HBS Unit 1
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
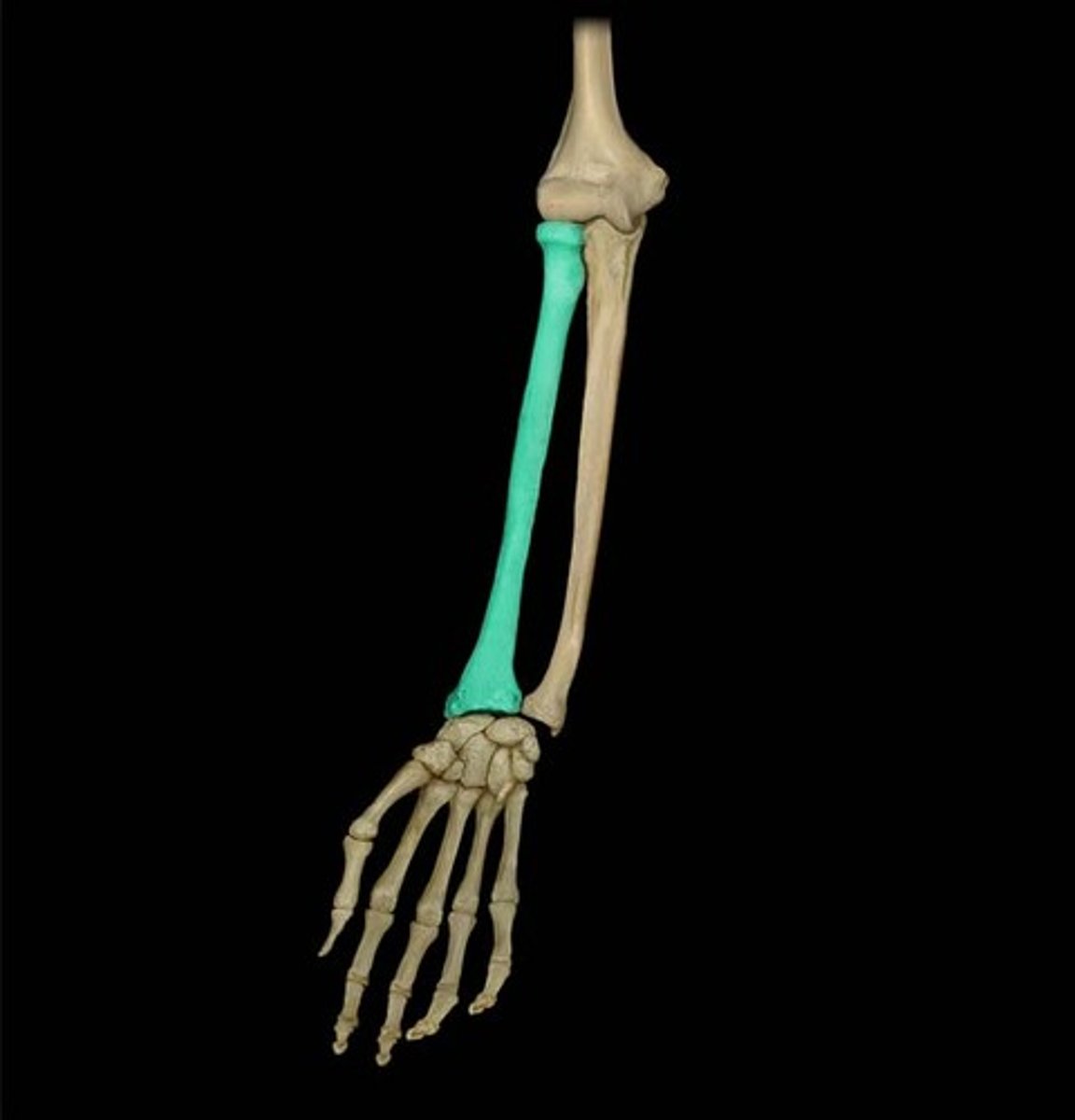
The Radius (follows the thumb)
What is highlighted in blue?
function of the temporlis
chewing
osten
basic unit of compact bone
function of yellow marrow
stores fat
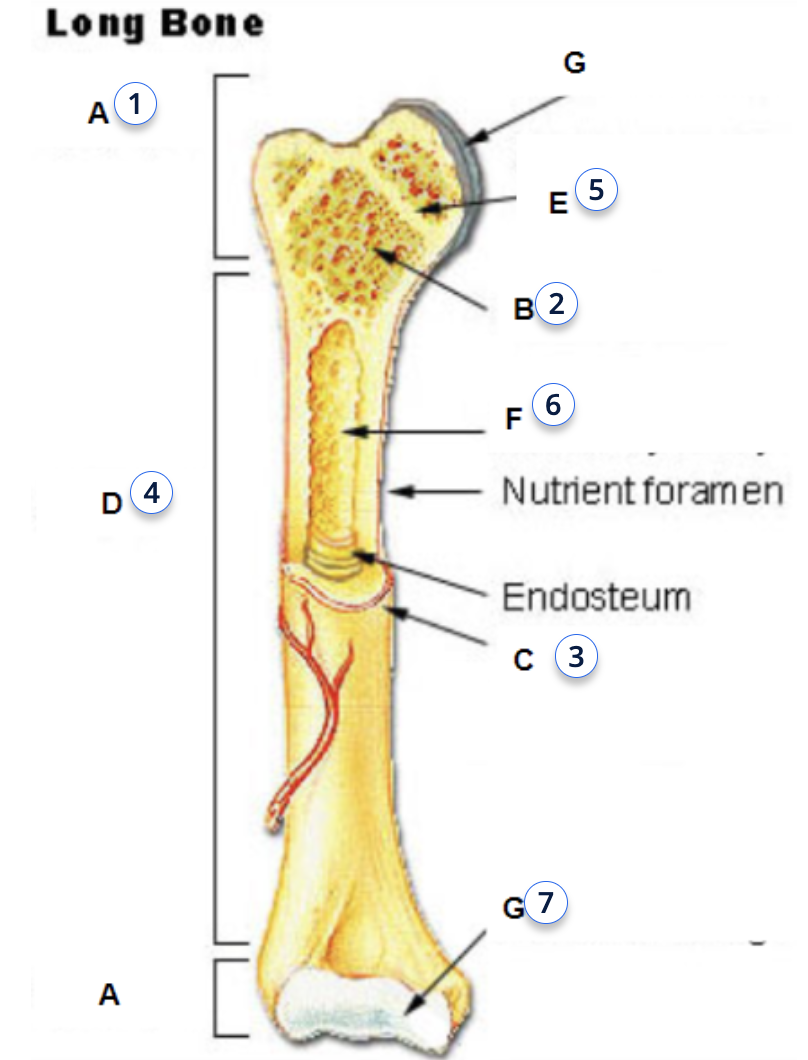
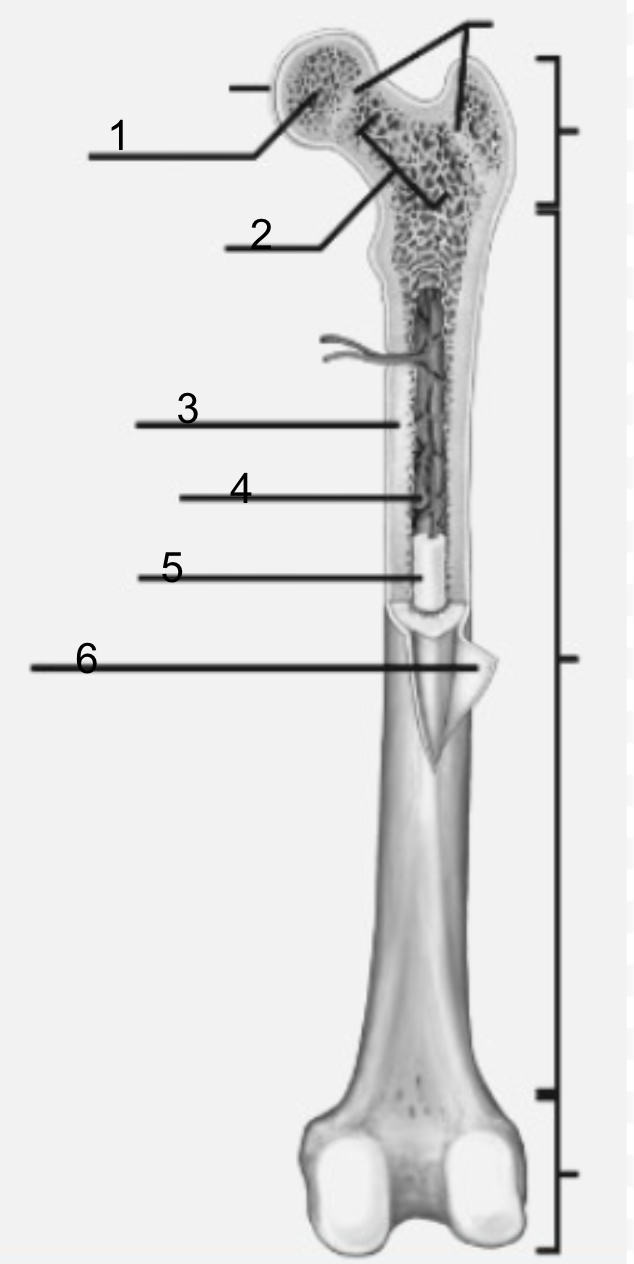
what is 1
epiphysis
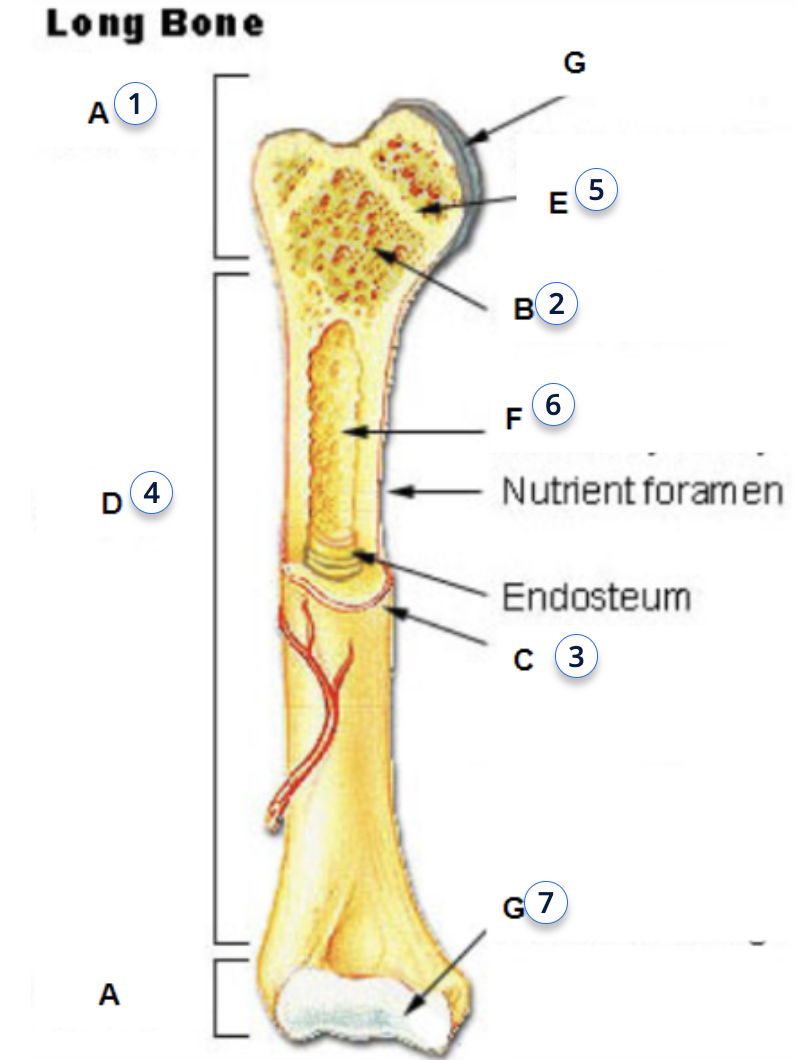
what is 2
spongy bone
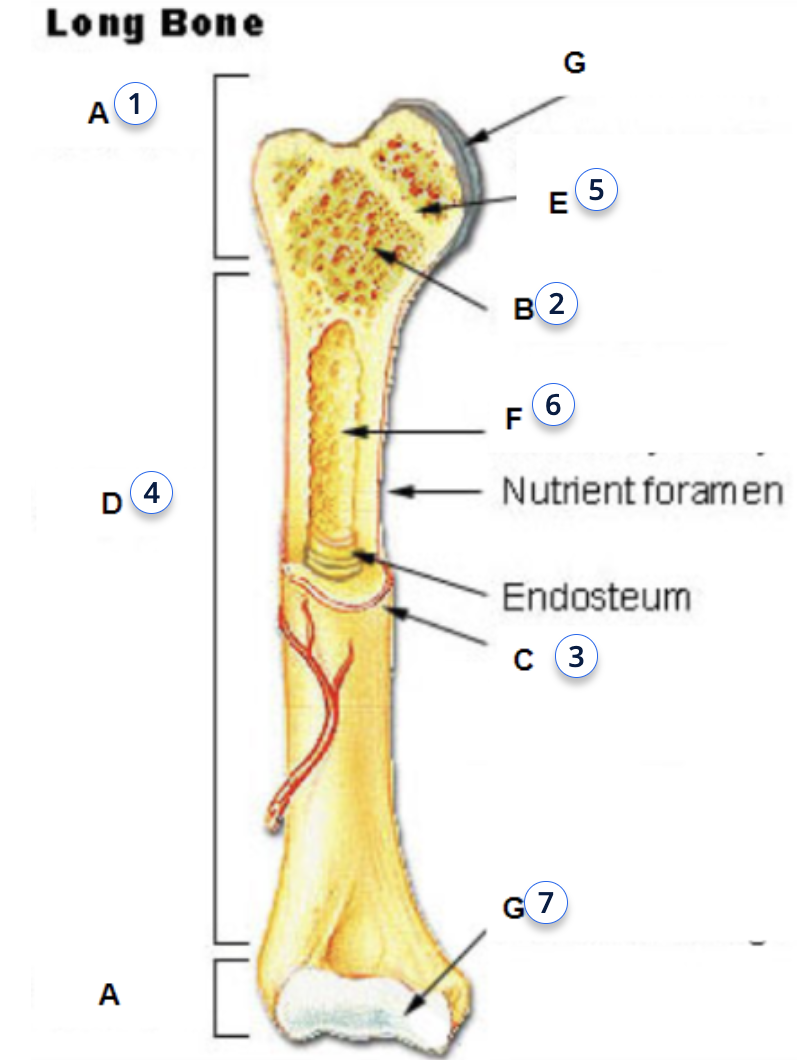
what is 3
periosteum
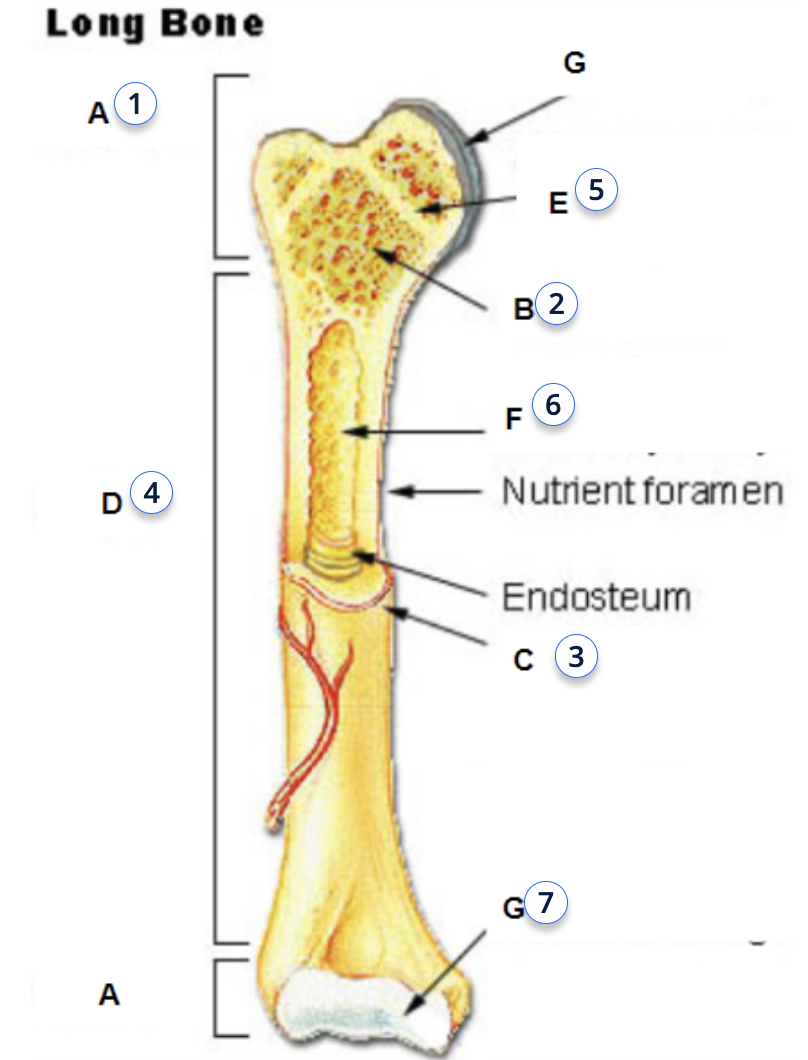
what is 4
diaphysis
osteclast
dissolves and breaks down old or damaged bone cells
ostenblast
cells that form new bones and grow and heal existing bones
what is 5
epiphyseal plate (line)
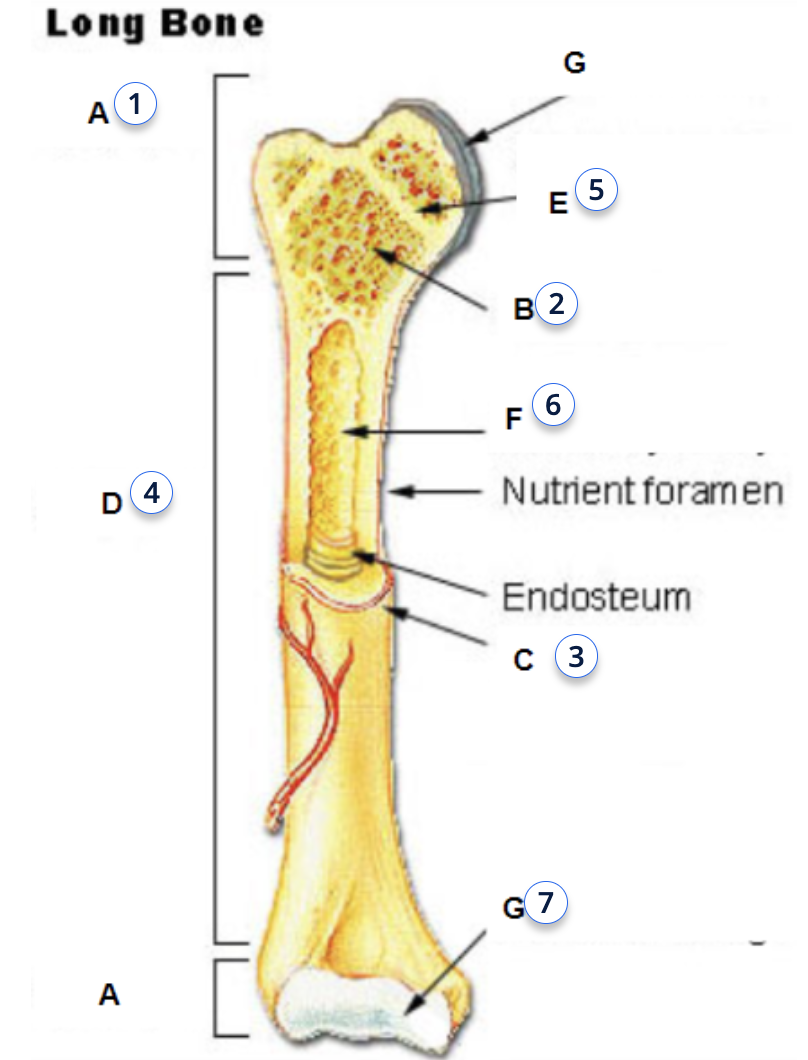
what is 6
yellow bone marrow
