Homeostasis - Responding to Stimuli
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
steps of the stimulus response model
stimuli —→ receptor —→ response —→ effect —→ feedback
a stimulus is defined as a —— in the internal or external environment that can be detected by an organism through ——
a stimulus is defined as a variable factor in the external or internal environment that can be detected by an organism through receptors.
a receptor is the —— or —— that are able to —— and ——the change from the internal or external environment
a receptor is the cell or tissue that are able to identify and detect the change from the internal or external environment.
a response is an —— that occurs because of the ————
a response is an outcome that occurs because of the initial stimulus.
an effector refers to a —— or —— that causes the —— to the stimulus
a effectors refers to a muscle or gland that causes the response to the stimulus.
feedback refers to the —— of the response, this could either be —— or ——
feedback refers to the impact of the response, this could either be positive or negative.
describe the role of sensory receptors
sensory receptors are specialised cells that detect the changes in the internal and external environment of the organism.
describe the role of effectors
effectors are muscles or glands that facilitates the organism in carrying out the response.
difference between regular and reflex responses
regular stimuli response involve conscious thought, involving decision making from the brain, while reflex responses are involuntary and do not require the brain for decision making. reflexes are primarily for survival.
describe the difference between negative and positive feedback
negative feedback refers to a response where the stimulus is being diminished or reversed, while positive feedback refers to a response where the stimulus is being increases or reinforces the initial stimulus.
describe the voluntary stimuli response pathway
The voluntary stimuli response pathway begins with a stimulus being detected by sensory receptors from either the external or internal environment. sensory neurons send electrical signal through the spinal cord into the brain. The brain processes the message and plans a response, and motor neurons carry this message out to its respective muscle or gland (effector). the effector then carries out the response.
describe the reflex stimuli response pathway
the reflex stimulus response model begins with sensory receptors detecting a stimulus from either the external or internal environment. sensory neurons then send electrical signals to interneuros located on the spine of the central nervous system. interneurons are connected to motor neurons which send electrical impulses to muscle or glands (effectors), to carry out its response.
provide an example of a positive feedback
when glucose blood levels are too low, the response is to increase the production of glucagon, a hormone which triggers liver cells release glycogen, stored glucose.
provide an example of a negative feedback
when blood glucose levels are too high, the response is to increase the production of insulin, a hormone which lowers the blood glucose levels by binding receptors on the cell surface and signalling to glucose transporters to facilitate the movement of glucose outside the cell.
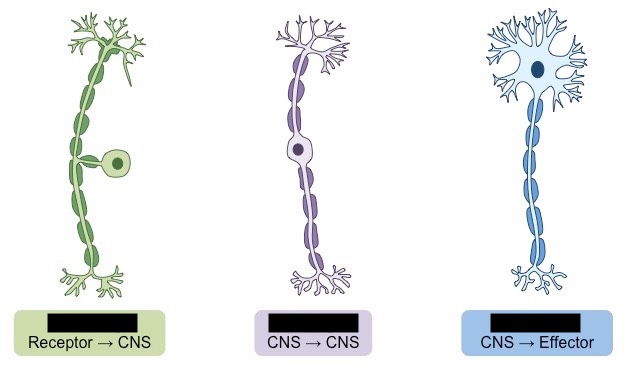
label each neuron
sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron