Hematology End Of Rotation, Hematology Success, BOC Hematology
1/761
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
762 Terms
What is the first type of cell produced by the developing embryo?
A. Erythrocyte
B. Granulocyte
C. Lymphocyte
D. Thrombocyte
A. Erythrocyte
What percentage of tissue located in the bone marrow cavities of adults is fat?
A. 10%
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
C. 50%
Which of the following is not characteristic of pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells?
A. Possess self-renewal ability
B. Produce progenitor cells committed to a single cell lineage
C. Express the stem cell marker CD 13
D. Are morphologically unrecognizable
C. Express the stem cell marker CD13
In an adult, what are the two best areas for obtaining active bone marrow by aspiration?
A. Vertebra,tibia
B. Sternum,vertebra
C. Anterior iliac crest, tibia
D. Posterior iliac crest, sternum
D. Posterior iliac crest, sternum
What is the normal ratio of myeloid to erythroid precursors in bone marrow (M:E ratio)?
A. 1:1
B. 1:3
C. 4:1
D. 8:1
C. 4:1
Which of the following does not accurately describe hematopoietic growth factors?
A. Bind to target cell receptors to express
activity
B. Action of majority is lineage restricted
C. May promote or suppress cell death
D. Can stimulate or inhibit cell
proliferation
B. Action of majority is lineage restricted
In the third month of gestation, what is the primary state of hematopoiesis?
A. Liver
B. Marrow of long bones C. Spleen
D. Yolksac
A. Liver
The mechanism that relays information about tissue oxygen levels to erythropoietin-producing sites is located in the
A. Brain
B. Kidney
C. Liver
D. Spleen
B. Kidney
Antigen-independent lymphopoiesis occurs in primary lymphoid tissue located in the
A. Liver and kidney
B. Spleen and lymphnodes
C. Peyer's patches and spleen
D. Thymus and bone marrow
D. Thymus and bone marrow
Programmed cell death is called
A. Necrosis
B. Apoptosis
C. Cellular senescence
D. Terminal differentiation
B. Apoptosis
In what area of the bone marrow does hematopoiesis take place?
A. Cords
B. Endosteum
C. Endothelium
D. Sinuses
A. Cords
Bone marrow cellularity refers to the ratio of
A. Red cell precursors to white cell precursors
B. Hematopoietic tissue to adipose tissue
C. Granulocytic cells to erythrocytic cells
D. Extravascular tissue to intravascular
tissue
B. Hematopoietic tissue to adipose tissue
Interleukins and colony stimulation factors are cytokines produced by
A. B lymphocytes and erythrocytes
B. Erythrocytes and thrombocytes
C. Monocytes and T lymphocytes D. Neutrophils and monocytes
C. Monocytes and T lymphocytes
What is the approximate total blood volume in an adult?
A. 1L
B. 2L
C. 6L
D. 12L
C. 6L
The myeloid progenitor cell can produce cells committed to
A. Granulocytic, erythrocytic, monocytic,
or megakaryocytic lineages
B. Granulocytic, monocytic, lympho-
cytic, or megakaryocytic lineages
C. Erythrocytic, granulocytic, monocytic,
or lymphocytic lineages
D. Erythrocytic, granulocytic, lympho-
cytic, or megakaryocytic lineages
A. Granulocytic, erythrocytic, monocytic,
or megakaryocytic lineages
The largest hematopoietic cells in normal bone marrow are
A. Osteoblasts
B. Osteoclasts
C. Megakaryocytes
D. Plasma cells
C. Megakaryocytes
When evaluating a bone marrow aspirate smear, which finding is considered abnormal?
A. A predominance of granulocyte
precursors as compared to nucleated
red cells
B. Detection of stainable iron in
macrophages and erythroid precursors
with Prussian blue
C. An average of three megakaryocytes
seen per low power (10X) field
D. The presence of 10% myeloblasts on the cell differential count
D. The presence of 10% myeloblasts on the cell differential count
As most blood cells lines mature, which of the following is characteristic?
A. Cell diameter increases
B. Nucleus to cytoplasm ratio (N:C) decreases
C. Nuclear chromatin becomes less condensed
D. Basophilia of the cytoplasm increase
B. Nucleus to cytoplasm ratio (N:C) decreases
Which of the following describes thrombopoietin (TPO)?
A. Renal hormone that regulates marrow
red cell production
B. Marrow hormone secreted by
developing megakaryoblasts
C. Hormone produced by the liver that
stimulates megakaryopoiesis
D. Pituitary hormone that controls
platelet sequestration by the spleen
C. Hormone produced by the liver that
stimulates megakaryopoiesis
When the hepatic phase of fetal life is reactivated in an adult, hematopoiesis can be termed
A. Myeloid ormedullary
B. Myeloid metaplasia or extramedullary
C. Myelophthisis or myelodysplasia D. Mesoblastic or mesenchymal
B. Myeloid metaplasia or extramedullary
What is the average life span of a normal red blood cell?
A. 1 day
B. 10days
C. 60 days
D. 120 days
D. 120 days
The Na+-K+ cation pump is an important mechanism in keeping the red blood cell intact. Its function is to maintain a high level of
A. Intracellular Na+
B. Intracellular K+
C. PlasmaNa+
D. Plasma K+
B. Intracellular K+
Which of the following depicts the structure of the hemoglobin molecule?
A. Two heme groups, two globin chains
B. Four heme groups, two globin chains
C. Two heme groups, four globin chains
D. Four heme groups, four globin chains
D. Four heme groups, four globin chains
Which of the following describes the process known as culling?
A. Release of red cells from the bone
marrow
B. Binding of free hemoglobin by
transport proteins
C. Incorporation of iron into proto-
porphyrin IX
D. Removal of abnormal red cells by the
spleen
D. Removal of abnormal red cells by the spleen
Hemoglobin forms that are incapable of oxygen transport include
A. Deoxyhemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin
B. Oxyhemoglobin and
carboxyhemoglobin
C. Carboxyhemoglobin and
methemoglobin
D. Methemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin
C. Carboxyhemoglobin and
methemoglobin
The majority of iron found in an adult is a constituent of
A. Ferritin
B. Myoglobin
C. Hemoglobin
D. Peroxidase
C. Hemoglobin
A senescent red blood cell is one that has
A. Been hemolyzed
B. Lived its life span
C. Become deformed
D. Lost its mitochondria
B. Lived its life span
What red cell morphologic abnormality is described by the term "poikilocytosis"?
A. Variations in size
B. Deviations from normal shape
C. Presence of inclusions
D. Alterations in hemoglobin concentration
B. Deviations from normal shape
Howell-Jolly bodies are composed of
A. DNA
B. Iron
C. Reticulum
D. RNA
A. DNA
When spherocytes are reported, what is observed on the peripheral blood smear?
A. Red cells without a central pallor
B. Red cells with blunt projections
C. Red cells with sharp projections
D. Red cells with intracellular rod-shaped
crystals
A. Red cells without a central pallor
The red cells found in lead poisoning characteristically exhibit coarse granules composed of ____ that are reported as ______
A. Precipitated hemoglobin; Pappen- heimer bodies
B. Aggregated ribosomes; basophilic stippling
C. Nuclear fragments; Pappenheimer bodies
D. Excess iron deposits; basophilic stippling
B. B. Aggregated ribosomes; basophilic stippling
Rouleaux of red blood cells when seen in the monolayer of a blood smear is characteristic of
A. Hypersplenism
B. Hypogammaglobulinemia
C. Cold hemagglutinin disease
D. Multiple myeloma
D. Multiple myeloma
Which of the following is not frequently associated with the inclusion bodies seen in Color Plate 1?
A. Iron overload state
B. Post-transfusion
C. Post-splenectomy
D. Iron-deficient state
C. Post-splenectomy
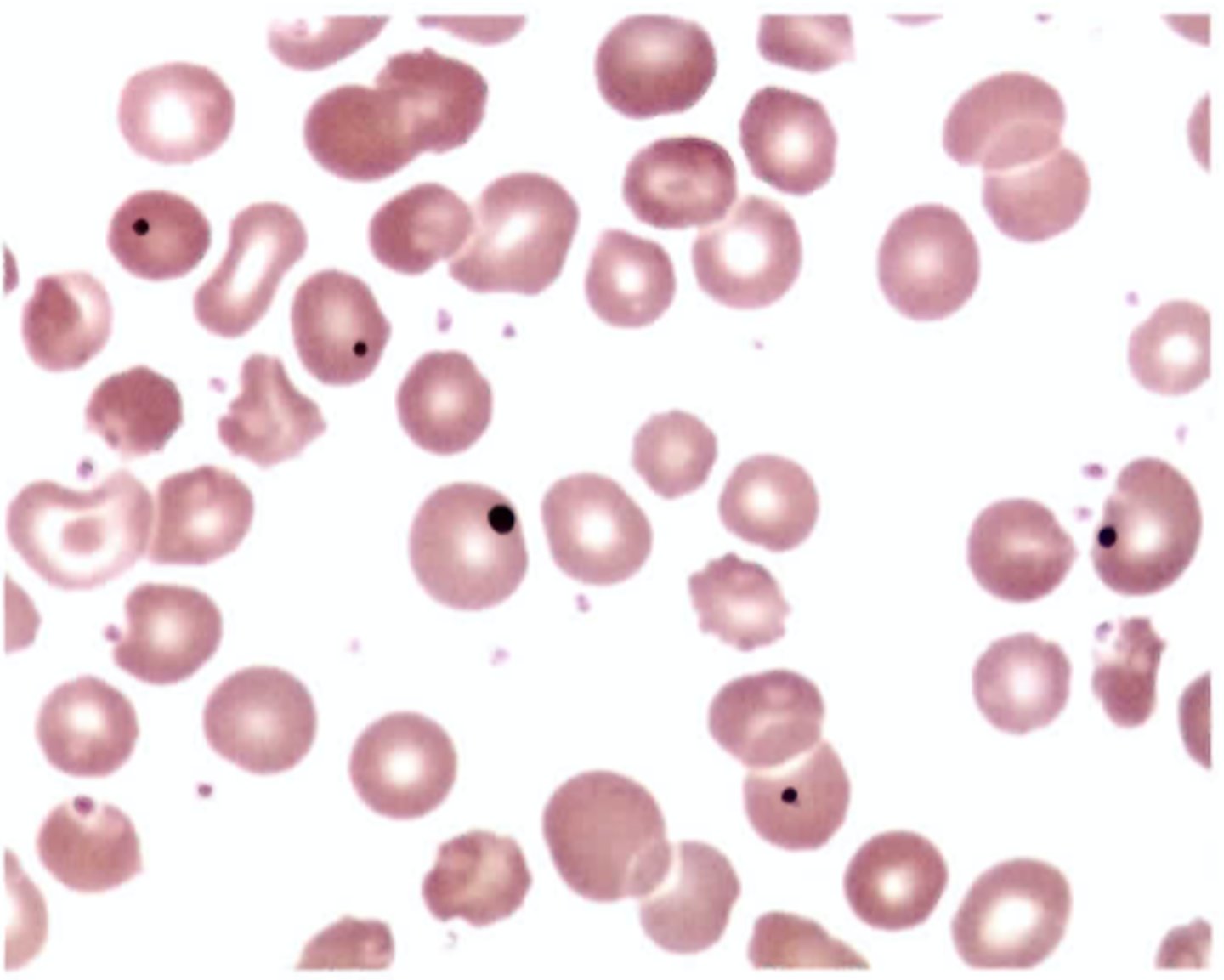
Which of the following statements about iron absorption is true?
A. Absorption occurs in the ileum.
B. The mucosal cell always absorbs the
correct amount of iron to meet needs.
C. Absorption increases when erythropoietic activity increases.
D. Alkaline pH favors absorption.
C. Absorption increases when erythropoietic activity increases.
What term describes a mature red blood cell that contains iron granules or deposits?
A. Siderosome
B. Sideroblast
C. Ringed sideroblast
D. Siderocyte
D. Siderocyte
Which of the following is associated with a "shift to the left" in the oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin?
A. Decreased pH and elevated temperature
B. Decreased oxygen affinity
C. Decreased oxygen release
D. Presence of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
(2,3-BPG)
C. Decreased oxygen release
Which of the following statements does not characterize erythropoietin (EPO)?
A. Transforms the CFU-E into the earliest
recognizable RBC precursor
B. Increases the rate of red blood cell
production by the bone marrow
C. Shortens the maturation time of
developing erythroid precursors
D. Decreases stimulation of erythropoiesis when cellular hypoxia increases
D. Decreases stimulation of erythropoiesis when cellular hypoxia increases
Which of the following factors will result in am immediate increase in oxygen delivery to the tissues?
A. Increased pH
B. High altitudes
C. Increased hemoglobin binding of 2,3-BPG
D. Increased renal release of erythropoietin
C. Increased hemoglobin binding of 2,3-BPG
Periods of intents erythropoietin activity cause premature cause permanent release of marrow reticulocytes into the blood. Which of the following is not true of these early reticulocytes?
A. Loss of residual RNA occurs immediately upon marrow release
B. Circulate longer than usual before reaching maturity
C. May be termed shift or stress reticulocytes
D. Show diffuse basophilia with Wright's stain
A. Loss of residual RNA occurs immediately upon marrow release
Which of the following inclusions is only visible with supravital staining?
A. Basophilic stippling
B. Cabot rings
C. Heinz bodies
D. Pappenheimer bodies
C. Heinz bodies
The presence of shistocytes on the peripheral blood smear is commonly associated with
A. Increased iron mobilization
B. Increased red cell destruction
C. Decreased erythropoietin activity
D. Decreased red cell proliferation
B. Increased red cell destruction
Which of the following may be a sign of accelerated bone marrow erythropoiesis?