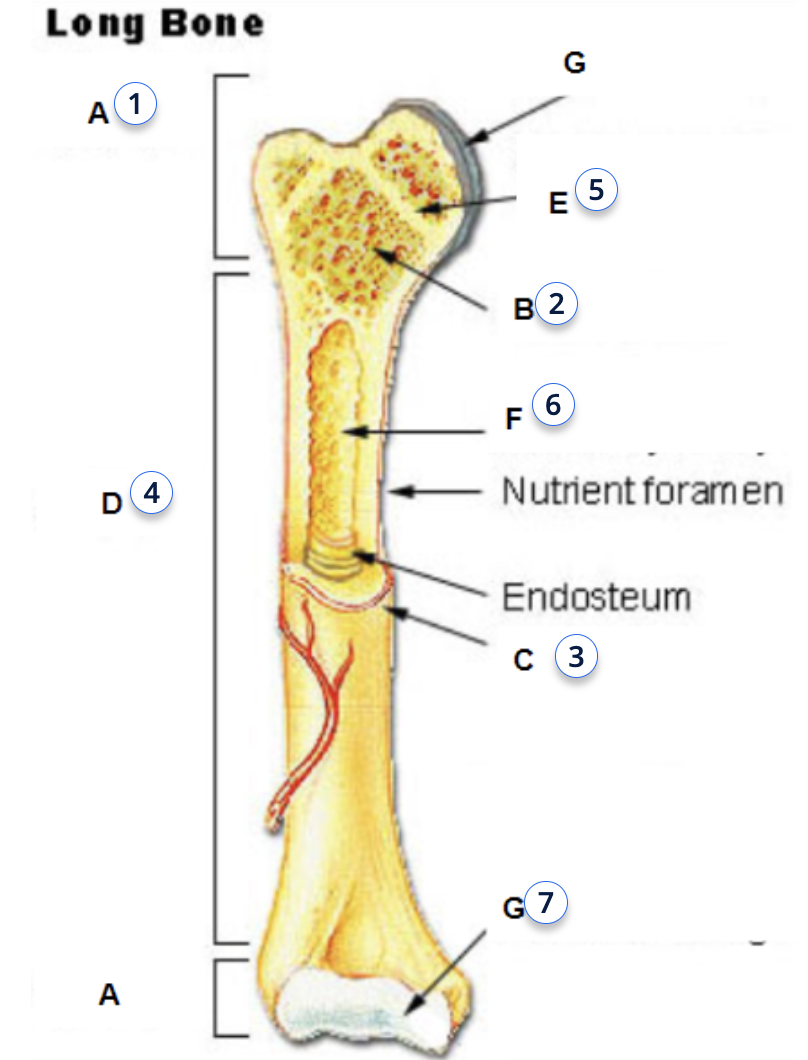
fucntion of bone marrow
to make blood cells
what is 7
articular cartilage
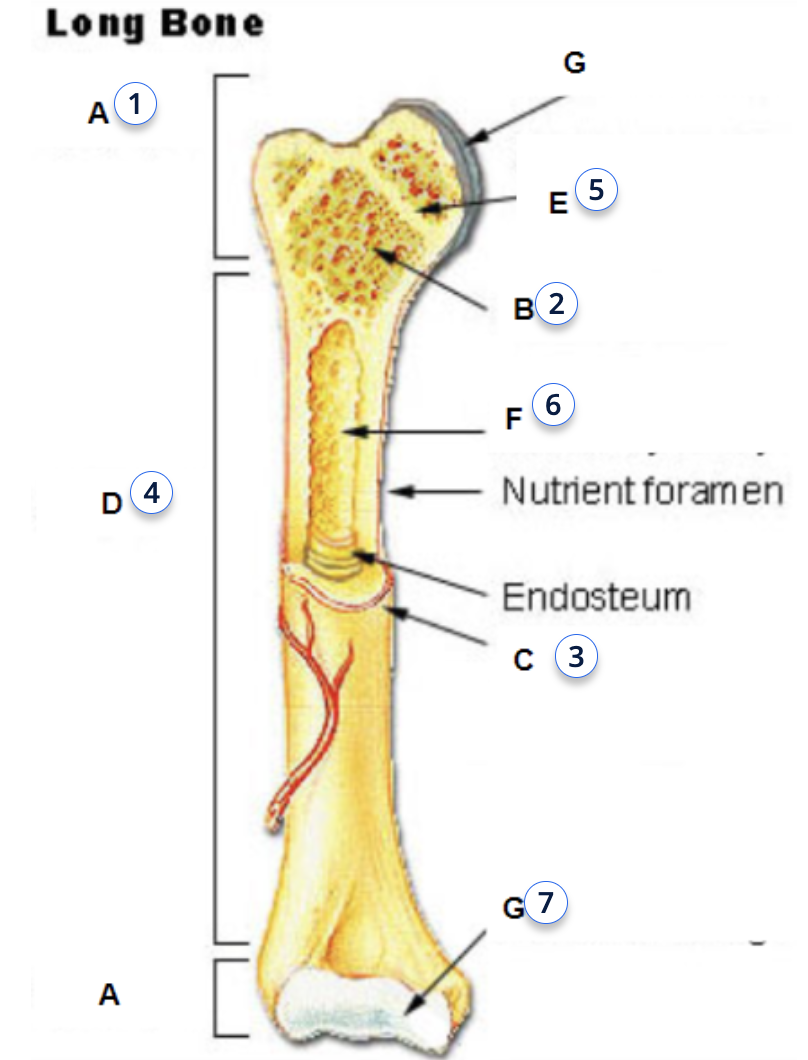
Osteoblasts function
form new bones and add growth to existing bone tissue.
Osteoclasts
dissolve and break down old or damaged bone cells. They make space for osteoblasts to create new bone tissue in areas that are growing or need repair
Provide an example of body systems working together for a specific function.
functions cells work together to from tissue
Group of tisse perfroms a spefcifc function to make up organs
Groups of organs that work together to perform one or more large function make an organ system.
functions of temporalis muscle
move the mandible or lower jaw.
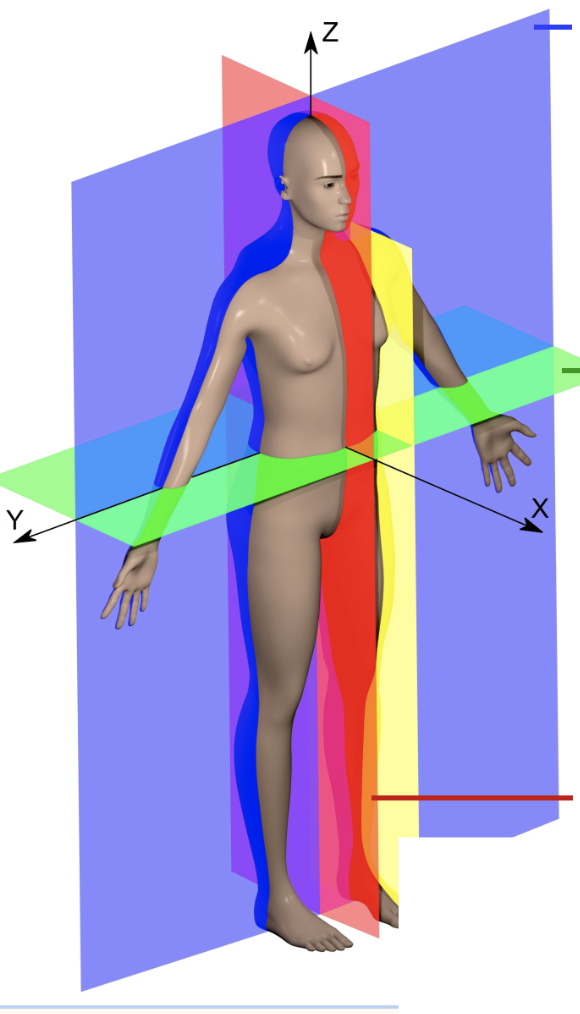
What is highlighted in blue?
