Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Three basic functions of the nervous system:
Gather sensory input, process and interpret it, and activate effector organs
CNS consists of:
The brain and the spinal cord
Sensory (afferent) division of PNS:
Carry impulses toward the CNS from sensory receptors in the body
Somatic sensory fibers:
Carry impulses from receptors in the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints
Visceral sensory fibers:
Carry impulses from organs within ventral body cavity
Motor (efferent) division of PNS:
Carry impulses from CNS to effector organs
Somatic nervous system:
Carry impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles and allow voluntary control of motor activity
Autonomic nervous system (ANS):
Involuntary system that regulates activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Sympathetic division of ANS:
Mobilizes body systems during activity
Parasympathetic division of ANS:
Conserves energy and allows for body systems to relax
Glial cells:
Provide protection and support for neurons
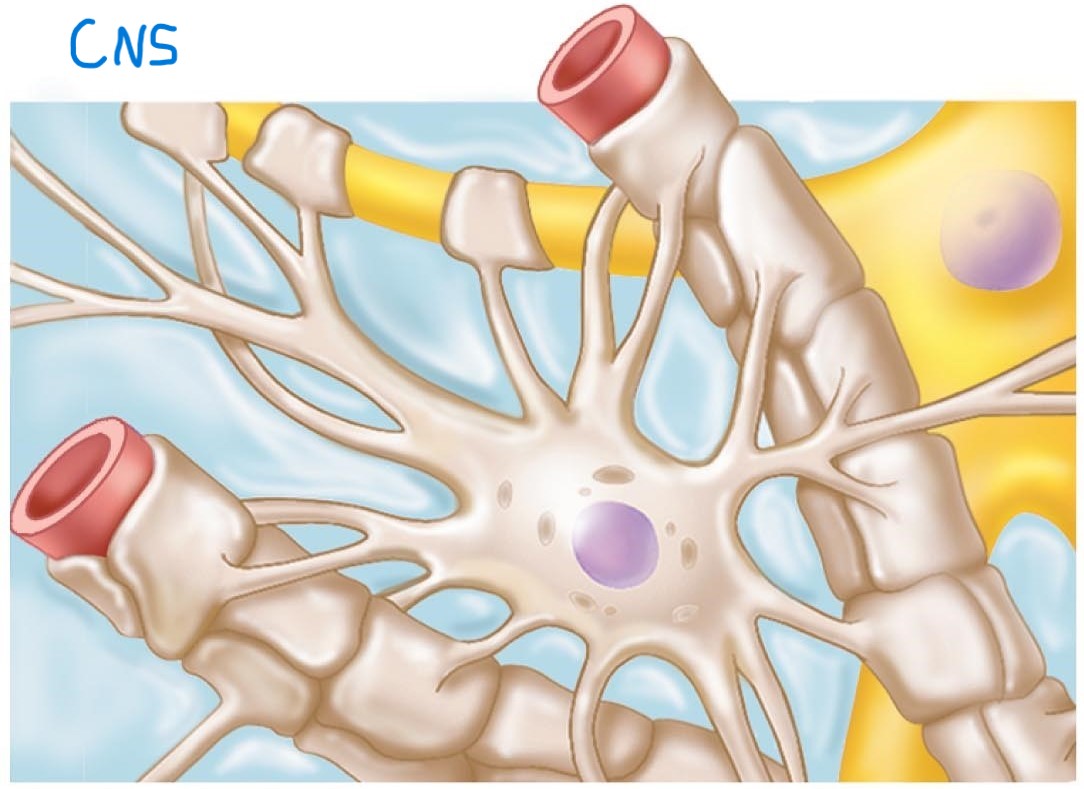
Astrocytes:
Most abundant; support and brace neurons; anchor to capillaries for energy
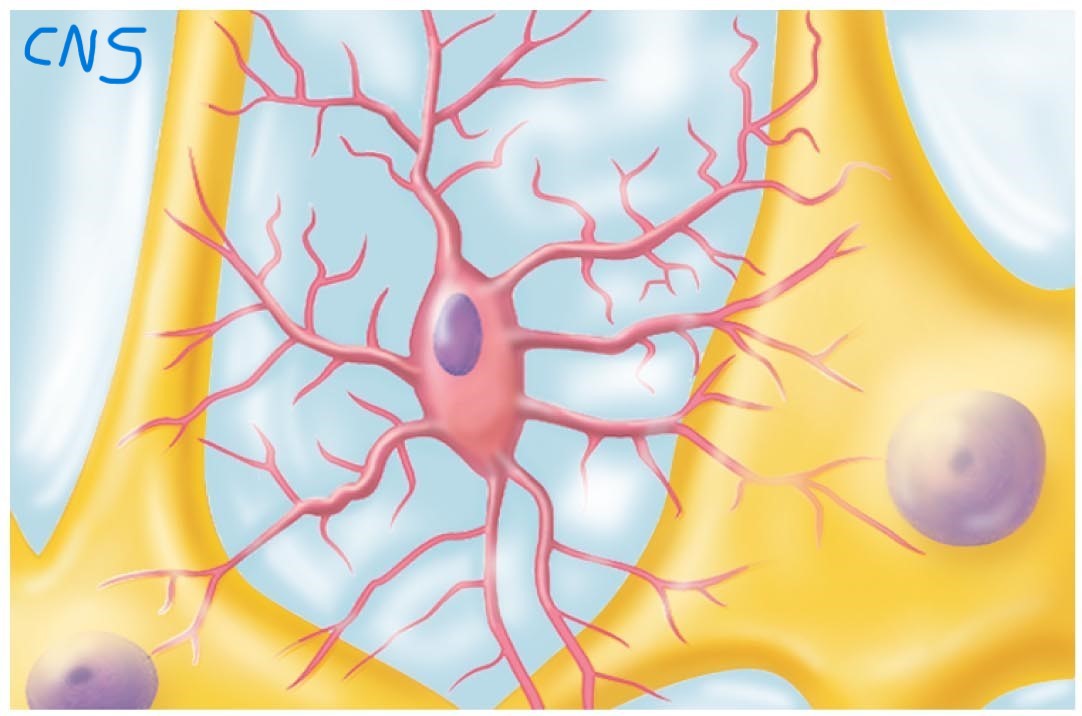
Microglial cells:
Transform into macrophages and phagocytize microorganisms or neuronal debris
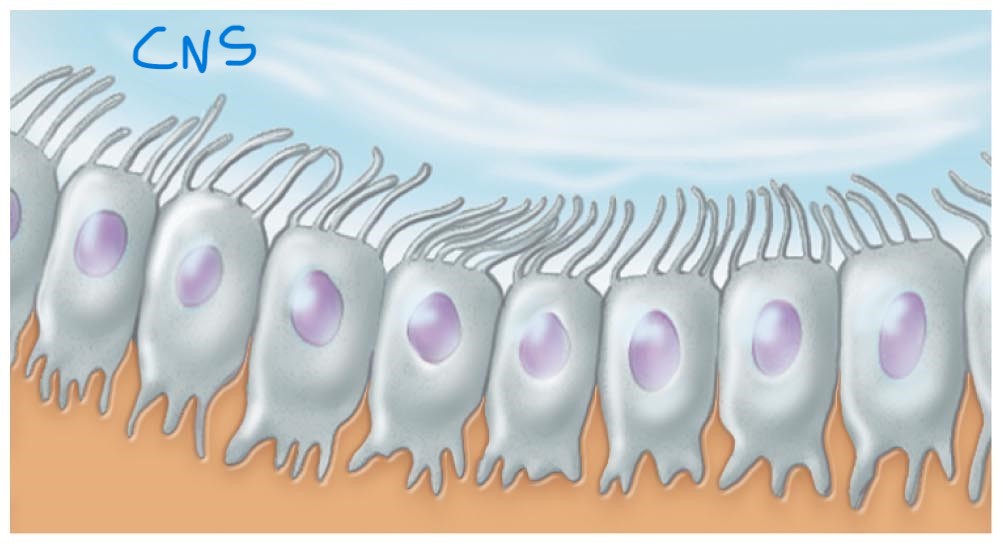
Ependymal cells:
Line central cavities of brain and spinal cord; circulate cerebrospinal fluid
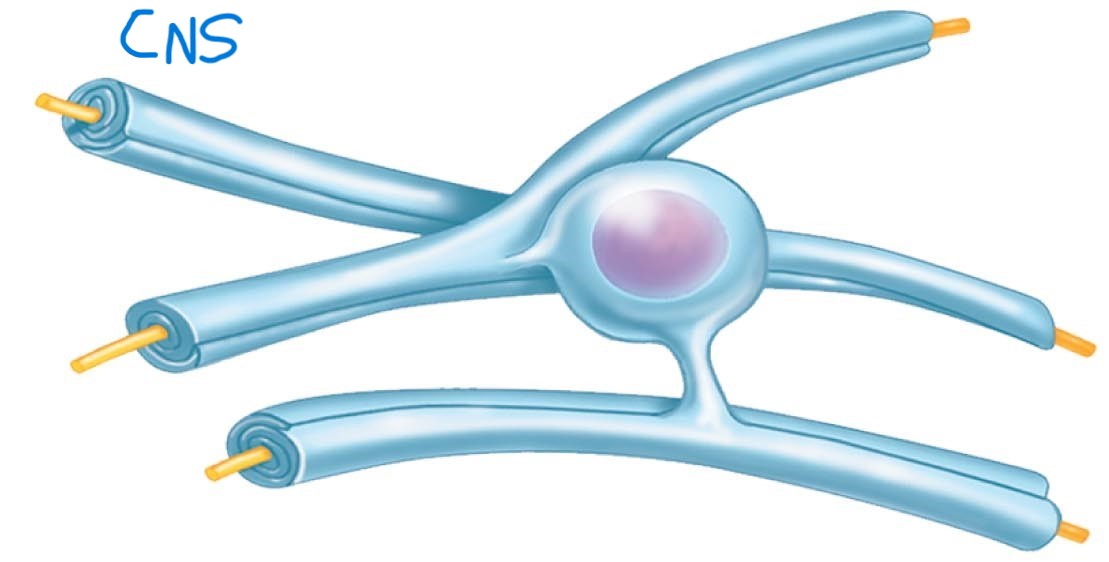
Oligodendrocytes:
Wrap around neuron fibers to form myelin sheaths
