SLP 210 (m4-m6)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
consonant sounds
speech sounds made by partial or total block of air flow through vocal tract
vowel sounds
speech sounds made through an open vocal tract
voicing
presence or absence of vocal fold vibration
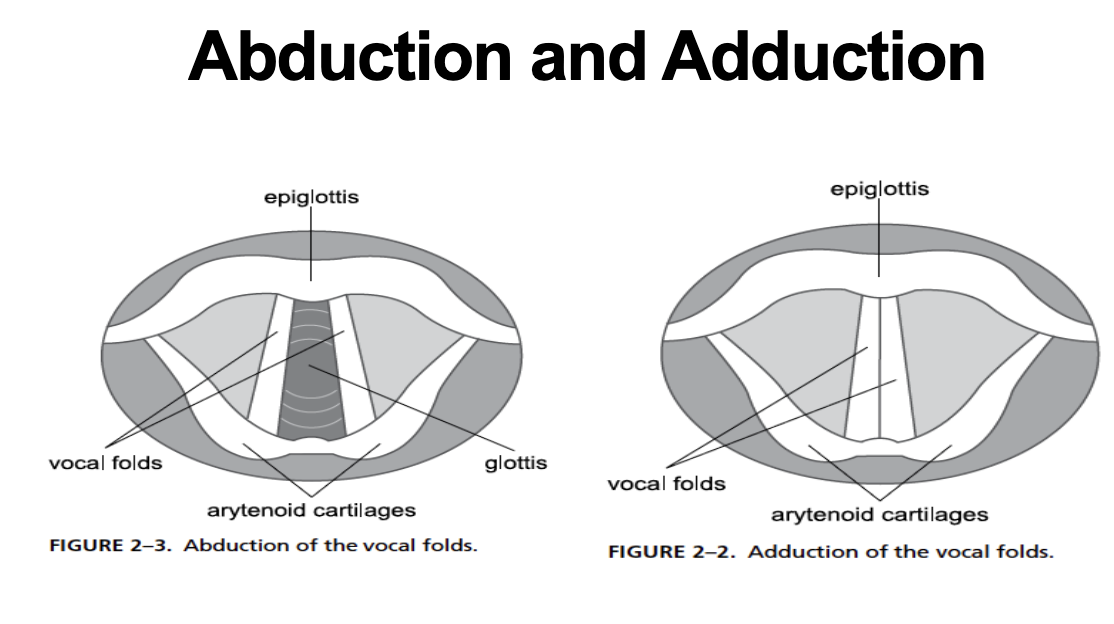
voiced vs unvoiced
voiced: vocal fold vibration (adduct)
voiceless: vocal folds are apart (abduct)
anatomical process of speech production
respiratory (airflow)
phonatory (vocal fold vibration)
resonatory (shaping the sound)
oro-nasal (mouth or nasal airflow)
articulatory (movement of articulators)
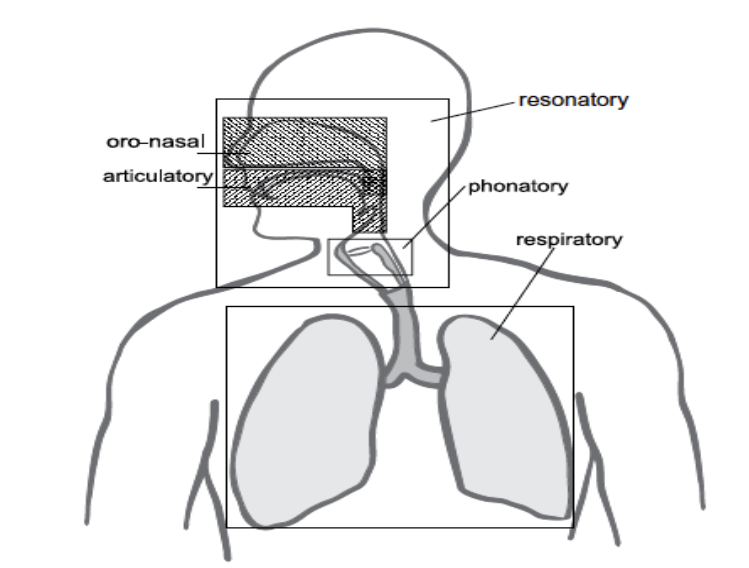
respiratory process
inhalation (breathing in) and exhalation (breathing out)
airflow (lungs → trachea → larynx)
phonatory process
larynx contains vocal folds
Bernoulli’s principle: pressure and velocity are inversely related
vibration: voiced
no vibration: voiceless
resonatory process
shaping sound
changing the shape of the vocal tract
amplifying: strengthening certain frequencies
attenuating: weakening certain frequencies
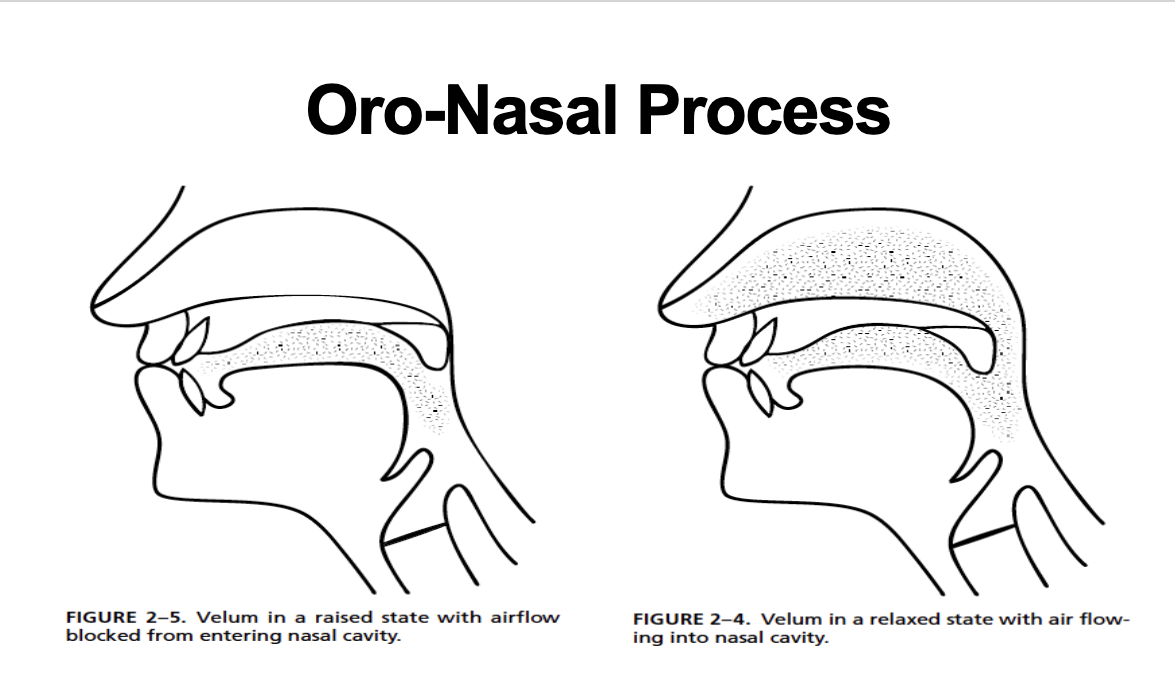
oro-nasal process
oral sounds: airflow travels through mouth (raised velum)
nasal sounds: airflow travels through nose (lowered velum)
hypernasal speech: too much nasal airflow
hyponasal speech: blocked nasal airflow
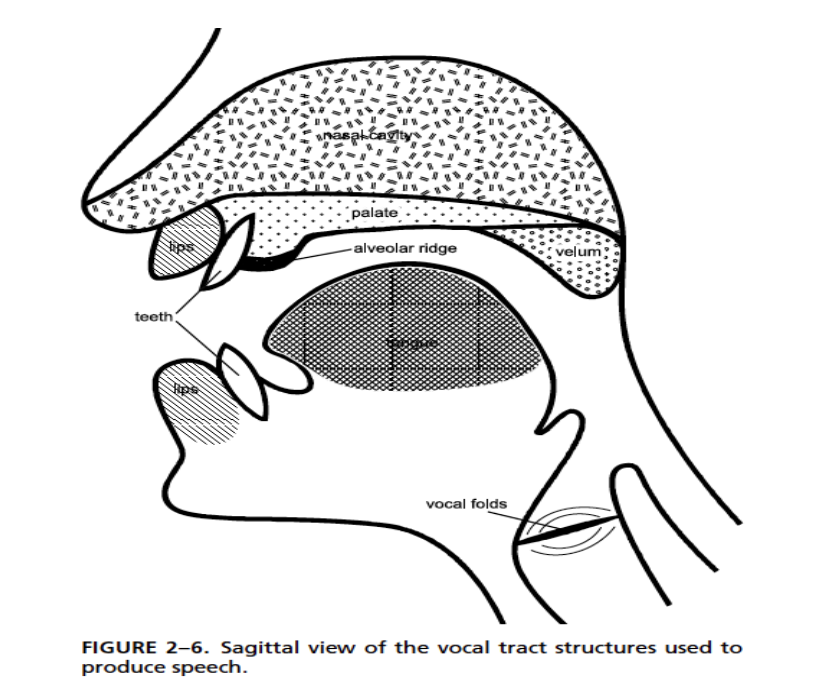
articulatory process
lips
upper teeth
tongue
alveolar ridge
hard palate
velum
uvala
pharynx
epiglottis
cognates
voiceless/voiced pairs of consonants
classifying consonants
place of articulation (where)
manner of articulation (how)
voicing (present/absent vibration)
PLACE OF ARTICULATION
bilabial
upper and lower lips involved
/p/, /b/, /m/
/w/ is labiovelar
labiodental
upper incisors resting on lower lip
/f/, /v/
interdental
tongue (tip or blade) touching upper teeth and protruding slightly through the upper and lower incisors
/θ/, /ð/
alveolar