coronal or frontal plane
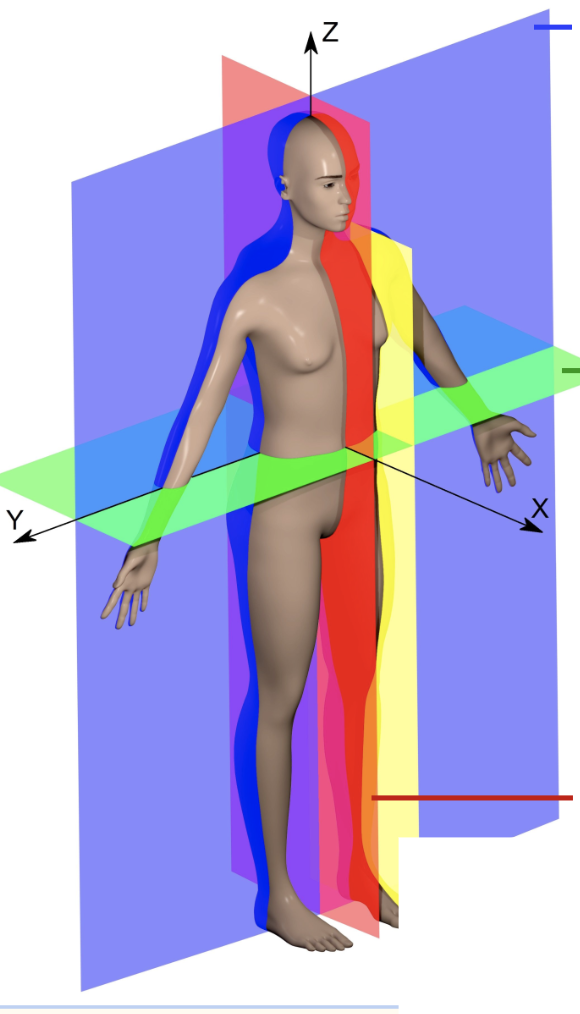
What is highlighted in green
horizontal axis or transverse plane
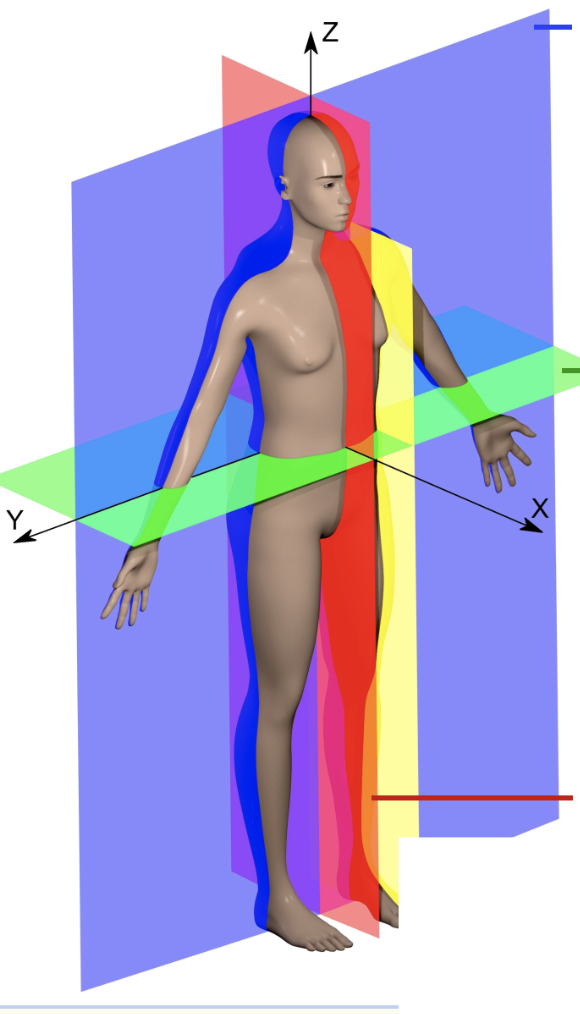
what is highlighted in red
medial plane or sagitittal or longitudinal (vertical, up and down)
what is 1
Epiphysis
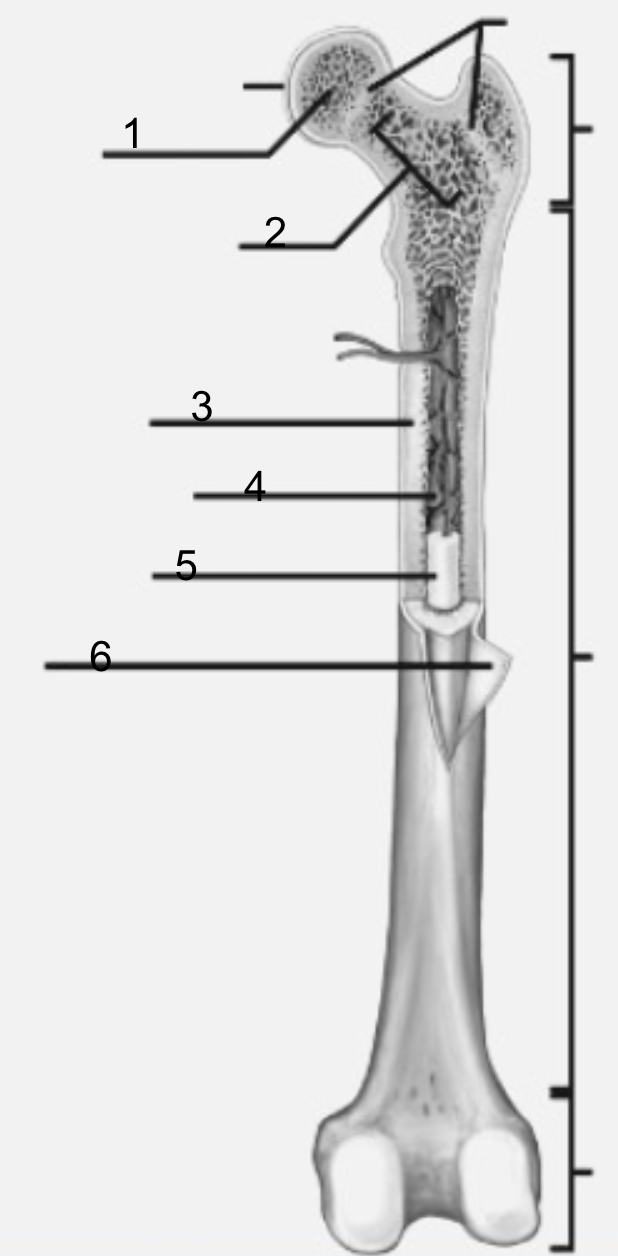
functions of Epiphysis
For articulations (when two or more bone meet and join )
what is 3
diaphysis
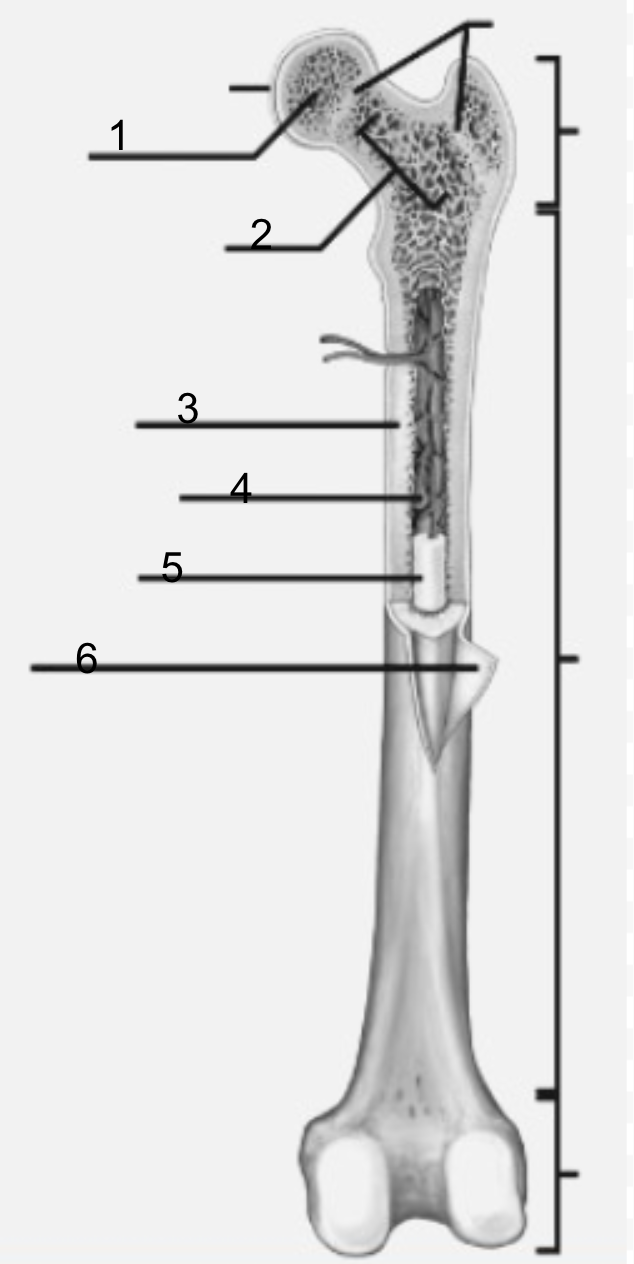
function of diaphysis
the transport of oxygen and immune support, and mineral and fat storage.
what are the three main body planes
coronal (frontal), sagittal, and transverse.
where is medullary cavity housed
diaphysis
ventral
front of the body
dorsal
back of the body
what is the medullary cavity
hollow part of bone that contains bone marrow. The bone marrow makes blood cells and stores fat
superfical
closer to the surface
deep
away from the surface
where is the yellow marrow loacted?
medullary cavity
what is 2
metaphysis
functions of metaphysis
transfer loads from weight-bearing joint surfaces to the diaphysis
what is included in the dorsal cavities
spinal cavity, Pelvic cavity. and cranial cavity
what is inluded in the ventral cavity
thoracic, diaphragm, abdominal cavity, adbominopelvic cavity
functions of body cavity
Hold and protects internal organs
medial
towards the center
lateral
away from the center
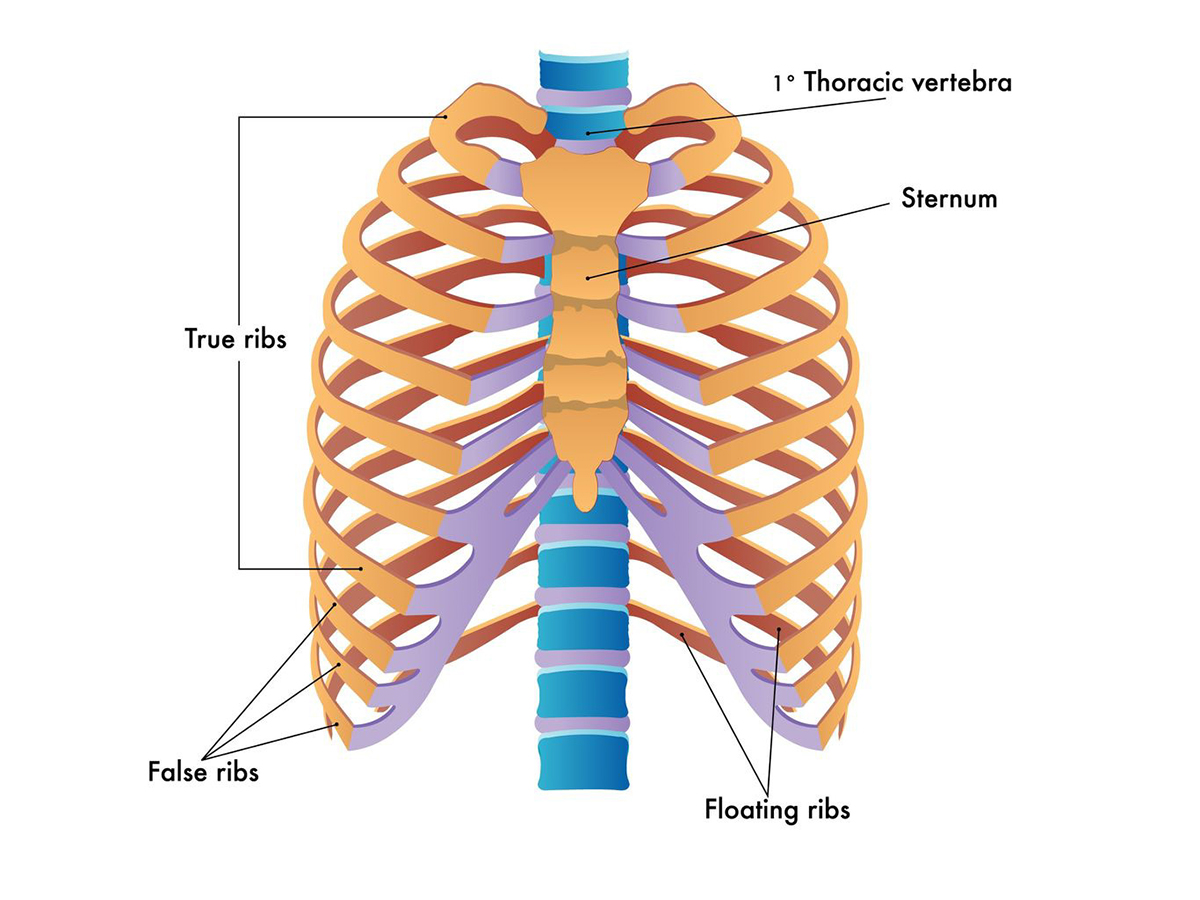
what is highlighted in blue?
true ribs
Flat bones
A layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. Have marrow but no Marrow cavity.
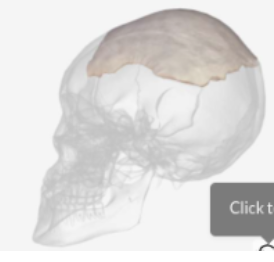
an example of flat bone
Left parietal bone
long bone
A shaft, with two ends, and is longer than it is wide. Consists of a thick outside layer with a marrow-filled cavity. The ends of the bone contain spongy bone. Consists of yellow and red bone
name an example of irregular bone
Thoracic Vertebra
Irregular Bone
Thin layers of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone and do not fit any previous bone descriptions
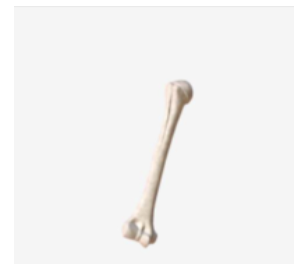
long bone example
Right Humerus bone
an example of short bones
Right carpal bone
short bones
Roughly a cube shape with vertical and horizontal dimensions being approximately equal. They consist of mostly spongy bone. The outside surface is a thin layer of compact bone.

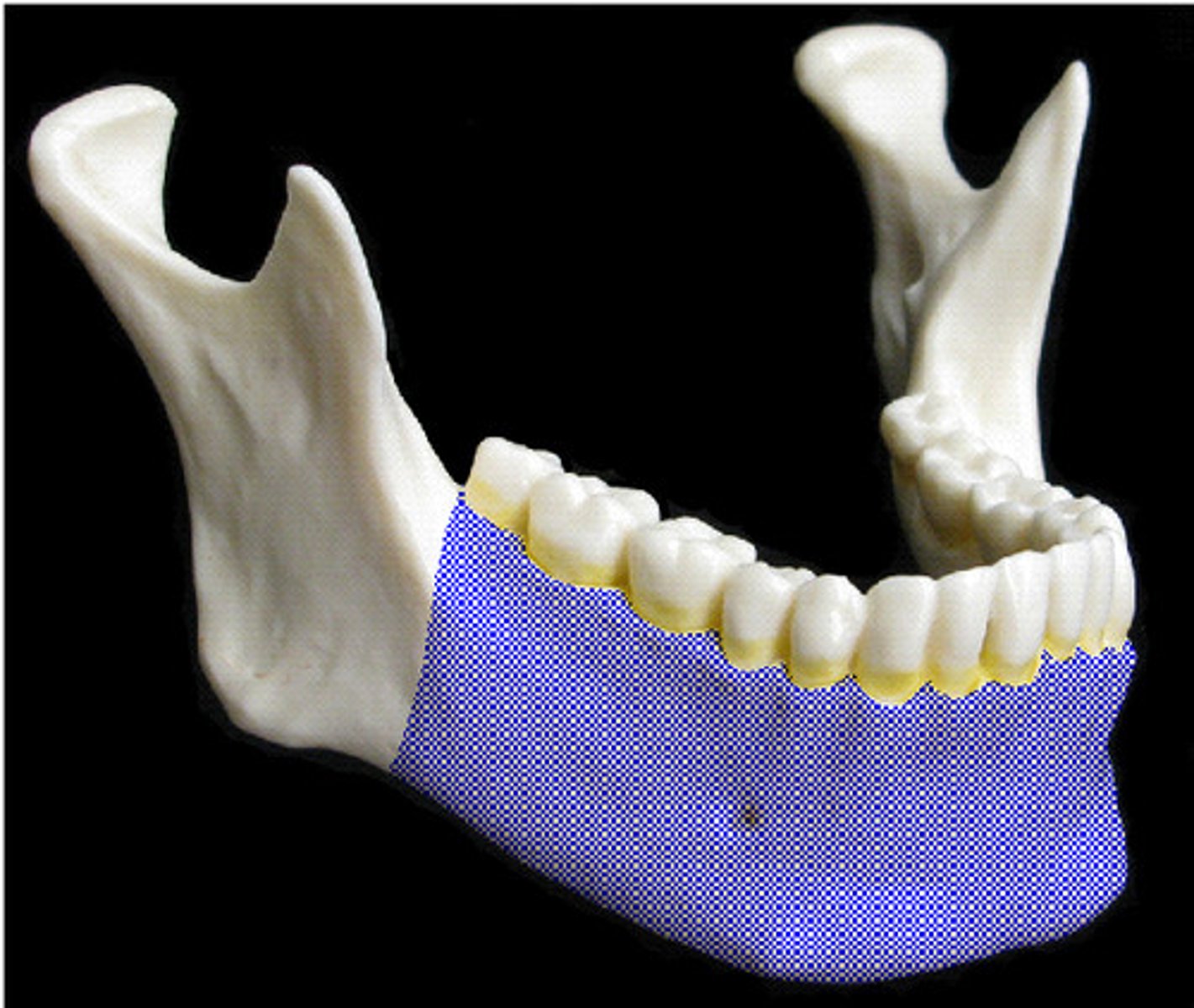
Mandible (Jaw)
What is highlighted in blue?
