A&P - Test 4 Review
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
Which areas of the brain have an out layer of grey matter?
Cerebrum and cerebellum - this forms the cortex of both of these
Match the following
The middle primary brain vesicle, the mesencephalon, gives rise to which adult brain structure?
medulla oblongata
cerebrum
midbrain
diencephalon
midbrain
What type of cells line the ventricles of the brain?
ependymal cells
neurons
epithelial cells
astrocytes
ependymal cells
Which of these would you NOT find in the cerebral cortex?
interneurons
cell bodies
dendrites
fiber tracts
fiber tracts
What anatomical landmark of the cerebral cortex separates primary motor areas from somatosensory areas?
a) central sulcus
b) longitudinal fissure
c) Transverse fissure
d) Lateral sulcus
a) central sulcus
The anteriormost area of the cerebrum is associated with which distinctive function
a) Perception of the visual stimulus
b) Applying intellect and cognition
c) conscious control of skeletal muscle movement
d) understanding written and spoken language
b) Applying intellect and cognition
Match the following:
Match the following:
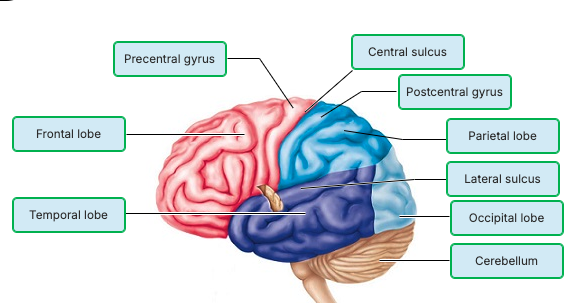
Which part of the brain is the "executive suite" that controls conscious brain activity?
brain stem
diencephalon
cerebellum
cerebral cortex
cerebral cortex.
_______ Controls basic life functions like breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
Brain stem
_________ Includes structures like the thalamus and hypothalamus; involved in sensory relay and autonomic functions
Diencephalon
________ Coordinates muscle movements and balance, but not conscious thought.
Cerebellum
Which type of white matter fiber tract connects the cerebrum to lower centers, like the spinal cord?
association fibers
commissures
corpus callosum
projection fibers
projection fibers
______ fibers either enter the cerebral cortex from lower brain or cord centers or descend from the cortex to lower areas.
Projection
_______ fibers – Connect different parts within the same hemisphere of the brain.
Association
_________ – Connect corresponding areas between the two hemispheres (e.g., the corpus callosum).
Commissures
______ _______ – The largest commissure, specifically connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres
Corpus callosum
Match the following:
_______ Auditory area.
______ Primary somatosensory cortex.
______ Primary (somatic) motor cortex.
______Motor speech (Broca's) area.
______ Premotor cortex.
______ Visual area.
______ Gustatory (taste) area.
_______ Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning.
Word bank: Insula, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe, frontal lobe
Temporal lobe: Auditory area.
Parietal lobe: Primary somatosensory cortex.
Frontal lobe: Primary (somatic) motor cortex.
Frontal lobe: Motor speech (Broca's) area.
Frontal lobe: Premotor cortex.
Occipital lobe: Visual area.
Insula: Gustatory (taste) area.
Frontal lobe: Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning
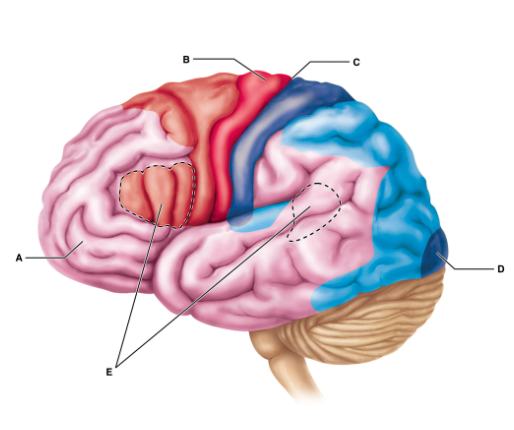
Which of the following is the best description of the function of region B?
Region B includes neurons whose axons carry motor commands from the cerebrum.
Region B coordinates the movement of several muscle groups into complex tasks.
