Antibacterials
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:59 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
What antiseptics inhibit urinary pathogens?
Nitrofurantoin and methenamine
2
New cards
Nitrofurantoin is used to treat what?
used in uncomplicated UTIs
3
New cards
Methenamine gets hydrolyzed at acidic pH to produced what?
produces ammonia and formaldehyde
4
New cards
What type of activity does formaldehyde have?
antibacterial activity
5
New cards
Why do mycobacterial infections require prolonged treatment?
They are extremely slow growing, inhibition can take weeks to months
6
New cards
What is the first line of drugs for 2 months for tuberculosis?
**RIPE** (__**R**__ifampicin, __**I**__soniazid, __**P**__yrazinamide, __**E**__thambutol)
7
New cards
Is Rifampicin bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
bactericidal
8
New cards
What is the MOA of Rifampicin?
binds to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, blocking the synthesis of mRNA
9
New cards
Can Rifampicin cross the blood-brain-barrier?
Yes
10
New cards
What is the MOA of Isoniazid?
inhibits mycobacteria specifically by inhibiting mycelia acid synthesis
11
New cards
Is Isoniazid bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
bactericidal
12
New cards
Why is pyridoxine administered alongside isoniazid?
Isoniazid can have neurological complications if taken along
13
New cards
Pyrazinamide is a synthetic analog of what?
nicotinamide
14
New cards
What is the MOA of pyrazinamide?
targets mycolic acid synthesis
15
New cards
What must pyrazinamide be used in combination with other first line agents?
due to resistance during monotherapy
16
New cards
What is a common toxicity associated with pyrazinamide?
hepatoxicity
17
New cards
What is the MOA of Ethambutol?
synthetic molecule that inhibits mycobacteria
18
New cards
Is Ethambutol bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
bacteriostatic
19
New cards
When does resistance occur in Ethambutol use?
when drug is used along
20
New cards
What are known toxicities associated with Ethambutol?
Optic neuritis
21
New cards
What pathogen causes leprosy?
*Mycobacteria leprae*
22
New cards
What must leprosy be treated for prolonged periods of time?
due to persistence of organism in the tissues for years
23
New cards
Mono-treatment of what drug to treat leprosy resulted in resistance?
Dapsone
24
New cards
What combination of drugs are commonly used as therapy for leprosy?
Dapsone, Rifampicin, Clofazimine
25
New cards
What type of tests, performed in a laboratory, examine the interactions between antibiotics and bacteria and are a helpful guide to the likely outcomes of therapy?
susceptibility tests
26
New cards
What patient factors must be taken into consideration during antibiotic therapy?
Age, Underlying disease, Sit and Type of Infection, Renal and Liver Function
27
New cards
Disk Diffusion
a type of susceptibility test that involves seeing the organisms on an agar plate and the application of filter paper disks containing antibiotics where overnight incubation is observed for zones of inhibition around each antibiotic disk
28
New cards
Dilution Test
susceptibility test that is a quantitative estimate of antibiotic susceptibility that can be assessed through minimum inhibitory concentration test (MIC test) and finds the lowest concentration that inhibit visible bacterial growth
29
New cards
For dilution susceptibility tests, where are serial dilutions of the test antibiotics prepared?
in broth or agar
30
New cards
Minimum Bacterial Concentration
the lowest concentration of an antibiotic required to kill the organism
31
New cards
What is the killing curve?
it provides a dynamic estimate of bacterial susceptibility
32
New cards
The killing curve is typically used in a research setting to determine what?
used to determine synergistic effects
33
New cards
Combination therapy can be described as what?
Synergistic or antagonistic
34
New cards
Synergistic
activity is greater than the sum of individual activities
35
New cards
Antagonistic
activity of one drug is compromised by the other
36
New cards
Do antiviral drugs kill viruses?
No, they only stop viral replication
37
New cards
Viruses are dependent on what part of the host?
dependent on host cell protein synthesis machinery
38
New cards
What medication is used in the treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV) and Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV)?