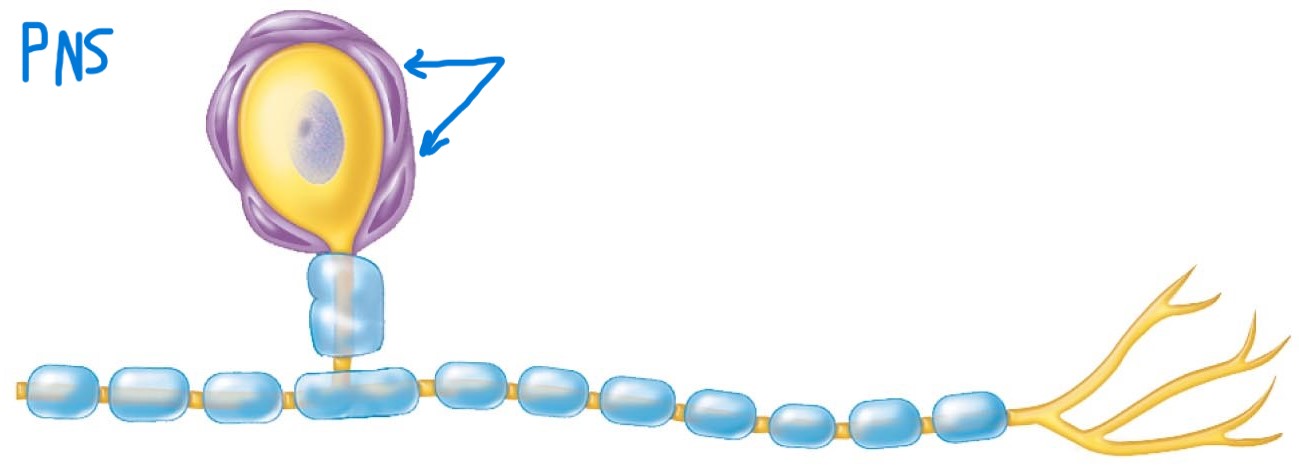
Satellite cells:
Unknown function; found surrounding neuron soma within ganglia
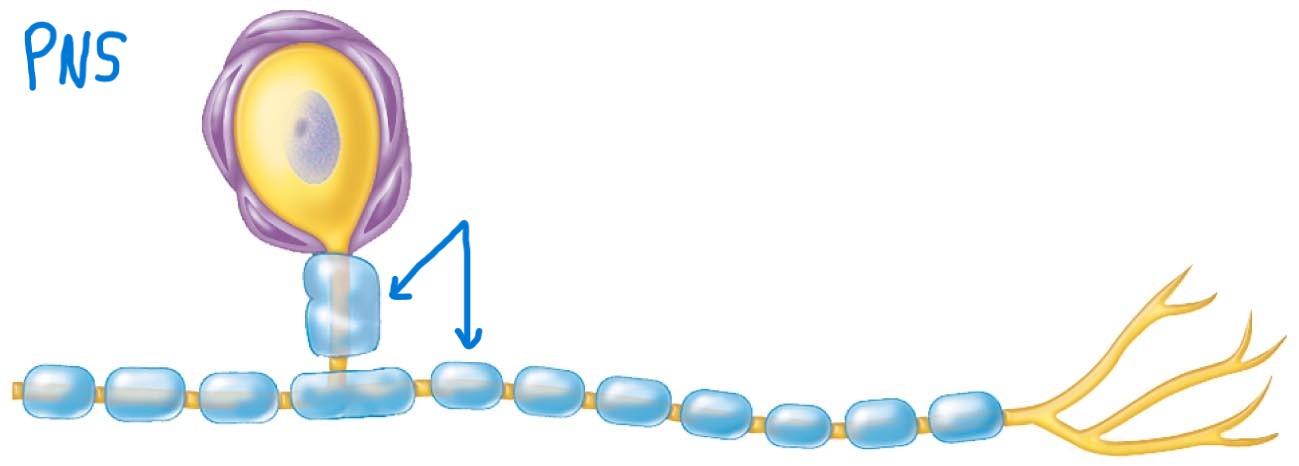
Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes):
Surround nerve fibers to form myelin sheath
Cell body clusters in CNS are called:
Nuclei
Cell body clusters in PNS are called:
Ganglia
Neurons:
Conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses in the body
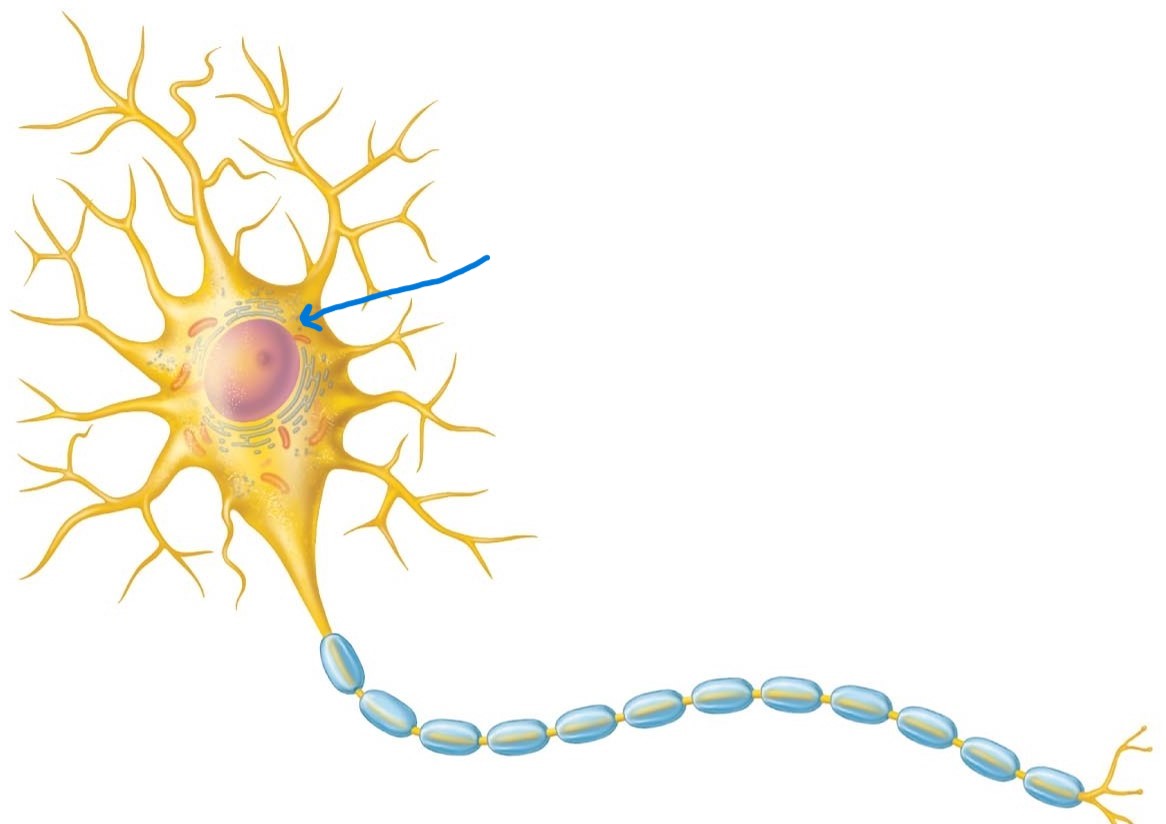
Neuron cell body (soma):
Major biosynthetic center containing usual organelles
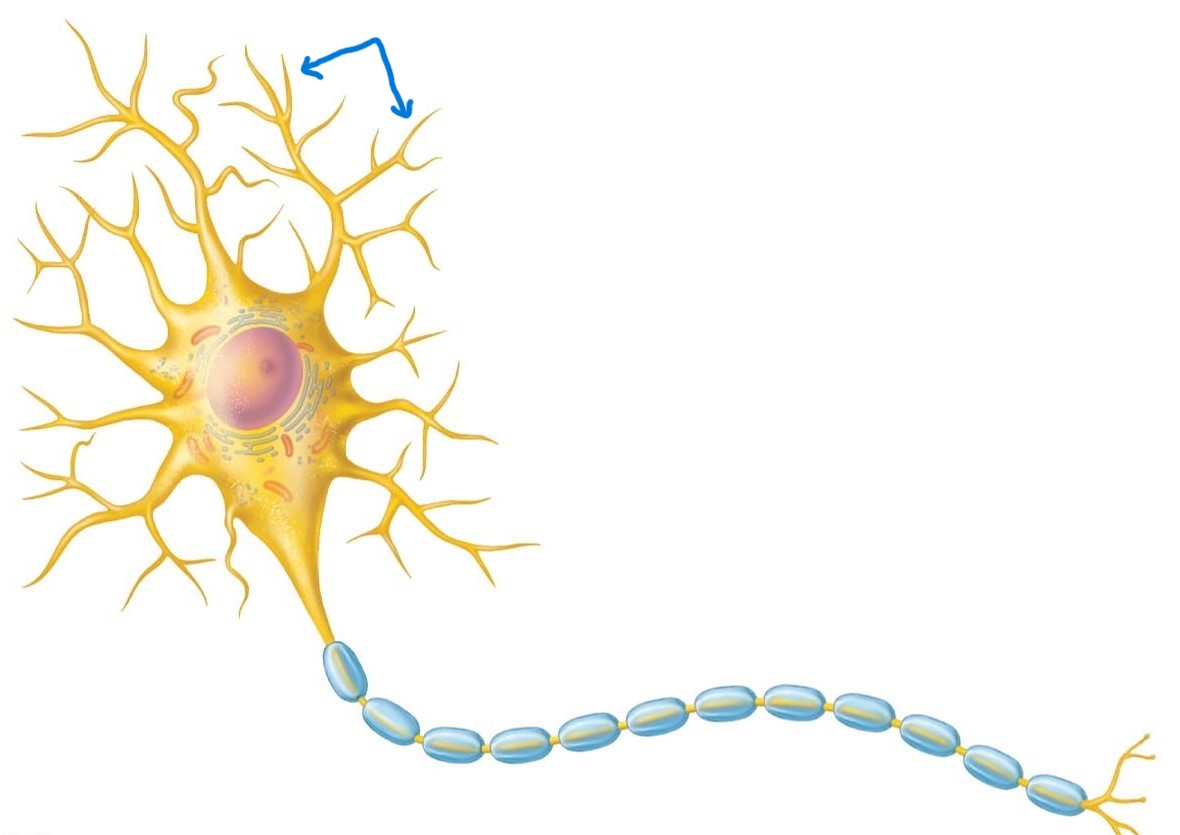
Dendrites:
Receptive regions; provide surface area for receiving signals from other neurons
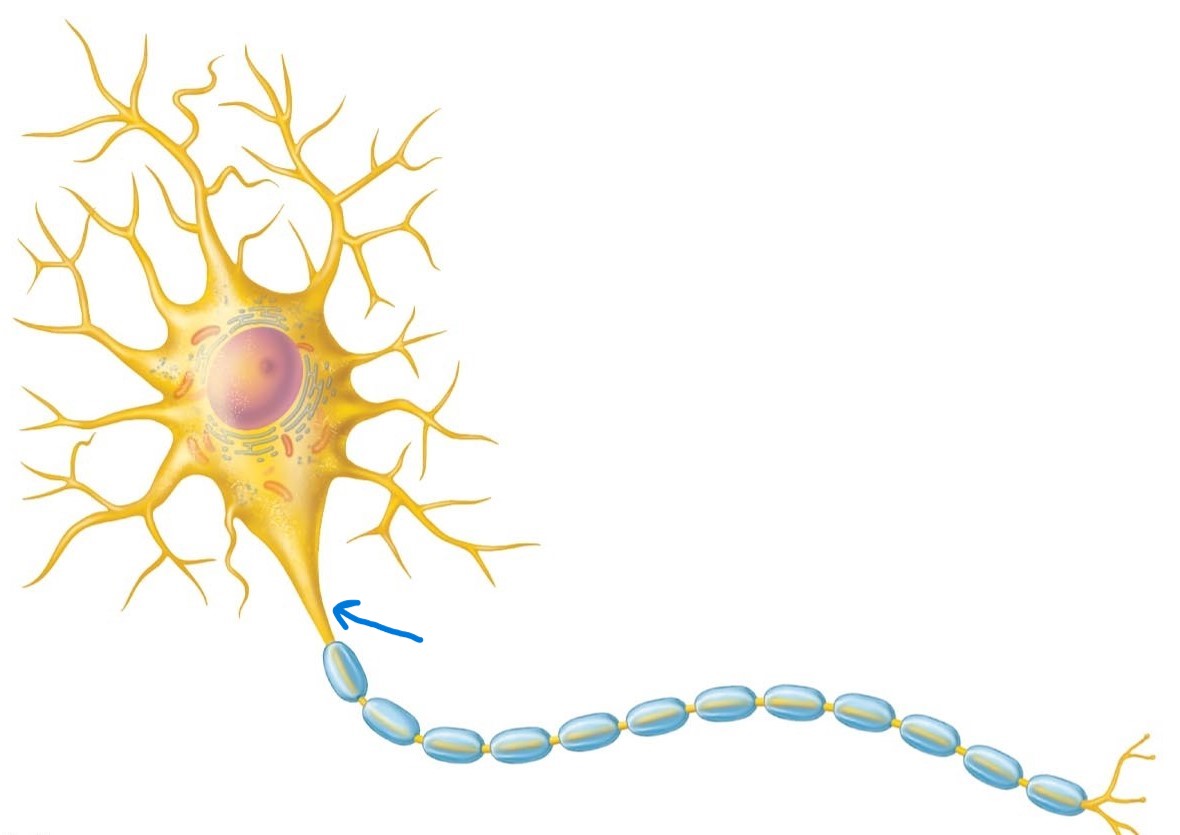
Axon (nerve fiber):