Region B is responsible for learning, working memory, judgement, reasoning, persistence, and planning.
Region B contains neurons receiving somatosensory input from the thalamus.
Region B includes neurons whose axons carry motor commands from the cerebrum.
Broca's area ________.
controls voluntary movements of the eyes
is usually found only in the right hemisphere
serves the recognition of complex objects
is considered a motor speech area
is considered a motor speech area
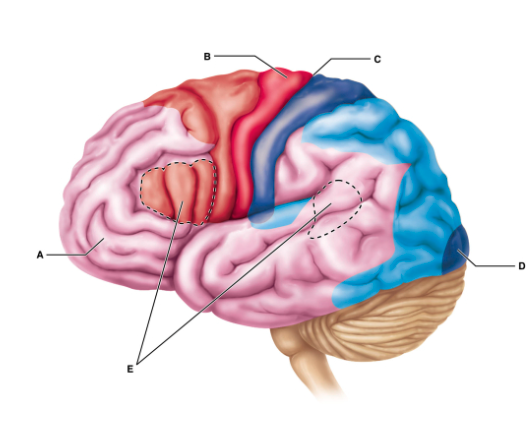
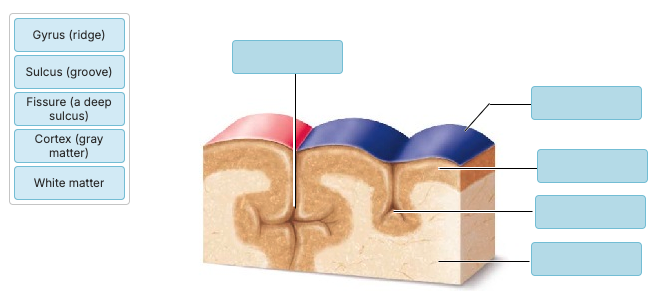
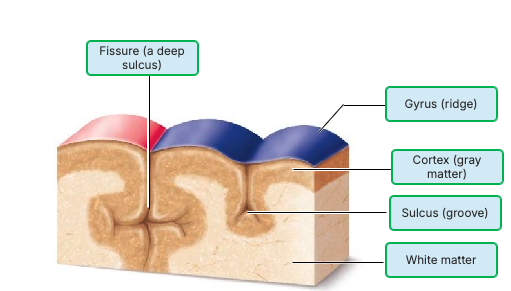
What is the groove indicated by C?
central sulcus
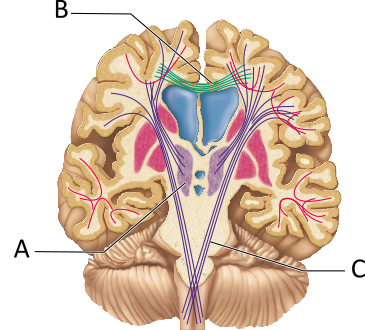
The fibers indicated by B are most associated with which structure(s)?
corpus callosum
The _______ ______ is the most prominent example of tracts that connect the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
corpus callosum
Which of the following is true of the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain?
Nearly the entire surface of the cerebral hemispheres is marked by shallow grooves called gyri.
Nearly the entire surface of the cerebral hemispheres is marked by elevated ridges called sulci.
The longitudinal fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres from the cerebellum.
The cerebral hemispheres account for about 83% of total brain mass.
The cerebral hemispheres account for about 83% of total brain mass.
Which of the following brain structures is paired with an inaccurate description of its function?
