OPT 217 Illumination
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
In WWII, they found that as lighting levels improved, _____________________________________?
increased production speed
decreased error rate
When does increasing illuminance have a large effect on performance? 2 stimulus qualities.
contrast is LOW
or
task is SMALL
What is luminous power and it's units?
total light power produced by a source, measured in lumens
What is luminous intensity and it's units?
light power produced by a source in a given direction, measured in candelas
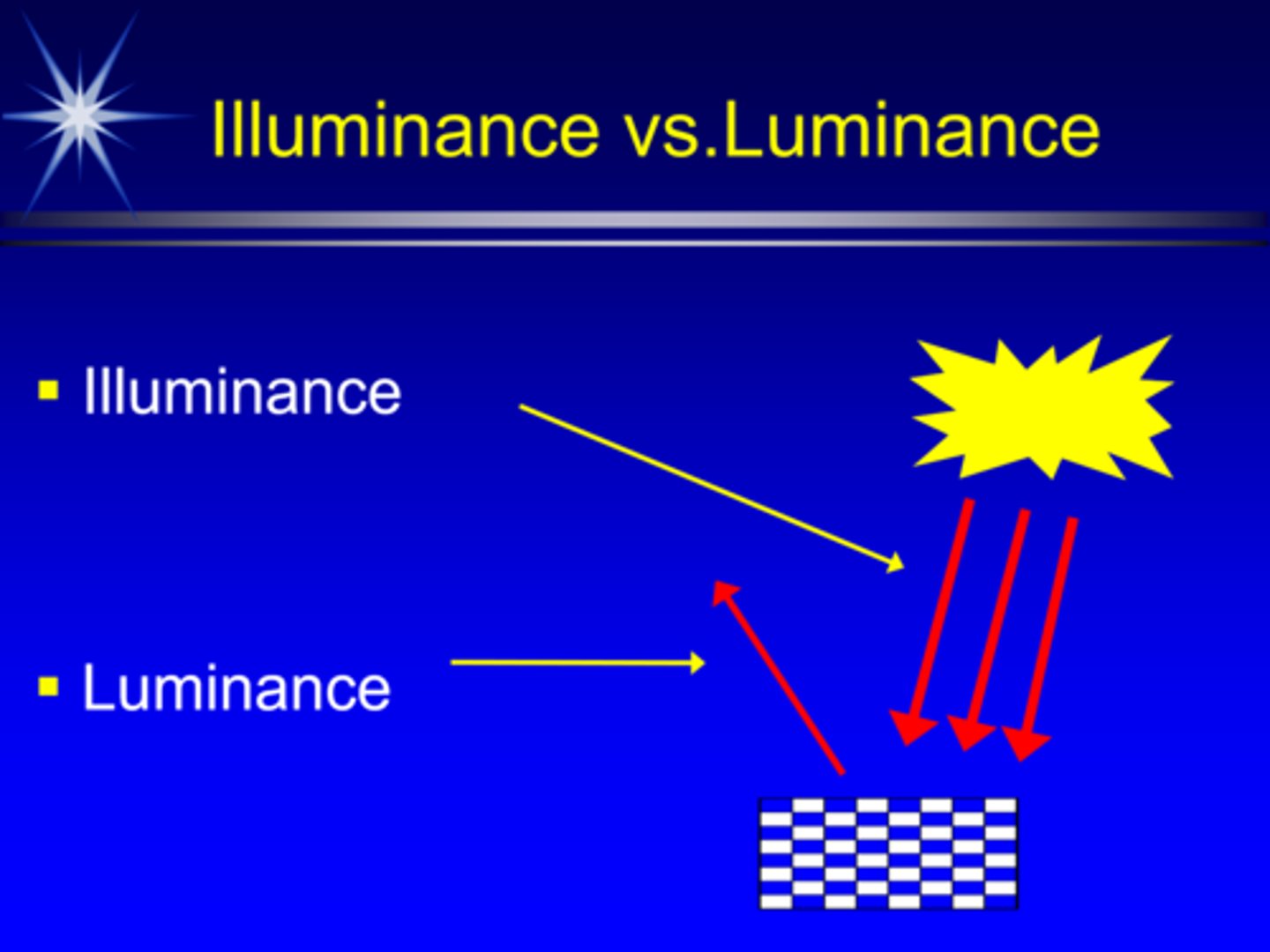
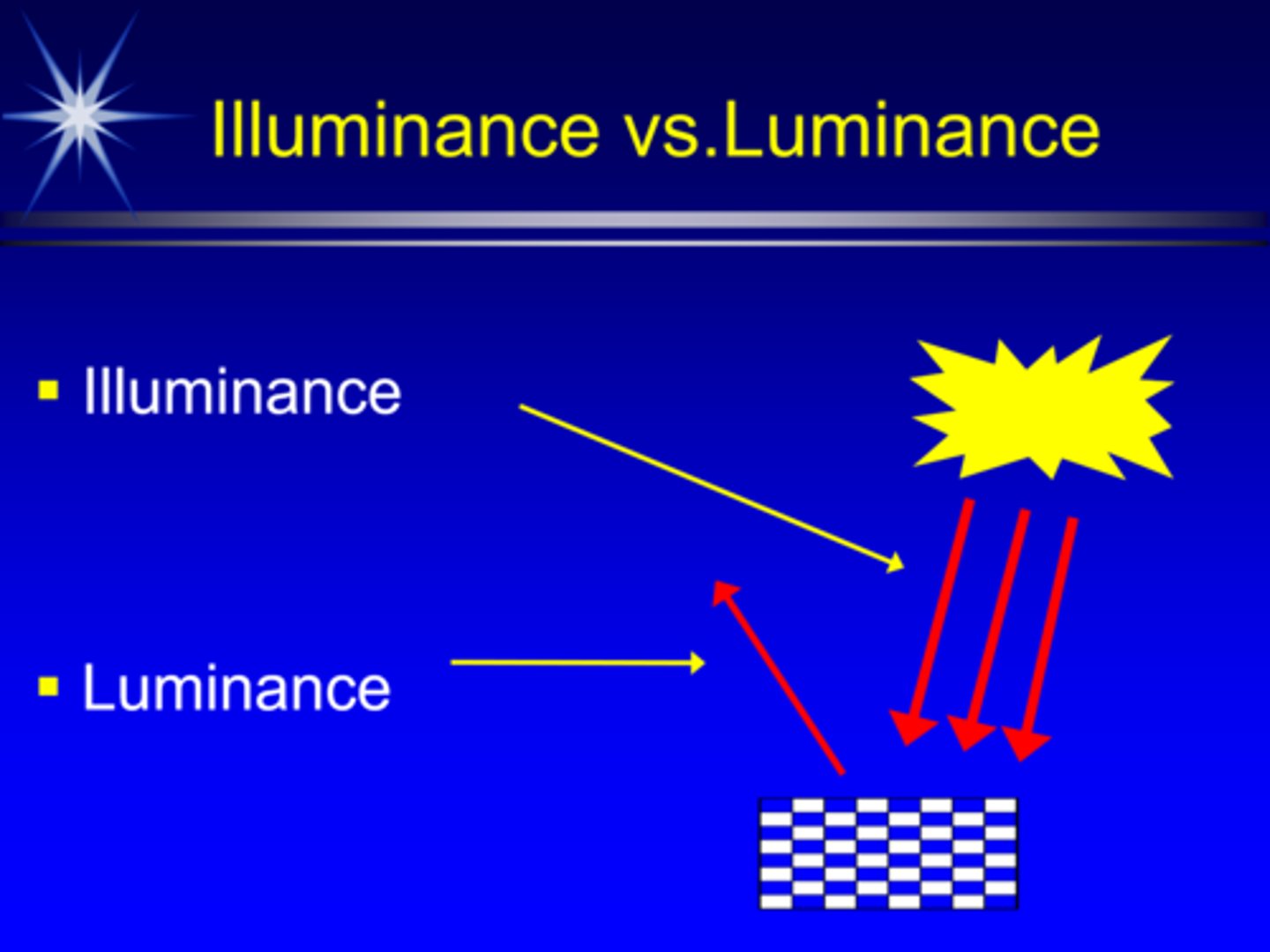
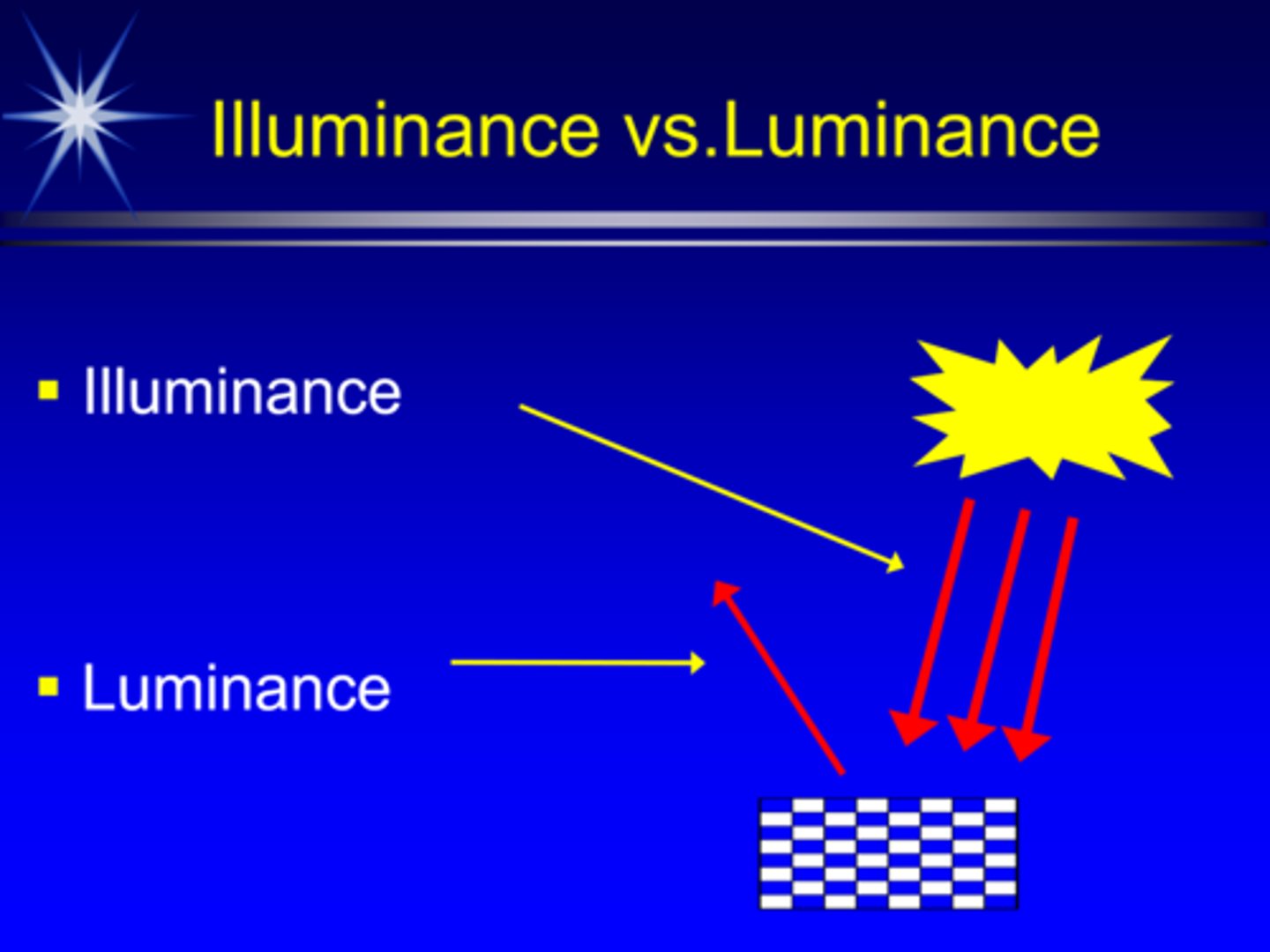
What is illuminance and it's units?
light incident on a surface, measured in foot-candles or lux
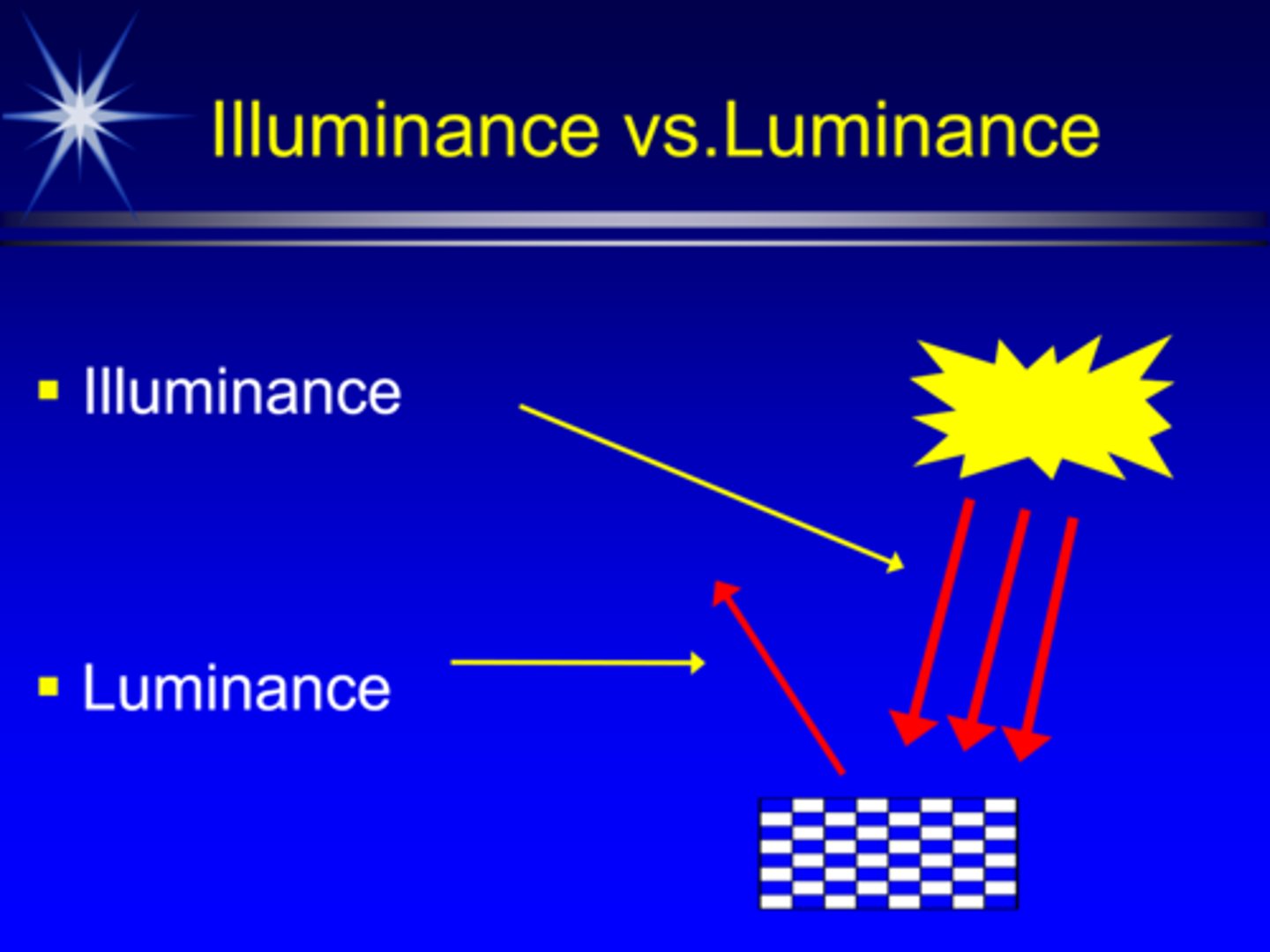
What is luminance and it's units?
light reflected off a surface in a specific direction, measured in foot-lamberts
sometimes called reflectance
What is a luminaire?
complete lighting unit consisting of a light source, housing, supports, shields, etc.
What is wattage?
amount of electricity consumed by a light source
What are lumens?
amount of light that a light source produces
What is efficiency?
lumens/watt
What is incandescent lighting like conventional light bulbs, halogen lamps?
produces light through heat = run electricity through a Tungsten filament (w/ argon gas in tube) = heats filament to light producing temp = filament glows