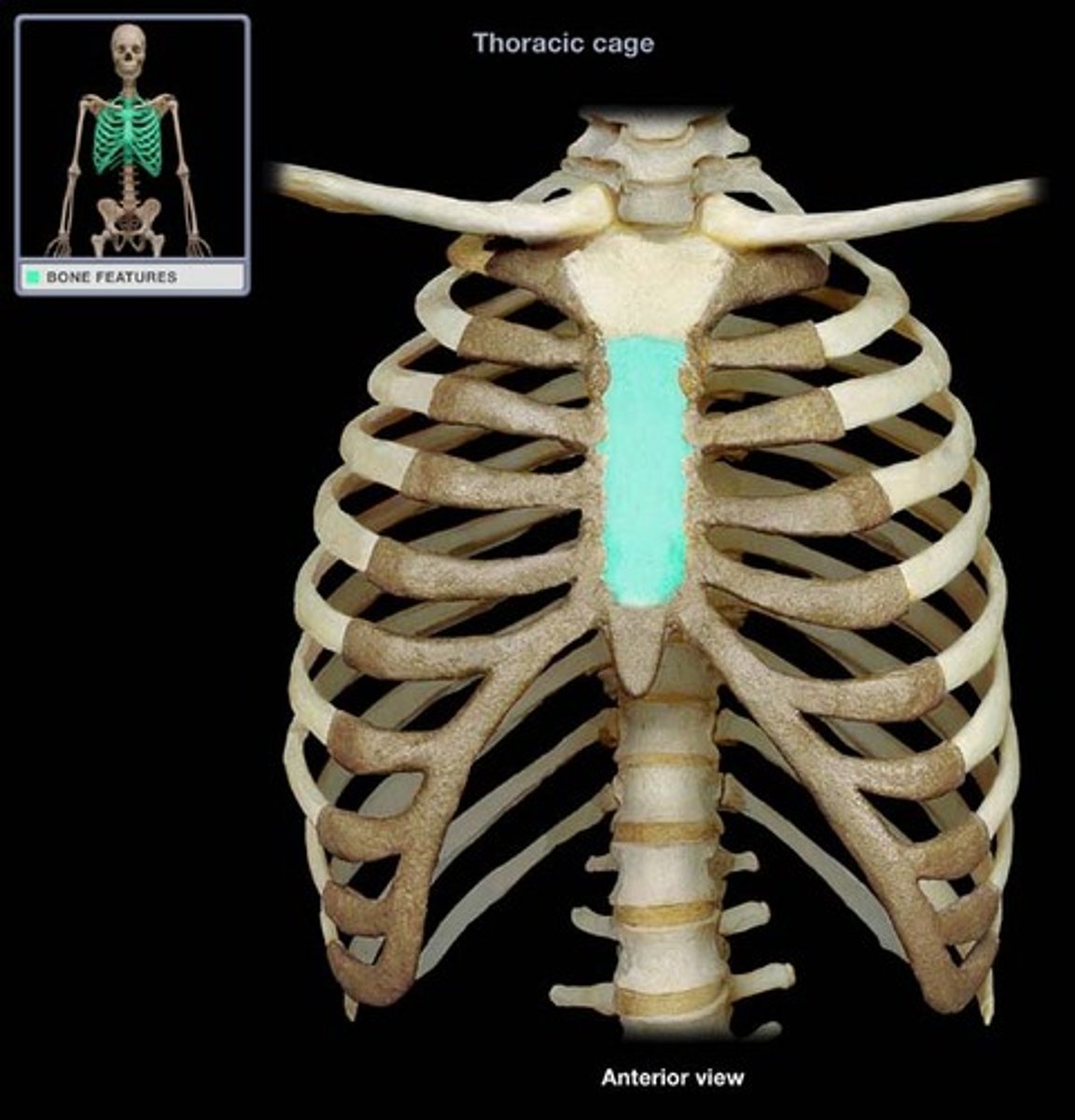
Sternum(in the Sternal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
what is highlighted in blue?
axial skeleton
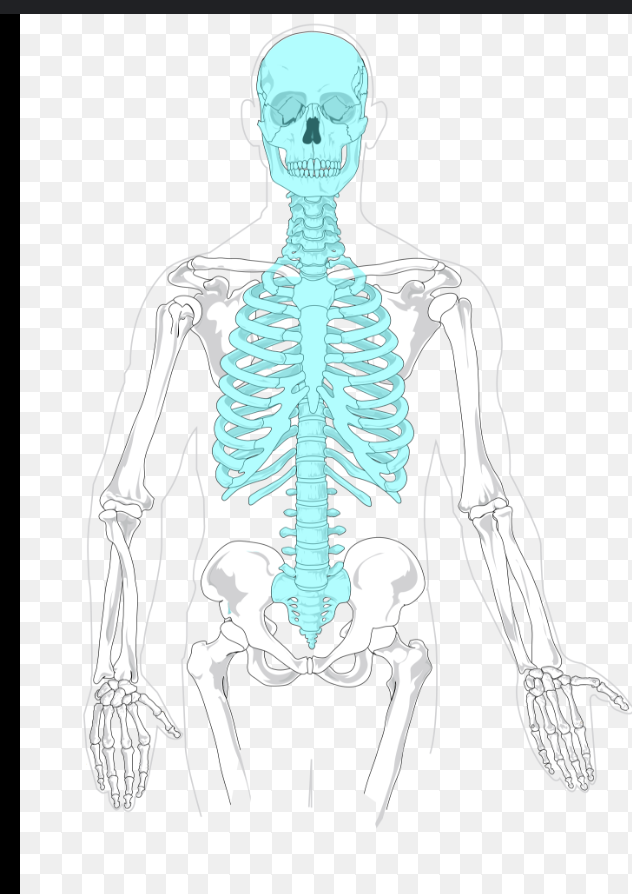
What is included in the axial skeleton
head, neck and trunk (chest pelvis, abdomen and back
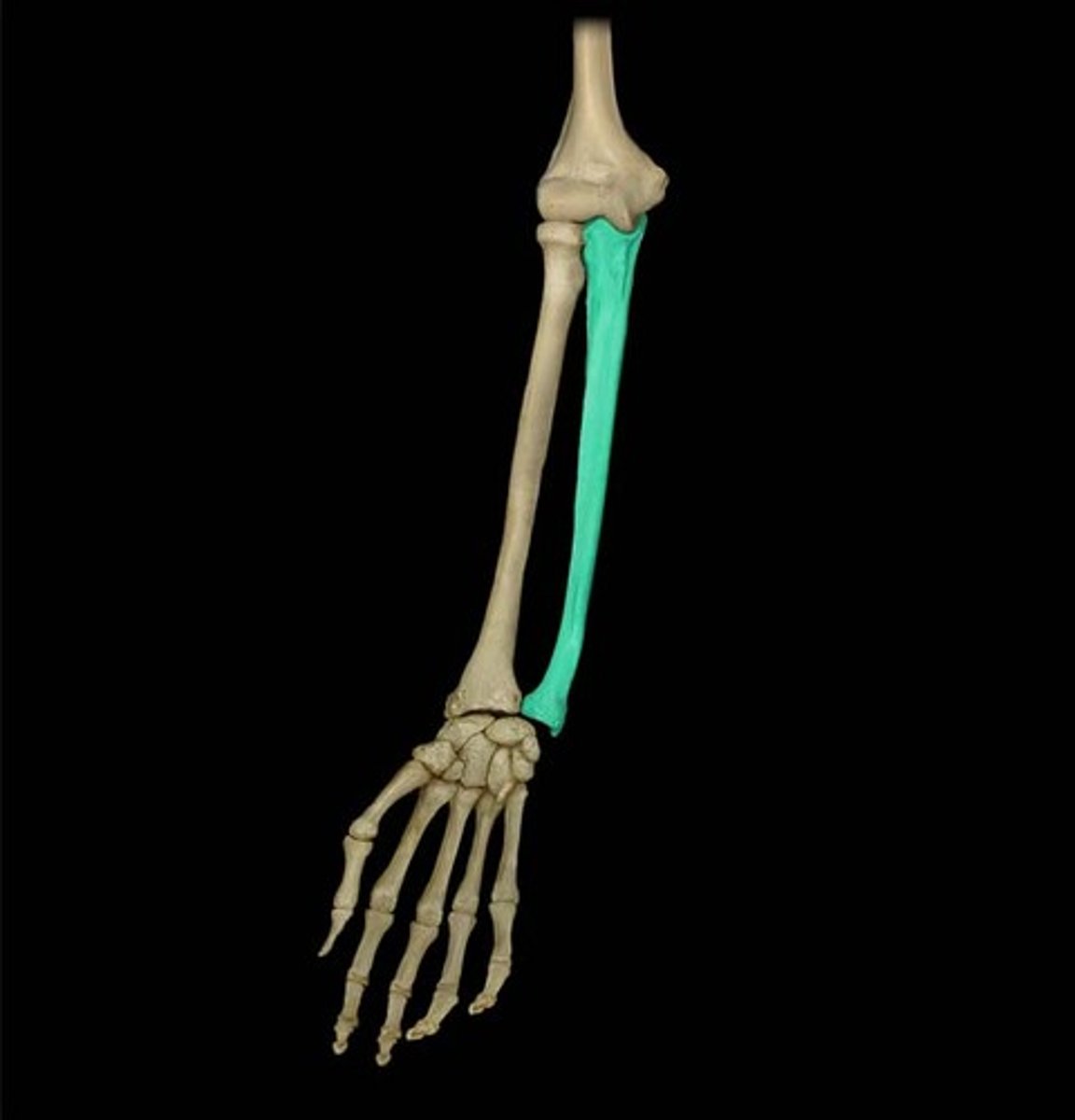
Ulna (follows the pinkie)
What is highlighted in blue?
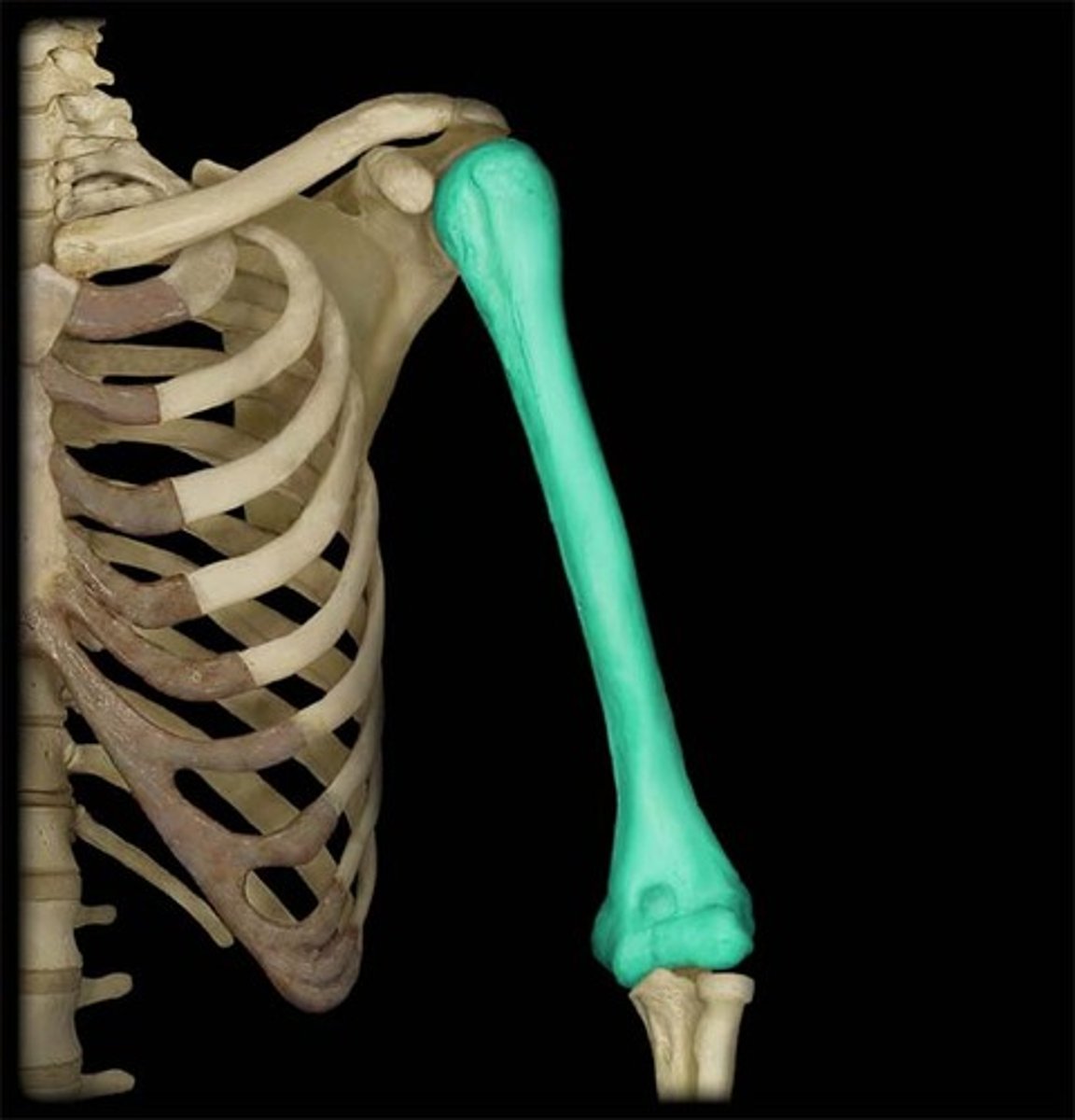
Humerus (in the Brachial area)
What is highlighted in blue?