a) Hypothalamus - control center for both autonomic nervous system and endocrine system
b) Epithalamus - regulation of sleep-wake cycles
c) Thalamus - relay of motor information form the cerebral cortex to the brain stem
d) Pituitary gland - release of hormones
c) Thalamus - relay of motor information form the cerebral cortex to the brain stem
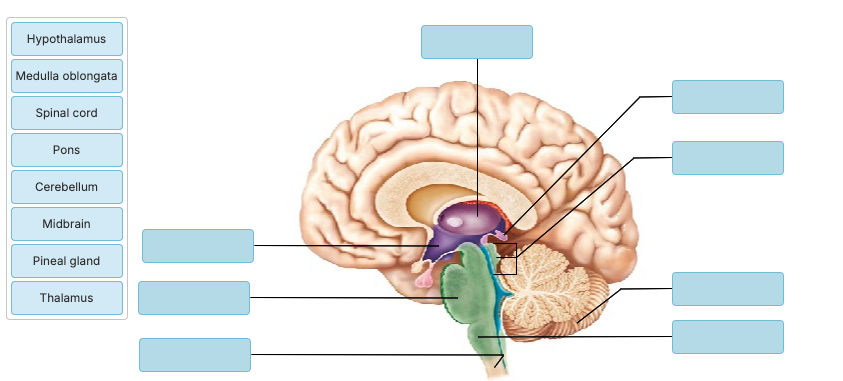
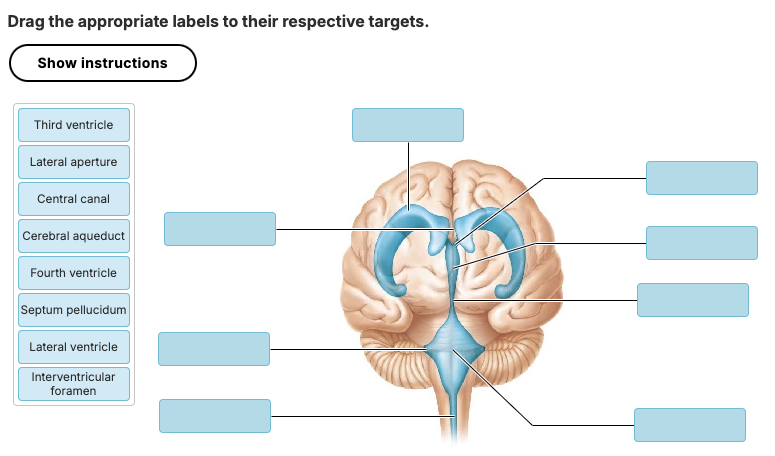
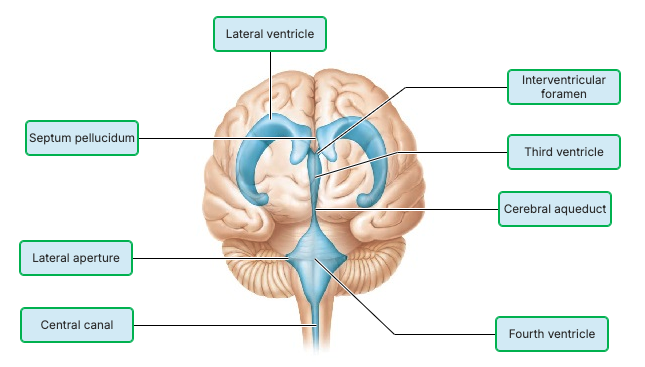
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
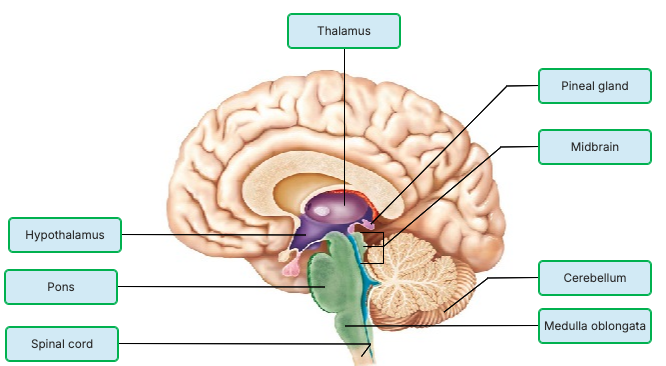
Which part of the CNS sorts almost all sensory information ascending to the cerebral cortex?
midbrain
thalamus
hypothalamus
pons
thalamus
___________ Involved in visual and auditory reflexes, motor control, and alertness.
Midbrain
__________ Regulates autonomic functions like temperature, hunger, thirst, and endocrine activity.
Hypothalamus
__________ Helps relay information between the cerebrum and cerebellum and plays a role in sleep and respiration.
Pons
Which of the following best describes the hypothalamus?
