fart
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
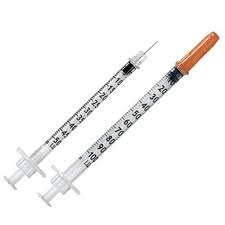
A device specifically designed for the injection of insulin, typically featuring a fine needle and a calibrated barrel for accurate dosage. It is used by individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels.
Insulin syringe
A specific formulation of medication designed for administration, including tablets, capsules, injections, and topical applications. Drug forms include solid, liquid, and semi-solid preparations.
Drug Form
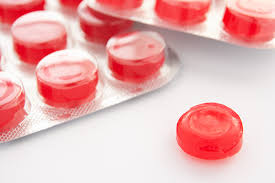
A small, medicated tablet designed to dissolve in the mouth for local, often used to relieve sore throats or coughs.
Lozenge
a pill that is entirely composed of medication. It's made by compressing powdered medicine into a solid, smooth pill
Tablet
A medical instrument used to inject substances into the body or withdraw fluids, typically consisting of a slender, hollow tube with a sharp point.
Needle
A small hollow tube used for injecting or withdrawing liquids
Syringe
a liquid solution that contains a medicinal substance dissolved in alcohol or another solvent, often used for therapeutic purposes.
Elixir

a solid dispersed in a liquid, where the solid particles are not dissolved but suspended throughout the liquid, often requiring shaking before use.
Suspension

A small, soluble container that holds a dose of medication, typically used for oral administration.
Capsule
A method of administering medication by placing it under the tongue, allowing it to dissolve and be absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
Sublingual
A type of medication formulation designed to resist dissolution in the stomach and dissolve in the intestines, protecting the drug from stomach acid.
Enteric coated

A topical preparation intended to be applied to the skin for moisturizing, soothing, or medicinal purposes.
Lotion

A tool used in pharmacies and laboratories to crush, grind, and mix substances, often for preparing medications.
Mortar & Pestle

A small container, typically made of glass or plastic, used to hold liquid medications or samples.
Vial

A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, often used in a medical or laboratory context for delivering medications.
Solution

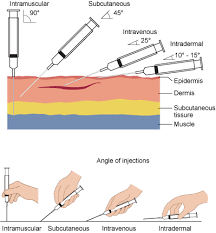
injection of medication directly into a muscle.
Intramuscular
A method of delivering medication through a fine aerosolized form, often used for respiratory treatments or localized effects.
Spray or Mist

A topical formulation applied to the skin for therapeutic or cosmetic purposes.
Cream or Ointment
delivery of medication through the skin, often using patches.
Transdermal
a method of delivering medication through the rectum, allowing for systemic or local effects.
Rectal administration

injection of medication into the dermis, just below the epidermis, often used for allergy tests or vaccinations.
Intradermal
injection of medication into the fatty tissue beneath the skin, commonly used for insulin or vaccines.
Subcutaneous
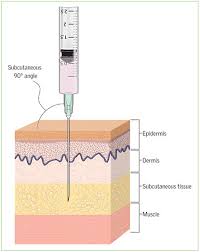
this usually means you can split your tablet in half
Scored

A concentrated solution of sugar in water to which specific medicinal substances are usually added
Syrup

a liquid that is used to dissolve a powdered medication or other substance
Reconstitution
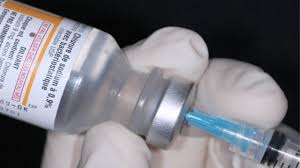
a sealed glass capsule containing a liquid, especially a measured quantity ready for injecting.
Ampule

a type of regional anesthesia that blocks pain signals from traveling to the brain
Epidural
the size of the hole in the needle
Gauge

A device used to cut pills into smaller pieces for easier consumption or dosage adjustment.
Pill cutter

A medical procedure involving the insertion of a needle directly into the bone marrow, used for administering medications or fluids in emergency situations when intravenous access is difficult.
Intraosseous
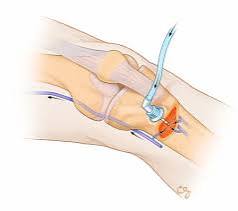
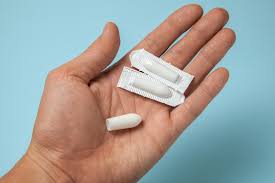
Suppository
a medication that is inserted into the rectum or vagina to dissolve and release its active ingredients
a way of giving a drug or other substance through a needle or tube inserted into a vein
Intravenous
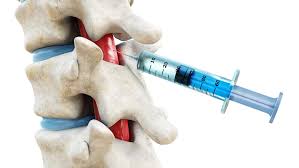
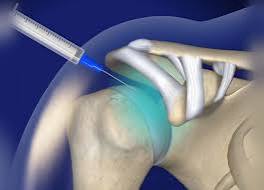
involves injecting medications into a joint or surrounding tissues to treat pain and inflammation
Intra-articular
how a drug is to be administered to a patient
Route of delivery
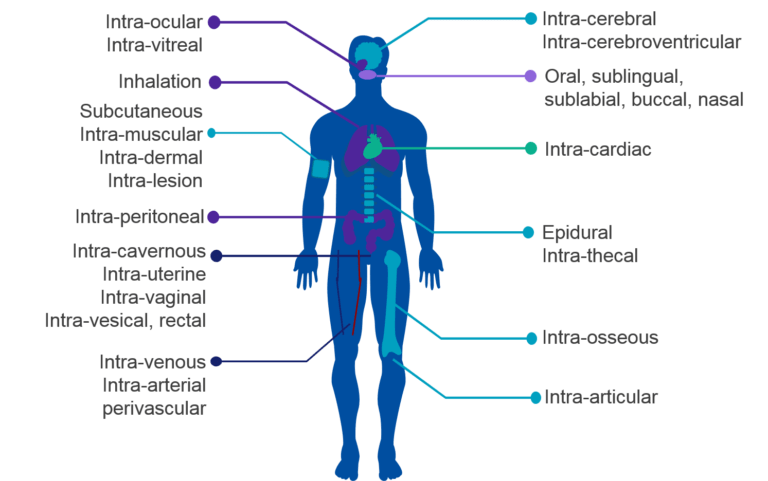
the input of drugs or medications into the human body in a way not involving the intestines or the digestive tract
Parenteral