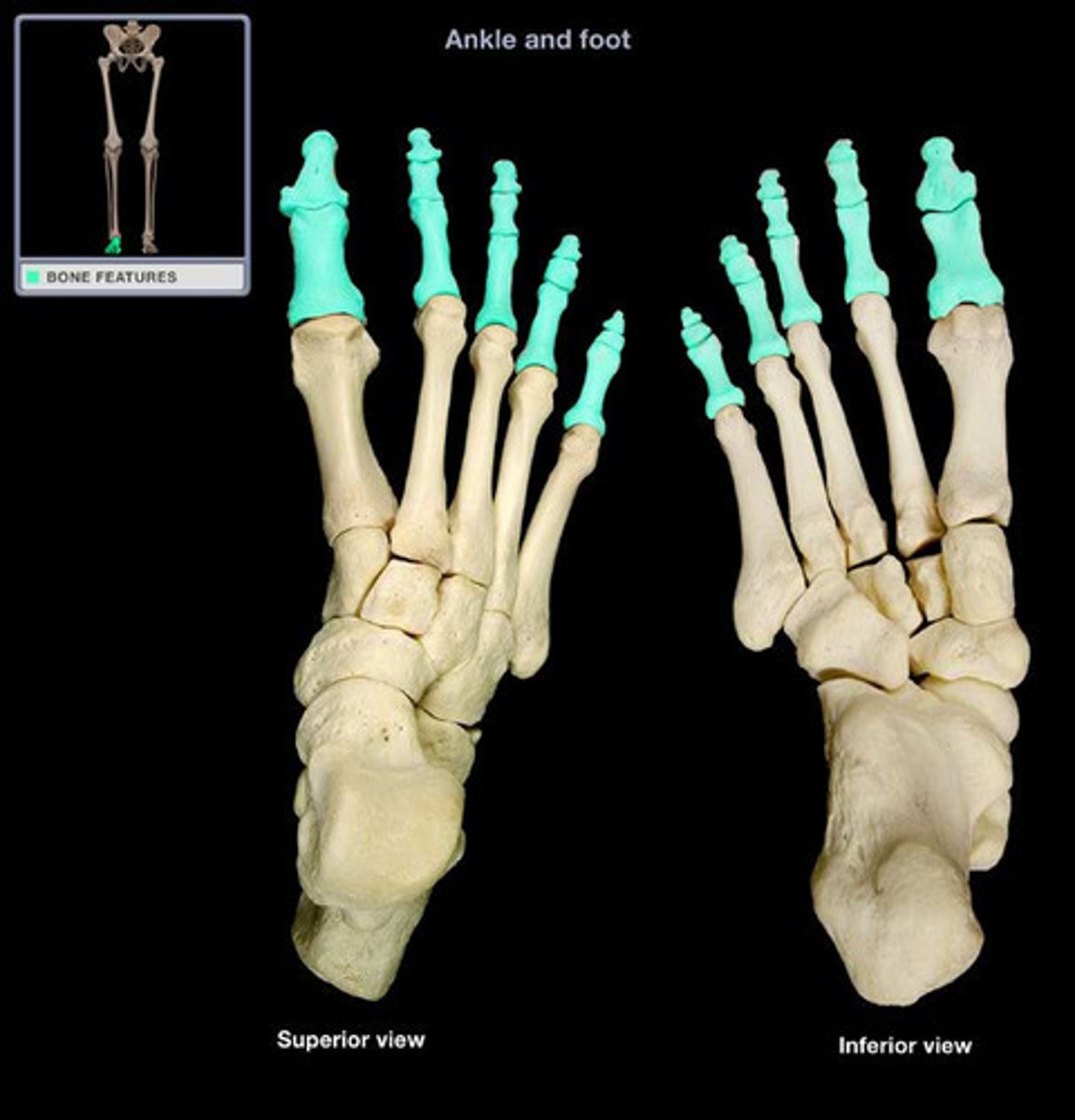
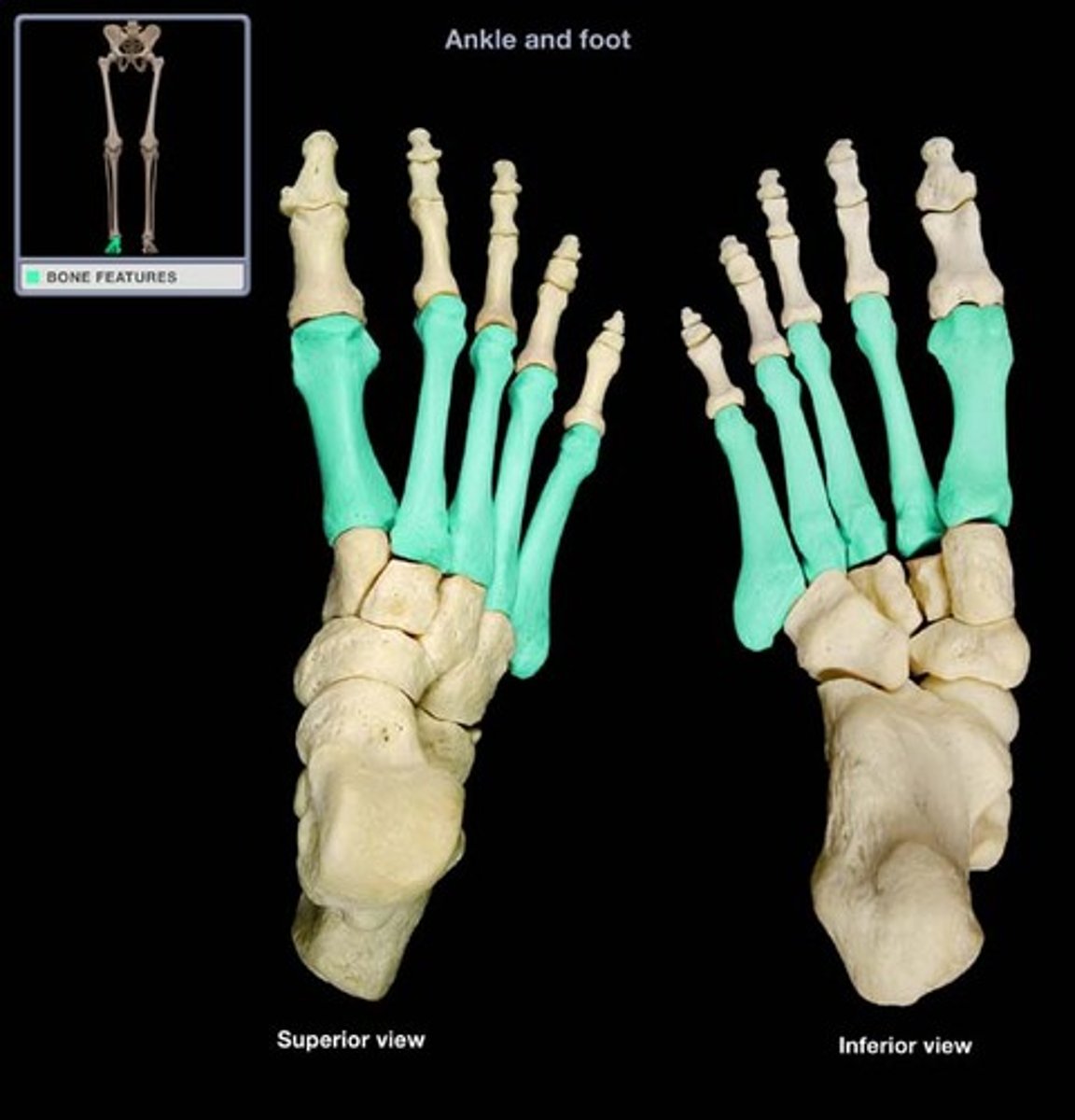
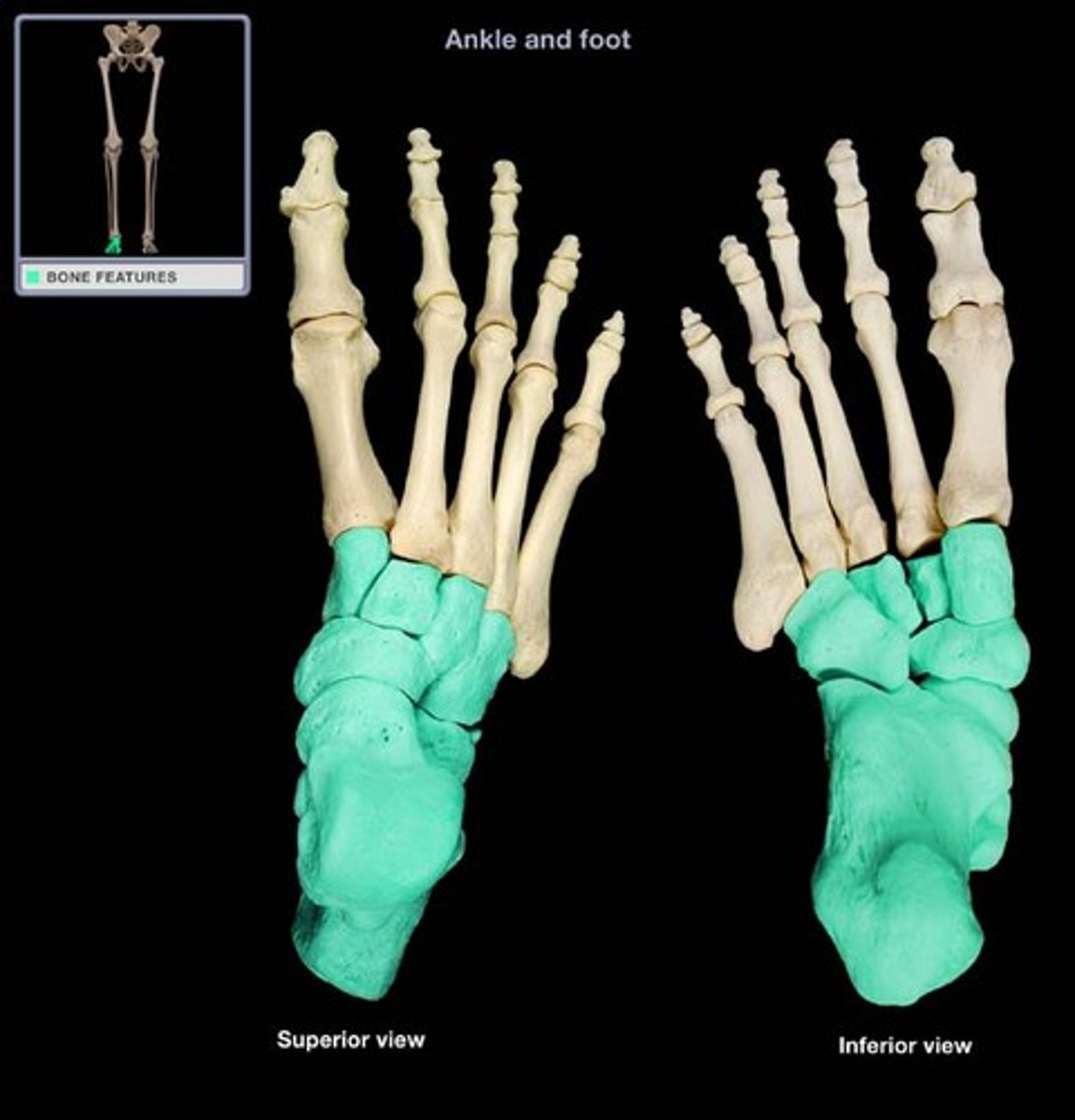
Phalanges (foot, in the tarsal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
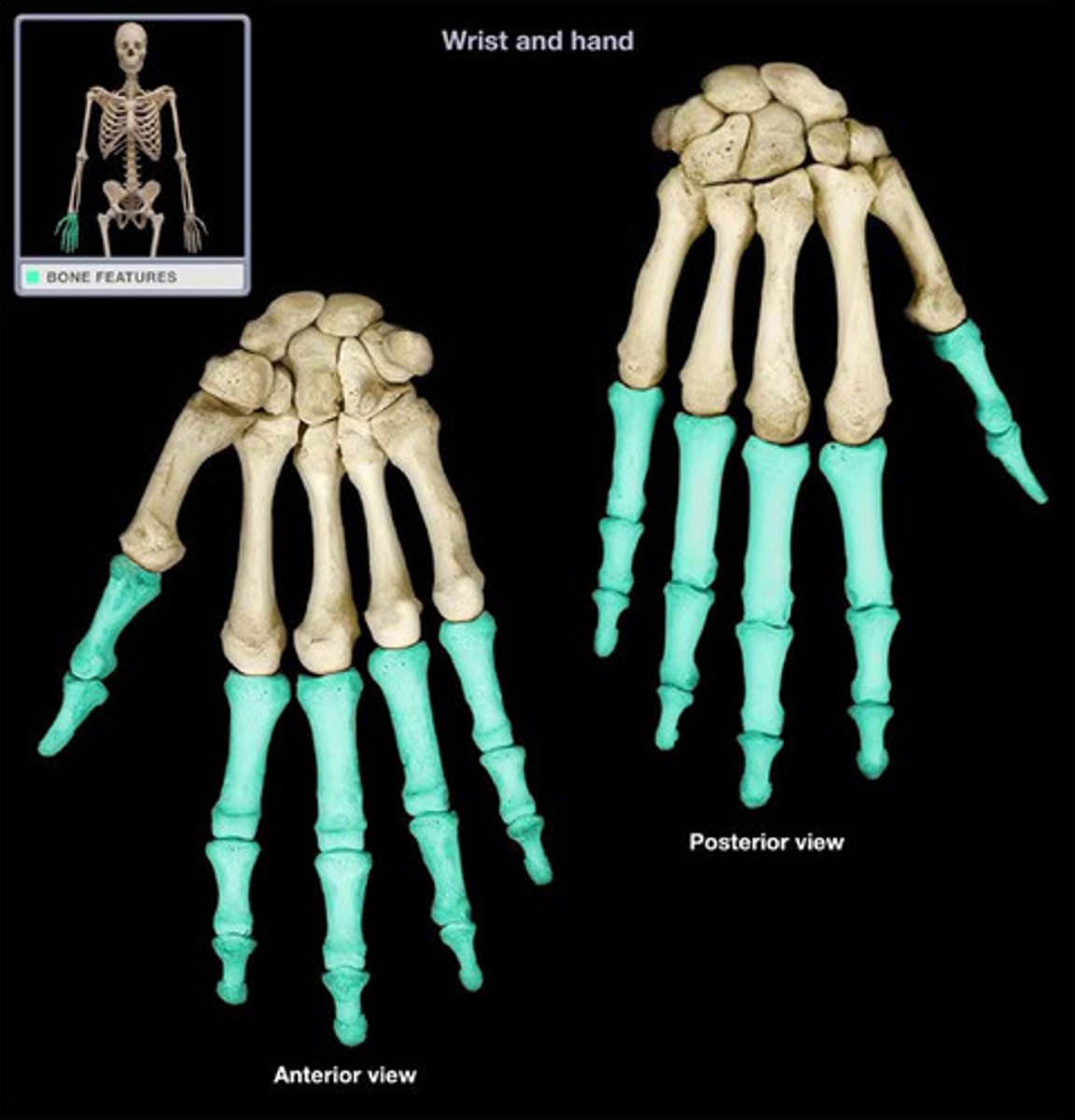
Phalanges (hand, in the digital area)
What is highlighted in blue?
Metatarsals (in the tarsal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
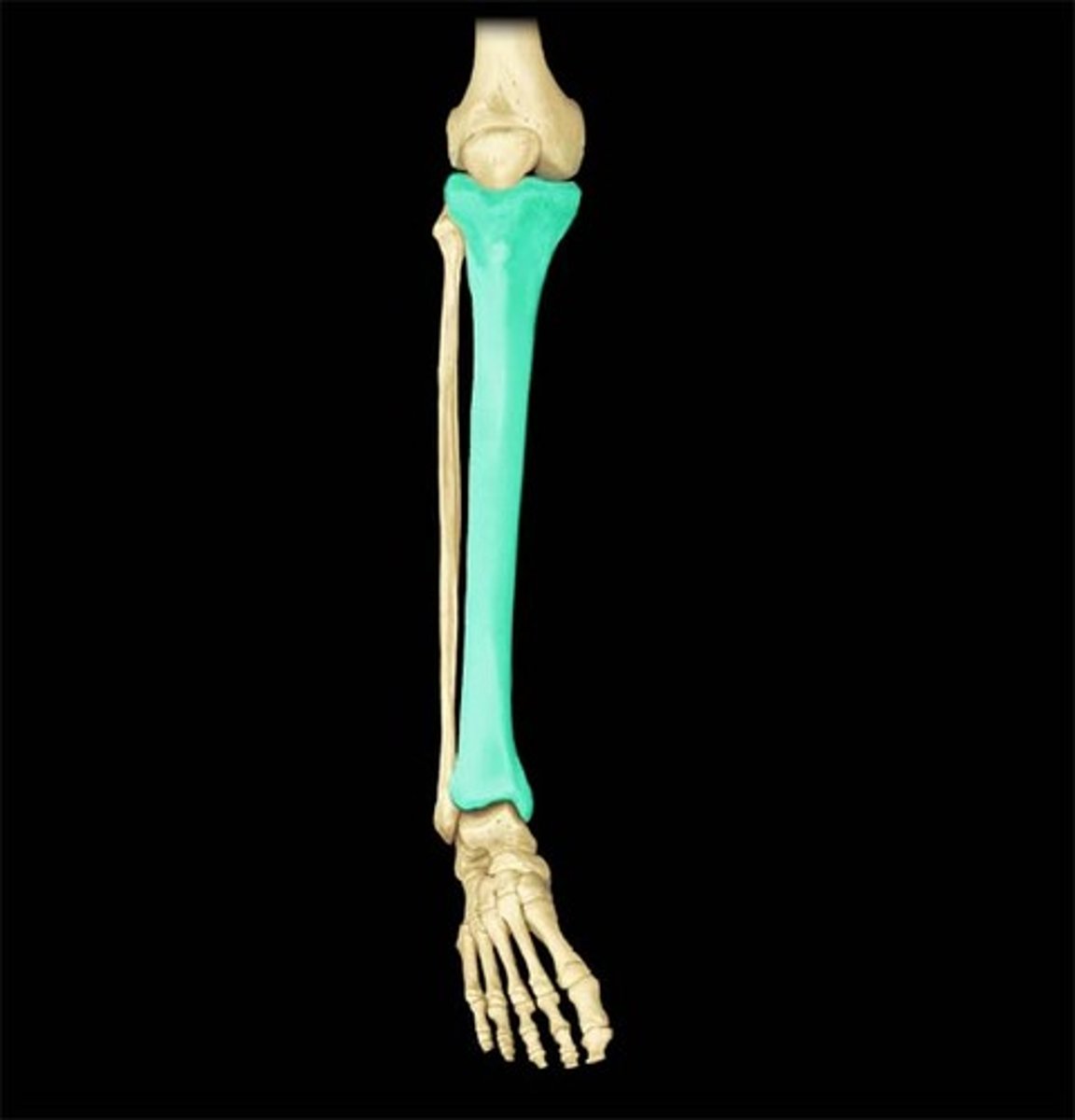
Tiba (shin)
What is highlighted in blue?