relay station for the special senses
visceral control center of the body
gateway to the cerebellum
somatic motor control center
visceral control center of the body
The ________ is vitally important to overall body homeostasis. Its chief homeostatic roles include controlling the autonomic nervous system; controlling endocrine system function; regulating the sleep-wake cycle, body temperature, hunger, and thirst; and initiating physical responses to emotions.
hypothalamus
The ________ includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.
diencephalon
midbrain
brain stem
basal nuclei
diencephalon
Head and eye movements associated with visual and auditory reflexes are controlled by which brain stem region?
a) pons
b) Midbrain
c) Medulla oblongata
d) Thalamus
b) Midbrain
Which of the following regions of the brain stem carries one-way communications that advise the cerebellum of voluntary motor activities initiated by the motor cortex?
medulla oblongata
thalamus
midbrain
pons
pons
The brain stem consists of the ________.
pons, medulla, cerebellum, and midbrain
midbrain, medulla, and pons
cerebrum, pons, midbrain, and medulla
midbrain only
midbrain, medulla, and pons
Vital centers for the control of heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure are located in the ________.
midbrain
medulla oblongata
pons
cerebrum
medulla oblongata
________ – Responsible for higher-level thinking, voluntary movement, and sensory processing
Cerebrum
The corpora quadrigemina are found in the ________.
pons
cerebellum
midbrain
diencephalon
midbrain
Which of the following statements best describes the function of the cerebellum:
a) Relays motor commands along descending pathways
b) Initiates consciously controlled movements of skeletal muscles
c) Relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex
d) Calculates appropriate force and direction of intended muscle movements
d) Calculates appropriate force and direction of intended muscle movements
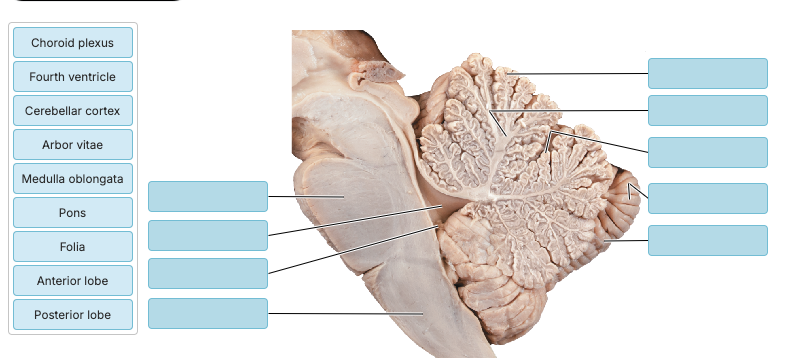
Match the following
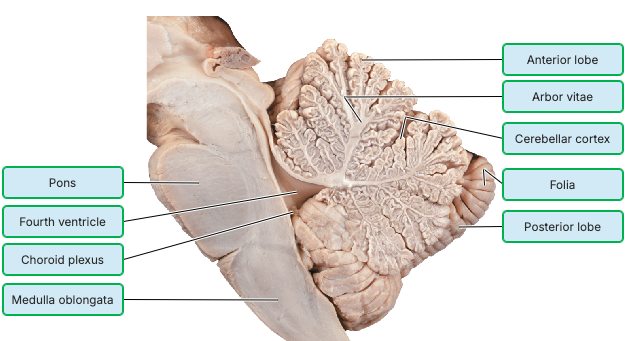
Which of the following statements about the cerebellum is NOT correct?
The cerebellum has a cortex and well-defined homunculus, just like the motor cortex.
Damage to the cerebellum could affect posture.
The cerebellum plays a role maintaining your balance.
The cerebellum generates conscious motor commands.
The cerebellum generates conscious motor commands.
The arbor vitae refers to ________.
flocculonodular nodes
cerebellar white matter
cerebellar gray matter
the pleatlike convolutions of the cerebellum
cerebellar white matter
Which of the following is not closely associated with brain structures making up the reticular formation?
a) Connecting emotional states to autonomic responses
b) Relaying ascending sensory signals that keep the cerebral cortex arounsed and alert
c) Filtering weak and repetitive sensory information
d) control center for subconscious motor activities
a) Connecting emotional states to autonomic responses
Which functional area of the brain is responsible for keeping the cortex alert and conscious and enhancing its excitability?
frontal eye fields
limbic system
reticular activating system
Broca's area
reticular activating system
Which of these statements is NOT correct regarding our limbic system?