A. Hypercellular marrow with a
decreased number of RBC precursors
B. Bone marrow M:E ratio of 6:1
C. Nucleated red cells in the peripheral
circulation
D. Low erythrocyte, hemoglobin, and
hematocrit levels
C. Nucleated red cells in the peripheral
circulation
Microcytic, hypochromic red cells are most often associated with impaired
A. DNA synthesis
B. RNA metabolism
C. Hemoglobin synthesis
D. Enzyme metabolism
C. Hemoglobin synthesis
When in bone marrow, the nucleated red cells present in color plate 2, would be staged as
A. Basophilic normoblasts
B. Polychromatophilic normoblasts C. Orthochromic normoblasts
D. Pronormoblasts
C. Orthochromic normoblasts
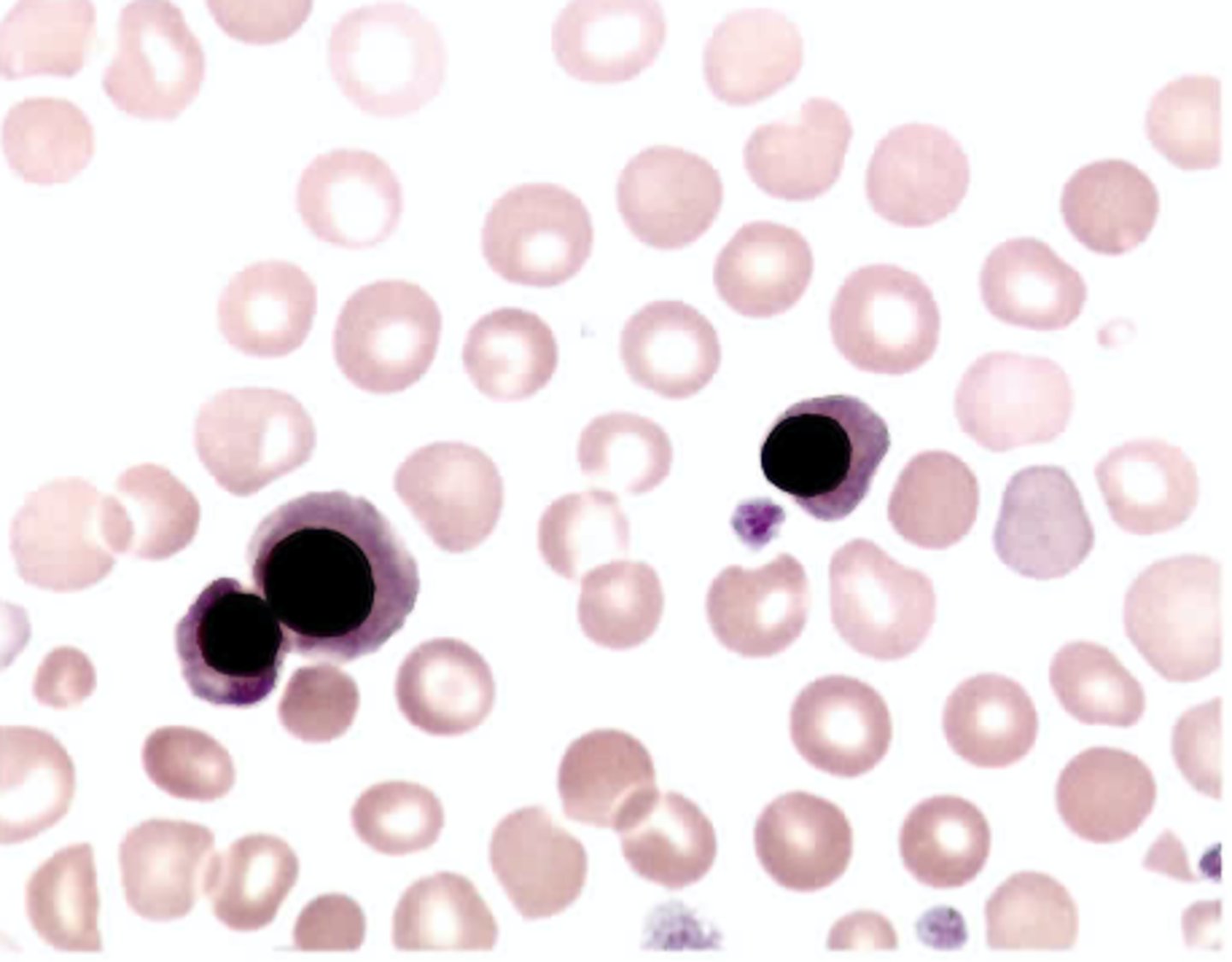
When acanthocytes are found on the blood smear, it is usually the result of
A. Abnormal membrane permeability
B. Altered membrane lipids
C. Mechanical trauma
D. Polymerization of hemoglobin
molecules
B. Altered membrane lipids
Which erythrocyte metabolic pathway generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via glycolysis?
A. Embden-Meyerhof
B. Hexose monophosphate
C. Rapoport-Luebering
D. Methemoglobin reductase
A. Embden-Meyerhof
Which of the following red blood cell precursors is the last stage to undergo mitosis?
A. Pronormoblast
B. Basophilic normoblast
C. Polychromatophilic normoblast D. Orthochromic normoblast
C. Polychromatophilic normoblast
The major adult hemoglobin requires the synthesis of the alpha-globin chains and
A. Beta-globin chains
B. Delta-globin chains
C. Epsilon-globin chains
D. Gamma-globin chains
A. Beta-globin chains
Defective nuclear maturation commonly results in the production of red cells that are
A. Normocytic
B. Hypochromic
C. Macrocytic
D. Microcytic
C. Macrocytic
The major storage form of iron is
A. Ferritin
B. Transferrin
C. Hemosiderin
D. Hemachromatin
A. Ferritin
The red cells observed on a peripheral blood smear show extreme anisocytosis with an equal number of macrocytes and microcytes. Which of the following values correlate with this finding?
A. MCV 108.0 fL, RDW 14.0%
B. MCV 90.0 fL, RDW 25.0%
C. MCV 75.0 fL, RDW 16.0%
D. MCV 88.0 fL, RDW 12.0%
B. MCV 90.0 fL, RDW 25.0%
Excessive extravascular red cell destruction is associated with
A. Hemoglobinemia
B. Bilirubinemia
C. Hemoglobinuria
D. Hemosiderinuria
B. Bilirubinemia
Which protein is primarily responsible for transport of hemoglobin dimers resulting from intravascular hemolysis?
A. Hemopexin
B. Albumin
C. Hemosiderin
D. Haptoglobin
D. Haptoglobin
The morphologic abnormality characteristic found in hemoglobinopathies is
A. Elliptocytes
B. Dacryocytes
C. Codocytes
D. Discocytes
C. Codocytes
Where do the early and late stages of heme synthesis occur?
A. On ribosomes
B. In mitochondria
C. Incytoplasm
D. In nucleoli
B. In mitochondria
Spectrin is a protein that occupies a major role in
A. Red cell membrane structure
B. Reducing ferric iron
C. Red cell transport and removal of CC>2
D. Iron recovery during hemoglobin
degradation
A. Red cell membrane structure
What is the function of reduced glutathione (GSH) in the red blood cell?
A. Promotes Kreb's cycle activity
B. Maintains anion balance during the
"chloride shift"
C. Neutralizes intracellular oxidants that
accumulate
D. Prevents oxygen uptake by hemoglobin
C. Neutralizes intracellular oxidants that accumulate
What does measuring the total binding capacity (TIBC) represent?
A. Amount of free iron in serum
B. Circulating protein-bound iron
C. Amount of iron that transferrin can bind
D. Indirect measurement of iron stores
C. Amount of iron that transferrin can bind
Serum ferritin is a good indicator of the amount of
A. Cytochromeiron
B. Storage iron
C. Hemoglobin iron
D. Transferrinsaturation
B. Storage iron
Fetal hemoglobin differs from adult hemoglobin in the hemoglobin F
A. Cytochromeiron
B. Storage iron
C. Hemoglobin iron
D. Transferrinsaturation
B. Storage iron
Impaired DNA metabolism is characteristic of
A. Hemoglobin C disease
B. Iron-deficiencyanemia
C. Sideroblastic anemia
D. Megaloblastic anemia
D. Megaloblastic anemia
Which of the following is associated with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency?
A. G6PD gene is located on the X chromosome
B. On going intravascular hemolysis
occurs.
C. All circulating red cells, including
reticulocytes, lack enzyme activity.
D. Splenectomy can relieve the rate of red
cell destruction.
A. G6PD gene is located on the X chromosome
In regard to the variant hemoglobin E, (alpha 2, beta 26 Glu -->Lys), which of the following statements is false?
A. There are two normal alpha chains.
B. Glutamic acid replaces lysine on
position 26 of the beta chains.
C. Hemoglobin E is the second most
common hemoglobin variant known.
D. Glutamic acid is normally found at
position 26 of the beta chain.
B. Glutamic acid replaces lysine on
position 26 of the beta chains.
