chapter 1-5 microbiology (fall semester 2023)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
introduction to microbiology, microscopes, microbes
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
1
New cards
biology
study of living organism
2
New cards
microbiology
study of microbes
3
New cards
microbes
extremely small (microscopic) living AND non-living organisms
4
New cards
living microbes are
cellular microbes or microorganism
5
New cards
examples of living microbes
viroids, prions, viruses
6
New cards
microorganisms are found
everywhere (aka ubiquitous)
7
New cards
germs
microbes that cause disease
8
New cards
pathogens
term for disease causing microbes
9
New cards
non-pathogens
term for microbes that DONT cause disease
10
New cards
opportunistic pathogens
microbes that may cause disease, but are mainly awaiting for the opportunity to
11
New cards
2 categories of disease caused by pathogens
infectious disease and microbial intoxication
12
New cards
who produces much of our oxygen
photosynthetic algae and bacteria (such as cyanobacteria)
13
New cards
decomposition
microorganisms work to decompose waste and dead organisms
14
New cards
microbe uses
decomposition, elemental cycles, digestion (inside of intestinal tract), industries, genetic engineering
15
New cards
Anton van Leewenhoek
father of microbio, not a trained scientist, animalcules, single lens microscope user
16
New cards
Louis Pasteur
french chemist, fermentation, yeast fermentation into alcohol, bacteria fermentation into vinegar, pasteurization, rabies + anthrax vaccine
17
New cards
germ theory disease
Louis Pastuer led the hypothesis that microorganisms cause disease
18
New cards
pasteurization
milk is heated to a specific temperature for a set period of time to kills harmful bacteria
19
New cards
Robert Koch
discovered cause of anthrax
20
New cards
koch’s postulate
step’s that relate a specific microbe to a specific disease, helped prove germ theory
21
New cards
cause of anthrax
bacillus anthracis
22
New cards
exceptions to koch’s postulate
cannot be cultured, species specificity, synergistic infection (needs microbes to work)
23
New cards
microscopes
an optical instrument that is used to observe objects so small that they cannot be seen with the unaided human eye.
24
New cards
resolving power/resolution
each optical instrument has a limit as to what can be seen using that instrument
25
New cards
resolving power of the unaided human eye
approximately 0.2 mm.
26
New cards
earliest simple microscope
a tube with the plate for the object at one end and a magnifying lens at the other end (the magnification was usually less than 10X the original size)
27
New cards
compound microscope
contains more than one magnifying lens
28
New cards
a compound light microscope
visible light is the source of illumination
29
New cards
This microscope contains two magnifying lens systems
the eyepiece/the ocular lens AND the objective lens
30
New cards
eyepiece/ocular lens
usually X10
31
New cards
the objective len
X4, X10, X40, and X100 are the four most common
32
New cards
how to calculate total magnification
multiply the ocular lens magnification with the objective lens magnification
33
New cards
fluorescence microscopy
neon uv colored, organisms absorb dye to view
34
New cards
phase contrast microscopy
gray colored, best way to observe LIVING matter
35
New cards
darkfield microscopy
no light at all, helpful to view thin and small microbes
36
New cards
electron microscopy
never uses staining, EM can magnify 2000x, very expensive
37
New cards
two types of electron microscopes
transmission and scanner
38
New cards
transmission electron microscope
2D
39
New cards
scanner electron microscope
3D, meant to view staph or strep
40
New cards
cell
unit of any living organism because it exhibits the basic characteristics of life
41
New cards
2 categories of cells
eucaryotic and procaryotic
42
New cards
Prokaryotes
NO membrane bound organelles, capsule and/or cell membrane
43
New cards
Eukaryotes
contain a "true" nucleus, membrane bound organelles
44
New cards
Viruses, prions, viroids are
acellular
45
New cards
Cell wall
seen in plant cells only (eukaryote), meant for shape/structure
46
New cards
Flagella and cilia
contain microtubules
47
New cards
Flagella
string-like appendage meant for movement, example \= sperm
48
New cards
Cilia
hair-like structure (found on protozoa and certain body cells)
49
New cards
Is eukaryote or prokaryote smaller?