What are advantages of incandescent lighting?
low initial cost
small lamps
easy to install
excellent/best colour rendering = things appear like their most true/normal colour (most similar to natural sunlight)

What are disadvantages of incandescent lighting?
short life
unpredictable of when they'll go out
not common anymore
least efficient = up to 95% of energy lost to heat

How are halogen incandescent lamps a slight upgrade?
halogen gas promotes redistribution of Tungsten onto filament where you want it (rather than on sides of bulb) = whiter, brighter, lasts longer, more efficient, more costly

What is luminescent lighting like fluorescent, high intensity discharge, low pressure sodium, LED?
produces light through excitation of individual atoms
How does fluorescent luminescent lighting work?
mercury vapour between 2 electrodes inside tube = excite vapour = produce UV radiation = phosphor fluoresces in tube
NOTE: ballast controls electrical flow into bulb = more complex design

What are some advantages of fluorescent luminescent lighting?
more efficient (than incandescent)
less heat
longer lifer
decent colour rendering

What are some disadvantages of fluorescent luminescent lighting?
glare, reflections, flicker
large size
contains Hg
higher initial cost
more complicated design

What are some advantages of high intensity discharge lamp luminescent lighting?
very efficient
lots of light over wide area = good for tunnels, parking lots, stadiums
long life

What are some disadvantages of high intensity discharge lamp luminescent lighting?
poor colour rendering
ballast delay in starting = only start when bulbs hit a certain cool temp
may contain Hg?

What are some advantages of low pressure sodium lamp luminescent lighting?
very efficiency
lots of light over wide area
long life

What are some disadvantages of low pressure sodium lamp luminescent lighting?
non-existent colour discrimination = worst for this!

How does LED luminescent lighting work?
solid state w/ chemical chip embedded in plastic capsule = apply voltage = creates tons of light

What are some advantages of LED luminescent lighting?
most efficient
extremely long-lasting
starts to dim when it wears out = know when to replace it

What are some disadvantages of LED luminescent lighting?
cost
dimmer
some colour degeneration
peak spectral transmission in blue light = potential retinal damage