Acyclovir
39
New cards
What type of drug is acyclovir?
a prodrug (it is unactivated until phosphorylated)
40
New cards
What phosphorylates Acyclovir to activate it?
herpesvirus thymidine kinase
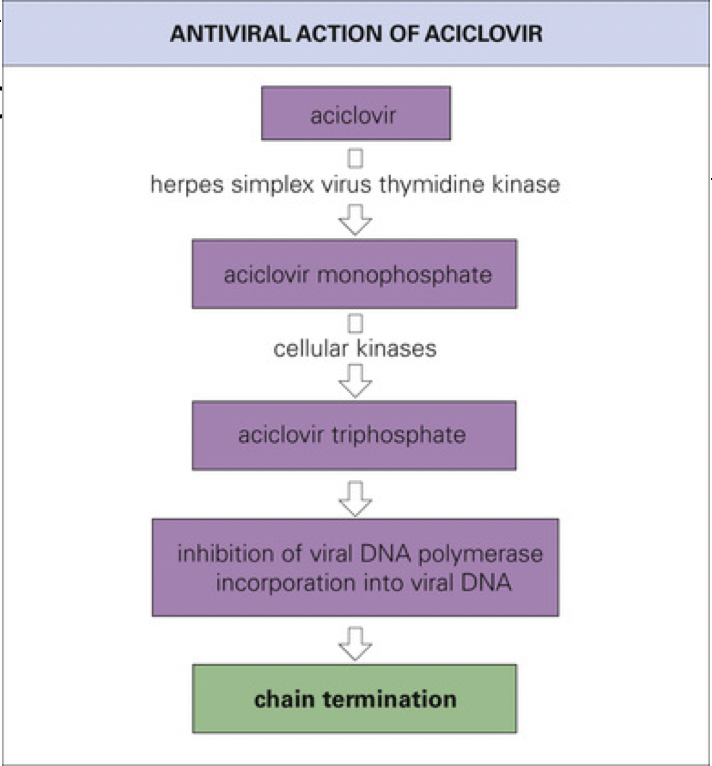
41
New cards
Acyclovir is incorporated into what, resulting in chain termination?
incorporated into the viral DNA
42
New cards
Acyclovir is used in the treatment of what?
HSV encephalitis
HSV and VZV infections
Primary and recurrent genital herpes
HSV and VZV infections
Primary and recurrent genital herpes
43
New cards
The use of Acyclovir in patients with HSV and VZV infections have experience an accelerated recovery if they have what underlying issue?
shingles
44
New cards
What toxicities are associated with Acyclovir?
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia (rare)
Possible crystallization in the renal tract in kidney patients
Possible crystallization in the renal tract in kidney patients
45
New cards
What virus is Ganciclovir active against?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
46
New cards
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) does not encode what enzyme?
thymidine kinase
47
New cards
Ganciclovir is monophosphorylated by what virus?
UL97 gene-specified kinase
48
New cards
Although selective toxicity is NOT seen for Ganciclovir, what type of toxicity is seen?
bone marrow toxicity
49
New cards
What are the clinical uses of Ganciclovir?
CMV retinitis
CMV encephalitis
CMV GI disease seen in immunocompromised patients
CMV encephalitis
CMV GI disease seen in immunocompromised patients
50
New cards
What medication is used as pre-emotive therapy in bone marrow transplant and solid organ transplant recipients?
Ganciclovir
51
New cards
What is the MOA of Cidofovir?
Chain terminating agent that targets viral DNA polymerase and is added to the 3’ end of the viral DNA chain
52
New cards
What are the clinical uses for Cidofovir?
effective against CMV and adenovirus infections
53
New cards
In what cases can Cidofovir be applied topically/intralesionally?
In cases of acyclovir-resistant genital warts caused by HSV
54
New cards
What is the MOA of Foscarnet?
Attaches to the pyrophosphate-binding site of the herpesvirus DNA polymerase, preventing nucleotide binding and inhibiting viral replication
55
New cards
What is the clinical use of Foscarnet?
used to treat CMV infections
Active against HSV and VZV
Acyclovir-resistant HSV
Active against HSV and VZV
Acyclovir-resistant HSV
56
New cards
Is Foscarnet a first-line drug or a second-line drug?
a second-line drug
57
New cards
What are the 6 classes of antiretroviral drugs?
Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Fusion inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors
Chemokine receptor antagonists
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Fusion inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors
Chemokine receptor antagonists
58
New cards
Zidovudine is an analog of what?
nucleoside thymidine (NRTI)
59
New cards
What is present on the ribose of Zidovudine instead of hydroxyl group?
an azido group
60
New cards
What is the MOA of Zidovudine?
acts as an inhibitor of/substrate for viral reverse transcriptase and acts as a competitive substrate of reverse transcriptase incorporated into proviral DNA
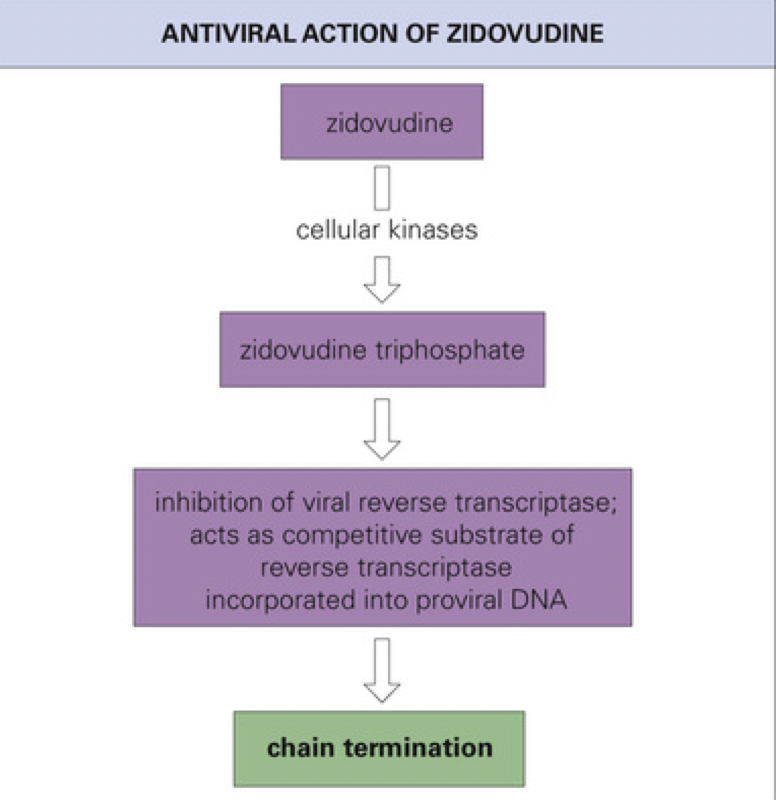
61
New cards
What are the adverse effects of Zidovudine?
Bone marrow suppression (Macrocytic anemia, neutropenia, leukopenia)
Vomiting, nausea, headache, myalgia, and malaise
Lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia, lipoatrophy, and insulin resistance
Vomiting, nausea, headache, myalgia, and malaise
Lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia, lipoatrophy, and insulin resistance
62
New cards
What is the MOA of Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)?
noncompetitive inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and bind to a hydrophobic pocket proximal to the enzyme catalytic site; induce cytochrome P450
63
New cards
What side effects are associated with NRTIs?
Pancreatitis
Peripheral neuropathy
Lipodystrophy
Hypersensitivity
Peripheral neuropathy
Lipodystrophy
Hypersensitivity
64
New cards
The following drugs are apart of what class of antiretroviral drugs?
* Nevirapine, efavirenz, delavirdine, etravirine, rilpivirine
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
* Nevirapine, efavirenz, delavirdine, etravirine, rilpivirine
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
65
New cards
Are Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors active against HIV-2?
No, only active against HIV-1
66
New cards
The following drugs are apart of what class of antiretroviral drugs?
* Nelfinavir, saquinavir, indinavir, ritonavir, kaletra, atazanavir, amprenavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, tipranavir
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
* Nelfinavir, saquinavir, indinavir, ritonavir, kaletra, atazanavir, amprenavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, tipranavir
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
67
New cards
What is the MOA of protease inhibitors?
Acts in post-translational cleavage of the gag and gag-pol polyproteins, inhibits the structural proteins and enzymes critical for viral replication which results in immature and defective viral particles
68
New cards
What side effects are associated with protease inhibitors?
GI distress, lipodystrophy, increased triglycerides, insulin resistance
69
New cards
The following drugs are apart of what class of antiretroviral drugs?
* •Enfuvirtide
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
* •Enfuvirtide
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
B. Fusion inhibitors
70
New cards
What is the MOA of fusion inhibitors?
blocks HIV before it enters the host cell and competitively binds to gp41; Blocks post-fusion structure from forming
71
New cards
What side effects are associated with fusion inhibitors?
pain at injection site and rare hypersensitive reactions
72
New cards
The following drugs are apart of what class of antiretroviral drugs?
