Unit 2: The Physical Environment
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
2 ways we move energy
conduction, convection
conduction
The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another
convection
The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid
sensible heat flux
Energy transfer from warm air immediately above the surface to the cooler atmosphere by convection and conduction
Examples of greenhouse gases
CO2, methane, water vapor, nitrous oxide
water vapor
spends little time as a green house gas due to the water cycle
Solar energy is ___ toward the poles and ___ near the equator
spread out, more concentrated
How clouds are formed
-warm air rises above warm surface
-warm air expands and cools
-water vapor condenses and forms clouds
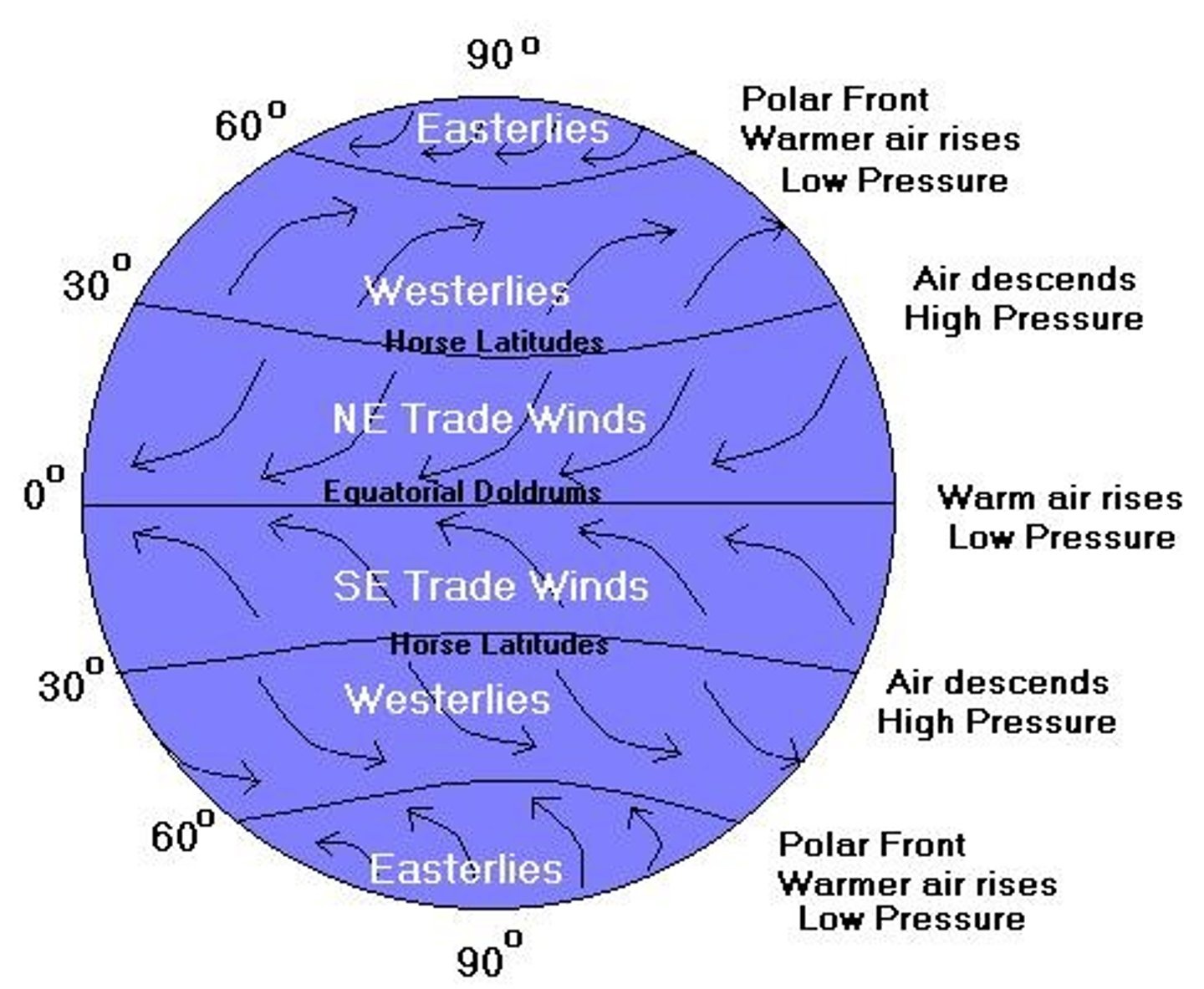
Hadley Cell
air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes
Pressure and precipitation have an ____ relationship
Inverse; ex. higher pressure = less precipitation
air currents
air moving from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
Air circulation is influenced by
the rotation of the earth
Coriolis Effect
Causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere due to Earth's hemisphere.