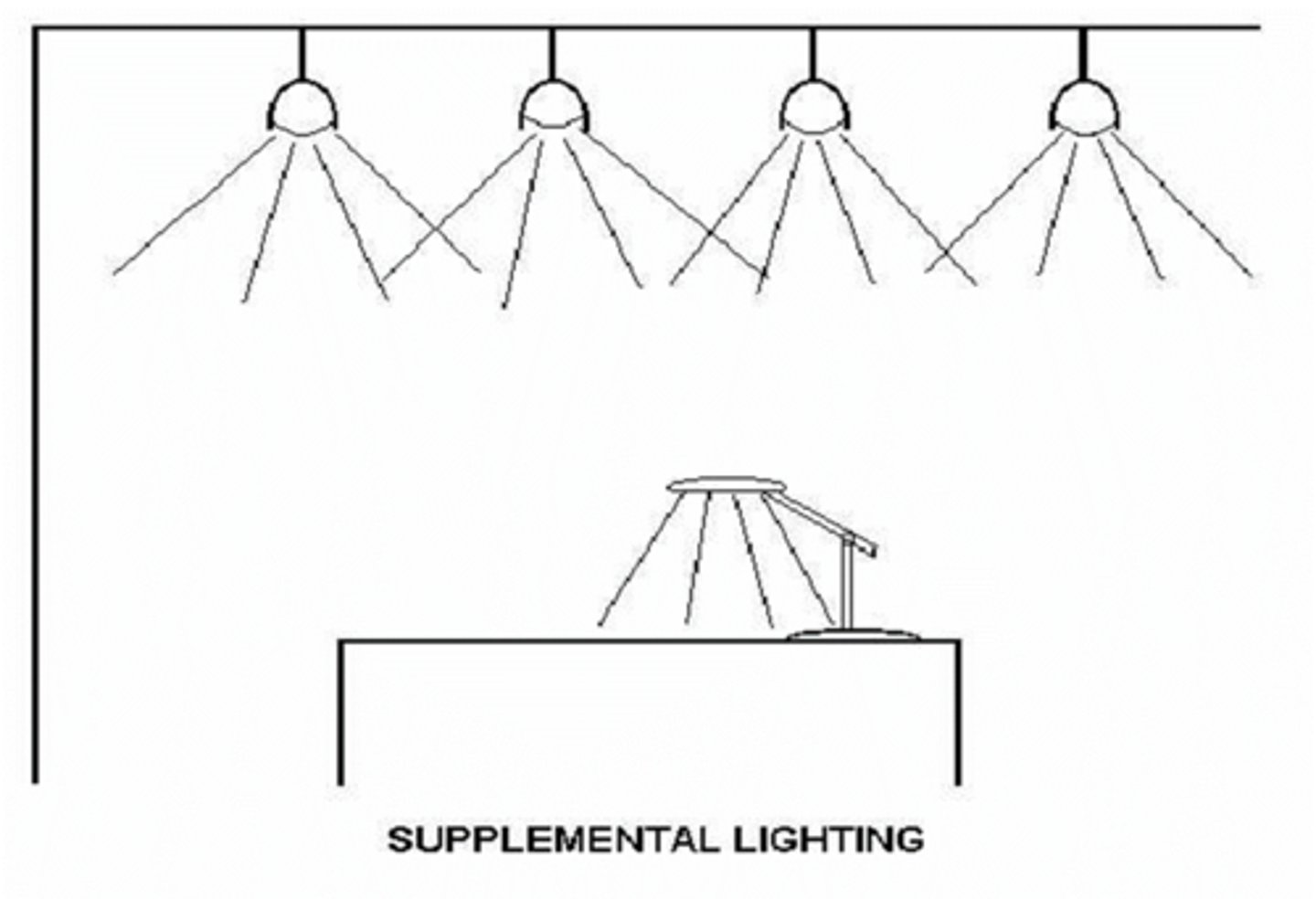
What is general vs supplemental lighting?
general = lateral, diffuse room lighting
supplemental = additional focused lighting
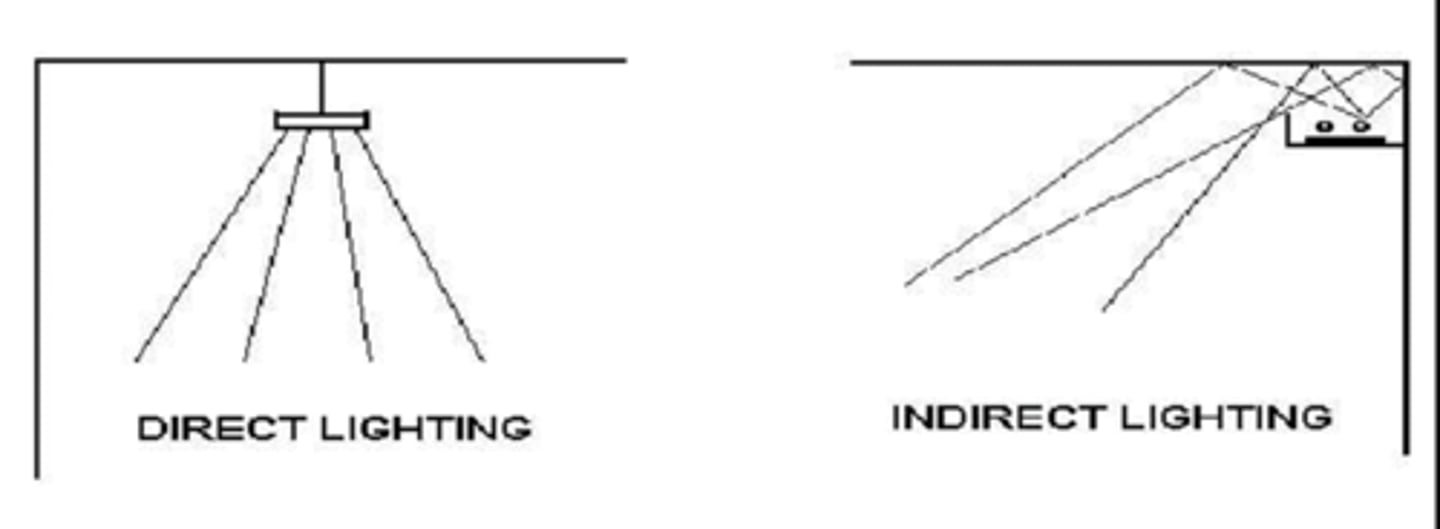
What is direct vs indirect general lighting?
direct = right from luminaire onto final surface = most efficient BUT shadows, reflections common
indirect = bounces off something before reaching final surface = minimal shadows, reflections BUT less efficient
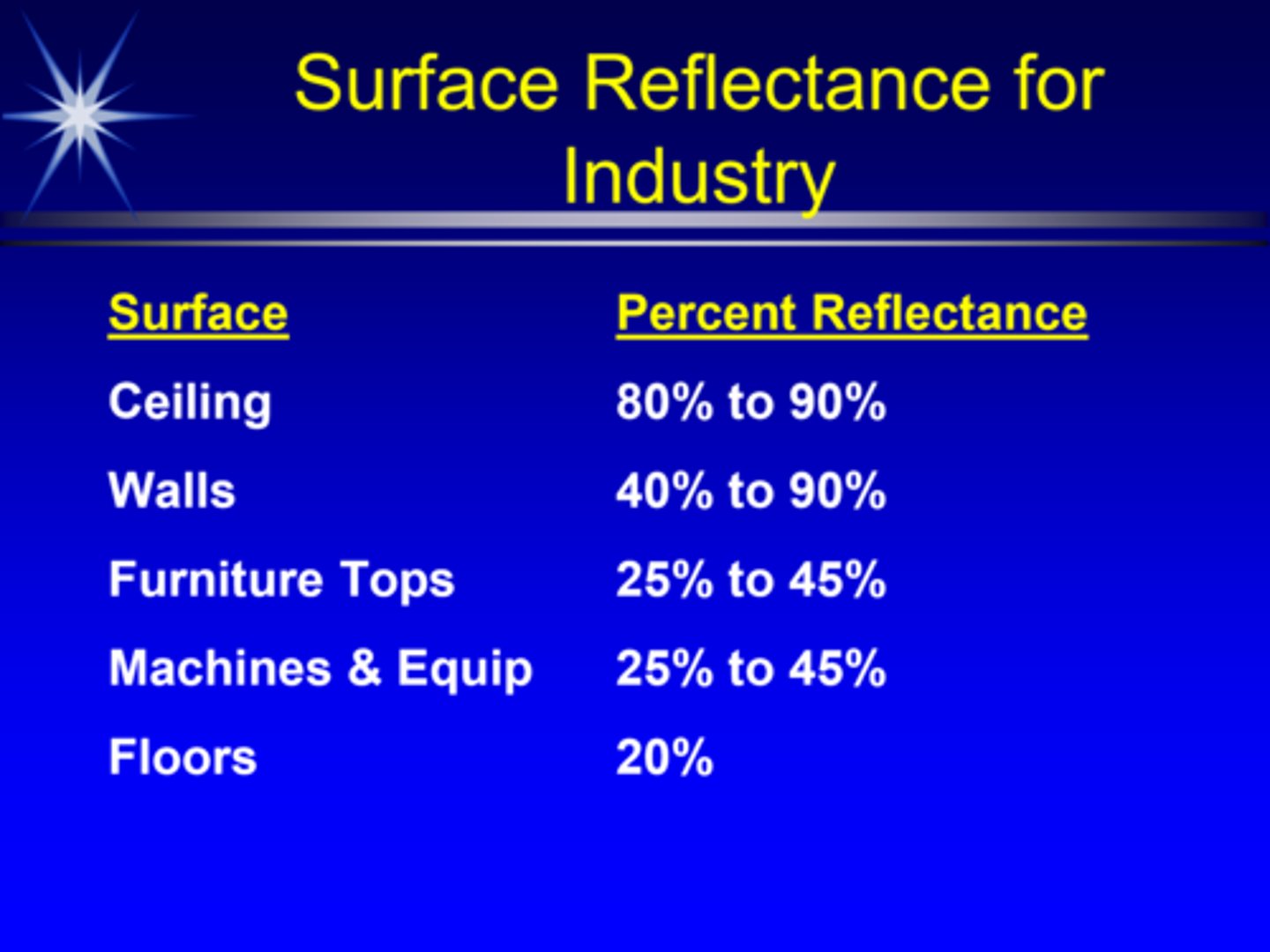
Which surface in a room has the highest reflectance?
ceiling
walls
furniture tops
machines
floors
What determines the best illumination level for a given task?
IESNA (Illuminating Engineering Society of North America) based on...
1. task characteristics
2. criticality of task
3. age of user
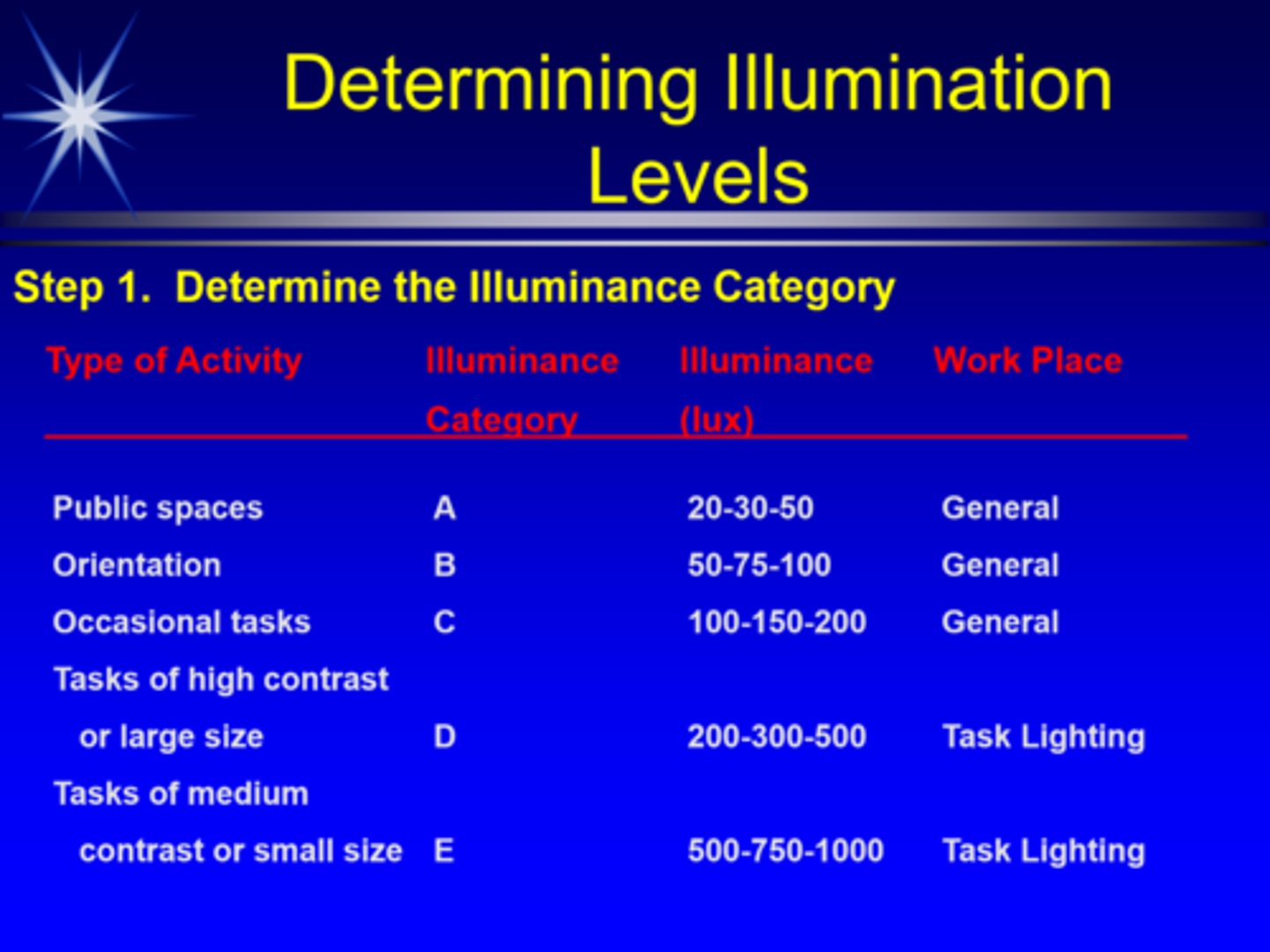
What is object colour?
perceived or spectral colour of an object based on it's reflecting characteristics in combination with the characteristics of the illuminating source
What is colour rendering?
how natural/normal will a light source make something appear
What is the colour rending index (CRI)?
scale of 1 to 100 of how true a light source will make something look, NOT about the average colour itself
Which light type has a CRI of 100?
incandescent
Which light type has a CRI of 0?
low pressure sodium lamps
What is the ideal CRI for indoor lighting?
80-85 = achieve by fluorescent
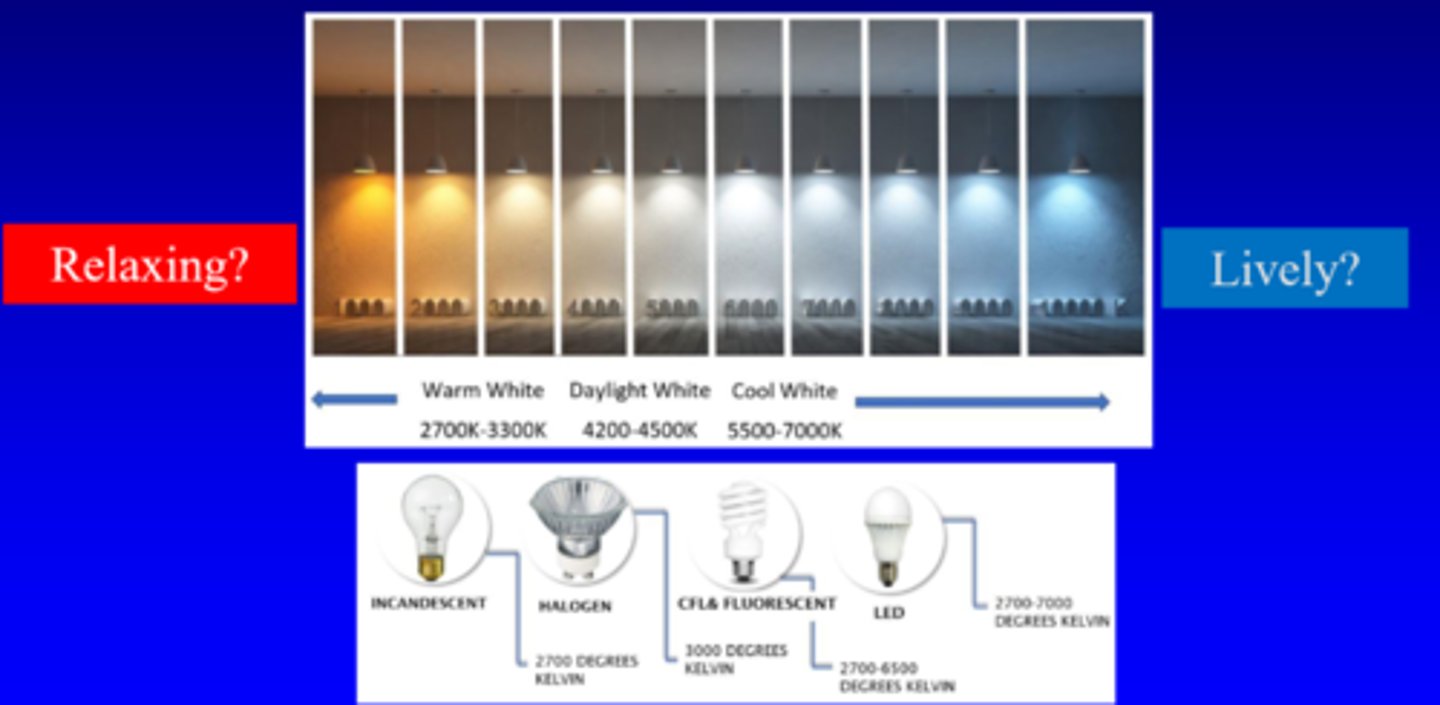
What is colour temperature vs correlated colour temperature (CCT)?
colour temp = matches light source exactly
correlated colour temp = measure of light's colour when light is illuminated = = correlates to spectral output of blackbody radiator = more of an estimate
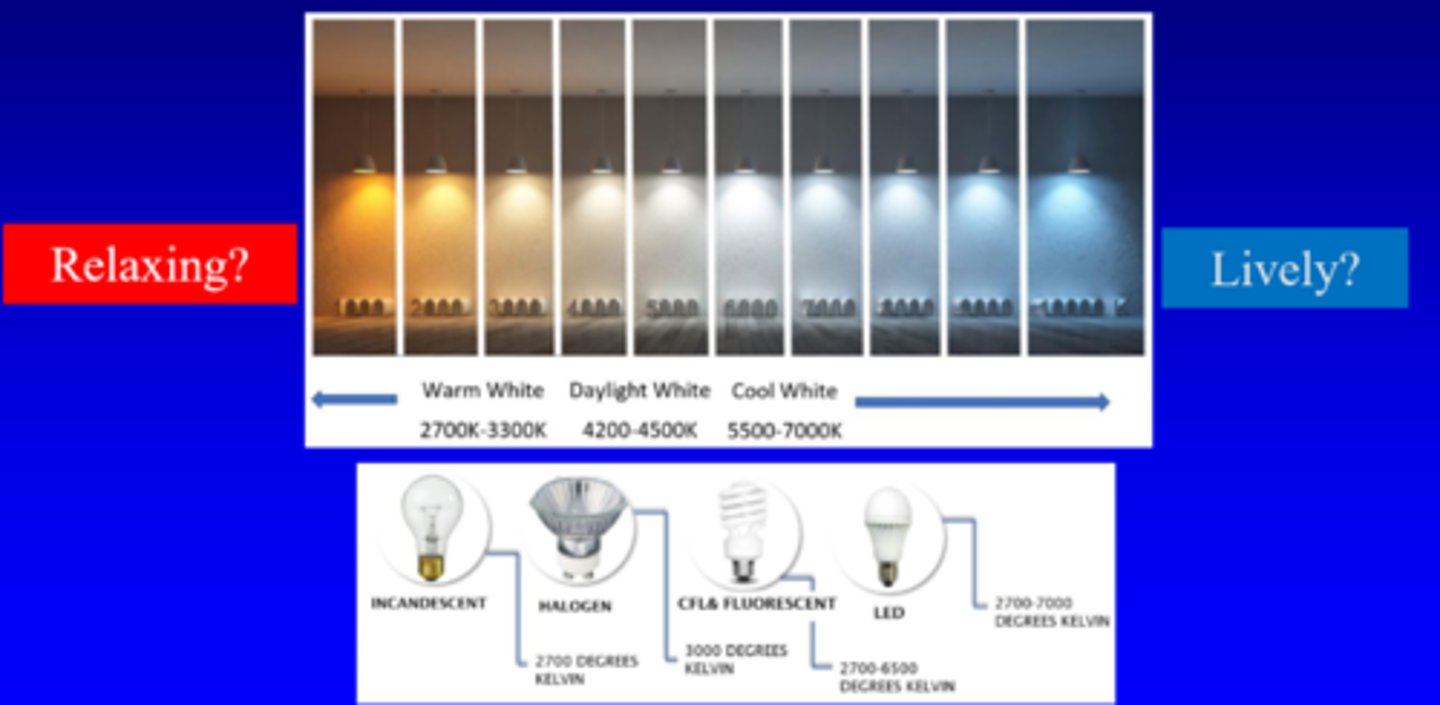
How does low vs high CCT look?
low CCT = 2000K = longer wavelengths = redder
high CCT = 10000K = shorter wavelengths = bluer
What is the spectral distribution of daylight?
uniform
What is the CCT and spectral distribution of an incandescent light?
redder

