+ can pass through the cell membrane, creating an electrical signal that goes through receiving cell
Transmembrane/Membrane-bound
Define Protein Kinase.
Enzyme that phosphorylates proteins to change structures.
Kinase takes phosphate from ATP to another kinase to change structure/activate.
Phosphorylation cascade: enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation domino effect (with each step, effects are amplified)
How does dephosphorylation occur to reset a protein to its inactive form so it can be reused?
Enzymes called Protein Phosphatases.
What are second messengers?
Small, non-protein molecules that are after the first messenger (ligand). They can activate multiple protein kinases.
Which of the following is NOT an example of a second messenger?
ATP
How is cAMP (a second messenger) used with GPCRs?
GPCR receives ligand, which activates the intracellular G protein and the membrane-bound enzyme adenylyl cyclase is then activated.
Adenylyl cyclase converts ATP to cAMP so that protein kinase can activate. This step can happen multiple times to amplify the signal.
Many signaling pathways regulate protein synthesis by _____.
acting as transcription factors, which can turn genes “on” (used to make specific protein) and “off” in the nucleus.
What happens if more receptors are added?
It enhances/amplifies the response.
Protein Kinases vs. Protein Phosphatases?
Kinase add phosphate groups, which activates. Phosphatases remove phosphate groups to deactivate.
Feedback inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
Hormone
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
Signal Cascade
An entire series of reactions which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound.
Type I diabetes
Insulin isn’t produced, so receptors are not activated. Glucose transport proteins don’t open, and blood sugar levels are high
Type II diabetes
Insulin is produced, but receptors don’t respond, so glucose transport proteins don’t open and blood sugar levels increase