prokaryotic is about 10x smaller than eukaryotic
50
New cards
Binary fission
how prokaryotic cells reproduce, one cell splits in half to become two daughter cells
51
New cards
Prokaryotic cytoplasmic particles
mainly ribosomes, 70s
52
New cards
Peptidoglycan
only found in bacteria, gram pos+ bacteria have thicker layer, gram neg- have thinner layer
53
New cards
Mitochondria
has its own ribosome (70s) and DNA from the mother, chemical powerhouse that drives cellular function
54
New cards
Glycocalyx
slimy material produce by the cell membrane
55
New cards
2 types of glycocalyx
slime layer (loosely connected to cell wall) or capsule (highly organized and firmly connected)
56
New cards
Pili (also called fimbriae)
hair-like structures, most often observed on Gram-negative bacteria
57
New cards
What is pili made of
composed of polymerized protein molecules called pilin
58
New cards
Pili and flagella difference
pili are thinner than flagella, have a rigid structure and are not associated with motility
59
New cards
Bacteria and Pili
enable bacteria to anchor themselves to surfaces, some bacteria possess a sex pilus for conjugation
60
New cards
Spores (Endospores)
A few genera (e.g., Bacillus and Clostridium) are capable of forming thick-walled spores as a means of survival
61
New cards
Sporulation
process of spore formation (repackaging a copy of DNA in a new form that contains little water) NOTE
62
New cards
Spores resistant
have been shown to survive for many years and are resistant to heat, cold, drying, and most chemicals
63
New cards
Germination
return to vegetative state by weakening a spore, then having a nutritious environment (if no autoclave, one may have to do this to destroy)
64
New cards
Taxonomy
the science of classification of living organisms (consists of classification, nomenclature, and identification)
65
New cards
Classification
the arrangement of organisms into groups (known as taxa).
66
New cards
King David Came Over for Good Spaghetti
K for Kingdom, D for Division, C for Class, O for Order, F for Family, G for Genus and S for species
67
New cards
Binomial system
“two names” aka what the science of taxonomy was established based on
68
New cards
How does the binomial system work?
each organism is given 2 names - genus and the specific epithet. Combined, both names constitute the species
69
New cards
Bional system example
Escherichia coli; Escherichia is the genus and coli is the specific epithet (e.g., E for Escherichia).
70
New cards
Fungi Classification
Kingdom Fungi
71
New cards
Plant Classification
Kingdom Plantae
72
New cards
Bacteria and Archaea
kingdom procaryotae
73
New cards
Algae and Protozoa
Kingdom protista
74
New cards
Animals Classification
Kingdom Animalia
75
New cards
Archaea and bacteria
prokaryotic
76
New cards
Algae, protozoa, fungi
eukaryotic
77
New cards
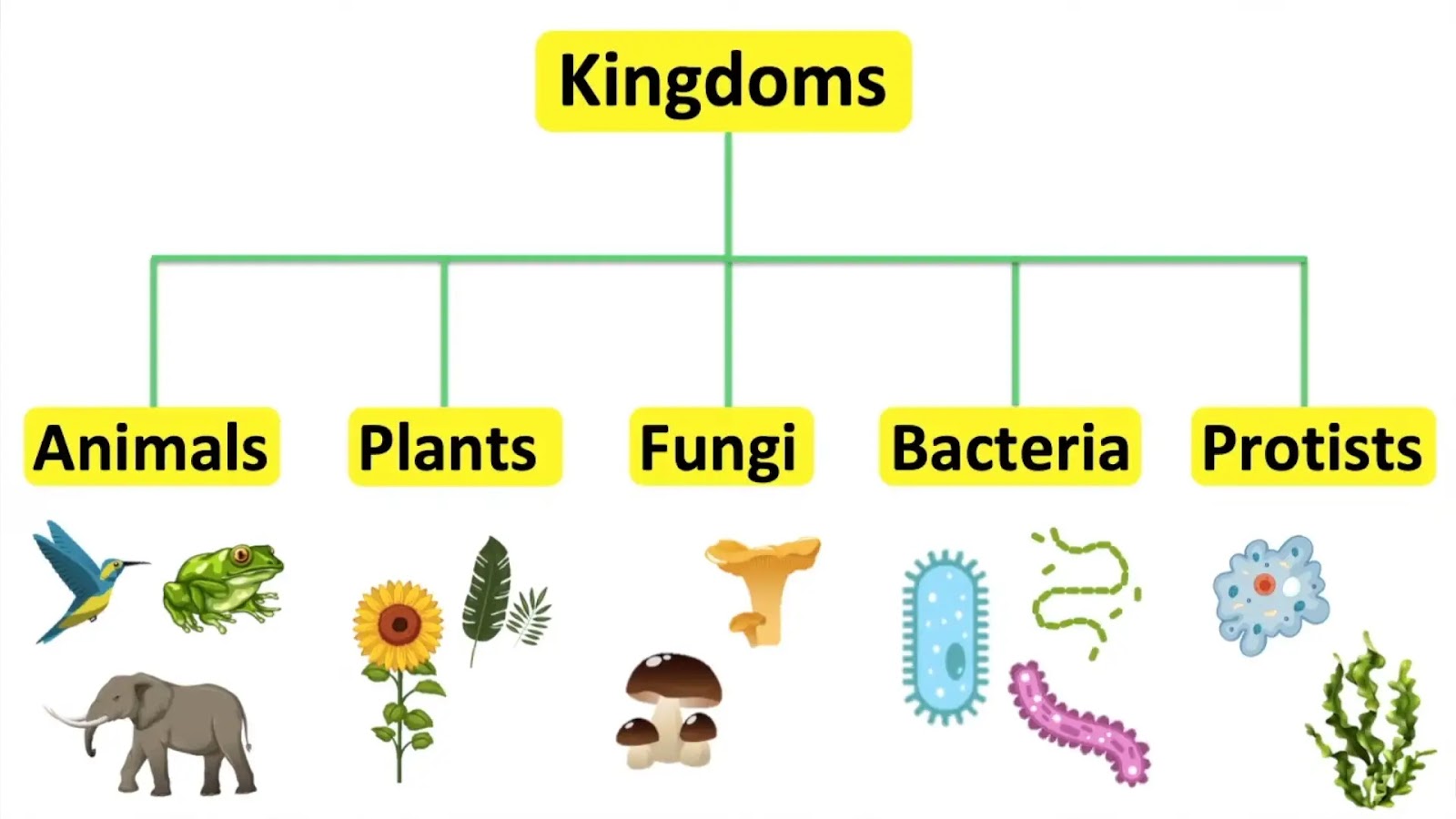
Five Kingdom System of Classification
* Kingdom: Animalia
Key Characteristics: Multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Humans, dogs, birds
* Kingdom: Plantae
Key Characteristics: Multicellular, autotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Trees, flowers, grass