What is the CCT and spectral distribution of a fluorescent light?
slight red bias w/ slight blue peak too
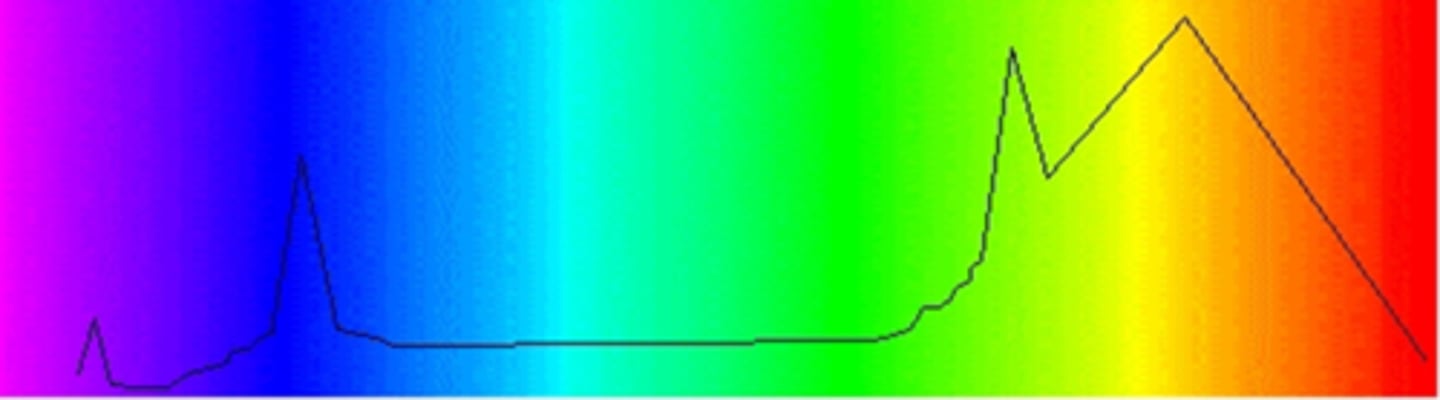
What is the CCT and spectral distribution of a high intensity discharge lamp light?
terrible colour rendering
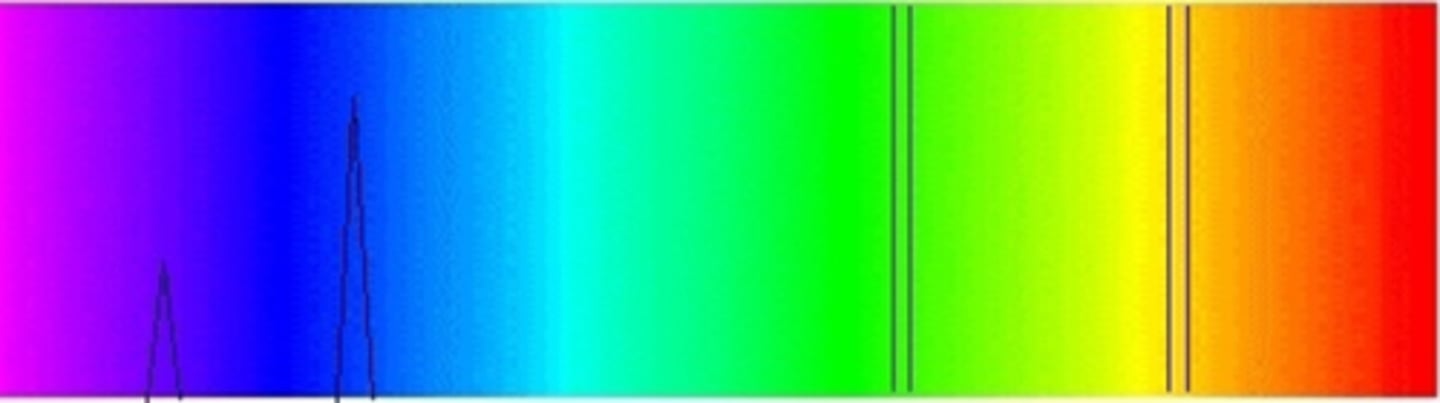
What is the CCT and spectral distribution of a low pressure sodium lamp light?
terrible colour rendering
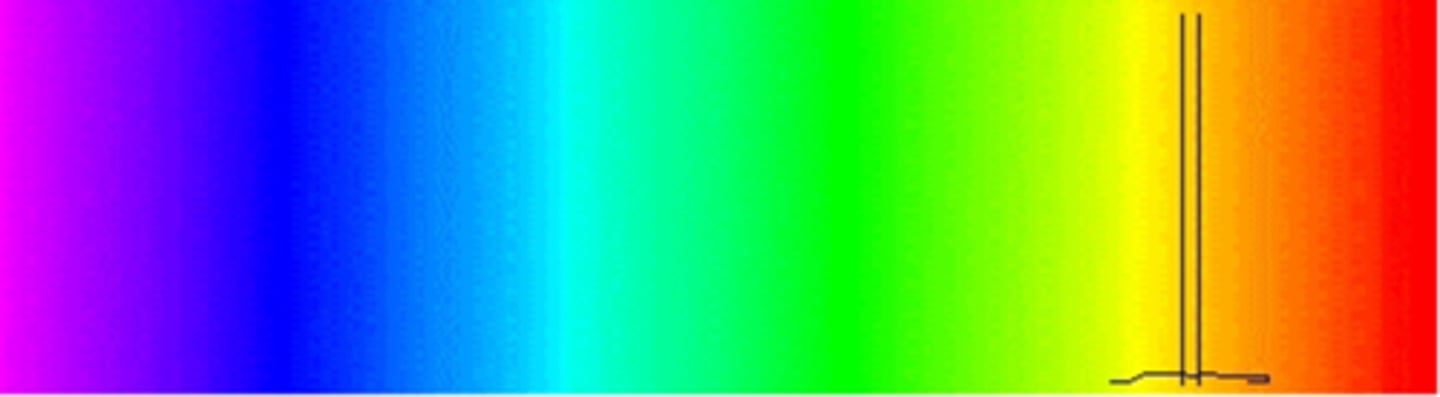
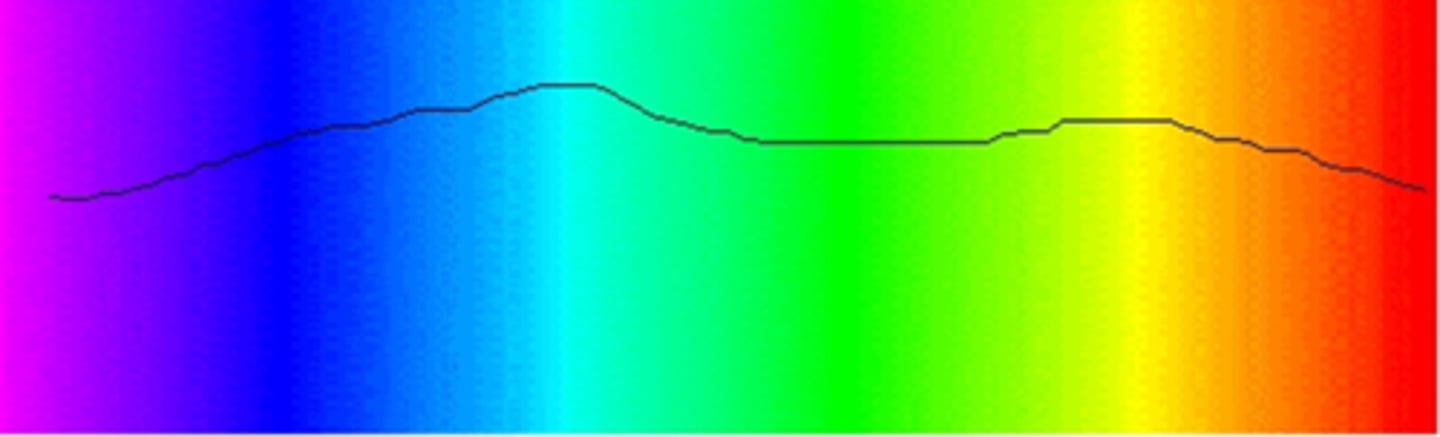
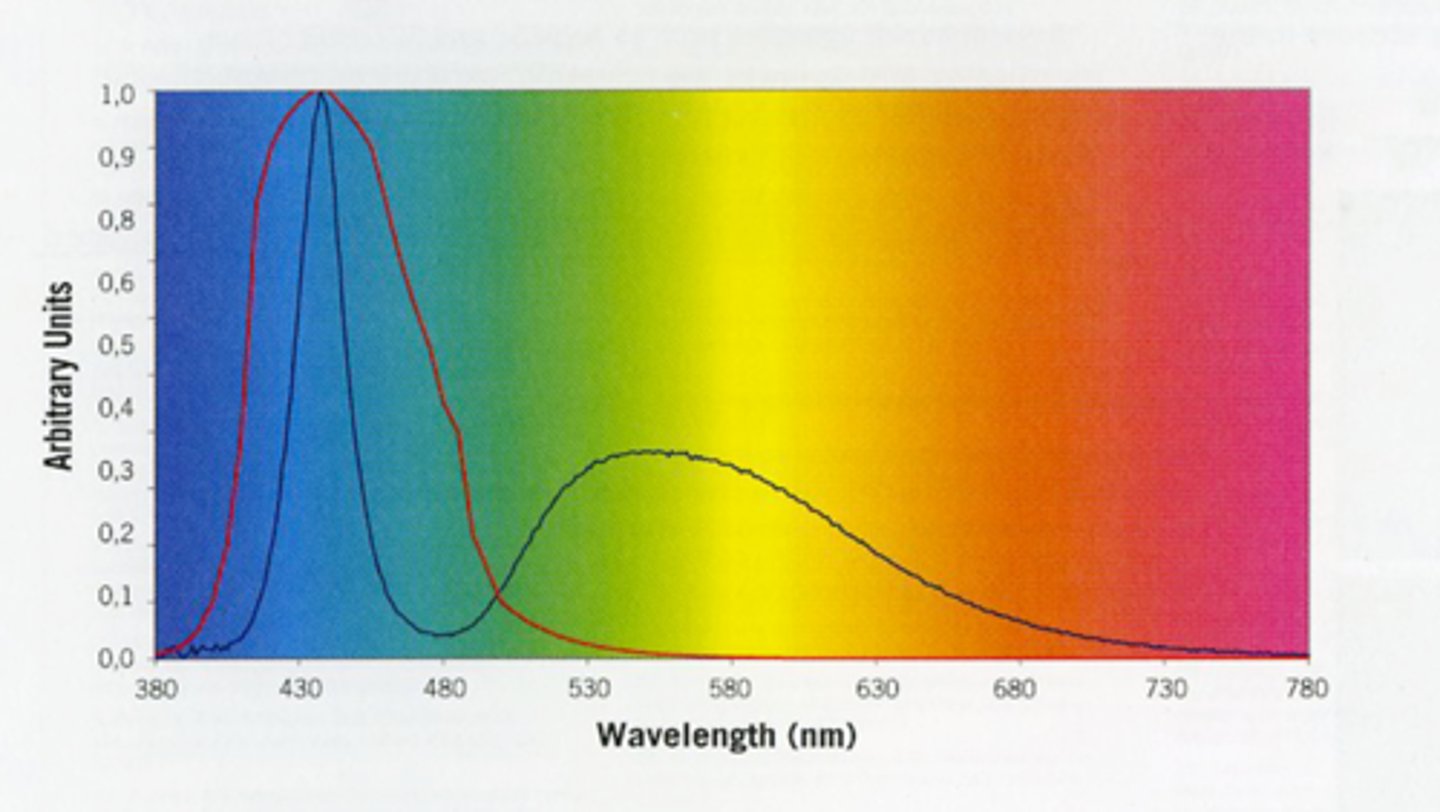
What is the CCT and spectral distribution of a LED light? What does each line represent here?
bluer
red line = light responsible for retinal damage
black line = light coming from LED (phosphor is second hump)
What are the 3 standard illuminants?
A = average incandescent light
B = direct sunlight at noon
C = average daylight
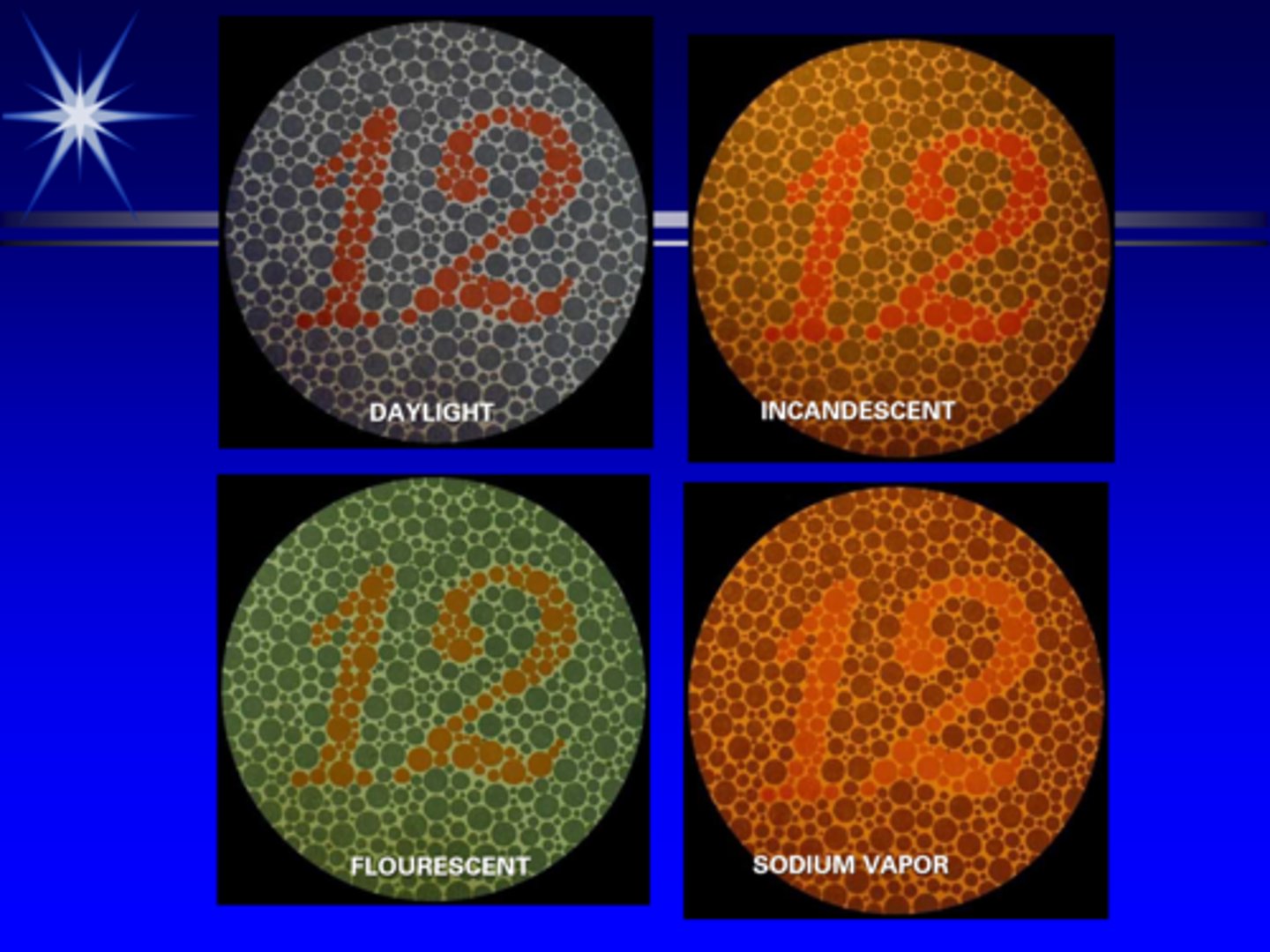

