Chapter 2 - The Chemistry of Life
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What three subatomic particles make up atoms?
The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Atom
The basic unit of matter.
Nucleus
The center of the atom that is formed by protons and neutrons bound together with strong forces.
Electron
A negatively charged particle ( - ) with only 1/1840 mass of a proton that surrounds the nucleus.
How are all of the isotopes of an element similar?
Because they have the same number of electrons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties.
Element
A pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons they contain.
In what ways do compounds differ from their component elements?
The physical and chemical properties of a compound are usually very different from those of the elements from which it is formed.
Compound
A substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions.
What are the main types of chemical bonds?
The main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Ions
Positively and negatively charged atoms because of transferred electrons.
Covalent Bond
Formed when moving electrons actually travel about the nuclei of both atoms and share them between atoms.
Molecule
The smallest unit of most compounds.
van der Waals forces
When molecules are close together, a slight attraction can develop between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. It's named after the scientist who discovered them.

How does the structure of water contribute to its unique properties?
Because water is a polar molecule, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of water's special properties.
Hydrogen Bond
The attraction between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and the oxygen atom.
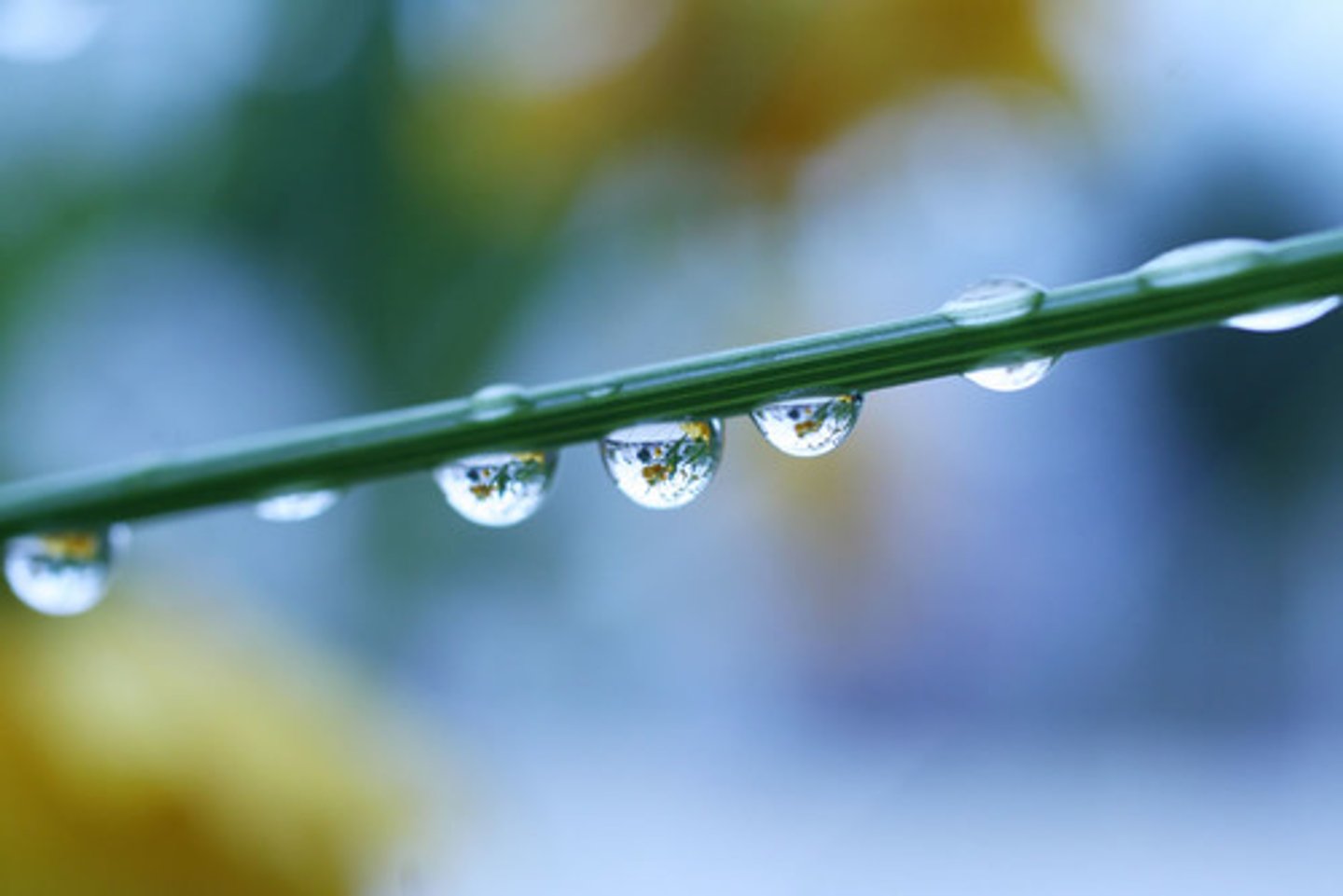
Cohesion
An attraction between molecules of the same substance.

Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances.

How does water's polarity influence its properties as a solvent?
Water's polarity gives it the ability to dissolve both ionic compounds and other polar molecules.
Mixture
A material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together but not chemically combined.

Solution
Formed when ions gradually become dispersed in water.
Solute
The substance of a solution that is dissolved.
Solvent
The substance of a solution in which the solute dissolves.
Suspensions
Mixtures of water and non-dissolved material.
Why is it important for cells to buffer solutions against rapid changes in pH?
Buffers dissolved in life's fluids play an important role in maintaining homeostasis in organisms.
pH Scale
A measurement system used to indicate the concentration of H+ ions in solution.
Acid
Any compound that forms H+ ions in solution.
Base
A compound that produces hydroxide (OH-) ions in solution.
Buffers
Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH.
What elements does carbon bond with to make up life's molecules?
Carbon can bond with many elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen to form the molecules of life.

What are the functions of each of the four groups of macro-molecules?
Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants, some animals, and other organisms also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information. Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Other form important cellular structures, while still others transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease.
Monomers
Smaller units that form polymers.
Polymers
Form macro-molecules by a process known as polymerization.
Carbohydrates
Compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, usually in a ratio of 1 : 2 : 1. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants, some animals, and other organisms also use carbohydrates for structural purposes.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules.
Lipids
Made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms. The common categories of lipids are fats, oils, and waxes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings.
Nucleic Acids
Macro-molecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information.
Nucleotides
Individual monomers of 5 carbon-carbon sugar, a phosphate group (-PO4), and a nitrogenous base that make up nucleic acids.
Proteins
Macro-molecules that contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Some proteins control the rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Other form important cellular structures, while still others transport substances into or out of cells or help to fight disease.
Amino Acids
Compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the end that make up proteins.
What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions involve changes in the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds
Chemical Reaction
A process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another. Mass and energy are conserved during chemical transformations.
Reactants
The elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction.
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
How do energy changes affect whether a chemical reaction?
Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. Chemical reactions that absorb energy will not occur without a source of energy.
Activation Energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started.
What role do enzymes play in living things and what affects their function?
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells. Temperature, pH, and regulatory molecules can affect the activity of enzymes.
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction.
Enzymes
Proteins that act as biological catalysts.
Substrates
The reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.