* Kingdom: Fungi
Key Characteristics: Multicellular or unicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Mushrooms, yeasts, molds
* Kingdom: Protista
Key Characteristics: Mostly unicellular, eukaryotic
Examples: Amoeba, algae, paramecium
* Kingdom: Procaryotae
Key Characteristics: Unicellular, prokaryotic
Examples: Bacteria, cyanobacteria
Key Characteristics: Multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Humans, dogs, birds
* Kingdom: Plantae
Key Characteristics: Multicellular, autotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Trees, flowers, grass
* Kingdom: Fungi
Key Characteristics: Multicellular or unicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic
Examples: Mushrooms, yeasts, molds
* Kingdom: Protista
Key Characteristics: Mostly unicellular, eukaryotic
Examples: Amoeba, algae, paramecium
* Kingdom: Procaryotae
Key Characteristics: Unicellular, prokaryotic
Examples: Bacteria, cyanobacteria
78
New cards
Microbes
truly cellular (bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, and fungi) + acellular (viruses, viroids, and prions)
79
New cards
Cellular microbes (microorganisms)
prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) +
80
New cards
eukaryotic (algae, protozoa, and fungi)
81
New cards
Viruses, viroids and prions
acellular microbes or infectious particles.
82
New cards
Types of Microorganisms
bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, algae, virus
83
New cards
Bacteria
unicellular, prokaryotes
84
New cards
Bacteria shapes
bacillus \= rod; spiral; or coccus \= spherical or ovoid
85
New cards
What can bacteria do?
can form pairs, chains, clusters (usually species specific), enclosed in peptidoglycan cell wall, many move using appendages called flagella
86
New cards
Archaea
unicellular, prokaryotes, NO peptidoglycans in cell wall; found in extreme environments, NO pathogens
87
New cards
Fungi
kingdom of unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes (unicellular yeasts, multicellular mold and mushrooms)
88
New cards
Protozoa
unicellular protists; eukaryotes, move by pseudopods, flagella, or cilia
89
New cards
Protozoa example
amebae
90
New cards
Algae
photosynthetic eukaryotes; unicellular or multicellular
91
New cards
Viruses
different, super small (electron microscope), cellular (acellular)
92
New cards
What do viruses contain
DNA or RNA (either or NOT both)
93
New cards
What turns a virus into something living
Viruses can only reproduce by using the cellular machinery of other organisms; therefore only considered living when they infect
94
New cards
Multicellular Animal Parasites
strictly microorganisms, medically important eukaryotes, microscopic during some stages of life cycle
95
New cards
Example of Multicellular Animal Parasites
helminthes (worms)
96
New cards
Virions
complete virus particles
97
New cards
Viruses infect what?
humans, animals, plants, fungi, protozoa, algae and bacterial cells.
98
New cards
oncogenic viruses or oncoviruses
cause specific types of cancer
99
New cards
a typical virion consists
a genome of either DNA RNA, surrounded by a capsid
100
New cards
Capsid
protein coat which is composed of protein units called capsomeres