Which standard illuminant should be used during colour testing?
standard illuminant C = daylight = Macbeth lamp is closest
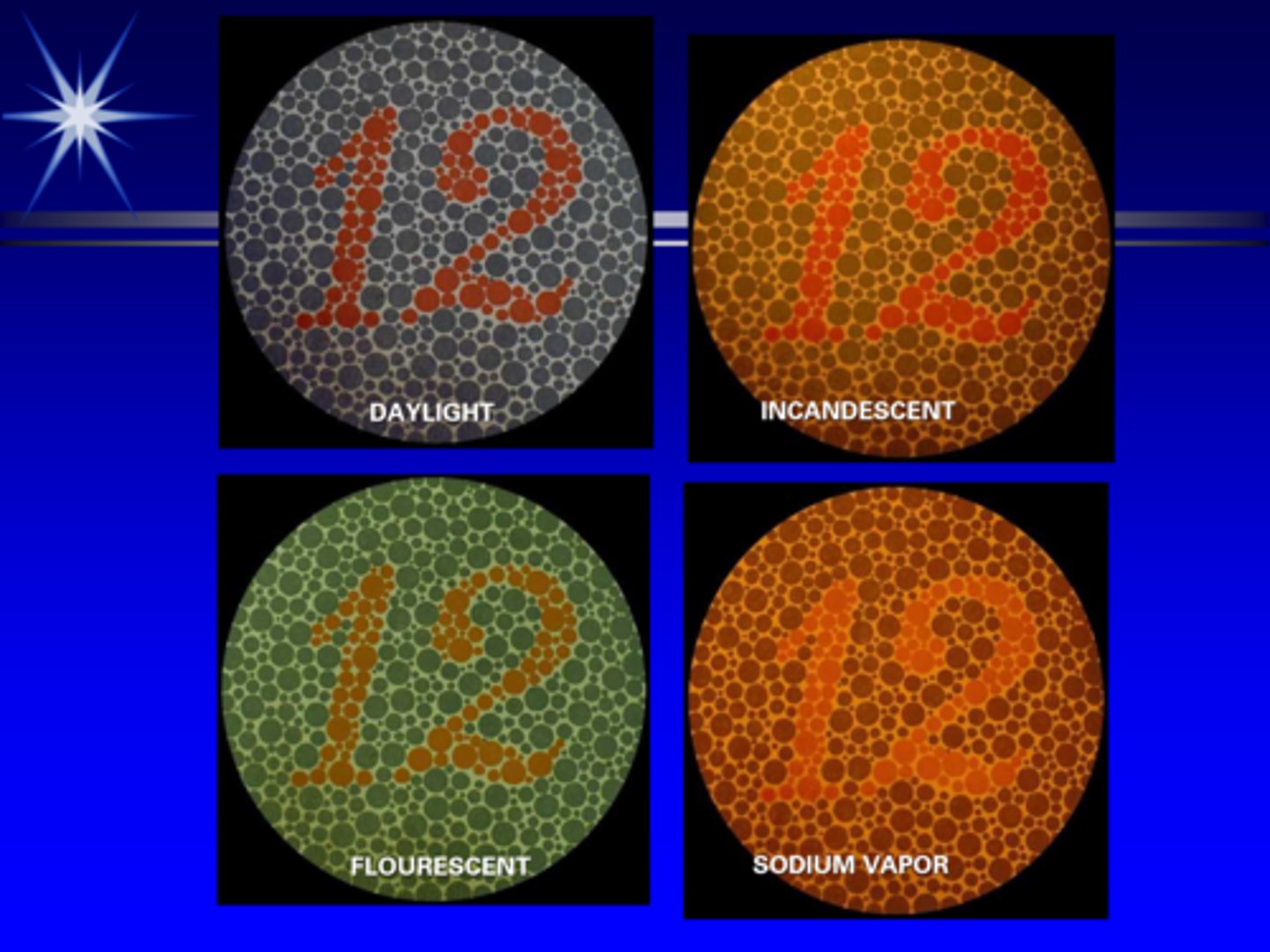

What does disability glare cause?
objects appear to have lower contrast = increased brightness background, decreases object brightness = reduced resolution
THINK: turning lights on when watching a projector
What does IESNA recommend about the uniformity of illumination?
max and min levels are within 1/6 of the average level

What 2 things can we do to improve uniformity of illumination?
room surface reflectance
closer spaced lights