Generates/conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body to axon terminals; part of trigger zone
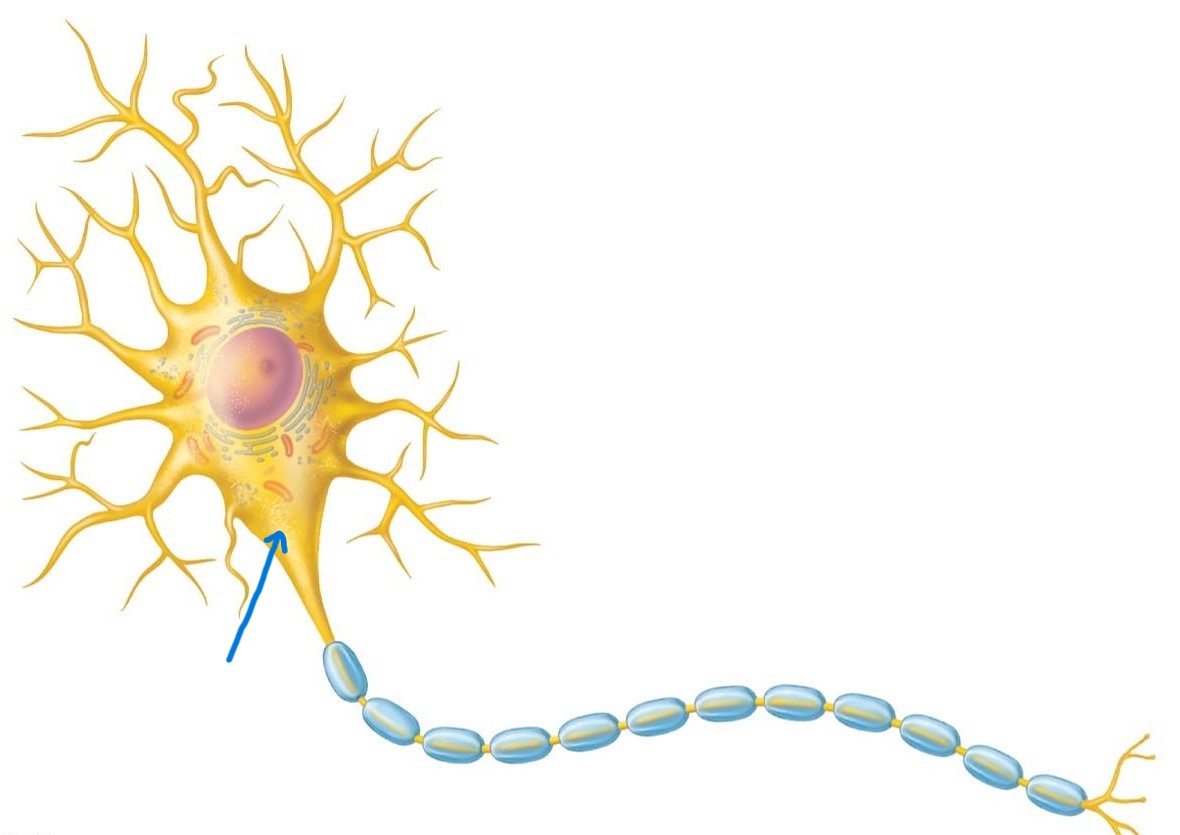
Axon hillock:
Part of trigger zone; superior to axon
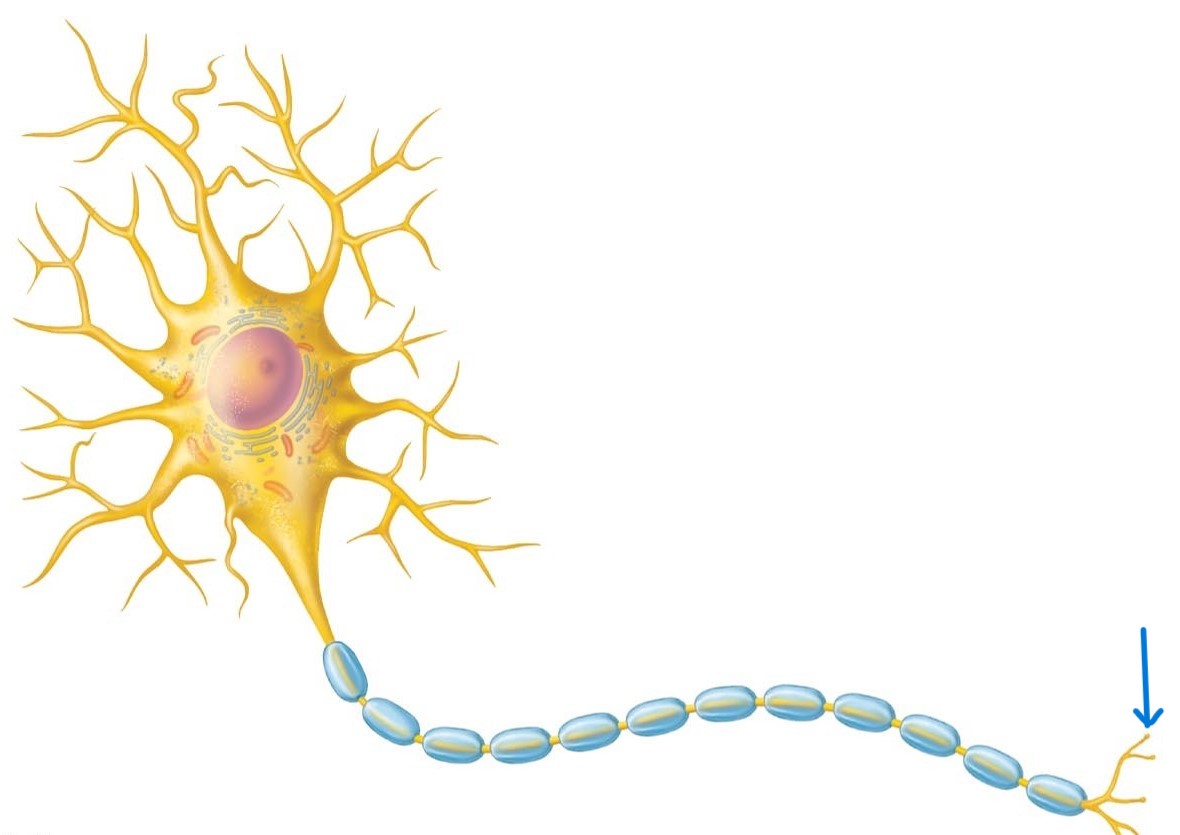
Axon terminals:
Secrete neurotransmitters that either excite or inhibit other neurons or effector cells
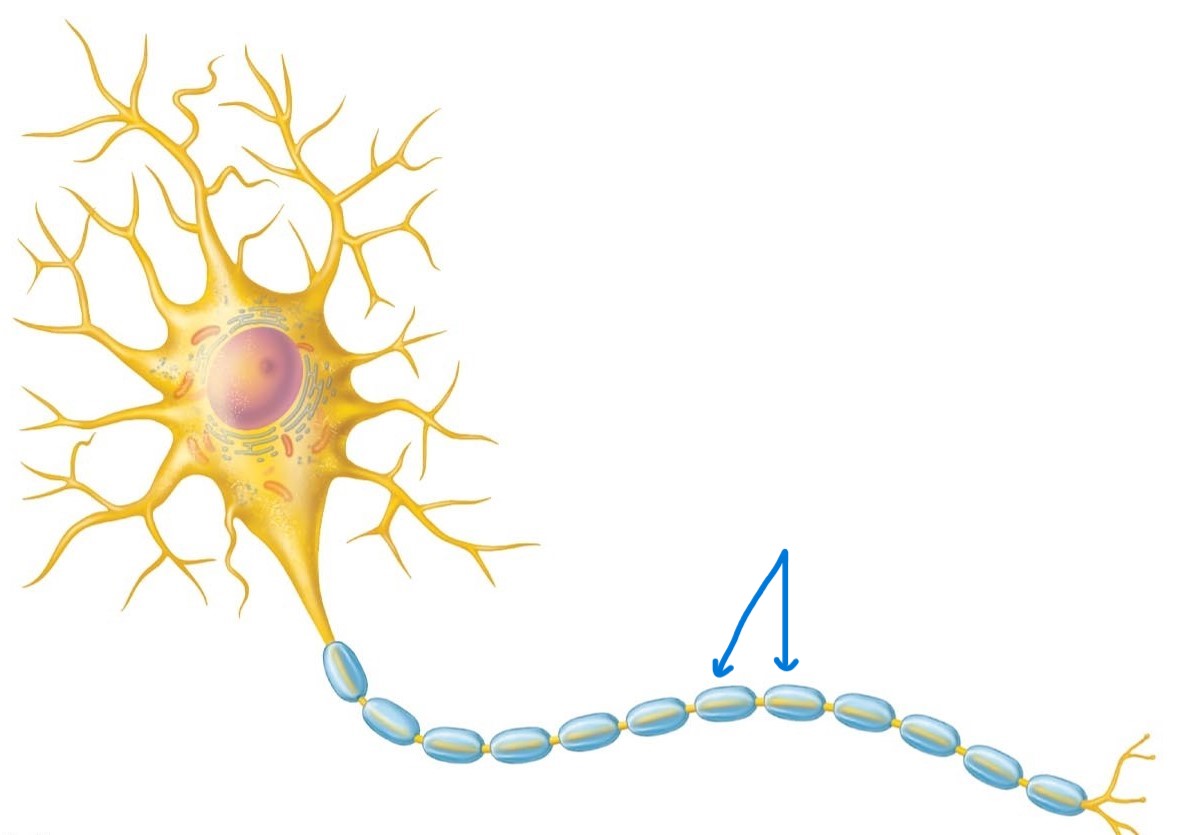
Myelin sheath:
Whitish and fatty; protects, insulates, and increases conduction velocity of axons
Axons within the CNS that HAVE myelin sheaths are called:
White matter
Axons within the CNS that DON’T HAVE myelin sheaths are called:
Gray matter
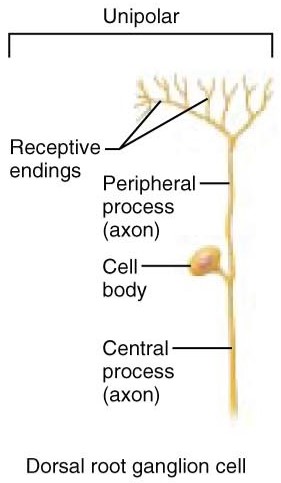
Unipolar neurons:
Have a single process extending from cell body that’s associated with receptors past the peripheral process and central process