tongue (tip or blade) on or near the upper alveolar ridge
/t/, /d/, /n/, /s/, /z/, /l/
post-alveolar
tongue blade behind the alveolar ridge, near the front of the hard palate
/ʃ/ (sh) and /ʒ/ (zh)
alveopalatal
beginning with the tongue (tip or blade) at the alveolar ridge, ending with the tongue front near the hard palate
/t͡ʃ/ (ch) and /d͡ʒ/ (j)
palatal
front of the tongue near the hard palate
/j/ (y) and /ɹ/ (r)
velar
back of the tongue near the soft palate
/k/, /g/, /ŋ/
glottal
vocal folds involved
/h/
MANNER OF ARTICULATION
sonorants
open vocal tract
unobstructed airflow
all vowels; some consonants
nasals, glides, liquids
obstruents
obstructed airflow through vocal tract
completely or partially impeded airflow
some consonants; no vowels
stops, fricatives, affricates
stops
produced by two articulators temporarily stopping airflow while velum is raised, resulting in a sudden release of air that travels through the mouth
voiceless: aspiration
voiced: no aspiration
/p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, /g/
nasals
produced by two articulators temporarily stopping airflow while velum is lowered, resulting in a sudden release of air that travels through the nose
/m/, /n/, /ŋ/
glides
produced with minimal friction by the smooth movement of the articulators
/w/, /j/ (y)
fricatives
produced by the partial obstruction of airflow by two articulators closely approximating one another to create turbulence
/f/, /v/, /θ/, /ð/, /s/, /z/, /ʃ/, /ʒ/, /h/
affricates
produced as a combination of a stop + fricative
/t͡ʃ/ (ch) and /d͡ʒ/ (j)
liquids
produced with minimal friction and allows airflow over the sides of the tongue
/l/, /ɹ/ (r)
alveolar tap flap
quick ‘d’ sound
between vowels where second syllable is unstressed (butter)
/r/
ed sound
/t/ or /d/
/t/ = voiceless + voiceless
/d/ = voiced + voiced
glottal stop
casual speech
break/stop
button, mountain
/?/
the t sound
true /t/
aspirated [t]
alveolar tap/flap
unreleased /t/