What is the brightness ratio?
brightness of task in relation to the brightness of surrounding area
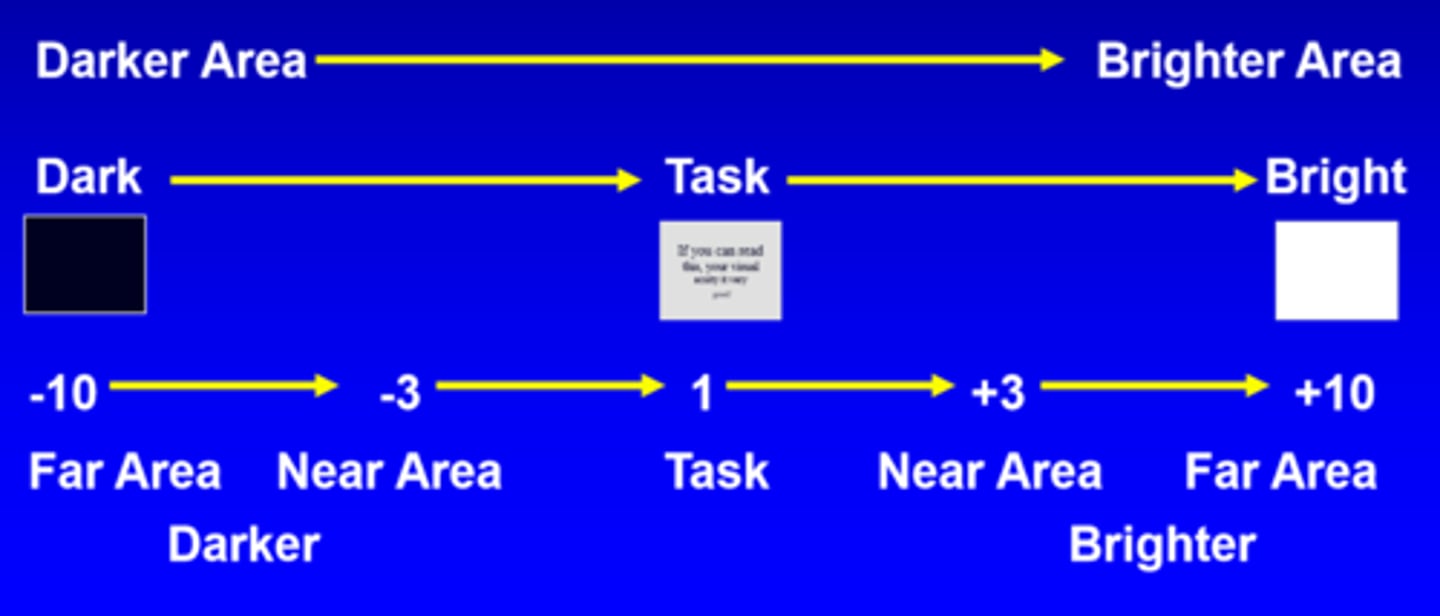
What brightness ratio is good for most near work and tasks?
3:1
or
1:3
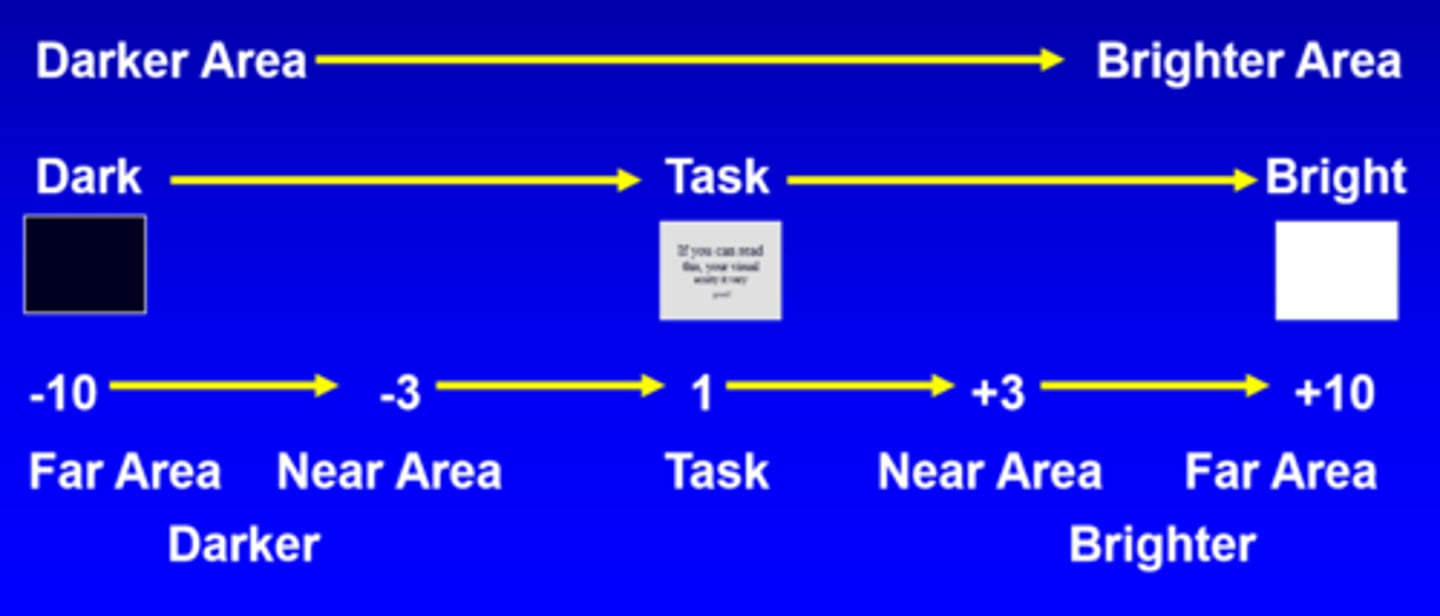
What brightness ratio is good for most distance tasks?
1:10
or
10:1
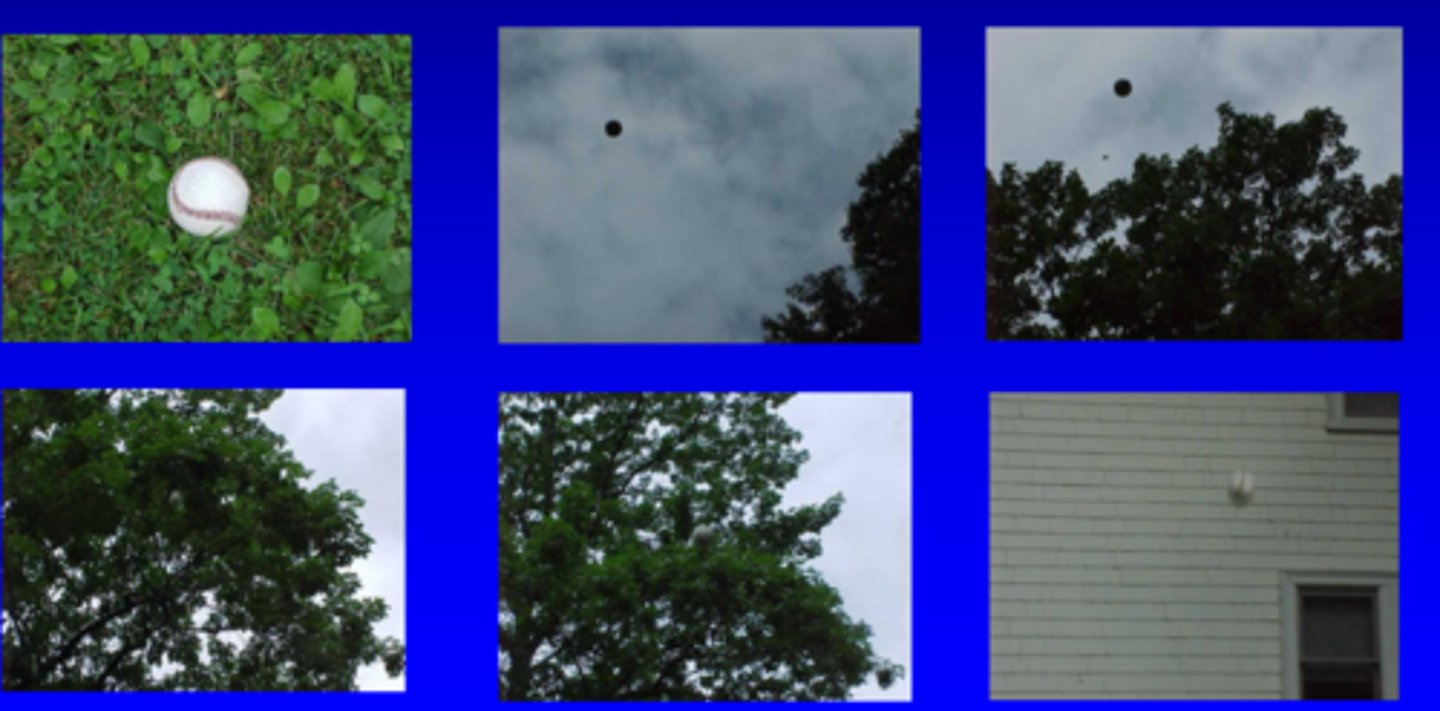

