Chapter 11 Quest
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
How can graded potentials become action potentials? (TF)
Pass the threshold: Critical minimum voltage to generate an AP (-55mV); caused by opening a sufficient number of Na channels and may require summation of graded potentials to be met
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential vs Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (TF & MC)
IPSP: hyper polarization of the neuron membrane->inhibits excitation; opens ligand gated Cl- or K+ channels (passive); less likely to reach threshold; IPSP summate with EPSP; decides AP or no AP
EPSP: depolarizes the neuron->excitation; ligand gated passive Na channels open; more likely to reach threshold; graded
What are Ganglia?
Collection of bodies in the PNS
What occurs at the end of an axon? (MC)
Release of neurotransmitter; Ca voltage gated channels open/calcium influx
Voltage gated/Ligand gated channels (MC)
Voltage Gated: respond to a change in membrane potential
Ligand Gated: Gated; respond to chemical stimuli
Saltatory Conduction (MC)
Myelin prevents leakage of ionsUnmyelinated: APs over entire surface > slowerMyelinated: insulation from myelin and action potentials only at nodes of Ranvier; saltatory conduction > faster
What is the slowest part of signal transduction? (TF)
Synapse
Oligodendrocytes vs Schwann Cells (TF)
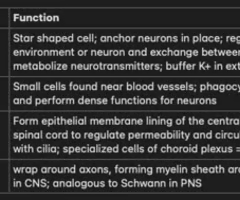
Oligodendrocytes: CNS cell; wrap around axons, forming myelin sheath around more than one axon in CNS; analogous to Schwann in PNS
Schwann Cells: PNS Cells; aka Neurolemmocytes; forming the myelin sheath; forms part of sheath of one axon; analogous to oligodendrocyte of CNS
What do presynaptic cells release? What allows a postsynaptic cell to respond? (TF)
Presynaptic cells releases neurotransmitters; postsynaptic cells have receptors that responds to the neurotransmitter
Depolarization vs Repolarization (TF)
Depolarization: Na channels open > partial loss of electrochemical gradient due to passive moment of Na in the cell through channels > more positive potential
Repolarization: Na Channels deactivate and K channels open > restoration of electrochemical gradient due to K exiting the cell > beginning to return to resting/more negative potential
Graded Potential vs Action Potential (TF)
Graded Potential: Generated when local stimuli initiate the opening of ion channels to make the inside of the cell to become more positive or more negative. Graded potentials Tavel short distances, are not self-propagating, quickly dissipate, undergo decrement (decay); Varies in strength
Action Potential: Generated when the inside of the cell becomes more positive through Na entry and reaches threshold to create a signal that ravels long distance, is self propagating, is long lasting, and does not decay; All the same strength
Characteristics of neurons and their function (MC)
functional units of the nervous system specialized to conduct electrical messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body; long lived and mostly amitotic=great longevity; high metabolic rate with absolute requirement of glucose and oxygen
What happens when a synapse is used repeatedly? (MC)
Enhances presynaptic neuron's ability to excite postsynaptic neuron; "learning effect;" influenced by higher Ca concentrations->more vesicles release; more postsynaptic receptors
Function of Myelin Sheath (MC)
white, protein/lipid, segmented covering that protects, insulates and increases conduction velocity of axons; found on the axon
What is the sodium/potassium pump's role in the body? (MC)
ATP powered membrane transporter that pumps 3Na+ out and 2K+ into the cell to maintain resting potential
Absolute vs Relative refractory period (MC)
Absolute: From when Na Channels open until they reset; no stimulus can trigger and AP; causes APs to propagate away from its point of origin and not restart at the point of origin
Relative: Follows absolute; Na closed and K are still open; only extremely strong stimuli can trigger an AP
What are endorphins responsible for? (MC)
Classified as a peptide; inhibits pain
Division of the Nervous System (MC)
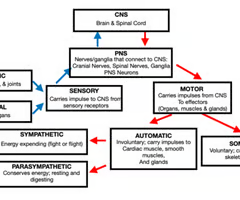
Schwann Cells are found in what division of the nervous system? What cell of the CNS is similar to Schwann Cells? (MC)
In the PNS; analogous to oligodendrocyte of CNS
What type of fibers would elicit a fast response? (APP)
Group A; large diameter/myelinated; somatic and motor; Fastest/shorten conduction time
Cells of the CNS and their Function (APP)
Temporal vs Spatial Summation (APP)
Temporal: Rapid firing of one or more presynaptic neurons
Spatial: Multiple neurons firing; more=more likely to reach threshold
What is the Voltage of...?
1. Resting Potential
2. Threshold
3. Maximum
1. -70mV
2. -55mV
3. +30mV
How are neurotransmitters eliminated? (SAQ)
1. Diffusion
2. Degradation by enzyme
3. Reuptake by neurons or glia-primarily astrocytes or presynaptic neurons
Ligand vs Voltage gated channels (SAQ)
Ligand Gated Channels: respond to chemical stimuli
Voltage Gated Channels: respond to a change in membrane potential
Acetylcholine
Excitatory or Inhibitory, Ans& skeletal muscle
E/NE
Monoamine Excitatory or inhibitory: SNS
Dopamine
Monoamine Excitatory or inhibitory feel good
Histamine
Excitatory or Inhibitory Wakefulness, appetite, learning/memory
Serotonin
Monoamine Inhibitory, Sleep ,moody, and memory
Glutamate
Amino Acids Excitatory learning/memory
GABA
Amino Acids Inhibitory Brain
Glycine
Amino Acids Inhibitory SC
Endorphins
Peptide Inhibitory Inhibits pain
Adenosine
Purines Inhibitory sleep/wake cycles
Endocannabinoids
Lipid Excitatory or inhibitory nausea, memory, appetite, and neuronal development