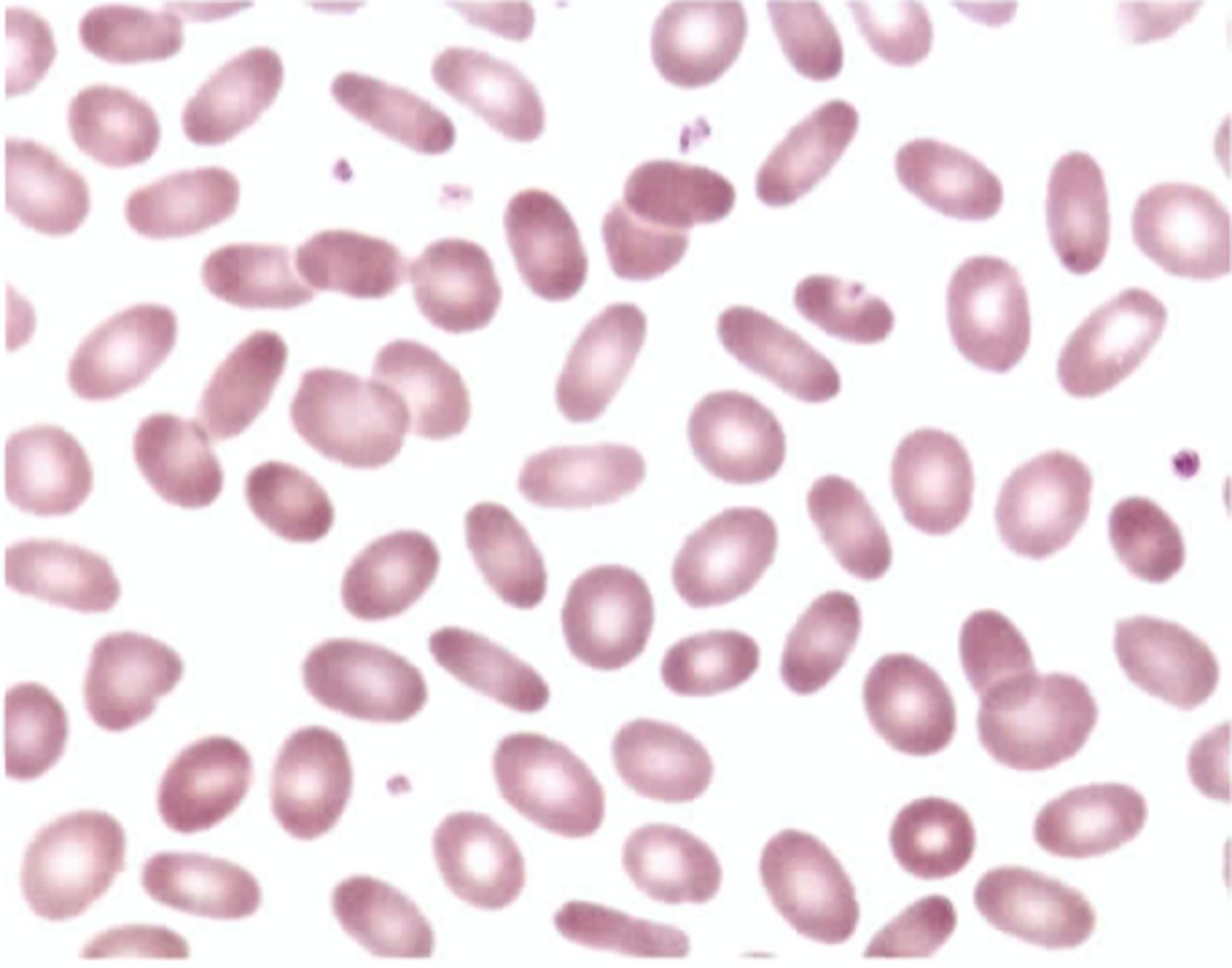
Color Plate 3 shows the peripheral blood of a 16-year-old female with a sporadic history of dizzy spells, fainting, and jaundice. This patient also had a history of periodic abdominal pain related to gallstones. Upon physical examination, she exhibited mild splenomegaly. Her hemoglobin was 107 g/L (10.7 g/dL), hematocrit was 0.32 L/L (32%), red cell indices were normal, and the direct antiglobulin test was negative. Based on history and peripheral blood morphology, which of the following statements is most likely true?
A. Hemoglobin S will be revealed by electrophoresis.
B. Tests to confirm iron deficiency should be ordered.
C. An intrinsic hereditary defect of red cells should be suspected.
D. The anemia is secondary to spleen and gallbladder disorders.
C. An intrinsic hereditary defect of red cells should be suspected.
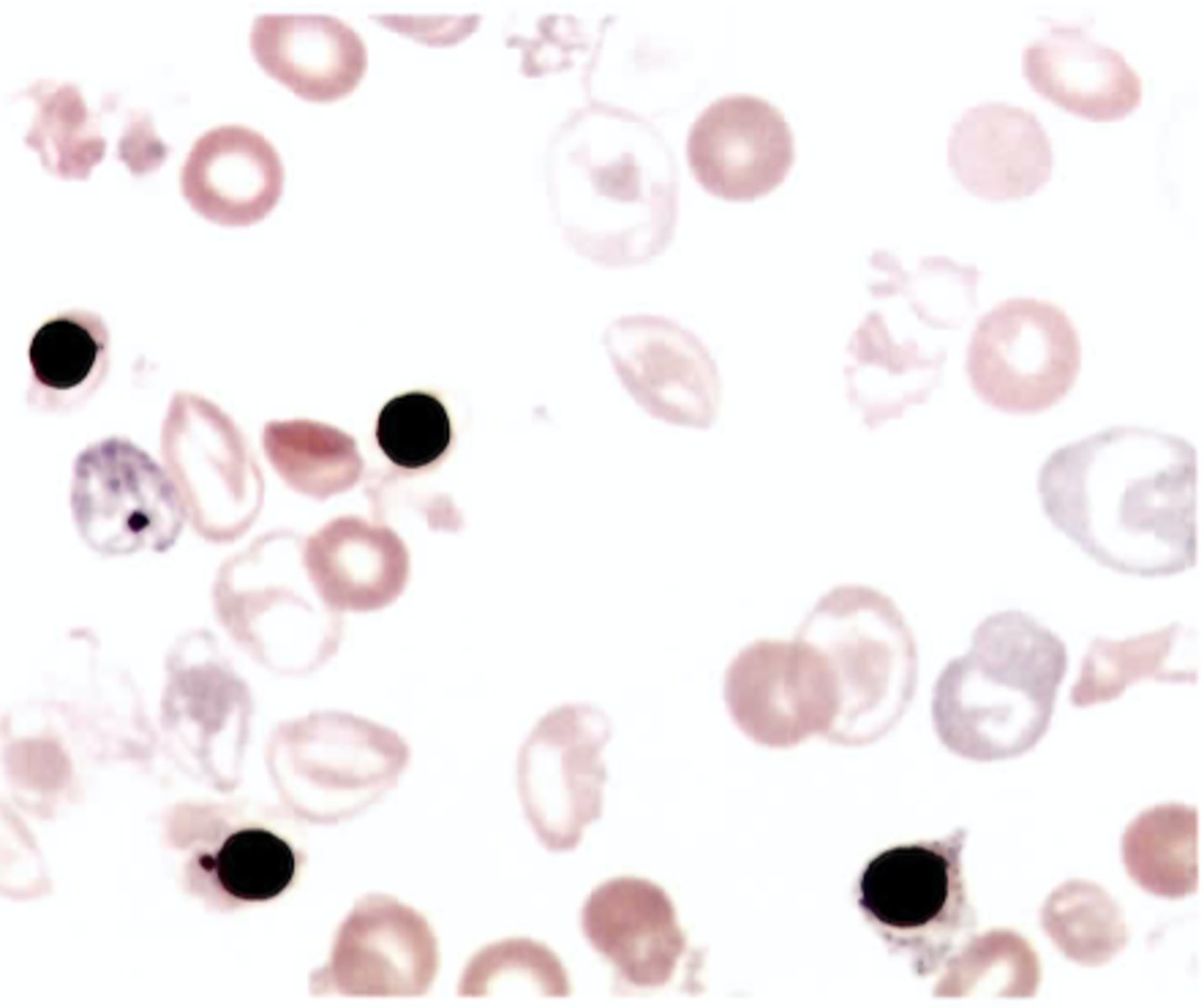
A 9 month old male was seen int he ER with a femur fracture that had occurred from a fall down the stairs. Upon physical examination the physician noted hepatosplenomegaly, extreme pallor, and a slight arrhythmia. A complete blood count revealed the following:
WBC: 12.2
RBC: 3.05
Hgb: 61
Hct: .20
MCV: 65.5
MCH: 20
MCHC: 30.5
RDW 25%
The wrights stain blood smear showed the findings seen in the color plate 4. Hemoglobin electrophoresis was ordered with results as follows:
Hgb A : 0%
Hgb A2: 3%
Hgb F: 97%
Which conditions is most likely causing the hematologic abnormalities?
A. Alpha-thalassemia major
B. Cooley beta-thalassemia major C. Hemoglobin H disease
D. Hereditary persistence of
hemoglobin F
B. Cooley beta-thalassemia major
A 14 year old african male was seen in the clinic for abdominal pain. A compelte blood count revealed the following
WBC: 7.0
RBC: 2.90
Hgb: 85
Hct: .25
MCV: 86.2
MCH: 29.3
MCHC: 340 g//L
RDW: 21%
The peripheral smear showed the red blood cell morphology seen in the Color Plate 5. What condition is suggested by these findings?
