Module 1: Population and scarcity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
people didn’t live in ecological balance, they ?
died in ecological balance
explain the perspectives of $1, $10, $100 a day
those who are very rich look down and see everyone else is poor
those with 1 dollar a day look up and see it would be so much better for them if they were at the 10 dollar a day
lots of population growth in areas that are not emitting a lot of GHGs?
not much need for concern environmentally
the more education there is among young women…
the lower birthrates are
malthus perspective on women and population growth
malthus called for greater restraints on women
this perspective has led to population control efforts that target the poorest and most marginal populations, even though the poorest are often not the primary cause of degradation
targeting the poor and women diverts attention away from systemic causes of degradation
easier to blame poor people and women
phase 1 of demographic transition model
pre-industrial
high turnover of births and deaths, close to zero pop growth
many deaths, multiple children per family because some die
traumatic for families to deal with so much death
lots of children both to ensure they lived and also so they could work on the farm
phase 2 of demographic transition model
mortality revolution
death rate declines, still high birth rate
population growth accelerates
medical innovation and technology allows less death
agricultural advances allows more food production and less starvation
takes time for society to adapt to new survival rate, people realize its expensive to have many kids if they all survive
death rate was external, it happened no matter what, but birth rate is a personal change that must happen. Baked into culture to have many kids, took a while for that to change
phase 3 of demographic transition model
fertility transformation
birth rate declines, low death rate
population growth decelerates
2 children as a replacement for the 2 adults that will eventually die
population still increasing, but the rate is decreasing
phase 4 of demographic transition model
industrial
low turnover of births and deaths
close to zero population growth
high total population, rate not changing
when is largest population increase?
when the birth rate and death rate are the most different
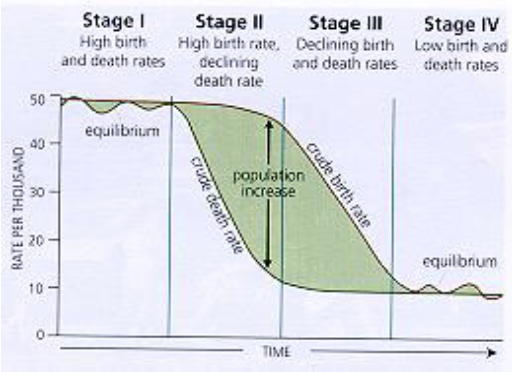
more detail on fertility transformation in stage 3
medical: higher life expectancy, lower infant mortality
economic: higher socioeconomic standards, higher cost to raise a child, no longer an asset on the farm to have children
social: state-based pension system, change of values
motivation to have less children
explanation of replacement fertility rate
how many children are families having
ideally 2.1, not just 2.0 because of accidents and disease
industrialized and urban places have less than 2 kids, sometimes none.
values have changes, career success, don’t need kids to be happy, don’t need to be married
summary of demographic transition
mortality revolution is induced externally (medical air, technology import)
fertility transformation required internal changes of society
many less developed countries have partially achieved the first, but not yet conquered the second
population grows enormously until the transformation is complete
immense problems (social, healthcare, economic, etc) in the meantime
total fertility rate in the world has ___ in 50 years from 1950 to 2000
halved
transition time between over 6 children per woman to fewer than 3 has varied a lot, give examples
UK took almost a century
Iran took 10 years, less than 1 generation
in the 60s, women’s rights movements, lower birth rates, more autonomy and educated in the workforce
details on population pyramids
between 1950s and today, widening of the pyramid base, increase in number of children = increase in world population
from now on its a filling up of the population above the base
number of children will barelly increase and then start to decline, but number of people of working age and old age will increase substantially
everyone who was already born has a better chance of staying alive
as life expectancy goes up, shape becomes more like funnel/beehive shape
low births and low deaths
canada’s pop pyramid
in 1950s some missing because of war, during it babies weren’t being born
later big bulge = baby boomers moving up the pyramid
don’t want an economic shock from that
who really contributes the most to global emission
top 1% of global emitters each had carbon footprints of over 50 tonnes of CO2 in 2021, more than 1000 times greater than those in bottom 1% of emitters
10% of emitters were responsible for almost half of global energy related emissions in 2021, compared to 0.2% for bottom 10% 200 times less
46.8 million individuals are considered millionaires or billionaires
richest of world is not changing, no wealth restrictions, and being passed on to children