What brightness ratio is good for storage, outdoor activities?
up to 40:1
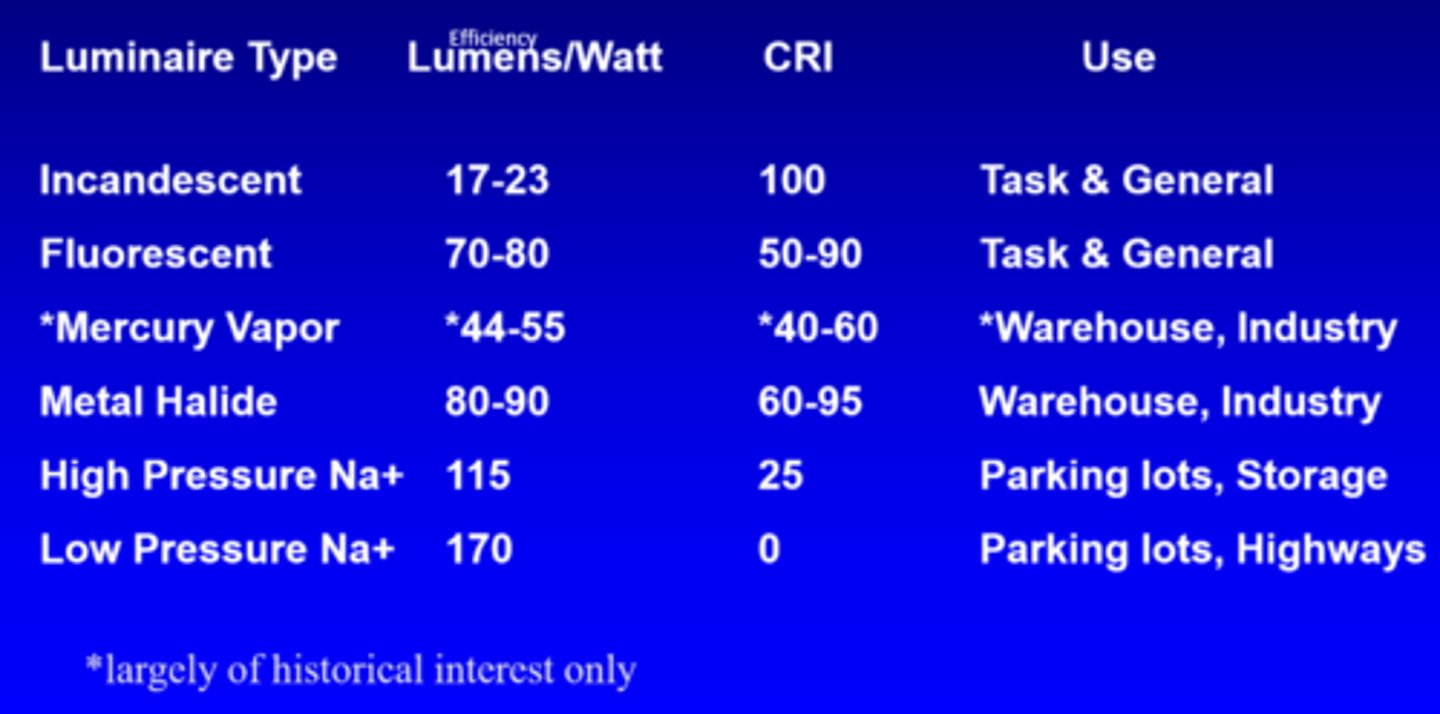
What is the efficiency of incandescent lights?
17-23 lumens/watt
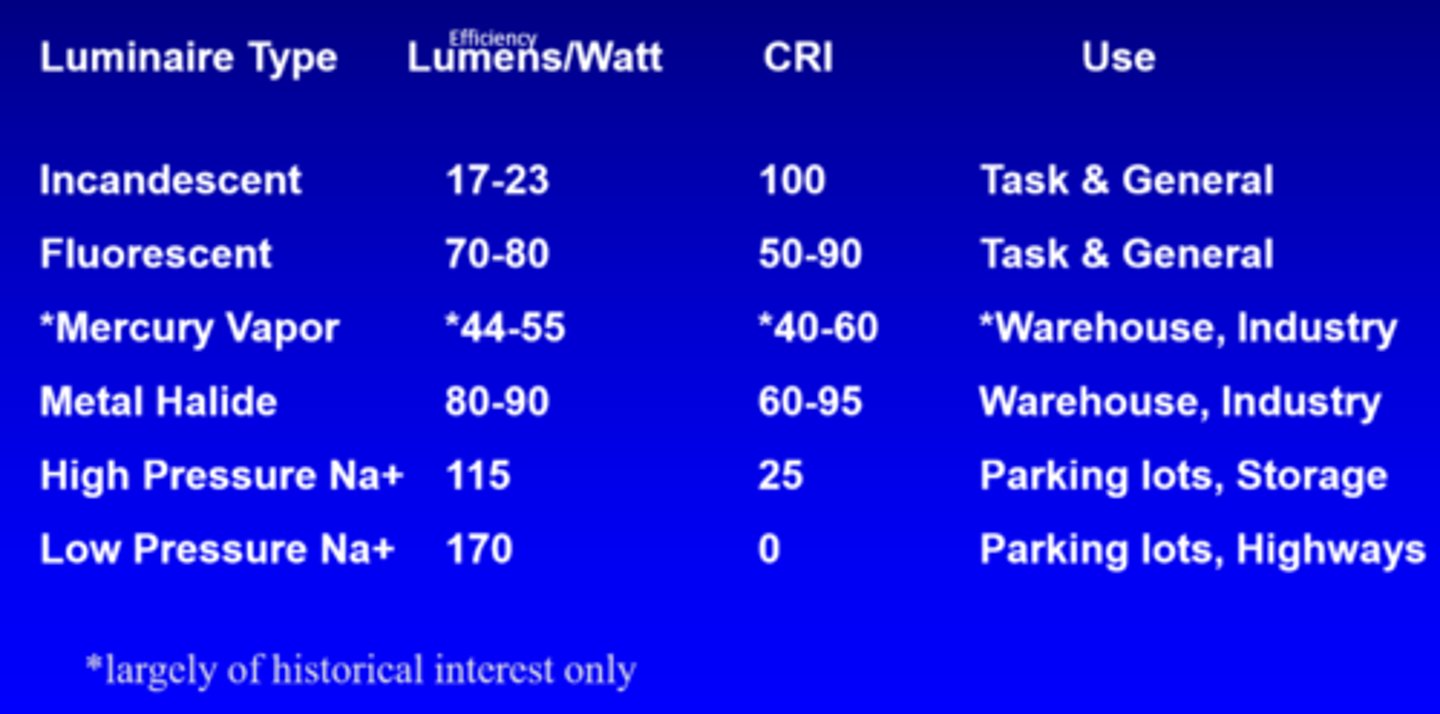
What is the efficiency of fluorescent lights?
70-80 lumens/watt
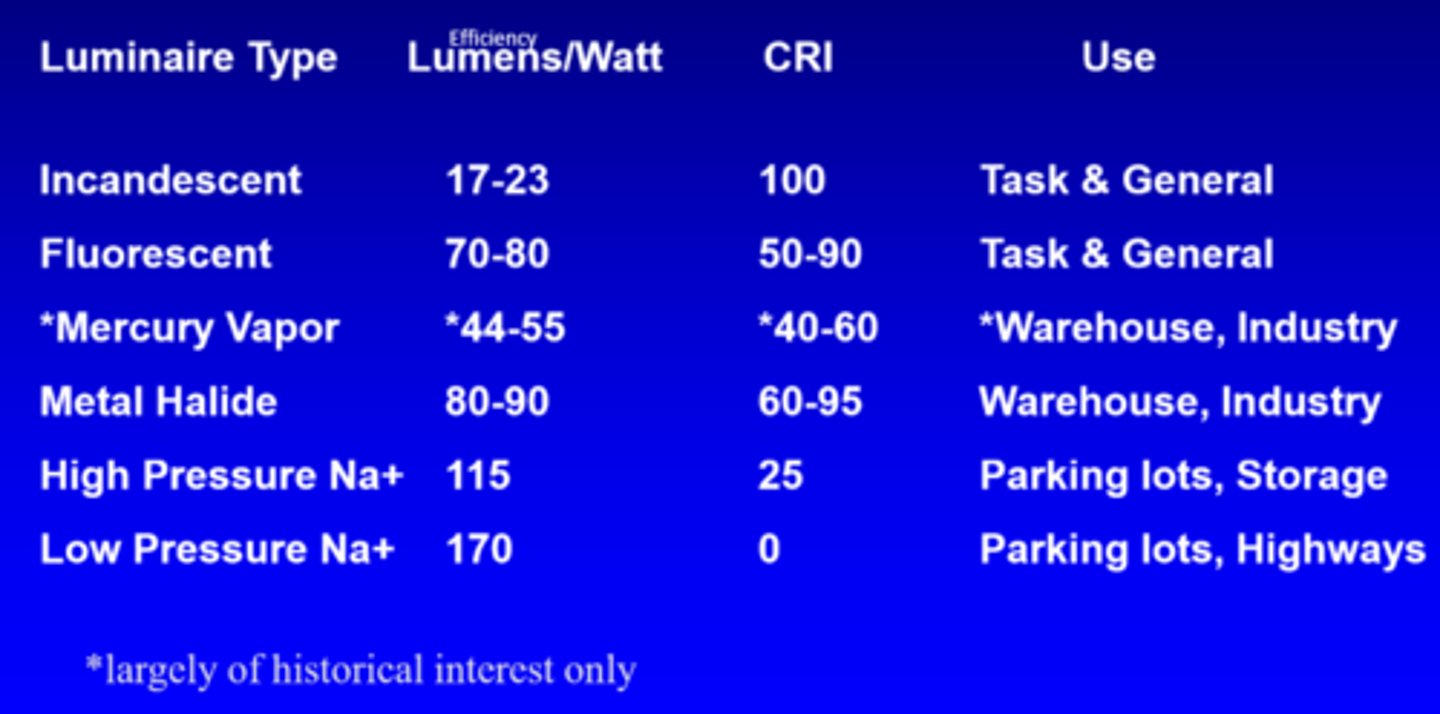
What is the efficiency of mercury vapour lights?
44-55 lumens/watt
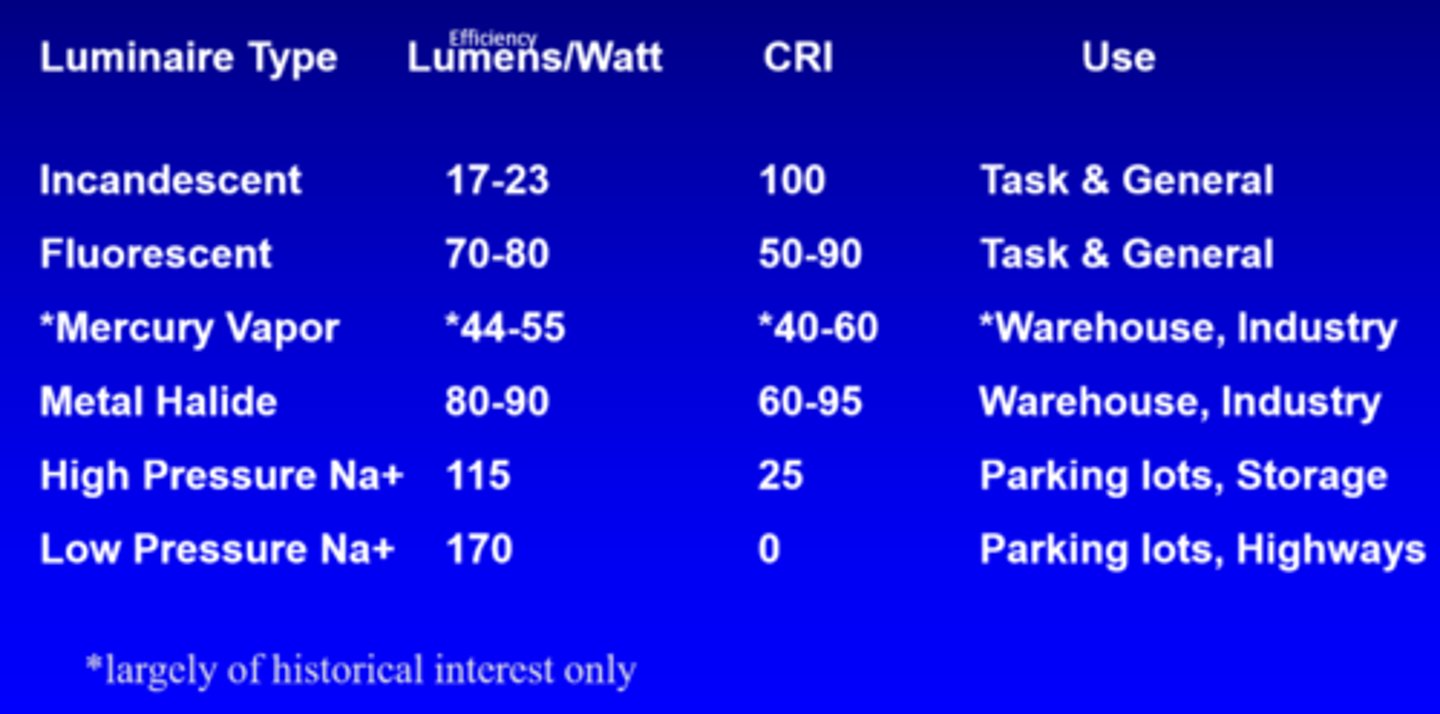
What is the efficiency of metal halide lights?
