Shapes of molecules
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:24 PM on 10/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
what is a chemical bond
an electrostatic force of attraction between positively and negatively charged species
2
New cards
what are the three types of chemical bonding
1. covalent bonds
2. ionic bonds
3. metallic bonds
3
New cards
what is a covalent bond
where electrons are shared by two positive nuclei
4
New cards
what is an ionic bond
a bond formed when positive and negative ions are attracted to each other
5
New cards
what is a metallic bond
a bond formed when metal atoms are packed closely together and are bonded to each other by delocalised, free-moving valence electrons
6
New cards
description of a covalent molecule/bond
* negatively charged bonding electrons are attracted to the positively charged nuclei of both atoms
* this attraction holds the atoms together strongly
* force of attraction is as a result of sharing a pair of electrons
* this attraction holds the atoms together strongly
* force of attraction is as a result of sharing a pair of electrons
7
New cards
description of an ionic lattice
* strong electrostatic attraction between ions
* each ion is attracted to the neighbouring, oppositely charged ion
* resulting in a three-dimensional array of positively and negatively charged ions
* each ion is attracted to the neighbouring, oppositely charged ion
* resulting in a three-dimensional array of positively and negatively charged ions
8
New cards
description of a metallic lattice
* three dimensional arrangement of metal ions
* surrounded by delocalised valence electrons
* surrounded by delocalised valence electrons
9
New cards
when does a covalent bond form
when a pair of electrons are shared between the two atoms (usually between two non-metals)
10
New cards
description of a covalent bond forming
* as the atoms get closer, valence electrons from each atom are attracted to the protons from the neighbouring atoms
* this attraction pulls the atoms close together and the electron from each atom are shared
* this attraction pulls the atoms close together and the electron from each atom are shared
11
New cards
what are lewis structures used to demonstrate
only valence electrons
12
New cards
what is the centre atom for lewis diagram
whichever atom is closest to the left hand side
13
New cards
exceptions of having an octet of electrons
H, Be and B
14
New cards
where will regions of high electron density be arranged
as far as possible from the each other
15
New cards
why are regions of high electron density arranged so far away
to minimise the repulsion between the regions of high electron density
16
New cards
what does the shape of the molecule depend on
* the number of regions of electron density around the central atom
* the number of atoms bonded to the central atom
* the number of atoms bonded to the central atom
17
New cards
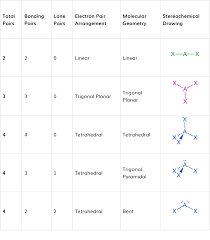
description of tetrahedral shape
4 sets of electrons arranged as far apart as possible
18
New cards
what is the bond angle for tetrahedral
109
19
New cards
description of trigonal planar shape
3 sets of electrons arranged as far apart as possible
20
New cards
what is the bond angle for trigonal planar
120
21
New cards
description of linear shape
2 sets of electrons arranged as far apart as possible
22
New cards
what is the bond angle for linear
180
23
New cards
what are the steps to determine the shape of the molecule
1. draw lewis structure for molecule
2. count the sets of electron on the central atom
3. count the number of bonded atoms (bonding sets of electrons)
24
New cards
overall molecule shape table