Unemployment
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Define unemployment
It is the situation where people are unable to find employment, even though they are of legal working age and are both willing and able to work at current wage rates
Define demand-deficient/cyclical unemployment
It is unemployment caused by insufficient aggregate demand, which can arise due to business or economic shocks
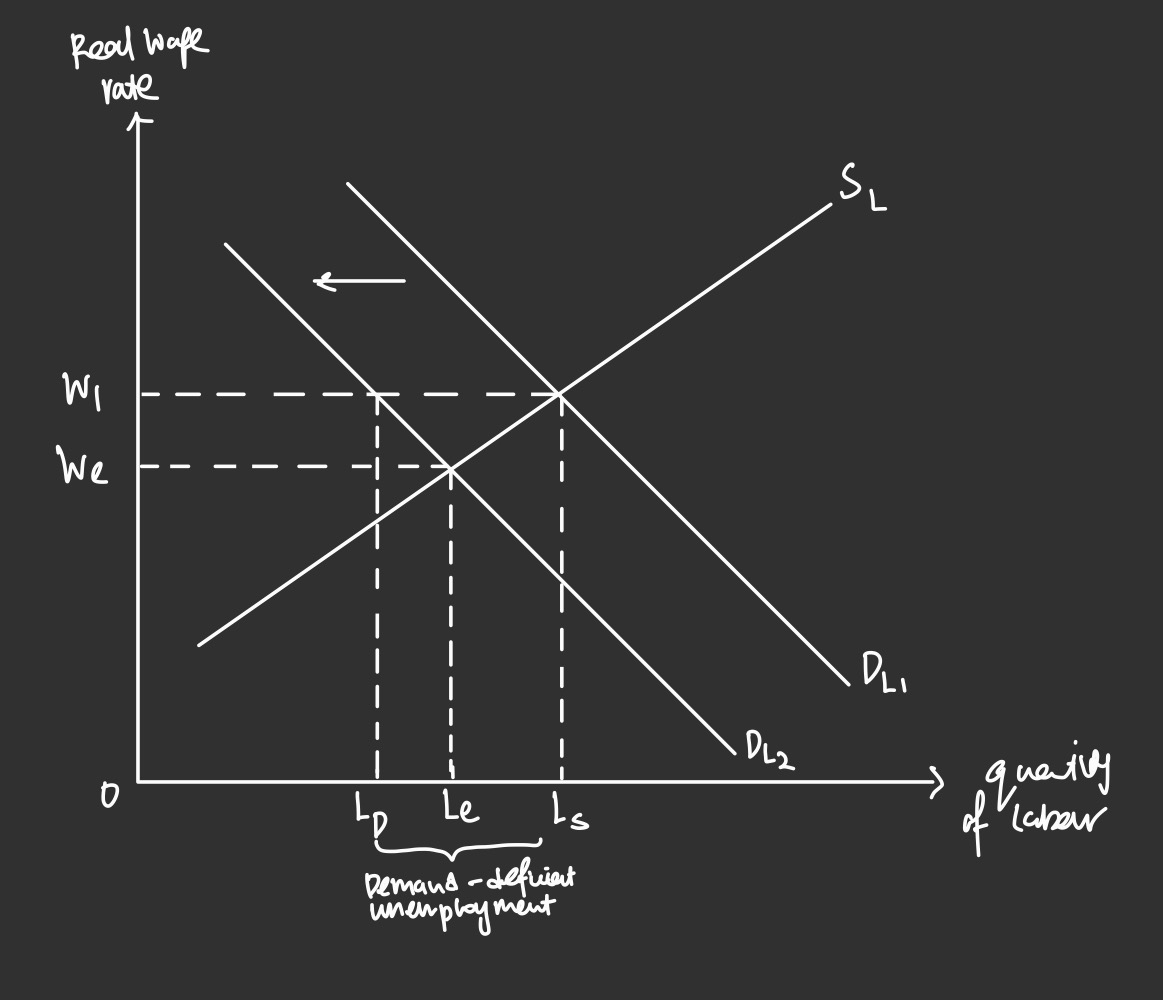
Describe demand-deficient unemployment using the graph
The labour market is initially at equilibrium at A where demand for labour, DL1 is equals to supply of labour SL at wage rate of W1. However, due to fall in AD and fall in demand for labour since it is a derived demand, labour demand curve shifts left from DL1 to DL2. Wages are considered to be inflexible due to contracts and unions, hence despite fall in demand, wage cuts are unlikely to fall from W1 to We. There is hence a surplus of labour supplied at W1 as firms are only willing and able to employ at LD at current wage rate. Demand-deficient unemployment is hence LDLS
Outline a possible IEV for demand-deficient unemployment based on state of economy
The extent of demand deficient unemployment resulting from the fall in AD depends on the space capacity of the economy. Should AD fall while it is in the horizontal SRAS, then there will be a greater rise in DD unemployment but if the economy is operating near full capacity and AD falls at the LRAS region, then there is a smaller rise in DD unemployment
Outline one IEV for demand-deficient unemployment based on labour intensiveness
The extent of fall in DD unemployment depends on how labour intensive the production activities are. The more labour intensive the industry, the larger the proportion of wages in total cost, then the greater the impact of labour demand curve when AD falls
Define structural unemployment
It arises from a mismatch of skills between the unemployed and employers, which may be caused by structural changes in the economy, such as technological advancements and economic restructuring
Define frictional unemployment
It is the situation when there are information imperfections in the labour market
Explain frictional unemployment
Workers have imperfect information and are not fully informed of available job opportunities elsewhere and employers have similar imperfect information and are not fully informed of what labour are available.
Explain how SG uses exchange rate policies to tackle DD unemployment
The MAS can make use of our managed float regime for the Singapore dollar to reduce the pace of appreciation of SGD, like in 2019 when there were rising trade tensions between US and China, we allowed more room for the currency to depreciate relatively to maintain export competitiveness. The fall in price of SG exports in terms of foreign dollars will lead to more than proportionate rise in X and (X-M), assuming PEDx>1 due to close substitutes and Marshell Lerner condition of PEDx + PEDm>1. This leads to AD rising and DD unemployment is mititgated
Outline how expansionary fiscal policies can be used to tackle DD unemployment
SG maintains low tax rates such as attractive corporate tax rates capped at 17% and provides tax holidays to new firms. By keeping such competitive tax rates, and maintaining a conducive infrastructure for the growth of industries like the development of Punggol digital district, there will be both a rise in G and I, leading to rise in AD and hence mitigating DD unemployment