intrusive /t/
light vs dark l sound
light: prevocalic (leaf)
dark: postvocalic (pull)
listener-oriented approach
transcribing the words the speaker produced (focusing on meaning)
speaker-oriented approach
how sounds were articulated
systemic transcription
phonemes (mental representation)
impressionistic transcription
actual speech (articulation)
segmental
consonants, vowels
suprasegmental
pitch, stress, loudness, rate of speech
monophthongs
steady-state, single articulatory movement
diphthongs
dynamic, multiple movements during production
rhotics
vowels with r-coloring (rhotic diphthongs or tripthongs)
tongue height
how near the tongue body is to the roof of the mouth
high, mid, low
vertical axis
tongue advancement
tongue forward to back in oral cavity
front, central, back
horizontal x-axis
rounding
rounded vs unrounded
tenseness
tense vs lax
front vowels
/i/ as in beet
/ɪ/ as in ship
/eɪ/ as in rain
/ɛ/ as in bed
/æ/ as in cat
central vowels
/ə/ as in alive (unstressed)
/ʌ/ as in up (stressed)
/ɚ/ as in mother (unstressed)
/ɝ/ as in bird (stressed)
back vowels
/u/ as in boot
/ʊ/ as in book
/o/ as in boat
/ɔ/ as in bought
/a/ as in hot
diphthongs
/aɪ/ as in ice
/aʊ/ as in count
/ɔɪ/ as in toy
/eɪ/ as in wait
/oʊ/ as in soap
rhotics
/ɪɚ/ as in fear
/ɛɚ/ as in fair
/ʊɚ/ as in cure
/ɔɚ/ as in four
/ɑɚ/ as in far
/aɪɚ/ as in fire
/aʊɚ/as in hour
double long diacritic (ː)
open syllable (see)
half-long diacritic (ˑ)
closed syllable w/voiced consonant (seed)
short diacritic (◌̄)
closed syllable w/voiceless consonant (seat)
voiceless vowels
in between two voiceless stops/consonants
vowel reduction to a schwa
ex. first o in potato is voiceless
vowel nasalization
all vowels are nasalized in syllables closed by a nasal consonant
(~) on vowel before nasalized consonant
closed by [m/, /n/, /ŋ/]
vowel retraction
light vs dark /l/
closed syllable ending with /l/
occurs before velarized /ɫ/
ex. all = [aɫ] (a is retracted)