A. Hemoglobin E disease
B. Hemoglobin S disease
C. Hemoglobin SC disease
D. Hemoglobin C disease
C. Hemoglobin SC disease
Pica is most commonly associated with which of the following conditions?
A. Pyridoxine deficiency
B. Lack of erythrocyte folate
C. Iron deficiency
D. Porphyrias
C. Iron deficiency
Of the following, the leading cause of folate deficiency is
A. Increased requirements
B. Dietary insufficiency
C. Drug inhibition
D. Malabsorption
B. Dietary insufficiency
Which of the following statements abut sickle cell syndromes is false?
A. Asplenism may result from repeated
sickling crises in the homozygous
state.
B. Heterozygous persons may be partly
protected from infection by falciparum
malaria.
C. Hemoglobin S is more soluble in
dithionite than is normal hemoglobin.
D. Trait conditions are generally
asymptomatic with no sickle cell formation.
C. Hemoglobin S is more soluble in
dithionite than is normal hemoglobin.
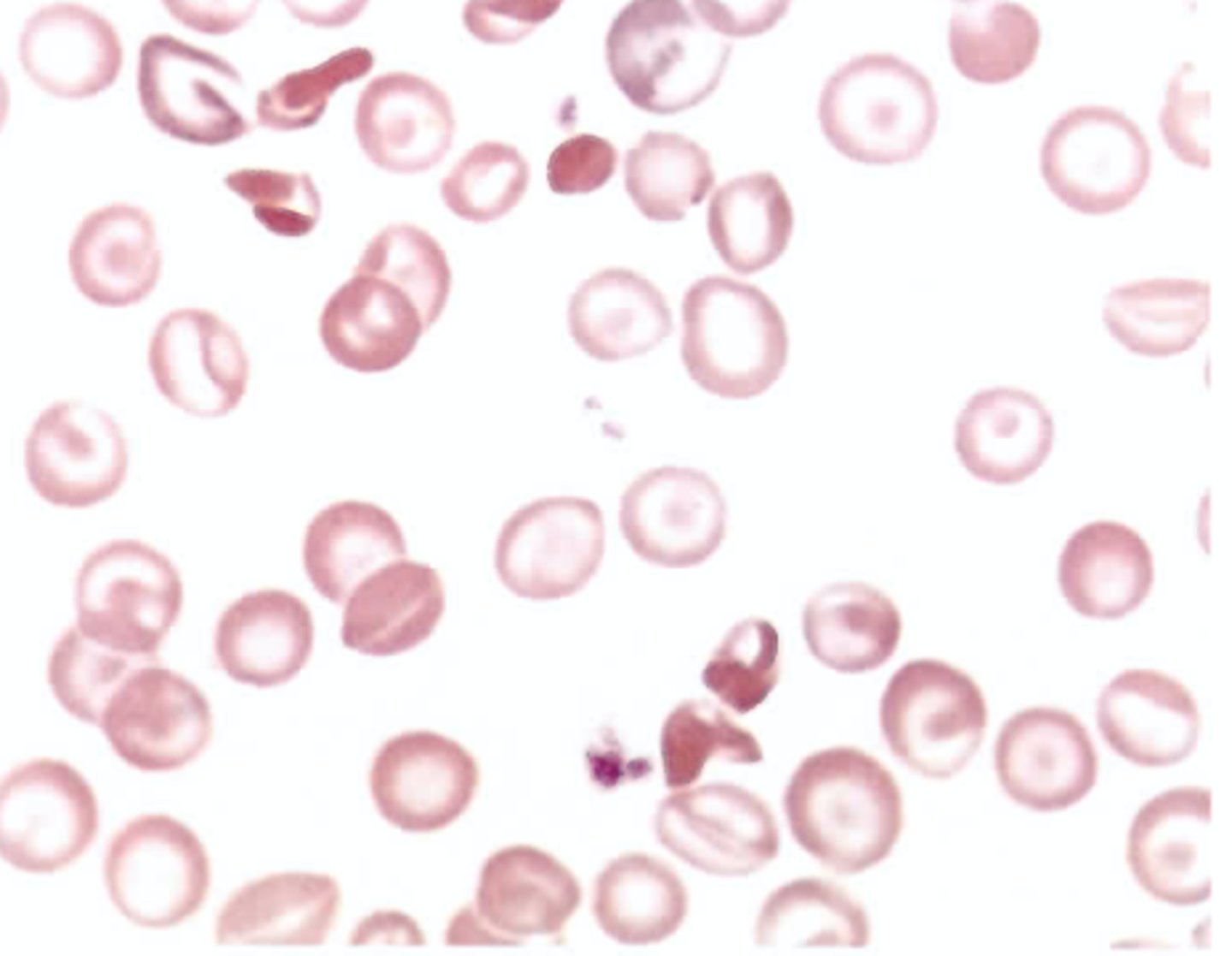
The findings seen in color plate 6 can be found in patients with microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA). Which of the following conditions could not be responsible for this type of red cell destruction?
A. Disseminatedintravascular coagulation (DIG)
B. Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
C. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic
purpura (TTP)
D. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
(ITP)
D. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
(ITP)$
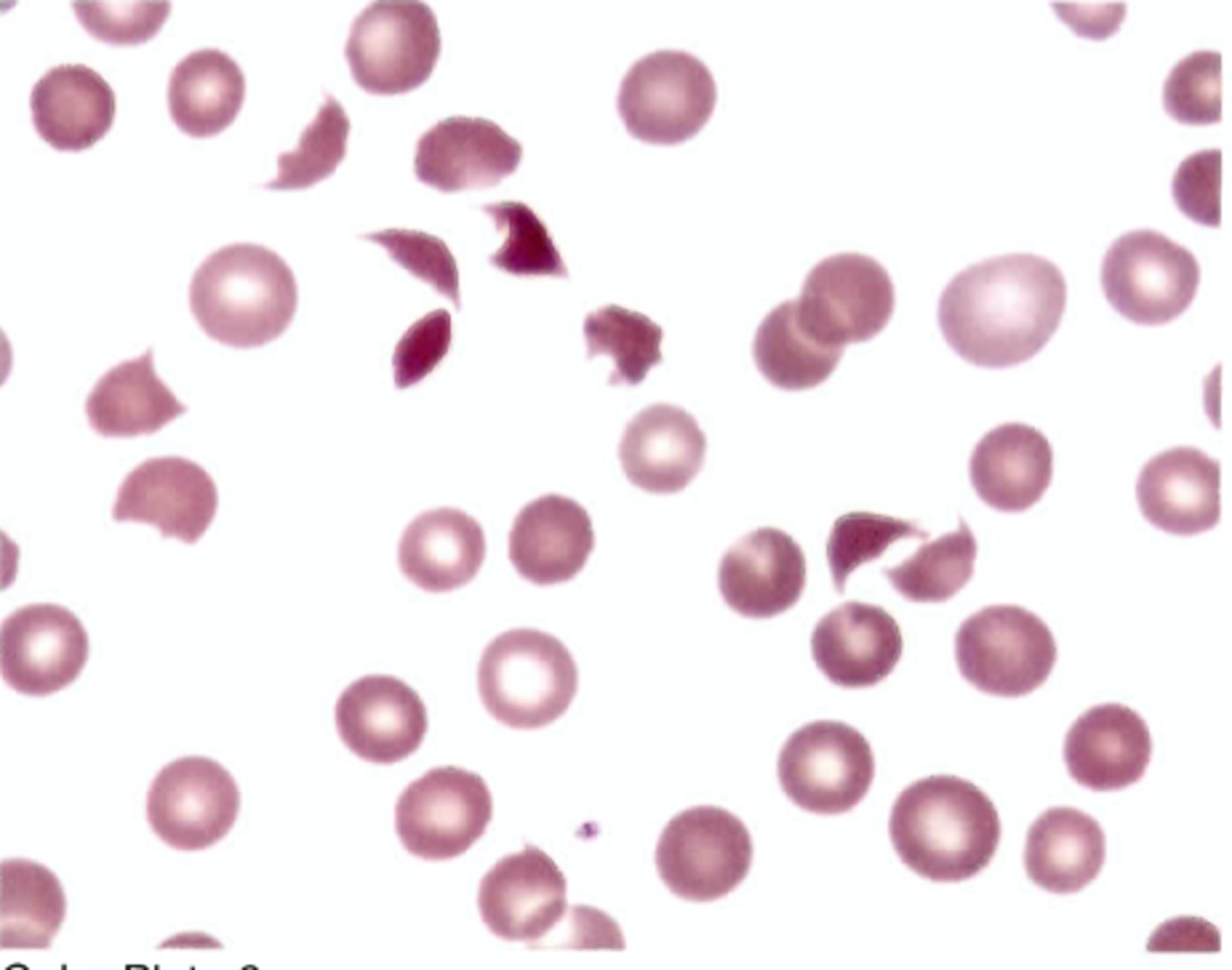
Which of the following blood findings does not correlate with the presence of ringed sideroblasts in the bone marrow?