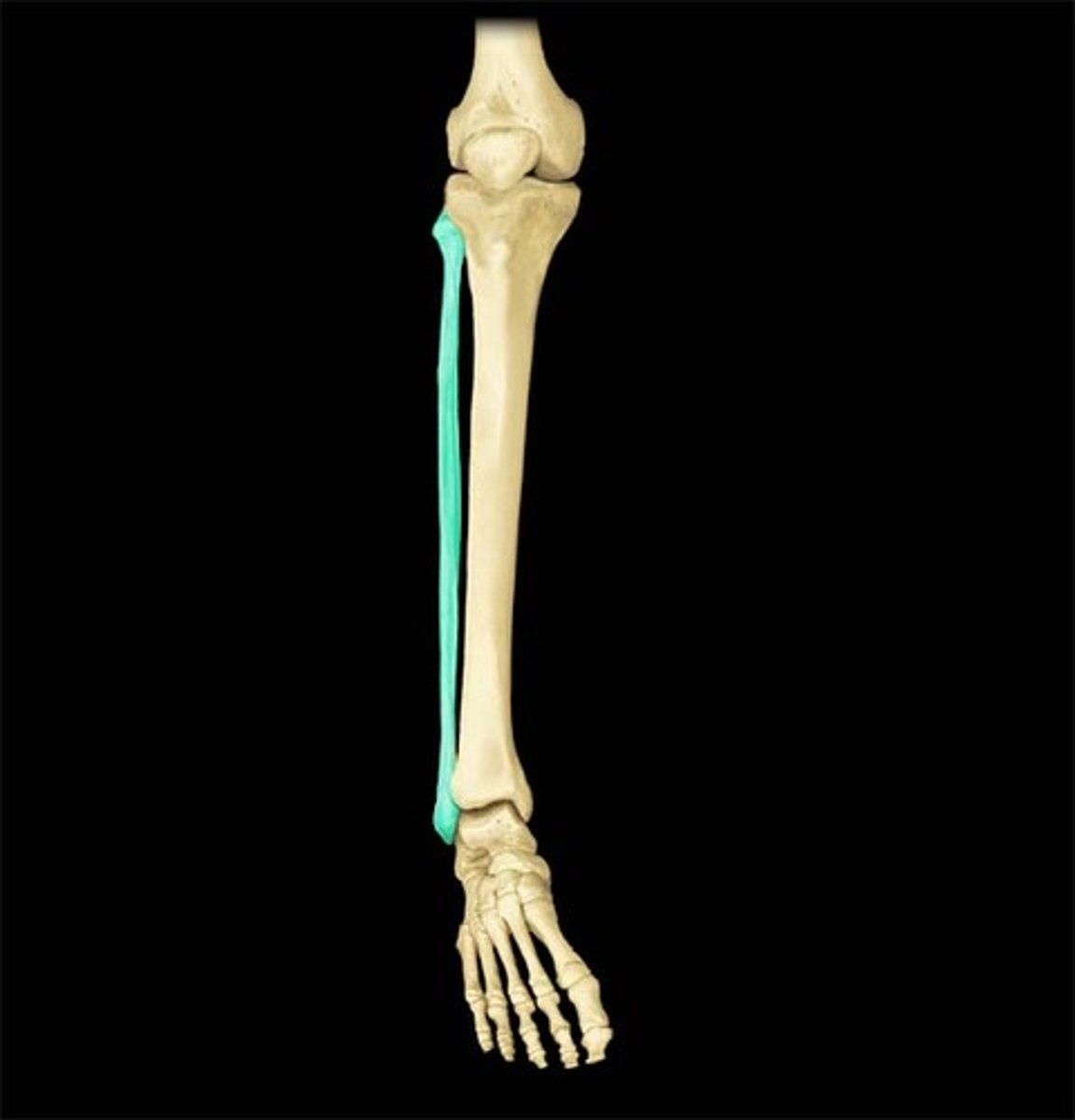
Fibula
What is highlighted in blue?
what is apart of the cranial cavity
the skull
Femur (also known as the thigh, in the femoral area)
What is highlighted in blue?)
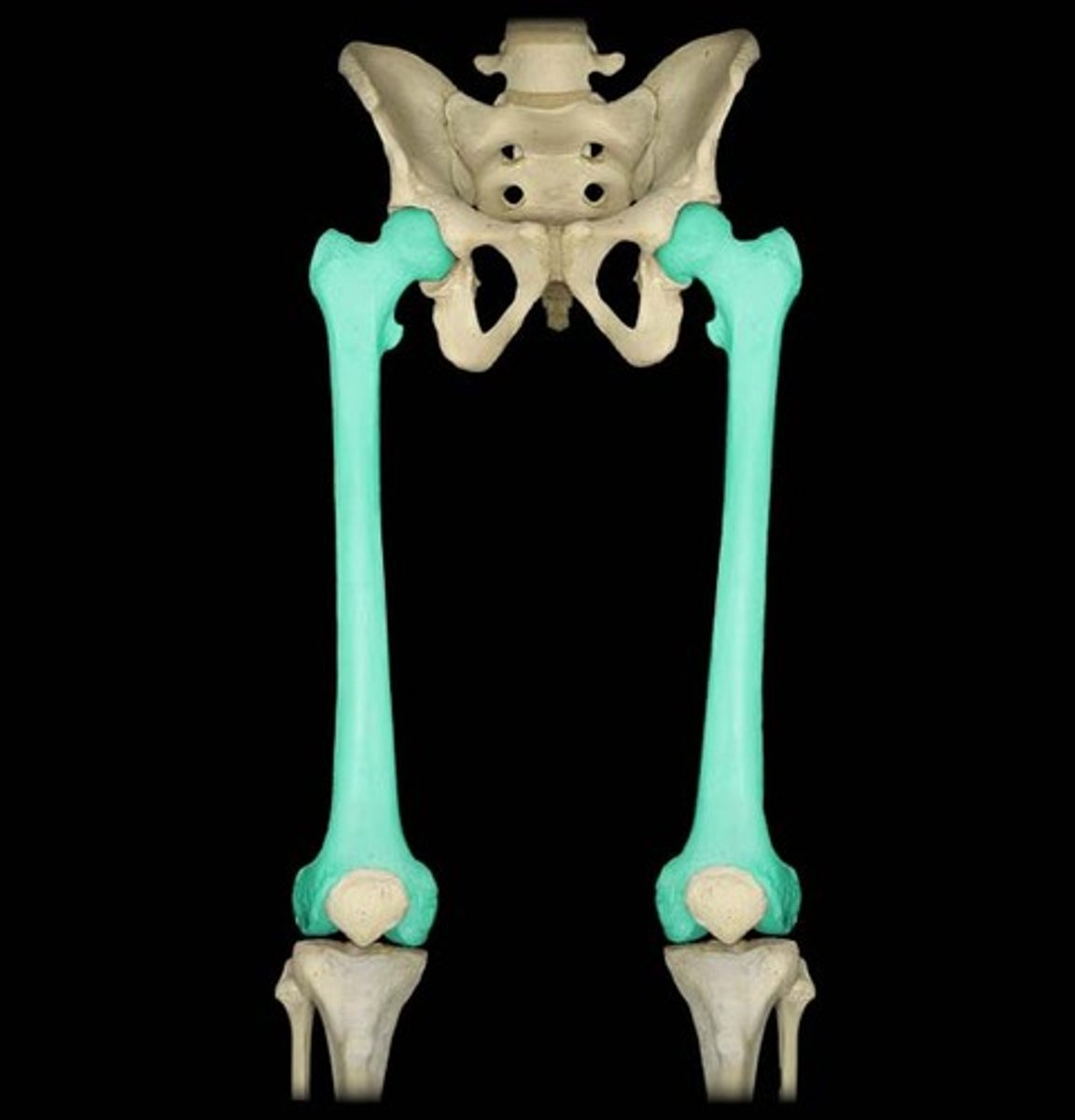
Patellar (kneecap,)
What is highlighted in blue?
Metacarpals
What is highlighted in blue?
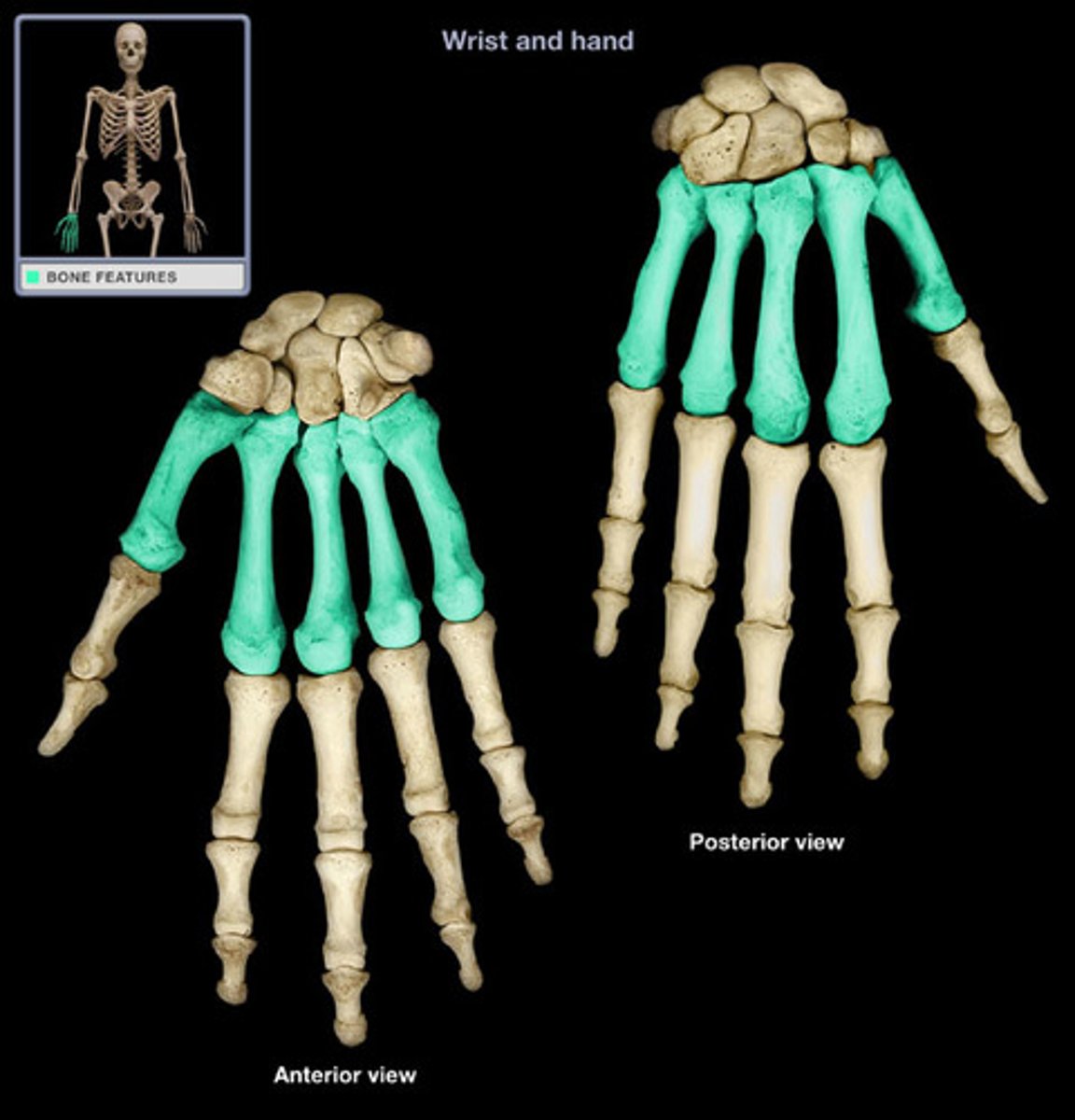
Carpals (in the carpal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
Tarsals (Ankle, in the tarsal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
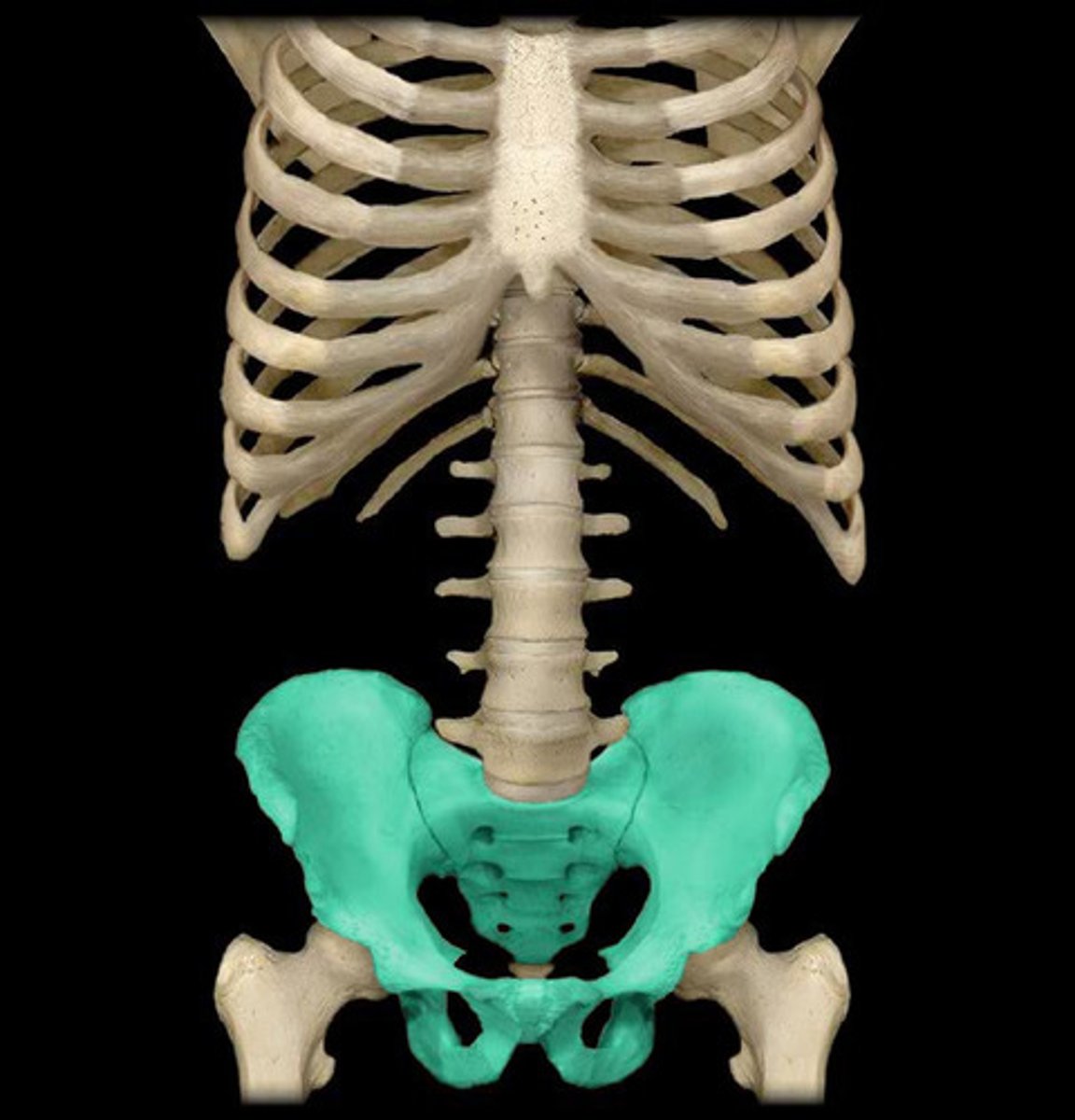
Pelvic Girdle (in the pelvic area)
What is highlighted in blue?
