Cellular Organelles - NUCLEUS AND DNA
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
nucleus features
largest organelle
stores genetic information
contains chromatin and nucleolus
double membraned
nuclear pores - connect with nucleoplasm
which type of cells dont have a nucleus
enterocytes - red blood cell
why they dont live very long
nucleoplasm
cytoplasm of the nucleus
contains nuclear structures like chromosomes and nuclear matrix
gel-like substance
surrounded by nuclear membrane
Nuclear Lamina
Nuclear matrix
Nuclear matrix
found in the nucleoplasm
dense network of fibres
provides support (like cytoskeleton)
nuclear lamina
dense fibrillar network - intermediate filaments
also found in nucleoplasm
provides mechanical support
keeps spherical shape of nucleus
regulates DNA replication and cell division
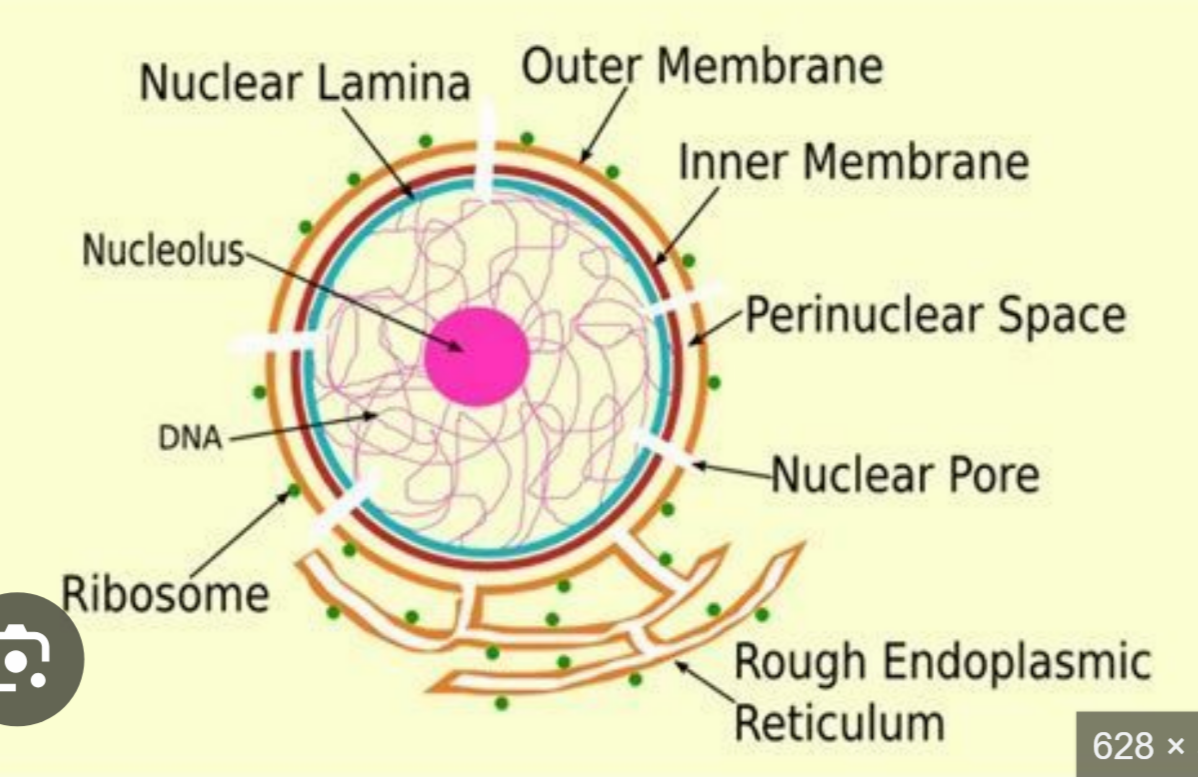
nucleolus
largest dark staining part of nucleus
synthesis of rRNA
nuclear envelope
membrane around the nucleus
made up of 2 phospholipid bilayers
inner nuclear membrane
outer nuclear membrane
Perinuclear space
space between inner and outer nuclear membrane
function of which is still being studied
nuclear pores
channel found in the nuclear envelope where two membranes fuse tg
allows for transport of molecules
cytoplasmic and nuclear face
communication between nucleus and cytoplasm
what molecules does the nuclear pore transport
proteins; for nuclear lamina or catalyze nuclear activities
RNA and RNA-protein complexes formed in the nucleus and exported to cytoplasm
chromatin
double-stranded helical DNA molecule
wound around globular proteins (histones) - form nucleosomes
many nucleosomes are packed tightly to form chromatin
located in nucleoplasm
forms of chromatin
heterochromatin and euchromatin
heterochromatin
darkly staining and irregularily scattered
genetically inactive
DNA protection, gene regulation, chromosome stability
it stays inactive to keep certain genes turned off
euchromatin
dispersed and not readily stainable
loosely coiled → accessed often
genetically active
carry genes for protein synthesis
chromosomes
formed during cell division
tightly coiled chromatin
Store and organize genetic information