Upwelling effect
blowing wind parallel to the coast creates surface current flowing away from the coast
maritime influence
heat is absorbed by the water and keeps temperature of the land relatively constant
continental effect
land areas have greater range of temperatures
Heat and pressure have a ____ relationship
direct; ex. high pressure = high heat
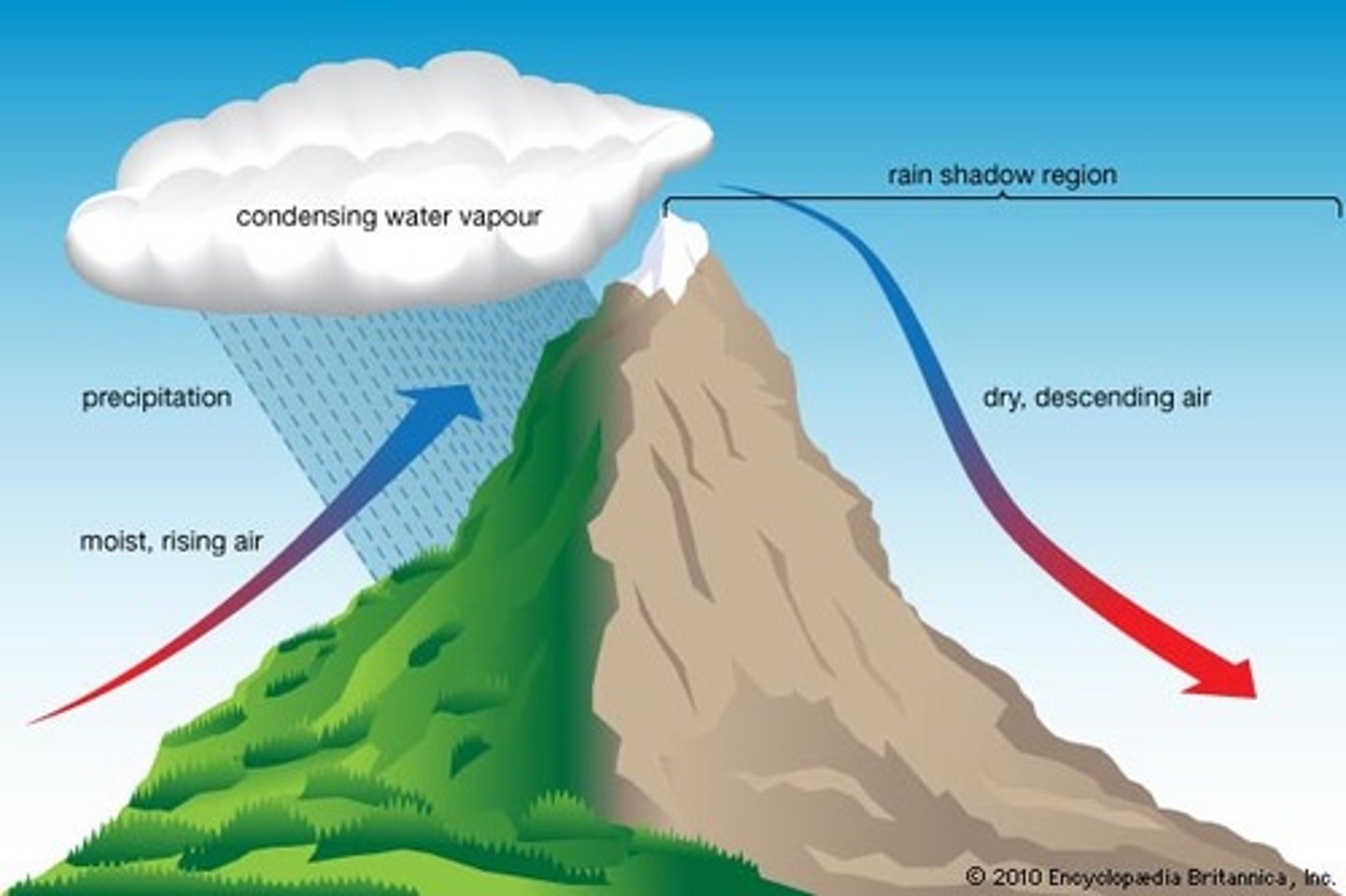
Rain Shadow Effect
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
Albedo
Ability of a surface to reflect light
As albedo goes down ____ energy is absorbed
more
Removing trees ____ the albedo of the land, _____ its absorption of solar radiation
increases; decreasing
Evapotranspiration
The evaporation of water from soil plus the transpiration of water from plants
What effects the seasons
Earth's 23.5° rotation
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
recurring changes in the temperature and air pressure of tropical pacific ocean
El Nino
Warming Phase
La Nina
Cooling phase
ITCZ (Intertropical Convergence Zone)
Band of clouds + low pressure that encircles the Earths near the equator