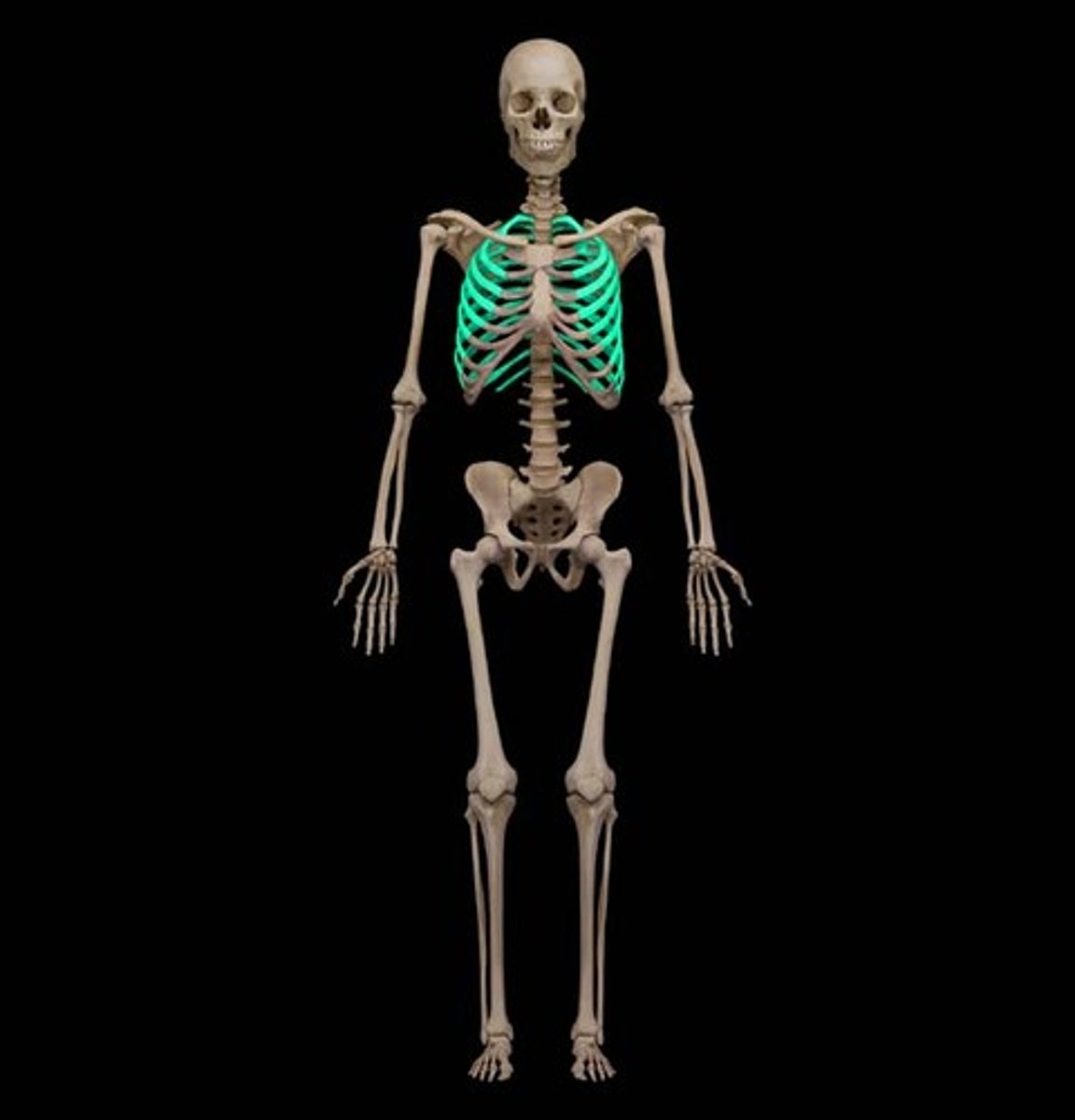
Rib Cage (In the sternal area)
What is highlighted in blue?
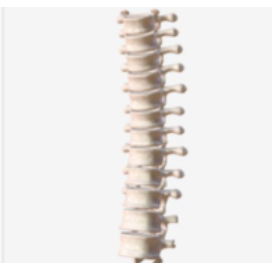
thoracic
What is highlighted in blue?
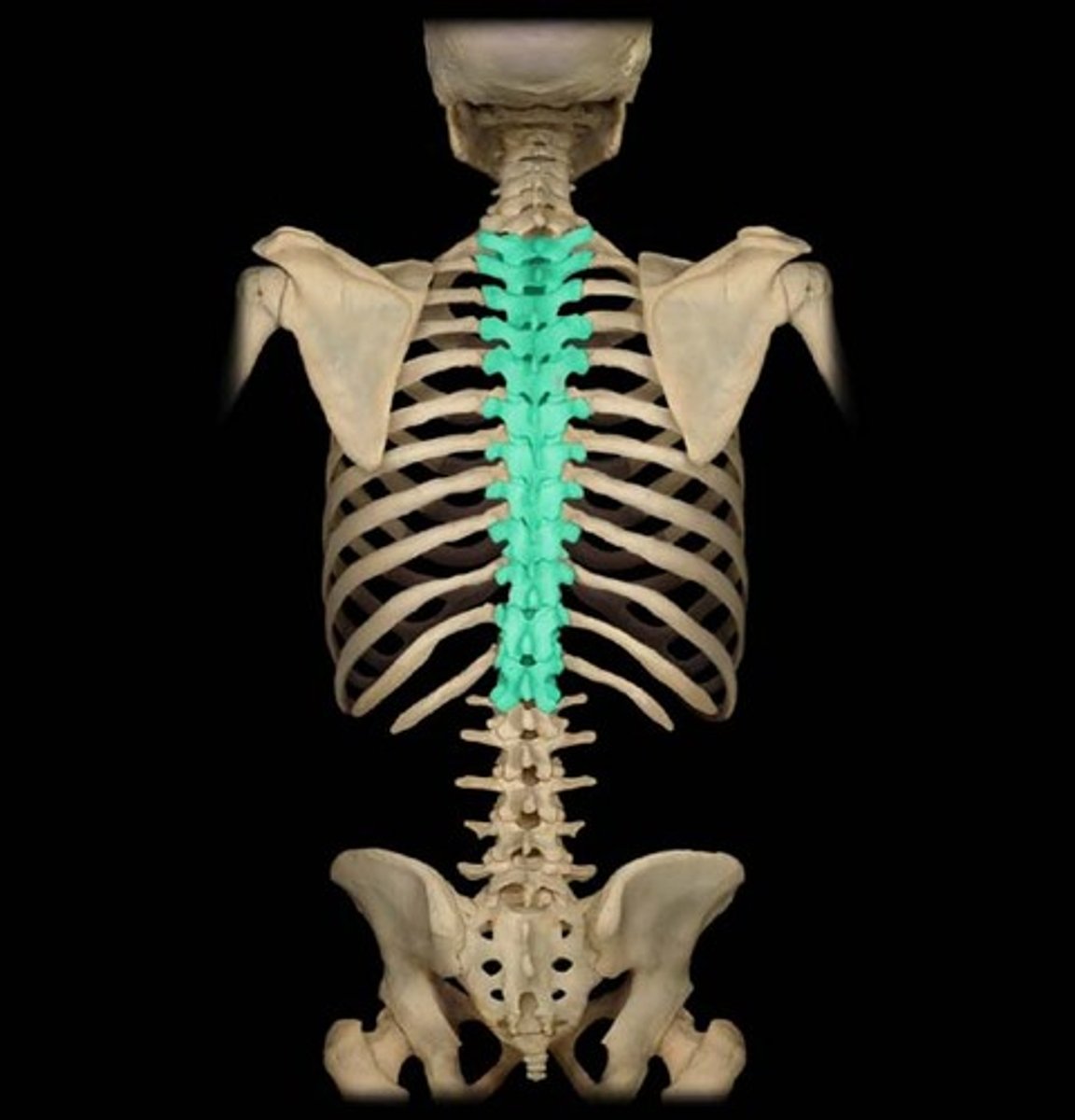
Vertebral Column Section
What is highlighted in blue?
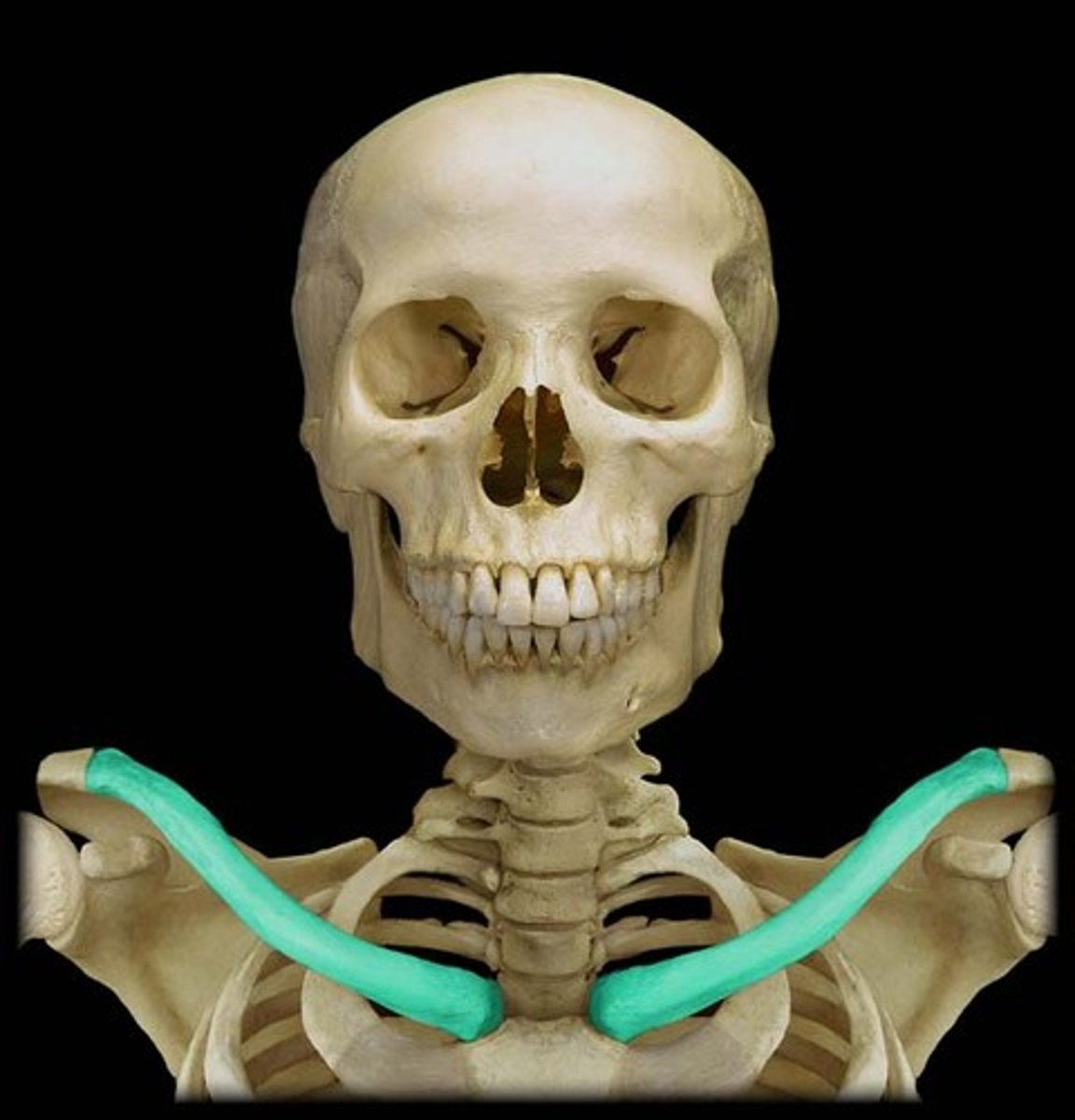
Clavicle (collarbone)
What is highlighted in blue?
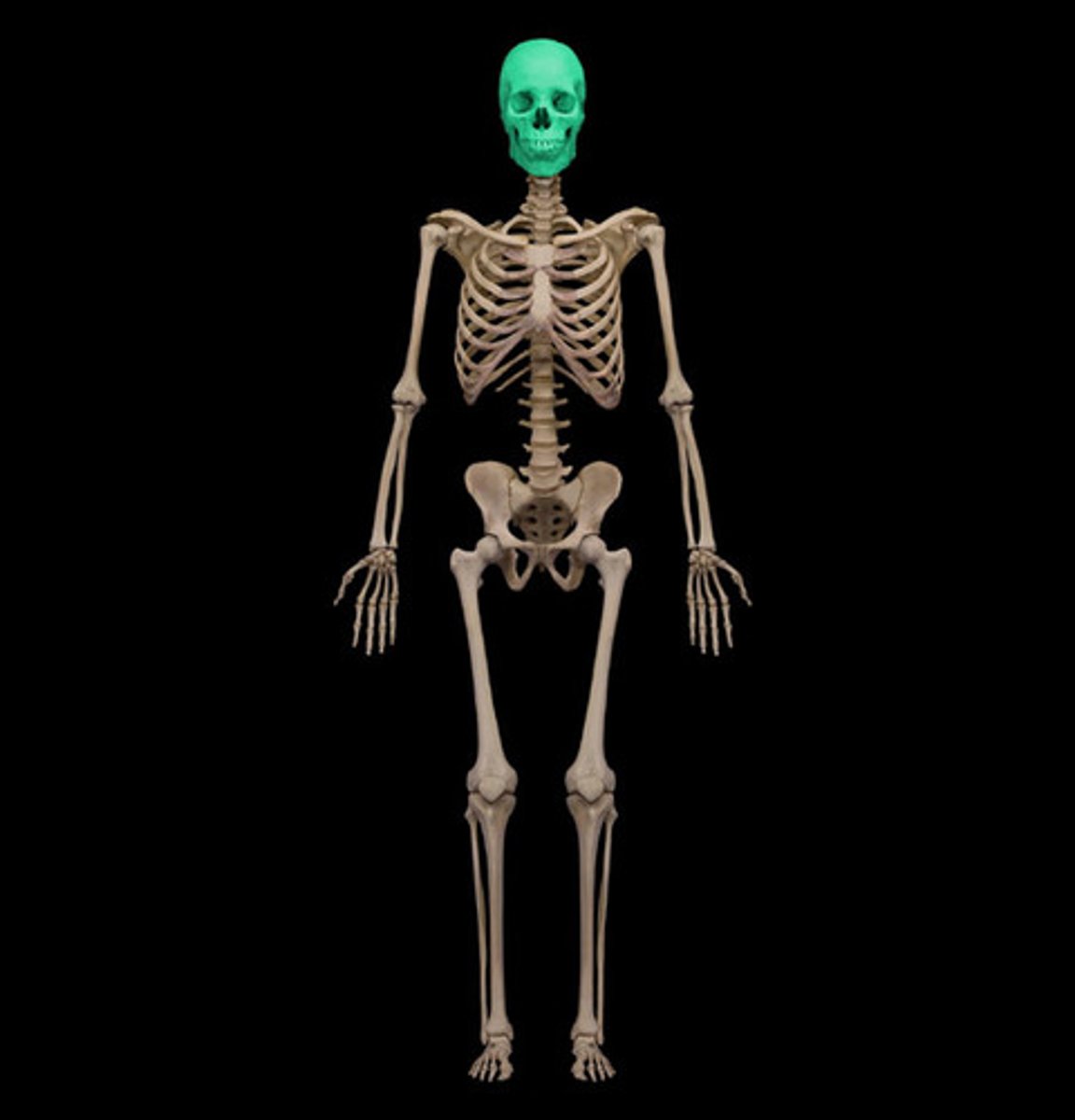
Skull(in the cephalic area)
What is highlighted in blue?