A. Pappenheimer bodies
B. Basophilic stippling
C. Increased total iron-binding capacity
D. Increased percent transferrin
saturation
C. Increased total iron-binding capacity
Which of the following conditions is not usually associated with marked reticulocytosis?
A. Four days after a major hemorrhage
B. Drug-inducedautoimmunehemolytic
anemia
C. Sickle cell anemia
D. Pernicious anemia
D. Pernicious anemia
Hereditary stomatocytosis is manifested physiologically by changes in
A. Hemoglobin oxygen affinity
B. Membrane cation permeability
C. Efficiency of hemoglobin reduction
D. Glycolytic ATP production
B. Membrane cation permeability
In addition to an increase in red blood cells, which of the following is characteristic of polycythemia vera?
A. Decreased platelets, decreased
granulocytes, decreased erythropoietin
level
B. Decreased platelets, decreased
granulocytes, increased erythropoietin
level
C. Increased platelets, increased
granulocytes, increased erythropoietin
level
D. Increased platelets, increased
granulocytes, decreased erythropoietin level
D. Increased platelets, increased
granulocytes, decreased erythropoietin level
Which of the following is not characteristic of aplastic anemia?
A. Extramedullary hematopoiesis
B. Bone marrow hypoplasia
C. Absolute reticulocytopenia
D. Blood findings of pancytopenia
A. Extramedullary hematopoiesis
What values would you expect to obtain on hemoglobin and hematocrit determinations done immediately after a major hemorrhage, if hemoglobin and hematocrit values were normal prior to the hemorrhage?
A. Both normal
B. Both decreased
C. Hemoglobin decreased, hematocrit
normal
D. Hemoglobin normal, hematocrit
decreased
A. Both normal
Results from a 1-day-old infant include a hemoglobin of 201 g/L (20.1 g/dL), hematocrit of 0.60 L/L (60.0%), MCV of 110.2 fL, and 4 nucleated red cells/100 WBCs. How should these results be interpreted?
A. The elevated hemoglobin and hematocrit values indicate possible dehydration.
B. The nucleated red cells suggest accelerated erythropoiesis due to a hemolytic process.
C. Testing should be done to identify the cause of the macrocytosis.
D. No further testing is indicated.
D. No further testing is indicated.
When viewing Color Plate 7 1m, the red blood cells with a single elongated projection are known as and may be seen in
A. Acanthocytes; liver disease
B. Echinocytes; liver disease
C. Drepanocytes; myelofibrosis
D. Dacryocytes; myelofibrosis
D. Dacryocytes; myelofibrosis
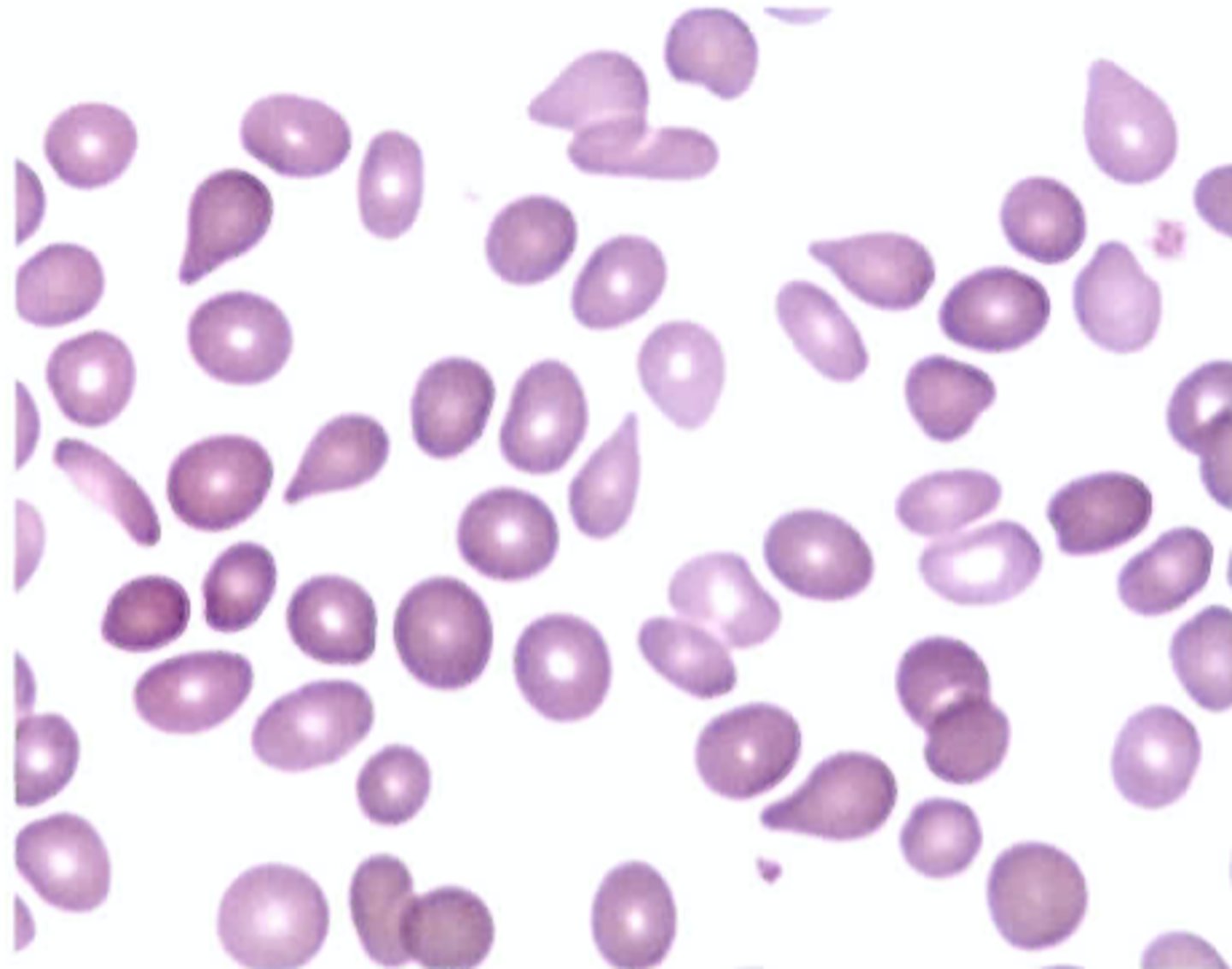
A patient with normocytic, normochromic anemia secondary to small cell carcinoma may be exhibiting an anemia designated as
A. Hemolytic
B. Megaloblastic
C. Myelophthisic
D. Sideroblastic
C. Myelophthisic
Idiopathic aplastic anemia is best defined as a form of anemia that
A. Has no identifiable cause
B. Is caused by a physician's treatment
C. Follows exposure to ionizing radiation
D. Develops after a viral infection
A. Has no identifiable cause
Which of the following is a true red blood cell aplasia?
A. Marrow replacement anemia
B. Fanconi anemia
C. Diamond-Blackfananemia
D. Donath-Landsteiner anemia
C. Diamond-Blackfan anemia
Which of the following is not a cause of absolute secondary erythrocytosis?