* Dolutegravir, raltegravir, elvitegravir
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
* Dolutegravir, raltegravir, elvitegravir
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
73
New cards
What is the MOA of integrate inhibitors?
transferring virally encoded DNA into the host chromosome and inhibiting the strand transfer step
74
New cards
The following drugs are apart of what class of antiretroviral drugs?
* Marviroc
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
* Marviroc
\
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
B. Fusion inhibitors
C. Integrase inhibitors
D. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
E. Nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
F. Protease inhibitors
A. Chemokine receptor antagonists
75
New cards
HIV-1 enters the cells via what type of receptors?
CD4 and either CCR5 or CXCR4
76
New cards
In what type of patients are chemokine receptor antagonists used?
Used in patients who have been given HAART and have an R5 HIV-1 infection
77
New cards
What is the typical treatment combination of antiretroviral drugs?
2 Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
1 Integrase inhibitor
1 Integrase inhibitor
78
New cards
What is the MOA of Ribavirin?
guanosine analog that inhibits production of guanosine triphosphate pool needed viral nucleic acid synthesis
79
New cards
What type of viruses can Ribuvirin target?
Both RNA and DNA viruses
(After triphosphorylation, can interfere with RNA polymerases too)
(After triphosphorylation, can interfere with RNA polymerases too)
80
New cards
What are the clinical uses for Ribavirin?
Used as an aerosol to treat RSV in infants, Lassa fever, active against measles, Hep C, and Hep E
81
New cards
Of the following drugs, which are used for influenza A?
A. Amantadine
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
D. Rimantadine
E. Zanamivir
A. Amantadine
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
D. Rimantadine
E. Zanamivir
A. Amantadine
D. Rimantadine
D. Rimantadine
82
New cards
Of the following drugs, which are used for both influenza A and B?
A. Amantadine
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
D. Rimantadine
E. Zanamivir
A. Amantadine
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
D. Rimantadine
E. Zanamivir
B. Oseltamivir
C. Peramivir
E. Zanamivir
C. Peramivir
E. Zanamivir
83
New cards
What is the MOA of Amantadine and Rimantadine?
Inhibit the penetration of the virus into the cell, fusion of the viral envelop is prevented
84
New cards
On what channel does Amantadine act?
acts on the viral matric protein ion channel
85
New cards
Neuraminidase
a glycoprotein on the influenza virus surface that cleaves sialic acid residues on the host cell to release the influenza virus and further spread
86
New cards
What are examples of neuraminidase inhibitors?
Oseltamivir, zanamivir, peramivir
87
New cards
What is the MOA of neuraminidase inhibitors?
Acts as a competitive reversible inhibitors of the neuraminidase enzyme active site
88
New cards
Interferons
natural glycoproteins produced by the innate immune system in response to infections; encode proteins thought to inhibit intracellular virus multiplication
89
New cards
Interferons are used to treat what?
Used to treat chronic HBV and HCV infections; has effect on HPV infections
90
New cards
What is the role of IFNα?
binds to immune cells and results in class I MHC antigen expression, activation of effector cells, cytokine cascade, and production of Th1 cells
91
New cards
What tests are critical in the diagnosis, treatment, assessment, and prognosis of viral infections?
Qualitative and quantitative nucleic acid test
92
New cards
What can detect the presence of viral RNA?
Reverse-transcriptase PCR
93
New cards
What can determine the number and percent of T cell counts?
Flow cytometry
94
New cards
What can detect gene expression of specific viruses?
Quantitative real-time PCR
95
New cards
What is the MOA of azoles?
Inhibits cell membrane synthesis and inhibits the lanosterol C14-demethylase (which is important for sterol synthesis)
96
New cards
What type of Azole is used to treat Candida infections?
Fluconazole
97
New cards
What newer azole is used to treat aspergillosis?
Posaconazole
98
New cards
What azole is used to treat invasive mucormycosis?
Isavuconazole
99
New cards
What is the MOA of Echinocandins?
Interfere with cell wall synthesis by inhibiting β-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase – required for fungal cell wall synthesis
100
New cards
Echinocandins are used to treat what?
invasive *Aspergillus* infections, candidemia, invasive candiadiasis, and *Pneumocystis*