Emotional states can alter our blood pressure.
Your amygdala judges facial expressions for danger.
The cingulate gyrus helps you express your emotional state.
Sights often create strong emotional responses.
Sights often create strong emotional responses.
Your sense of ____ is more directly attached to your limbic system and is, therefore, more likely to cause emotional responses.
smell
All of the following are structures of the limbic system EXCEPT the ________.
cingulate gyrus
caudate nucleus
hippocampus
amygdaloid body
caudate nucleus
Which of the following does not enhance the conversion of short-term to long-term memories?
memory consolidation
association
your emotional state
rehearsal
memory consolidation
_______ is the process of learning new facts by storing them in already-learned categories.
Consolidation
The process of linking new facts with old facts already stored in the memory bank is called ________.
long-term memory
association
automatic memory
rehearsal
association
Which category of memory is involved when playing the piano?
emotional
declarative
motor
procedural
procedural
REM sleep is associated with ________.
decreased vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure
decreased oxygen use, especially in the cerebral cortex
temporary skeletal muscle inhibition except for ocular muscles and diaphragm
decreased activity of the brain, especially the cerebral cortex
temporary skeletal muscle inhibition except for ocular muscles and diaphragm
Which brain waves are uncommon for awake adults, but are common for children?
theta
beta
alpha
delta
theta
Which of the following cell types is not directly involved in forming the blood brain barrier?
a) pericytes
b) endothelial cells
c) neurons
d) astrocytes
c) neurons
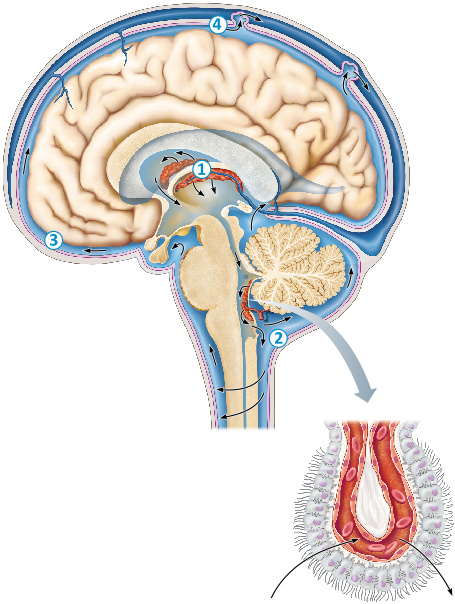
Put the following structures in order to summarize the flow of CSF from its site of formation to its return to cardiovascular circulation
cerebral aqueduct
choroid plexus
median aperture
subarachnoid space
superior sagittal sinus
2 - 1 - 3 - 4 - 5
Match the following
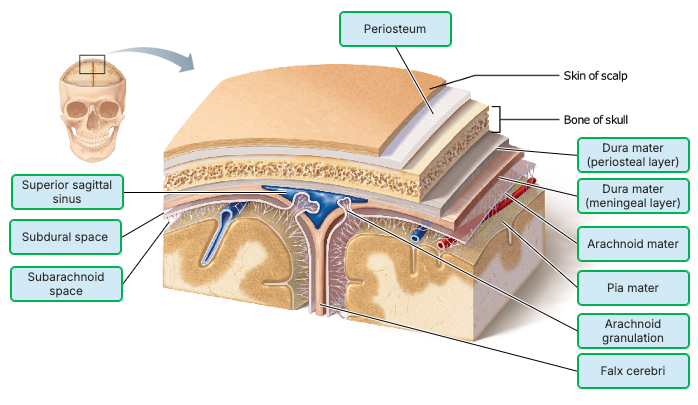
Which of the meninges is a delicate connective tissue membrane that clings tightly to the brain like cellophane wrap following its every convolution?
meningeal layer of the dura mater
arachnoid mater
periosteal layer of the dura mater
pia mater
pia mater
The subarachnoid space lies between what two layers of
meninges?
arachnoid and epidura
arachnoid and dura
arachnoid and pia
dura and epidura
arachnoid and pia
The blood-brain barrier is effective against ________.
metabolic waste such as urea
alcohol
anesthetics
nutrients such as glucose
metabolic waste such as urea
Which of the following is NOT a function of the CSF?
reduction of brain weight
protection from blows
nourishment of the brain
initiation of some nerve impulses
initiation of some nerve impulses
Which type of glial cells are shown in this figure?