A. Defective cardiac or pulmonary
function
B. High-altitude adjustment
C. Dehydration secondary to diuretic use
D. Hemoglobins with increased oxygen
affinity
C. Dehydration secondary to diuretic use
A cellulose acetate hemoglobin electrophoresis (alkaline pH), performed on the blood of a stillborn infant, revealed a single band that migrated farther toward the anode than did the Hb A control. What is the most likely composition of the stillborn infant's hemoglobin?
A. Four beta chains
B. Four gamma chains
C. Two alpha and two beta chains
D. Two alpha and two gamma chains
B. Four gamma chains
The most likely cause of the stillborn infant's condition in question 83 is
A. Erythroblastosis fetalis
B. Rh hemolytic disease of the fetus
C. Hydrops fetalis
D. ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn
C. Hydrops fetalis
Which of the following conditions show similar CBC and blood smear findings?
A. Beta-thalassemia major and minor
B. Folic acid and vitamin B12 deficiencies
C. Acute and chronic blood loss
D. Sickle cell disease and trait
B. Folic acid and vitamin B12 deficiencies
Which of the following would be useful in identifying the cause of the blood profile seen in Color Plate 8«?
A. Osmotic fragility test
B. Reticulocytecount
C. Direct antiglobulin test
D. Urine urobilinogen level
C. Direct antiglobulin test
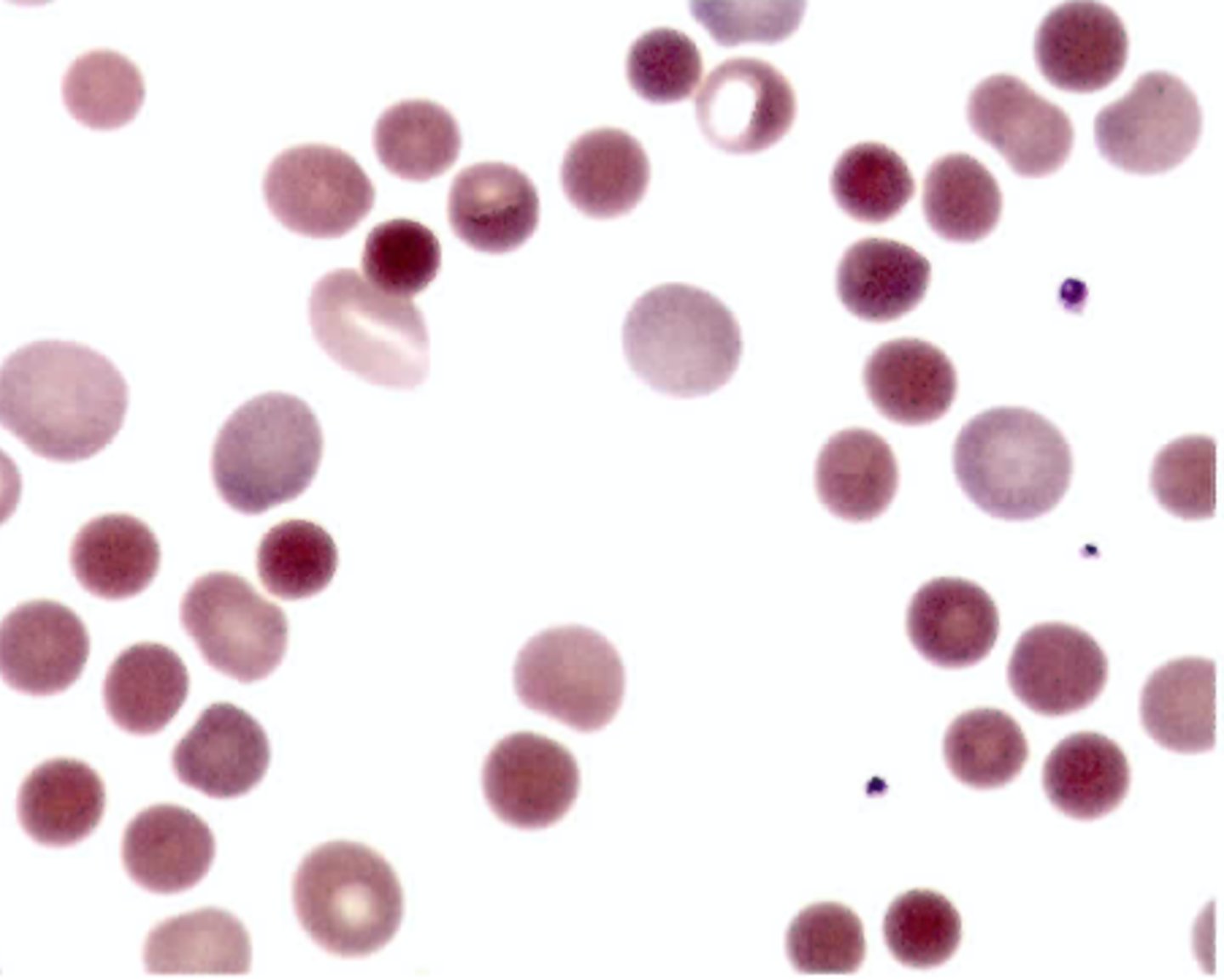
Which of the following conditions is not associated with the presence of schistocytes and spherocytes?
A. Clostridial septicemia
B. Prosthetic heart valves
C. Severe thermal burns
D. Aplastic anemia
D. Aplastic anemia
A 30-year-old woman who has been vomiting for 3 days has a hemoglobin value of 180 g/L (18.0 g/dL) and a hematocrit of 0.54 L/L (54.0%). Her results suggest the presence of
A. Absolute erythrocytosis
B. Primary polycythemia
C. Secondary polycythemia
D. Relative polycythemia
D. Relative polycythemia
An excessive accumulation of iron in body tissues is called
A. Hemochromatosis
B. Erythroblastosis
C. Megaloblastosis
D. Acrocyanosis
A. Hemochromatosis
Abetalipoproteinemia is characterized by mild anemia and numerous
on the peripheral
blood smear.
A. Acanthocytes
B. Elliptocytes
C. Echinocytes
D. Stomatocytes
A. Acanthocytes
What is the most common cause of iron deficiency?
A. Bleeding
B. Gastrectomy
C. Inadequate diet
D. Intestinal malabsorption
A. Bleeding
Which of the following does not characterize beta-thalassemia major?
A. Transfusion-dependent anemia
B. Decreased alpha chains result in
excess beta chains.
C. Iron chelation therapy is necessary.
D. Common in persons of Mediterranean
ancestry
B. Decreased alpha chains result in
excess beta chains.
In the anemia of chronic disease, what are the usual serum iron and transferrin levels?
A. Serum iron decreased, transferrin
decreased
B. Serum iron decreased, transferrin
increased
C. Serum iron normal, transferrin normal
D. Serum iron increased, transferrin
increased
A. Serum iron decreased, transferrin
decreased
In children, the most important effect of lead poisoning is on the
A. Liver
B. Kidney
C. Neurologic system
D. Development of erythrocytes
C. Neurologic system
Which of the following would not result in the dual population of red cells represented in Color Plate 9B?
