3.4.5 Making operational decisions to improve performance: managing inventory and supply chains
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Define Outsourcing (also known as subcontracting)
The use of an external organisation to complete part of or all of an activity in the production process/used to deal with unexpected increase in demand
Outsourcing pros (x2)
Allows business to focus on areas of core competence
Allows a business to increase production levels to beyond there capacity
Outsourcing cons (x2)
Issues with quality
Supplier may charge a higher price
Define part time staff
Permeant members of staff that work fewer then 30 hours a week
Define Temporary staff
Staff employed on a short term-basis often at specific times during the year
Part time/temporary staff pros (x2)
Give business flexibility
May incur lower costs
Part time/temporary staff cons (x2)
Introduction and training costs
The skill of the part time/temporary staff
Define Producing to order
Where products are manufactured only after an order has been placed by a customer e.g. new cars/sandwiches
Producing to order pros (x2)
Lower level of wastage
High level of customer satisfaction
Producing to order cons (x2)
Difficult to deal with unexpected changes in demand
Customer need to wait for the product
Define inventory control
The management of organisations level of stock to enable it to match the supply to the demand
Stock includes e.g. (x2)
Raw materials
Finished goods
Pro high level of inventory (x2)
Meet unexpected changes in demand
Able to benefit from bulk buying of raw materials (economies of scale)
Pro low level of inventory (x2)
Low costs incurred in storing and securing raw materials
Less money tied up in working capital
Define inventory control charts
A diagram used to represent an organisation's stock levels over a period of time
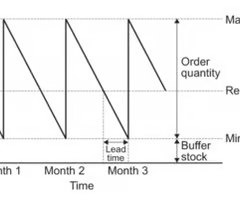
Inventory control charts: Re- order level
The stock level that triggers the purchase of new inventory
Inventory control charts: Lead time
The time taken for a supplier to deliver an order once it has been placed
Inventory control charts: Buffer level at inventory
The target minimum level of inventory to be held by a business
Inventory control charts: Re- order quantity
The amount of stock a business orders
Influences on the levels of inventory held (x4)
Production techniques (i.e. use of mass production/JIT)
Reliability of suppliers
Anticipated levels of demand
Finance
Stock managment techniques (x3)
Stock rotation
Reduction in security
Production techniques
Influences on choice of supplier (x3)
Quality: The experience of the customer when receiving the goods
Price: How much the business will pay for supplies which will directly affect costs
Capacity: The ability to meet demand at a constant quantity and on time
Define Suppliers
Organisations in the supply chain who provide goods and services used in the production process
Businesses rely on supplies to
Supply the necessary good: At the time they are needed/in the required quantity
Impact on operational performance measured via (x4)
Unit cost
capacity utilisation
flexibility
quality
Define Inventory
Refers to the stock a business has
Define supply chain
System of people, organisations , and information involved in the process of producing products and satisfying consumer demand
Managing a supply chain: specialisation
Where each organisation focuses on its core competence within the supply chain
Managing a supply chain pro (x2)
Increase focus on core competence
Increase efficiency
Define vertical integration
Where an organisation manages the whole supply chain
Vertical integration pro (x2)
Reduce raw material price
Increase security of suppliers
Value of managing supply chain
Impact on: unit cost , capacity utilisation , flexibility and quantity