Ependymal cells
Which condition is most specifically associated with functional deficits arising within the basal nuclei?
a) Concussion
b) CVA
c) Alzheimers
d) Parkinsons
d) Parkinsons
A patient suffering from memory loss, shortened attention span, disorientation, and eventual language loss is most likely suffering from
________.
Huntington's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Parkinson's disease
cerebellar disease
Alzheimer's disease
Which of the following is the mildest consequence of traumatic brain
injury?
hemorrhage
concussion
swelling
contusion
concussion
Your patient's CT scan demonstrates a cerebral vascular accident causing damage to the inferior and posterior portions of her left cerebral hemisphere. Your patient is right-handed. What deficits should you expect?
Difficulty with movement on the left side of her body and difficulty with speech
Difficulty with movement on the right side of her body and difficulty with speech
Cortical blindness
Deafness and difficulty maintaining balance
Difficulty with movement on the right side of her body and difficulty with speech
____ area, which controls the production of speech is found in the left frontal lobe in 90% of right-handed people. Her primary motor cortex for the right side of her body is in the posterior portion of her left frontal lobe
Broca's
You have a patient experiencing an essential tremor, which makes it hard for him to dress and feed himself. Imaging has detected a lesion in the basal nuclei. How would you best explain the function of these cerebral structures to him?
"The damage is preventing you from sending signals to your muscles."
"These structures control how many impulses you send to your muscles."
"This group of cells monitors all of our outgoing motor signals and makes sure there isn't any excessive activity. Your injury is preventing them from doing their job."
"Your brain is not receiving the proper input from your muscles."
"This group of cells monitors all of our outgoing motor signals and makes sure there isn't any excessive activity. Your injury is preventing them from doing their job."
Which structure is formed by the collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal?
a) Conus medullaris
b) Cauda equina
c) Filum terminale