A. Blood transfusion
B. Oral iron therapy
C. Spleen removal
D. Coexisting deficiencies
C. Spleen removal
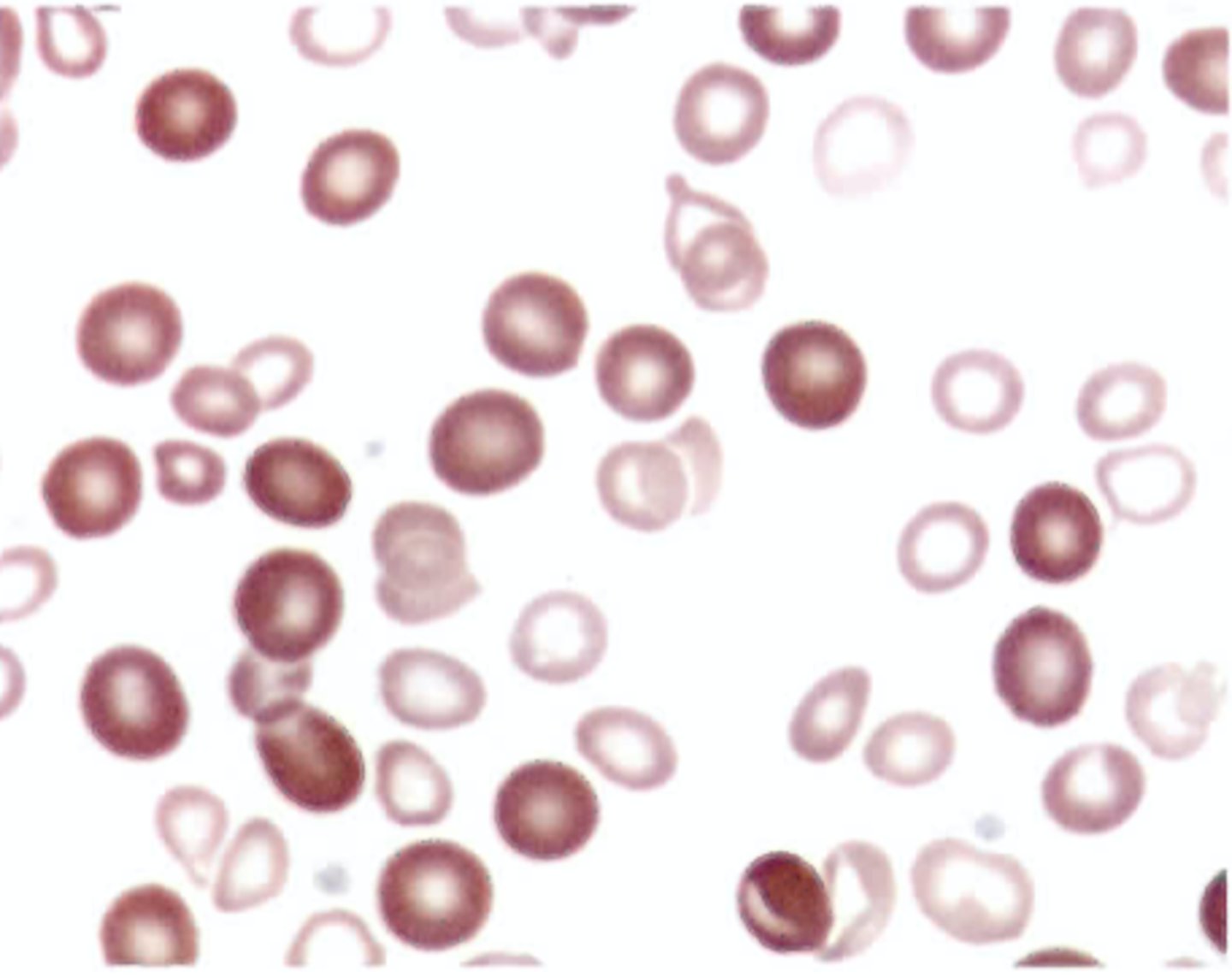
What is the most likely genetic defect in the hemoglobin of cells seen in Color Plate 10B?
A. Substitution of valine for glutamic acid
in position 6 of the alpha-globin chain
B. Substitution of valine for glutamic acid
in position 6 of the beta-globin chain
C. Substitution of lysine for glutamic acid
in position 6 of the alpha-globin chain
D. Substitution of lysine for glutamic acid in position 6 of the beta-globin chain
B. Substitution of valine for glutamic acid
in position 6 of the beta-globin chain
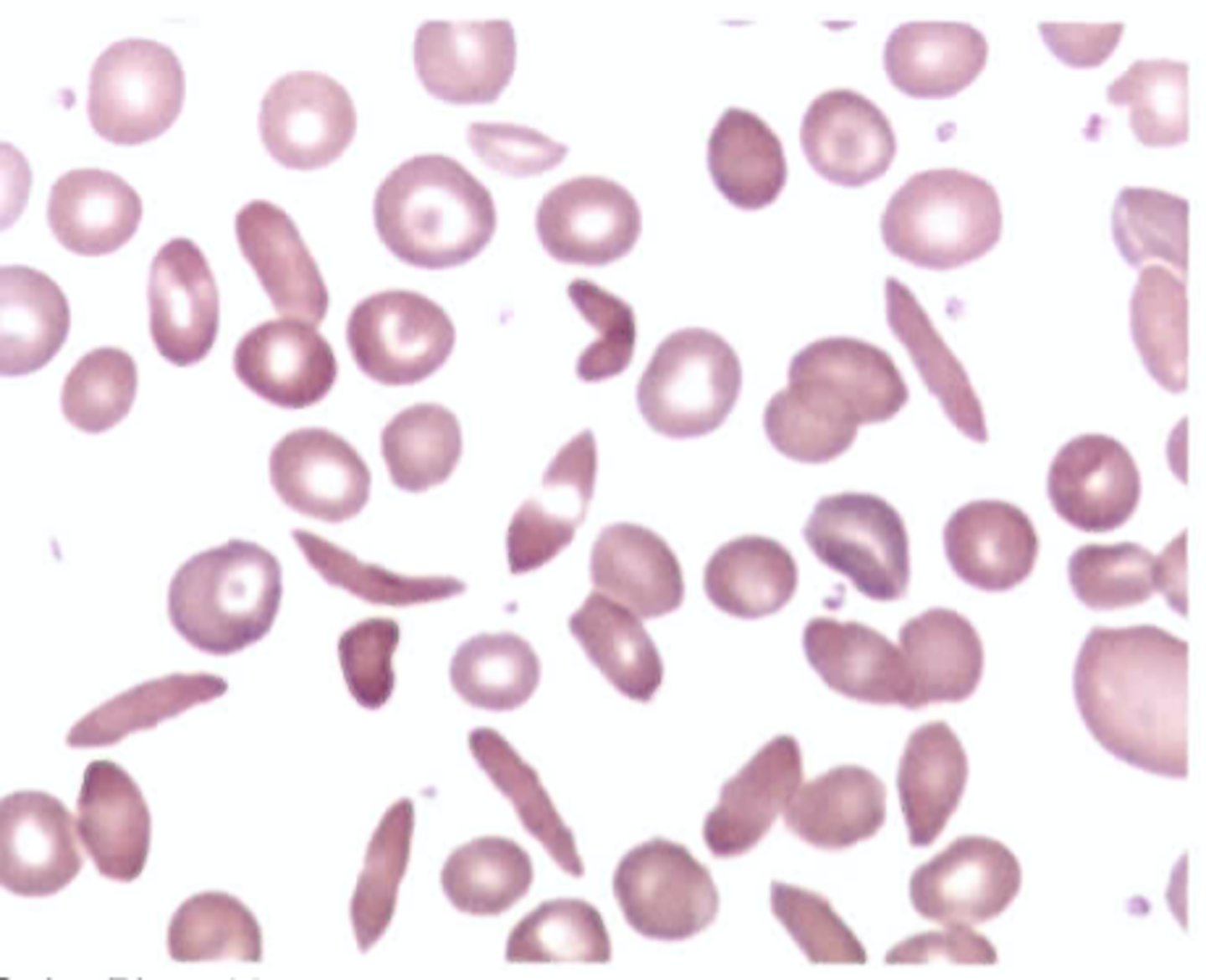
On what is the classification of sickle cell trait versus sickle cell disease based?
A. Severity of the clinical symptoms
B. Number of irreversibly sickled cells
(ISCs)
C. Level of compensatory hemoglobin F
D. Percentage of hemoglobin S on
electrophoresis
D. Percentage of hemoglobin S on
electrophoresis
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for sickle cell anemia?
A. Hydroxyurea
B. Supportive therapy
C. Hyperbaric oxygen
D. Iron
B. Supportive therapy
Which of the following values can be used to indicate the presence of a hemolytic anemia?
A. Hemoglobin level
B. Hematocrit level
C. Erythrocyte count
D. Reticulocyte count
D. Reticulocyte count
A pre-operative, 20-year-old female has a mild microcytic anemia, with target cells and stippled red cells observed on the blood smear. Her hemoglobin A2 level is quantified at 5%. What do these findings suggest?
A. Iron-deficiency anemia
B. Heterozygous alpha-thalassemia
C. Heterozygous beta-thalassemia D. Hemoglobin S/beta-thalassemia
C. Heterozygous beta-thalassemia