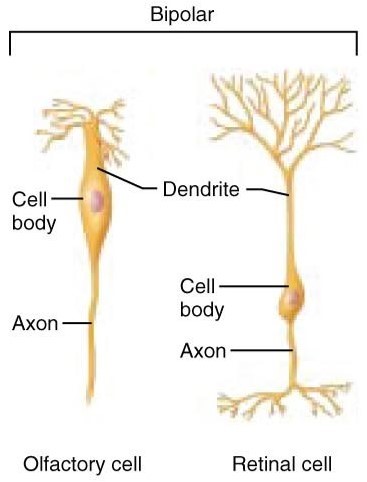
Bipolar neurons:
Have one axon and one dendrite
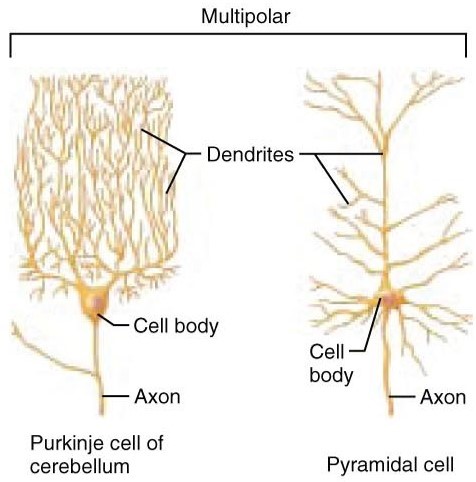
Multipolar neurons:
Most abundant; Have one axon and multiple dendrites
Interneurons (association neurons):
Conduct impulses between sensory and motor neurons, or in CNS integration pathways
Basic principles of electricity:
Voltage (difference in electrical charges), current (flow of charge), and electrical currents are due to the movement of ions across cellular membranes
Chemically gated (ligand-gated) channels:
Open when the appropriate chemical binds
Voltage-gated channels:
Open in response to a change in membrane potential
Mechanically-gated channels:
Open when membrane receptor is physically deformed
What happens when ion channels are open:
Ions diffuse across the membrane along their electrochemical gradients, creating electrical currents
The membrane of a resting neuron is:
Polarized
Resting membrane potential (RMP):
The potential difference of the polarity of a resting neuron and its membrane
RMP exists only across a membrane because:
Differences in ionic makeup of intracellular/extracellular fluids, and differential membrane permeability to those ions
Cytosol:
Lower concentration of sodium ions and higher concentration of potassium ions than extracellular fluid
Potassium ions:
Plays most important role in generating RMP; 25 times more permeable than sodium ions
Neurons use _______ in __________ __________ as _____________ _________
Changes, membrane potential, communication signals
Graded potentials:
Usually incoming signals that travel short distances
Action potentials:
**Principal way neurons send signals over long distances
1) Begins with increase in sodium ion permeability followed by restoration of sodium ion impermeability, and then short-lived increase in potassium ion permeability
2) Propagation (transmission) occurs as local currents of an area undergoing depolarization cause depolarization of forward adjacent area
3) Repolarization follows depolarization, restoring RMP
Depolarization:
Inside of membrane becomes less negative
Hyperpolarization:
Inside of membrane becomes more negative
Synapse:
Junction that mediates information transfer between neurons, or between a neuron and effector cell
Presynaptic cells:
Neurons conducting impulses towards a synapse
Postsynaptic cells:
Neurons carrying impulses away from a synapse
Electrical synapses:
Electrically coupled neurons that allow direct change of ions from cell to cell
Chemical synapses:
Specialized for release and reception of chemical neurotransmitters
All-or-none phenomenon:
Action potentials either happen completely OR don’t happen at all
Refractory period:
Related to the time required so that a neuron can generate another action potential
Absolute refractory period:
When a patch of membrane is generating an action potential, the neuron can’t respond to another stimulus
Relative refractory period:
Following absolute refractory period; strong stimuli causes more frequent generation of action potentials
Nonmyelinated axons:
Conduct impulses slowly; smaller diameters
Myelinated axons:
Conduct impulses faster; larger diameters