d) lumbar enlargement
b) Cauda equina
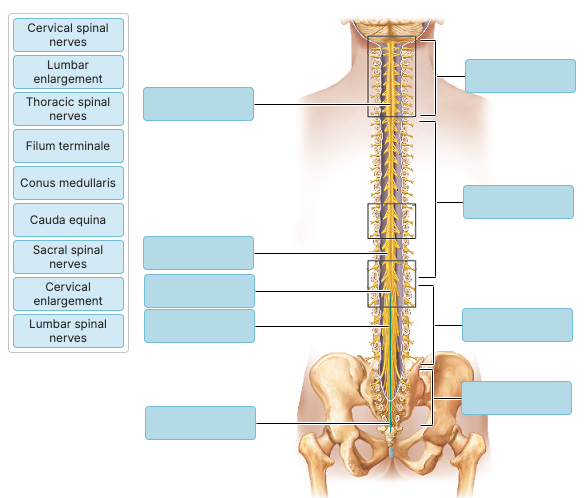
Label the following
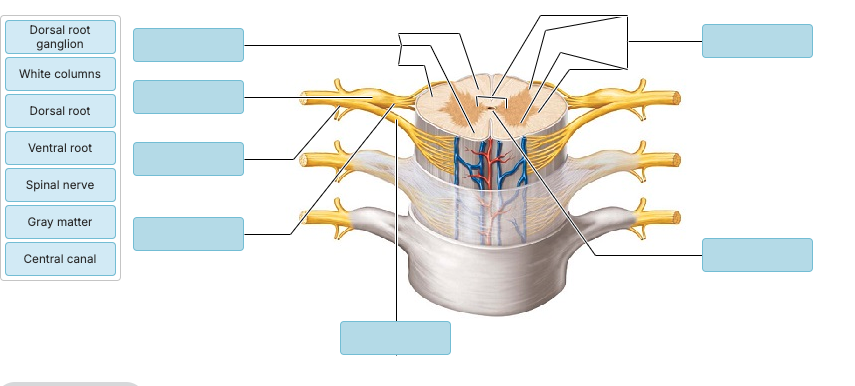
Label the following
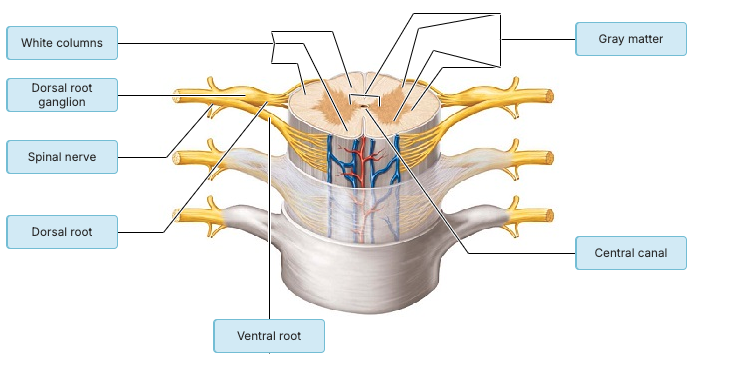
Which of the following statements is correct concerning the spinal cord?
Damage to sensory tracts in the spinal cord leads to paralysis.
The white matter contains neuron cell bodies for spinal nuclei.
Just like the cerebrum, the gray matter is found on the superficial surfaces.
Spinal nerves have mixed motor and sensory function.
Spinal nerves have mixed motor and sensory function.
Match the following:
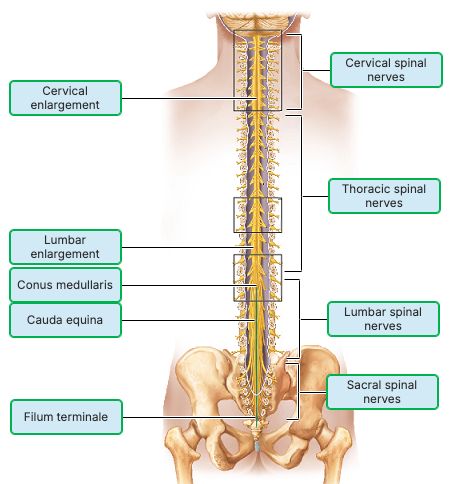
a) ________ where nerves serving the upper limbs arise
b) _______ Anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
c) _____Collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal
d) _______ Inferior point of termination of the spinal cord in an adult
Word bank: Cervical enlargement, cauda equina, filium terminale, conus medullaris
a) Cervical enlargement — where nerves serving the upper limbs arise
b) Filium terminale — anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
c) Cauda equina — collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal
d) Conus medullaris — inferior point of termination of the spinal cord in an adult
Cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in ________.
sympathetic ganglia
the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
the ventral root ganglia of the spinal cord
the thalamus
the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
Interneurons receiving input from sensory neurons are located in the ________.
dorsal root ganglion
dorsal (posterior) horn
lateral horn
ventral (anterior) horn
dorsal (posterior) horn
Which statement is true of both poliomyelitis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
Both conditions are caused by viruses.
Both diseases can be prevented.
Both conditions are caused by destruction of the ventral horn neurons in the spinal cord.
Both conditions are caused by destruction of the dorsal horn neurons in the spinal cord.
Both conditions are caused by destruction of the ventral horn neurons in the spinal cord.
(T/F) The adult spinal cord ends between the level L1 and L2 of the vertebral column.