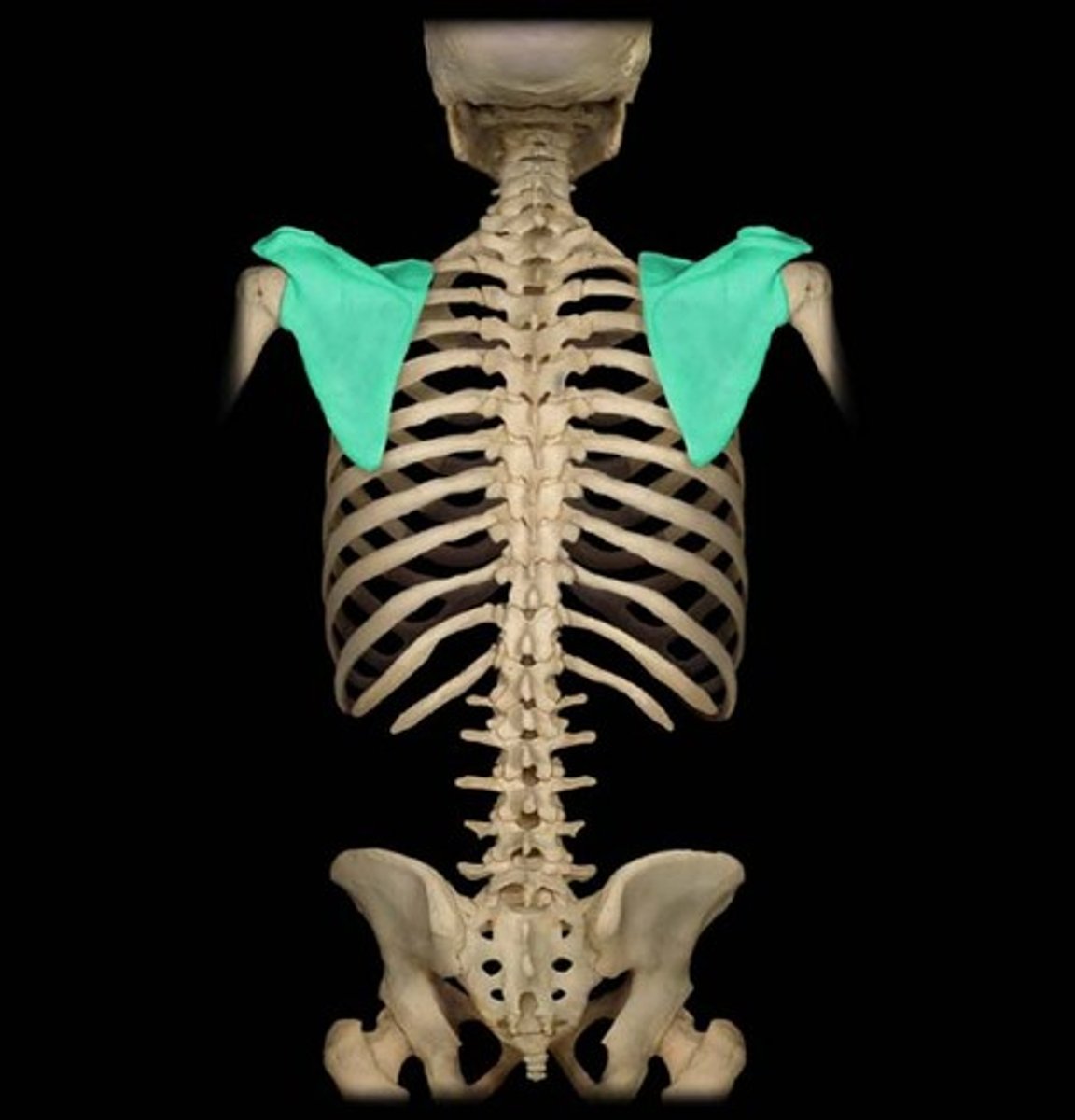
Scapula (shoulder blade, in the scapular area)
What is highlighted in blue?
Popliteal Area
what is the back of the knee called?
Anterior
front of the body
Posterior
back of the body
Superior
Situated toward the head and further away from the feet than another and especially, than another similar part of an upright body, especially of a human being. opposite of inferior
Inferior
Situated below and closer to the feet than another and especially, than another similar part of an upright body, especially of a human being. opposite of superior
Lateral
Of or relating to the side, especially of a body part. opposite of medial
Medial
Lying or extending in the middle, especially of a body part. opposite of lateral
Distal
Situated away from the point of attachment or origin or from a central point; located away from the center of the body. opposite of proximal
Proximal
Situated next to or near the point of attachment or origin or near a central point. opposite of distal
Superficial
Of, relating to, or located near the surface. opposite of deep
Deep
Away from the body surface; more internal. opposite of superficial
Ventral
Pertaining to the anterior or front side of the body; opposite of dorsal
Dorsal
Being or located near, on, or toward the back or posterior part of the human body; opposite of ventral
Epithial Tissue
Sheets of tightly packed cells that line organs and body cavities
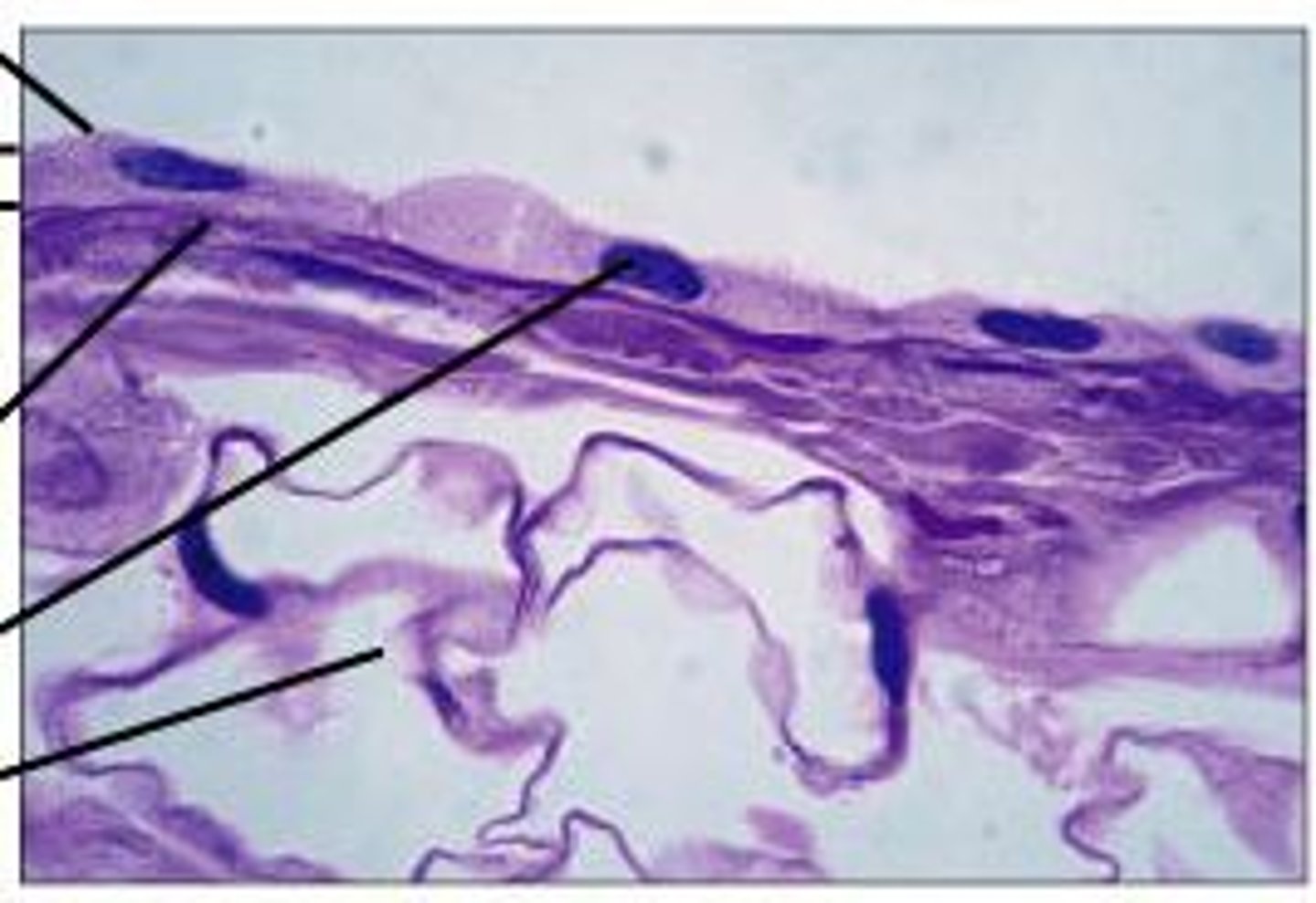
Connective Tissue locations
Atacched to and between other tissue types in the body, Adipose tissue (fat) is an example of this type of tissue
Muscle Tissue locations
Found throughout the body, and it is attached to bone via tendons.
Nervous Tissue
Tissue type that makes up the central and peripheral nervous systems
Cartalige
A usually translucent somewhat elastic tissue that composes most of the skeleton of vertebrate embryos and except for a small number of structures (as some joints, respiratory passages, and the external ear) is replaced by bone during ossification in the higher vertebrates.
Blood
A body fluid that transfers substances, such as oxygen and nutrients, to cells and transports waste products away from cells
Tendon
A white fibrous cord of dense regular connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
Ligament
Dense regular connective tissue that attaches bone to bone
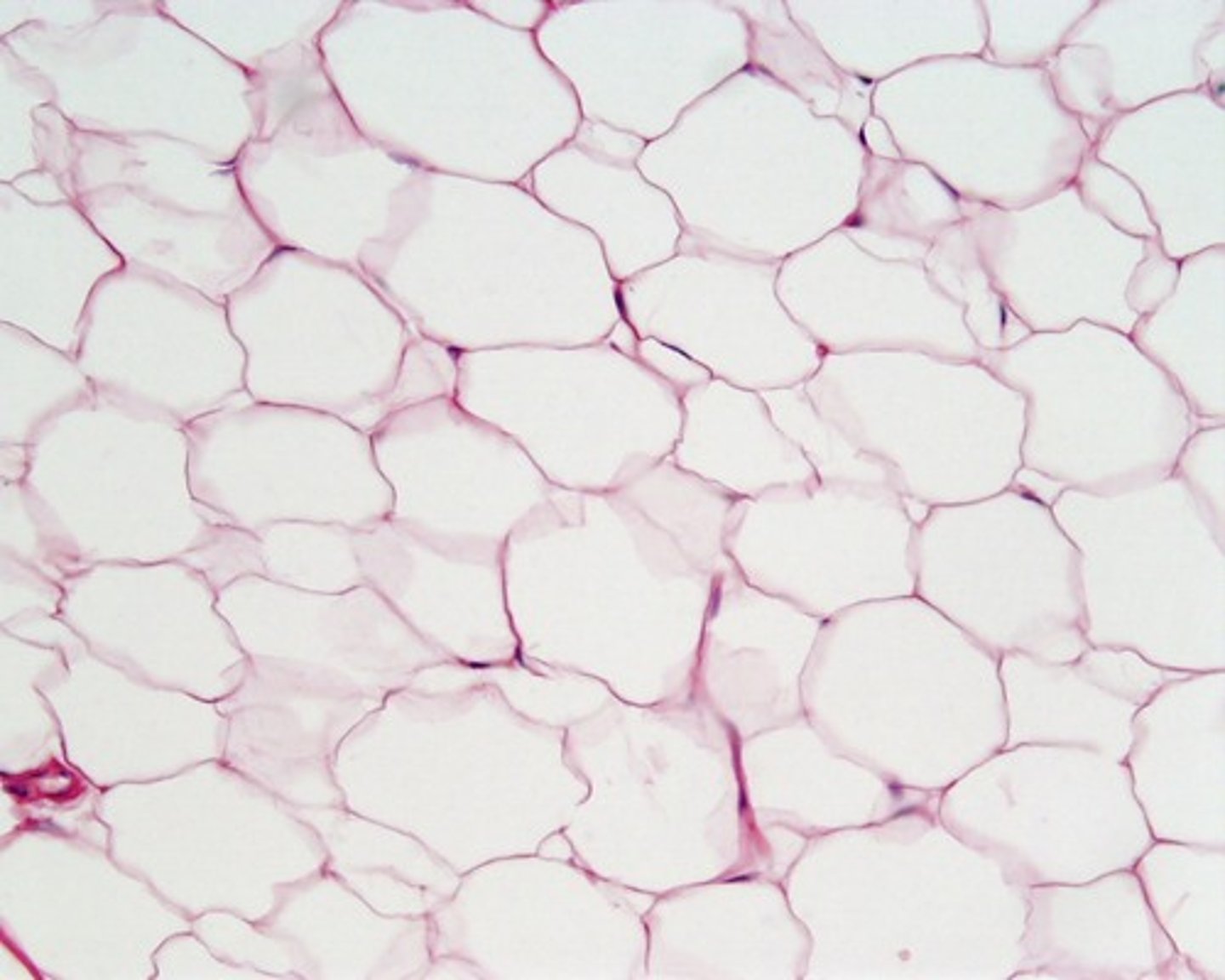
Adipose Tissue
Connective tissue in which fat is stored; has the cells distended by droplets of fat
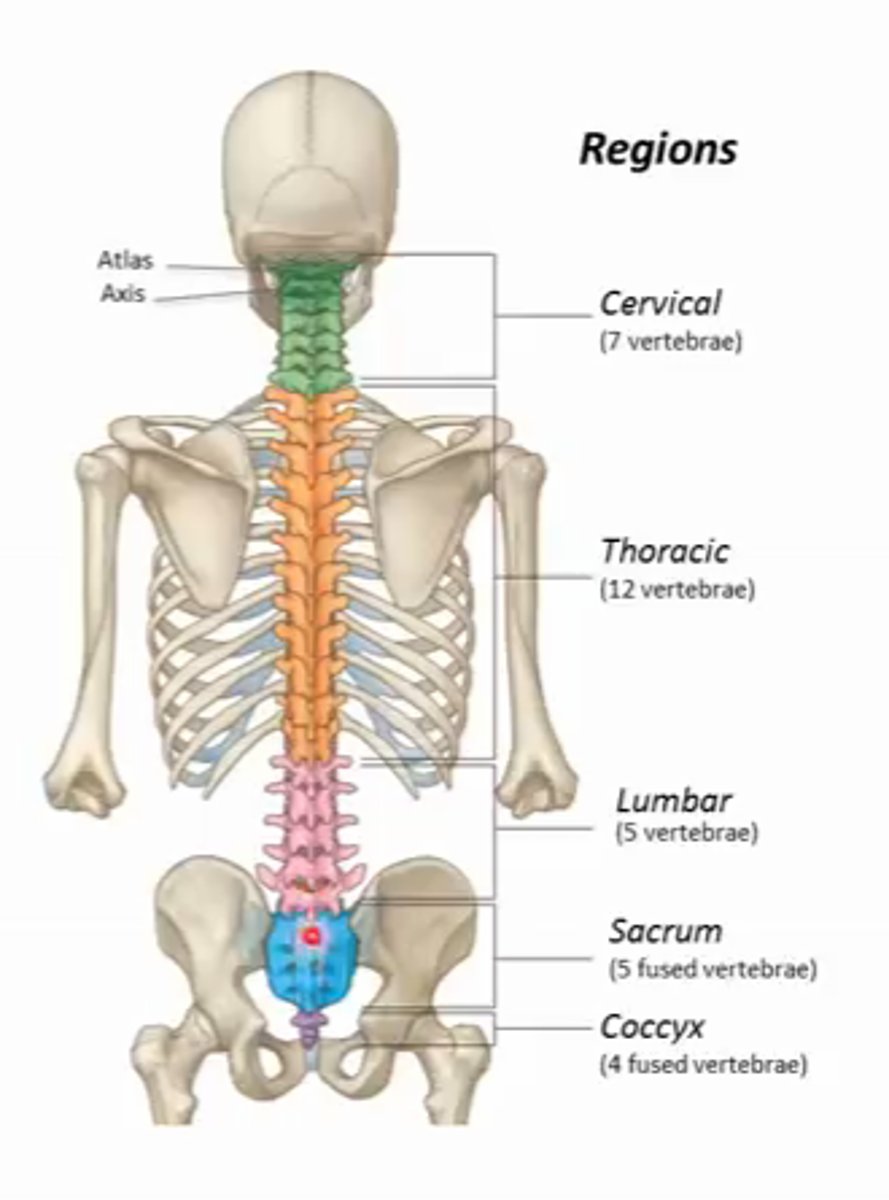
7
How many vertebraes are in the cervical area?
12
how many vertebraes are in the thoracic area?
5
how many vertebreas are in the lumbar area?
Appendicular Skeleton
arms, legs, pelvis
Axial Skeleton
RIbs and Head