SEPARATED Viral Infections, Vector Borne Illnesses, and Vaccines
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Viruses are
-no cells but obligate intracellular parasites
-can't independly replicate, synthezise their own proteins or energy
-composed of internal core DNA or RNA
Viral envelope
Lipoprotein composed of lipid from a host cell
Viral tropism
the ability of a virus to infect a specific cell or tissue type leading to a specific disease process
nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) is surrounded by
-protein coat (capsid) to form nucleocapids
-icosahedral and helical
Capsid and surface proteins
-protet genome from nucleases
-mediate attachment to cell receptor
-provide antigens for vaccination and immune system
-viruses with several serotupes are differentiated by surface proteins
Viral serotypes medical implications
-if infected with one serotype, you can get different serotypes of same virus
-vaccines contain protection to ALL serotypes to convey complete immunity
-hard to form vaccine against virus that constantly alters the antigens it expresses
viral envelopes
-lipoprotein membrane composed of lipid from host cell during budding (acquired during replication and virus specific proteins)
-antigen expression->serotype and immunity implications
-more sensitive to heat, drying, detergents and alcohol
Non-enveloped virus
-spread during direct contact or animal bites
-moist environments
-transmited through fecal oral route or body fluids
Stages of viral replication
Early: attach, penetration, uncoating
Middle: mRNA synthesis, protein synthesis/processing, genome replication
Late: assembly and release
DNA Viruses replication
nucleus of the host cell
-requries RNA polymerase
RNA viruses replication
cytoplasm
-retroviruses have signle stranded RNA which is transcribed into double stranded DNA by Reverse transcriptase (HIV)
Viral protein synthesis and replication
-mRNA is synthesized and translate by host ribosomes into viral proteins
-replicated viral genome and capsid proteins are packaged together to form progeny viruses
Non-envelope viral release
rupture the cell and release mature particles
Enveloped viral release
Budding from the host's cell membrane
Horizontal transmission
person to person
vertical transmission
parent to child
vector borne and animal reservoir transmission
animal to human (mosquito or animal bite)
Stages of infection
1. incubation (asymptomatic)
2. prodromal (non specific symptoms)
3. Specific illness (characteristic symptoms)
4. Recovery, chronic disease, latent disease
Provirus Model (viral tumorigenesis)
tumor-producing genes enter the cell at the time of infection by the Tumor Virus
Oncogenic Virus Model (viral tumorigenesis)
Malignant genes pre-exist within the cell prior to infection (allows inactive genes to become active-overproduction of growth factors)
Human T cell lymphoma virus (medically relevant tumor viruses)
adult t cell leukemia/lymphoma
Human Herpes Virus 8 (medically relevant tumor viruses)
Karposi's Sarcoma
Human Papillomavirus (medically relevant tumor viruses)
Cervical and penile cancer
Hepatitis B + C (medically relevant tumor viruses)
Associated with hepatocellular carcinoma
Epstein-Barr Virus
Assiciated with Burkitt's Lymphoma and Nasopharylgeal Carcinoma
Herpes virus structure
enveloped double stranded DNA
-budding from membrane
Type of infection herpesviruses cause
-Latent infection, can reactivate
-due to immunosuppression
Herpesviruses human pathogens
HSV-1+2
HHV 3-7
-HHV 4 is EBV
-HHV 5 is cytomegalovirus
KSHV (HHV-8)
herpes life cycle
-envelopes fuses with cell membrane and nucleocapside travels to nucleus
-DNA inserted and replicated, proteins form
-Treatment: Acyclovir and valvcylovir
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) transmission
Vertical and horizontal transmission
-MC congenital disease
-MC transmission is in utero
CMV disease
Healthy: asymptomatic
Immunocompromised: pneumonitis, esophagitis, Hepatitis, retinitis
-Diagnosis: PCR, histology
-antivirals
Epstein-Barr Virus transmission
Saliva
-affected B lymphocytes
Epstein-Barr virus causes what diseases?