T
Upper motor neurons of the pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts synapse with lower motor neurons in the?
a) Ventral horn of the spinal cord
b) Dorsal horn of the spinal cord
c) Dorsal root ganglion
d) Thalamus
e) Primary motor cortex
a) Ventral horn of the spinal cord
Which of the following pathways carry motor instructions for muscle tone and posture?
a) Spinothalamic
b) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal
c) reticulospinal
d) Spinocerebellar
c) reticulospinal
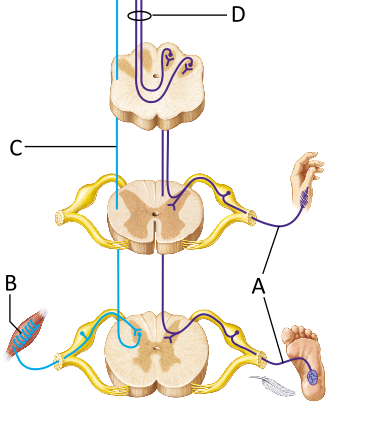
Which of the following describes the neuron indicated by the letter A?
first-order sensory neuron
second-order sensory neuron
third-order sensory neuron
first-order sensory neuron
_____-order sensory neurons transmit sensory information from receptors to the spinal cord, or, in some cases, the medulla oblongata.
First
The descending fibers in the figure provide for which of the following functions?
involuntary control of cardiac muscle
conscious awareness of sensory information
voluntary control of skeletal muscle
involuntary control of smooth muscle
voluntary control of skeletal muscle
Motor pathways originating in the _____ motor cortex allow for the conscious control of skeletal muscle.
primary
Select the true statement regarding first-order neurons.
First-order neurons descend with motor commands.
First-order neuron cell bodies reside in a ganglion.
First-order neurons originate in the CNS.
First-order neurons usually ascend directly to the thalamus.
First-order neuron cell bodies reside in a ganglion.
Second-order neurons of ascending pathways that contribute to sensory perception terminate in the ________.
medulla
somatosensory cortex
thalamus
spinal cord
thalamus
Two terms for the massive motor tracts serving voluntary movement are ________.
supplementary and cerebellar-pontine
segmental and nigrostriatal
pyramidal and corticospinal
extrapyramidal and rubrospinal
pyramidal and corticospinal
How do tracts and nerves differ? How do nuclei and ganglia differ?
Nerves and ganglia are in the CNS; tracts and nuclei are in the PNS.
Tracts and ganglia are in the CNS; nerves and nuclei are in the PNS.
Tracts and nuclei are in the CNS; nerves and ganglia are in the PNS.
Tracts and nuclei are in the CNS; nerves and ganglia are in the PNS.
which of the following is NOT a way in which sensory receptors are classified?
a) Whether the sensory receptor responds to stimuli that originate inside or outside the body
b) wether or not the sensory nerve fibers are enclosed in a connective tissue capsule
c) means by which the sensory receptors communicate to sensory neurons
d) the type of stimuli to which the sensory receptor responds
c) means by which the sensory receptors communicate to sensory neurons
proprioceptors are found in ______?
a) the retina
b) walls of blood vessels
c) the small intestine
d) muscles and tendons
d) muscles and tendons

Which of the receptor types might function as a nociceptor?
A

Which of the receptor types shown here functions exclusively as a proprioceptor?
B
Which type of sensory receptor allows us to feel an insect landing on our skin?
mechanoreceptor
chemoreceptor
thermoreceptor
nociceptor
mechanoreceptor
_______ respond to mechanical stimuli such as pressure, vibration, and touch. When an insect lands on your skin, it causes a slight deformation or pressure change
Mechanoreceptors
__________ are receptors that can respond to painful
stimuli.
Chemoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Photoreceptors
Nociceptors
Nociceptors
We can touch our finger to our nose while our eyes are closed in part because we can sense the position and movement of our joints as well as the length of stretch in our muscles. These sensations create awareness of our body's positioning. The following receptors are most likely responsible for this ability?
interoceptors
exteroceptors
nociceptors
proprioceptors
proprioceptors
_______ are specialized sensory receptors located in muscles, tendons, and joints. They provide information about body position, movement, and the degree of stretch, allowing you to know where your limbs are—even with your eyes closed.
Proprioceptors
Feeling a gentle caress on your arm would likely involve all of the following EXCEPT
________.
tactile corpuscles
hair follicle receptors
Meissner's corpuscles
Lamellar corpuscles
Lamellar corpuscles
___________ (another name for Meissner’s corpuscles) respond to light touch.
Tactile corpuscles
___________ detect light touch via hair movement.
Hair follicle receptors