Infectious mononucleosis and hairy leukoplakia (whitish hair on lateral tongue)
EBV associated diseases, dx, tx
-Burkitts lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma
-diagnosis with Monospot or lymphocytosis
-supportive care
Humans Herpesvirus 6 symptoms
Roseola Infantum
-young children (daycares)
-High fever
-defervenscene followed by rash of face and trunk
-immunocompromised: antitrivals
Human herpesvirus 8 causes
inactivation of tumor suppressor gene
-sex and saliva, organ transplant
HHV-8 disease
-Kaposi sarcome
-many dark purple flat/nodular lesions of skin, oral cavity, soles, GI tract, lungs
-biopsy
-HAART (antiviral)
Measles Virus (rubeola) structure
enveloped single stranded RNA
-respiratory droplets
Mealses Virus symptoms
-rhinorrhea, cough
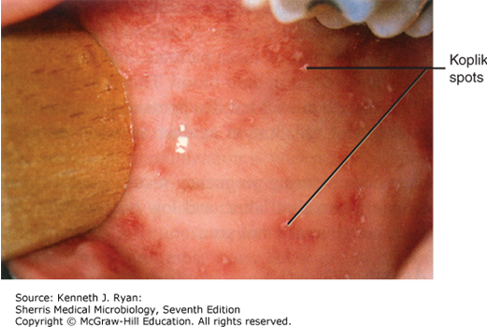
-Koplik's Spots (bright red lesions with central dot on buccal mucosa)
after prodromal^ phase →
Rash on face which spreads to lower extremities (palms and soles too)
complication: encephalitis
Measles diagnosis/treatment
-Clinical or PCR
-Supportive care
-vaccination to prevent
Mumps Virus Structure
Enveloped single stranded RNA
-respiratory droplets
Mumps symptoms
-swelling of salivary glands
-anorexia, fever, malaise
-painful orchitis
Mumps virus diagnosis + treatment
-clinical, PCR
-supportive care
-vaccine to prevent
Rubella Virus Structure
Enveloped single stranded RNA
-respiratory or vertical
Rubella Virus symptoms
-face rash and then extremities (x3 days)
-posterior auricle lymphadenopathy
-shorter/fainter than rubeola
-Congenital rubella: cataracts, ductur arteriosus, developmental delayR
Rubella diangosis and treatment
-clinical, PCR
-supportive care
-Vaccine to prevent
Parvovirus B19 structure
Non-enveloped single stranded DNA virus
-infected erythoblasts and endothelial cells
Parvovirus Transmission
Respiratory droplet and vertical transmission
Parvovirus symptoms
Erythema Infectiosum
-bright red rash of cheeks/trunk, rhinorrhea
-arthritis
-only symptomatic if chronic anemia
Chronic B19 infection
chronic anemia
Parovovirus B19 diagnosis/treatment
-IgM antibodies
-supportive care
Human Papillomavirus structure
Non-enveloped viruses with double stranded DNA
-squamous epithelial cells
-direct (skin to skin)
HPV symptoms
Cauliflower like lesions (skin/genital warts)
HPV Diagnosis
Koliocytes (Vacuolated Cells) on biopsy
HPV treatment
-Topical, liquid nitrogen, surgery
Skin and Plantar warts
HPV 1-4
Genital Warts (HPV)
HPV-6 and HPV-11
Premaglignant lesions and cervical carcincoma, penial cacinoma and anal carcinoma
HPV-16 and HPV-18
HPV prevention
-Immunization (Gardasil-9)
-safe sex
-circumcision
-screening for cancer (pap smear)
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) structure
Enveloped Retrovirus
HIV transmission
Sexual and blood-borne contact
vertical transmission
HIV related disease
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
HIV cell specific infection
CD4 Lymphocytes
HIV pathophysiology
1. go 120 binds to CD 4 on T helper cell
2. envelope fuses to cell membrane and genome enters cell
3. Reverse transcriptase turn RNA into DNA
4. Integrase mediates integration of DNA into Host DNA
5. DNA transcribed forming RNA for genome and is tranlated into viral proteins
6. New viruses is assembled and buds from affected cell via viral protease
HIV stages
Acute Stage (2-4 weeks): lethargy, generalized lymphadenopathy, rash (no palms or soles)
Latent Stage (7-11 years): asymptomatic
Immunodeficient Stage (AIDS): CD4 declines
CD4 cells >500
normal to non-infected
CD4 cells 350-499
Thrush, Hairy Leukoplakia, Molluscum Contagiosum
CD4 cells 200-349
Karposi Sarcoma
CD4 cells 100-199
Pneumocystis jiroveci, candida esophagitis
CD4 cells <100
Toxoplasma encephalitis, CMV Retinitis
HIV treatment and prevention
-Antirival
-no vaccine
-PEP (needle stick-ASAP) or PrEP (many sex partners, at high risk)
West Nile virus reservoir
Wild birds
-MC neuroinvasice arboviral disease
West Nile virus transmission
Culex mosquito to human
west nile symptoms and treatment
-asymptomic
-fever, headache
-supportive care
Dengue Virus transmission
-Aedes aegypti mosquito
Dengue Virus Reservoir
Humans and monkeys
classic dengue fever symptoms
dengue Fever (breakbone fever)
Malaise
Severe arthralgia and myalgias
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever symptoms
Classic Dengue
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhagic Shock
Dengue virus treatment
-supportive care
Lyme disease pathogen
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme disease vector
Ixodes tick (deer tick)
Lyme disease stage 1 symptoms (3-30 days)
Erythema Migrans (bull's eye) 75% of people
Flu-like symptoms
Lyme disease stage 2 (weeks-months)
Myocarditis, Meningitis, Bell's Palsy, Peripheral Neuropathy
Cardiac/neurologyc involvement
Lyme Disease stage 3
Arthritis of the large joints
encephalopathy
Early Lyme Disease Treatment
Doxycycline
Late Lyme disease treatment
ceftriaxone
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever pathogen
Rickettsia rickettsii
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever transmission
Dermacentor variabilis (dog tick)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever symptoms
fever
H/A
Myalgias
Rash after 2-6 days
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever treatment
Doxycycline
Malaria Pathogen
Plasmodium spp.
P. falciparum (most severe symptoms)
-destructs RBC
Malaria transmission
female anopheles mosquito
Malaria symptoms
abrupt fever
chills
H/A
Myalgias
Arthralgias
Splenomegaly
Jaundice
P. falciparum malaria treatment
NO Chloroquine
-Coartem or Malarone
Active immunity
immunity from developed of immunoglobulins through vaccine
Passive immunity
provided by administration of preformed immunoglobulins
Passive-active immunity
get vaccine and immunoglobuns for immune response (RABIES)
Capsular-polysaccharide vaccine
-Strep pneumoniae
-Pneumovax 23: PCV 15 or 20 (older than 65)
-Neisseria meningitis
-Hib
Pneumonia vaccine old regimen
Child: PCV 13
adult: above 65, PCV 13 then pneumovax after 1 year
Pneumonia vaccination new regimen
Child: PCV 15 or 20
Adult: older than 65, PCV 15, 20, or 21 if 15 then pneumovax 23 after 1 year