80-90 lumens/watt
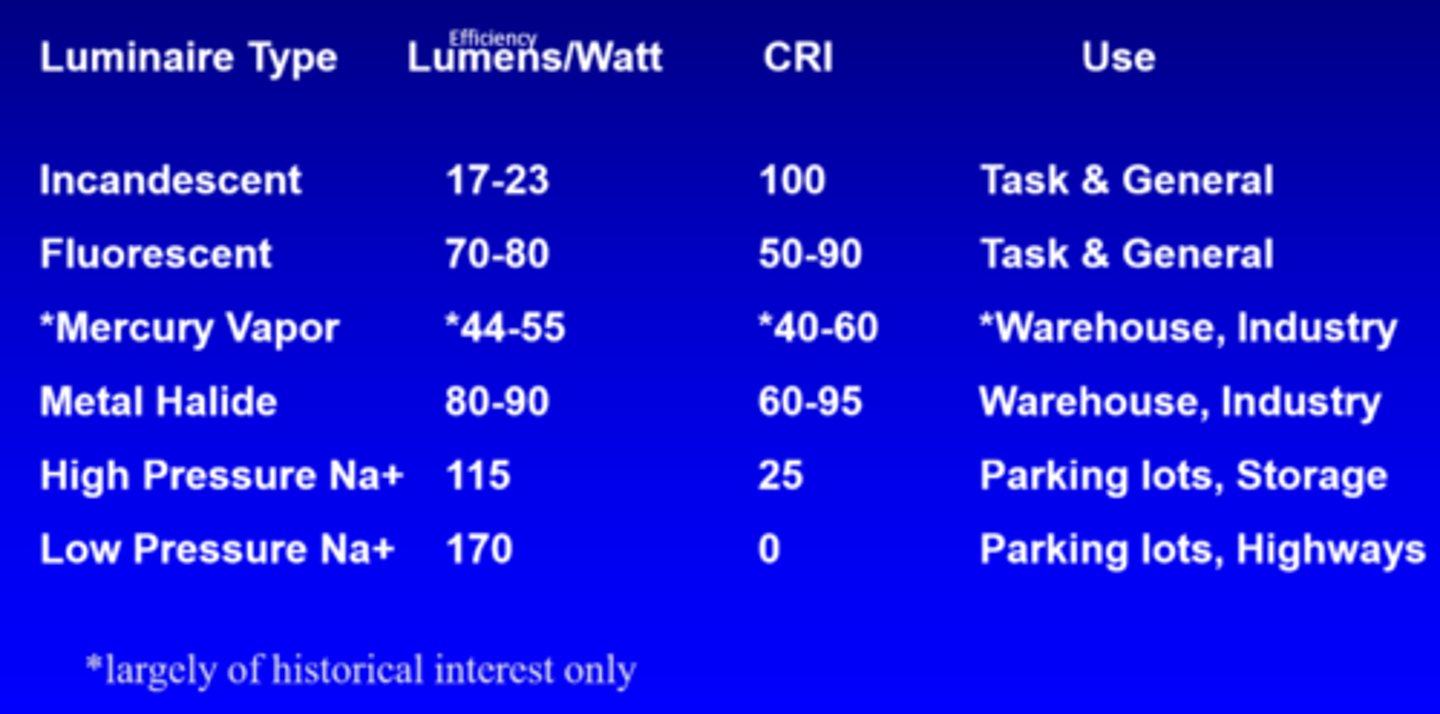
What is the efficiency of high pressure Na+ lights?
115
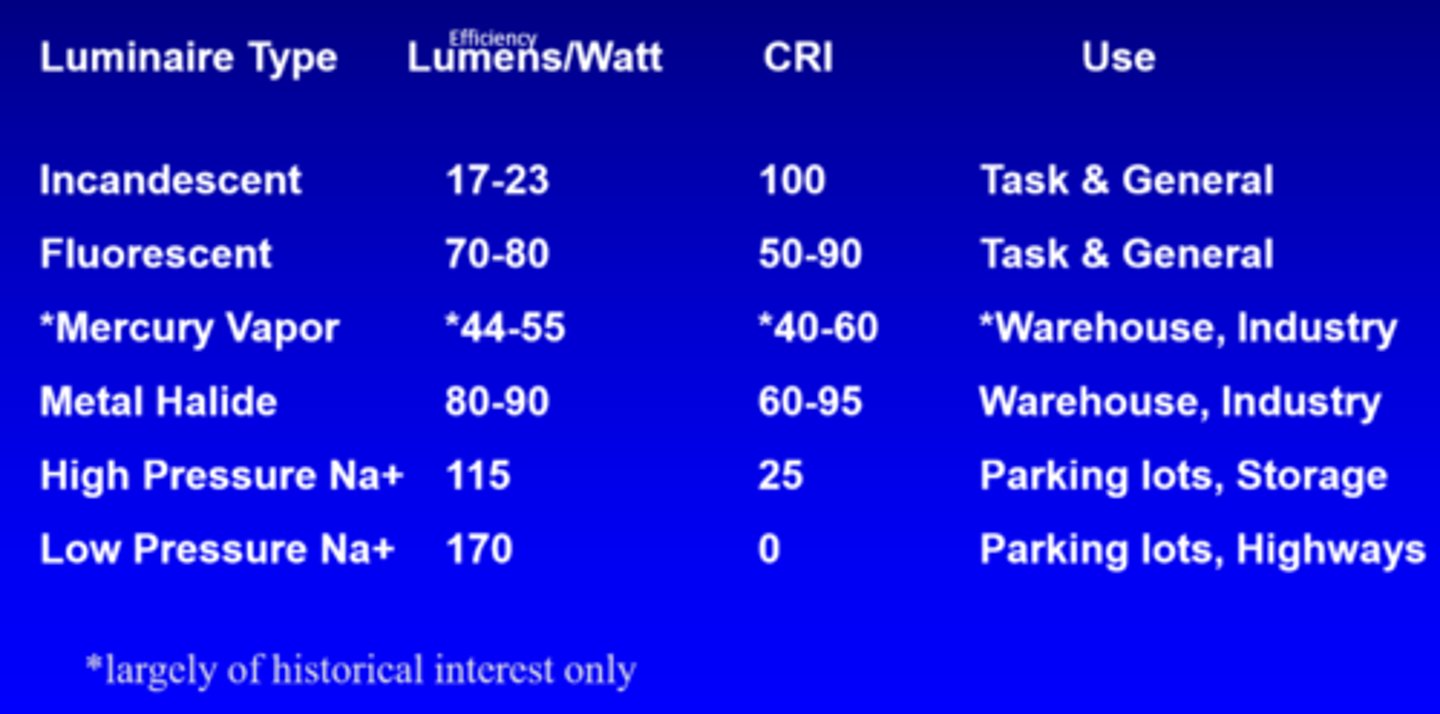
What is the efficiency of low pressure Na+ lights?
170
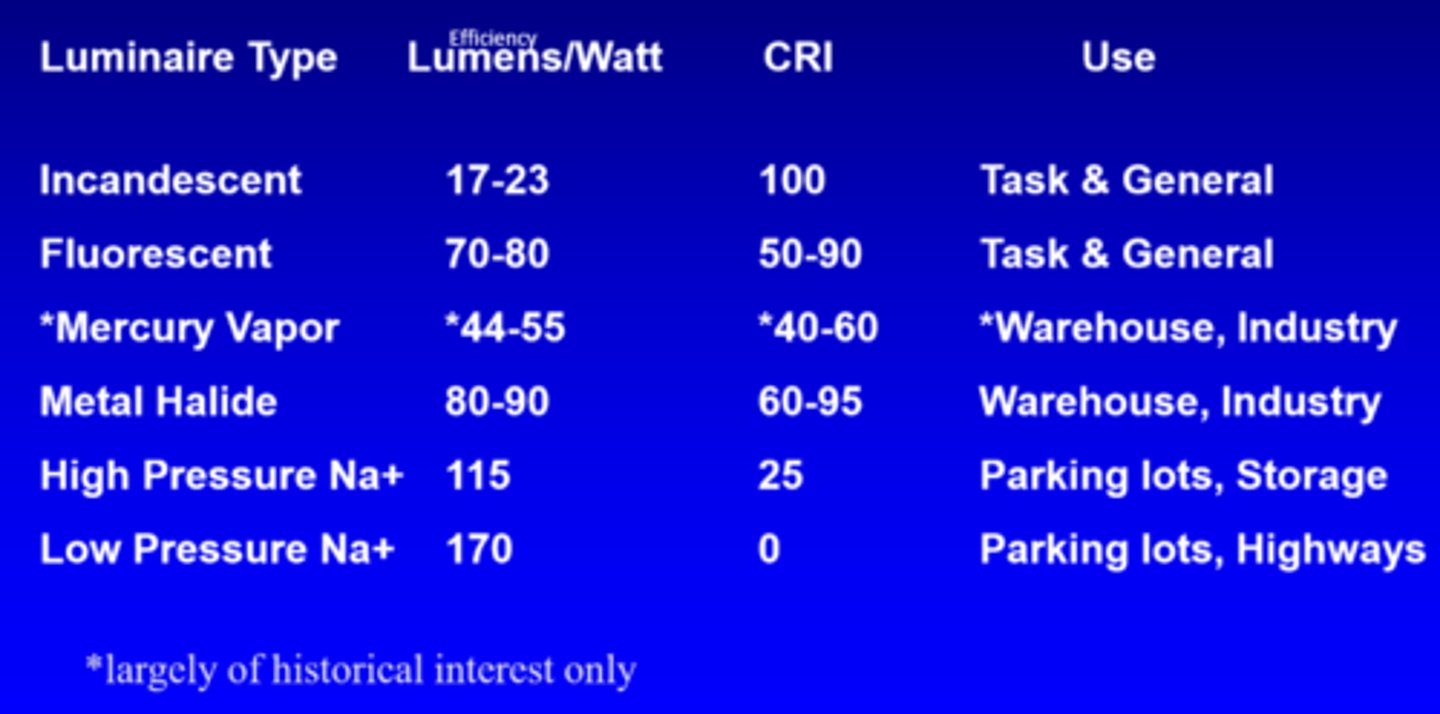
What is the CRI of incandescent lights?
100
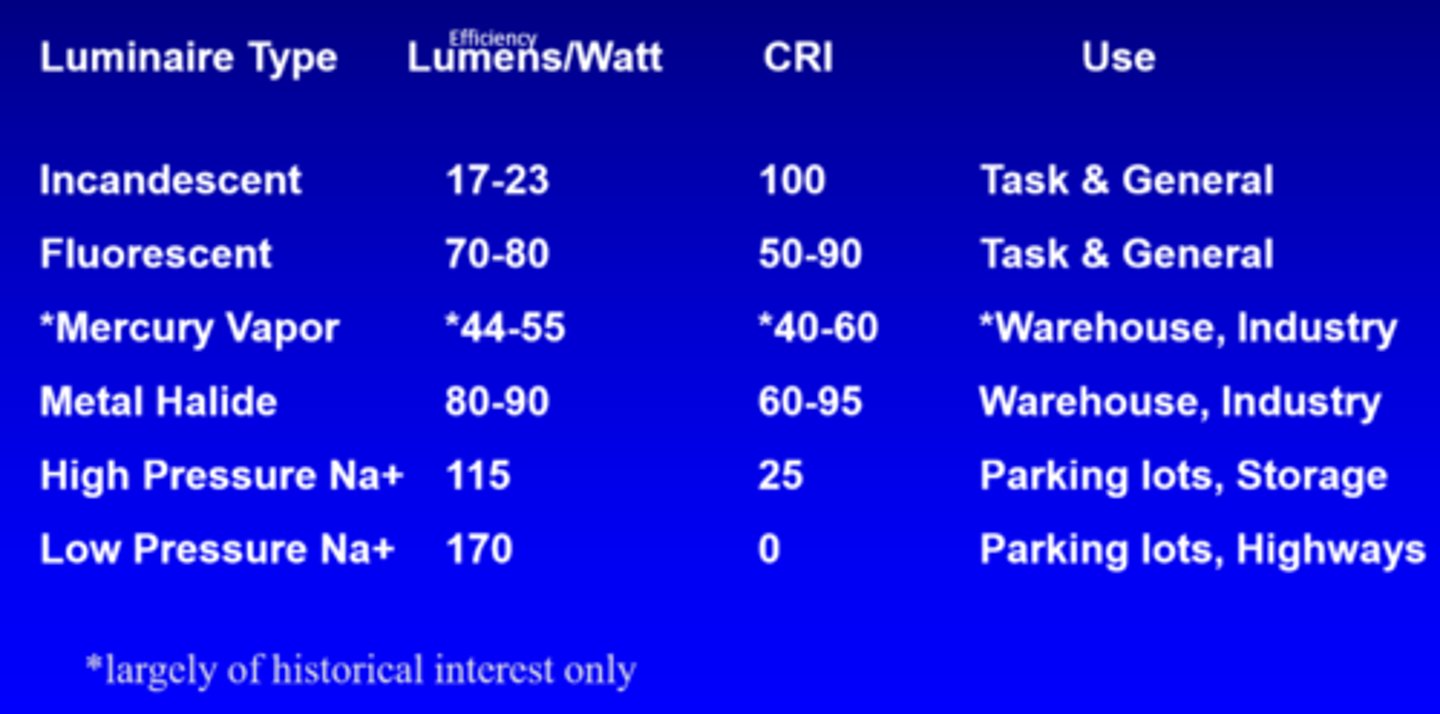
What is the CRI of fluorescent lights?
50-90
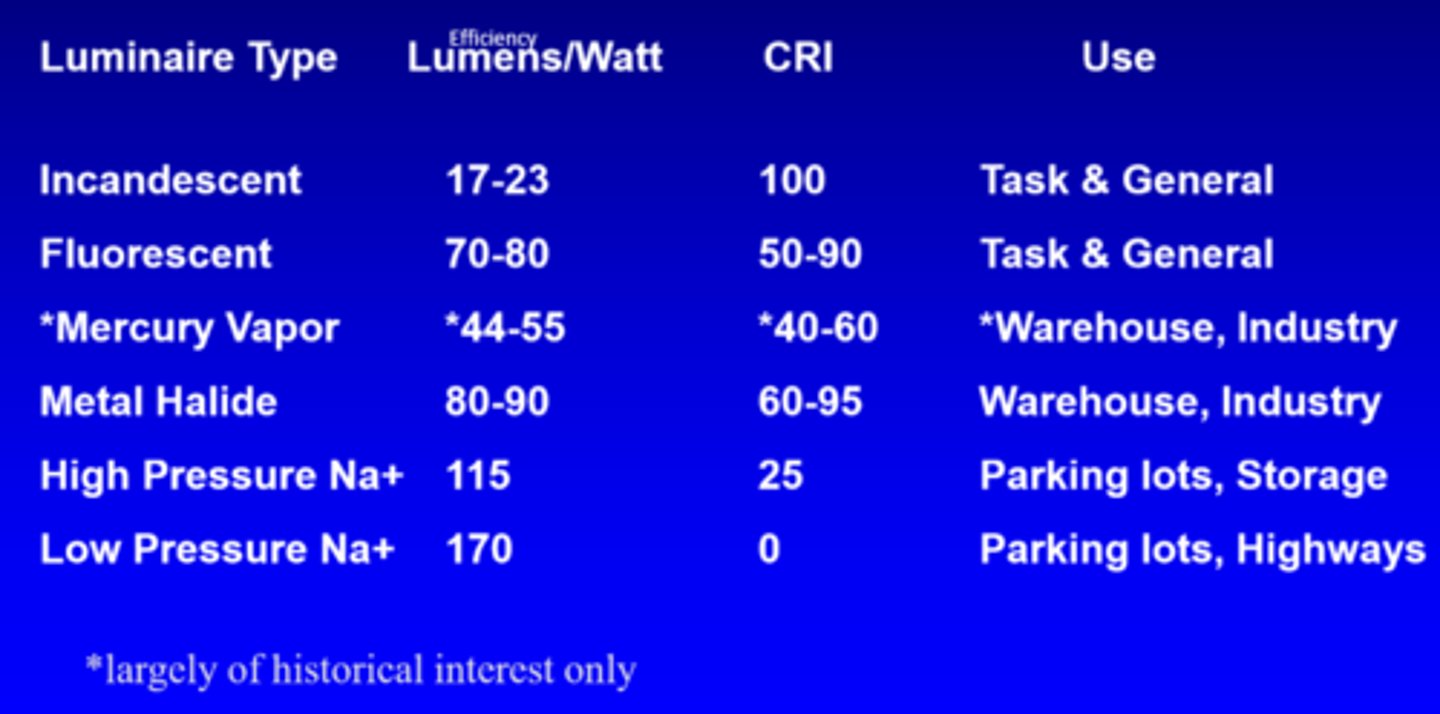
What is the CRI of mercury vapour lights?
40-60
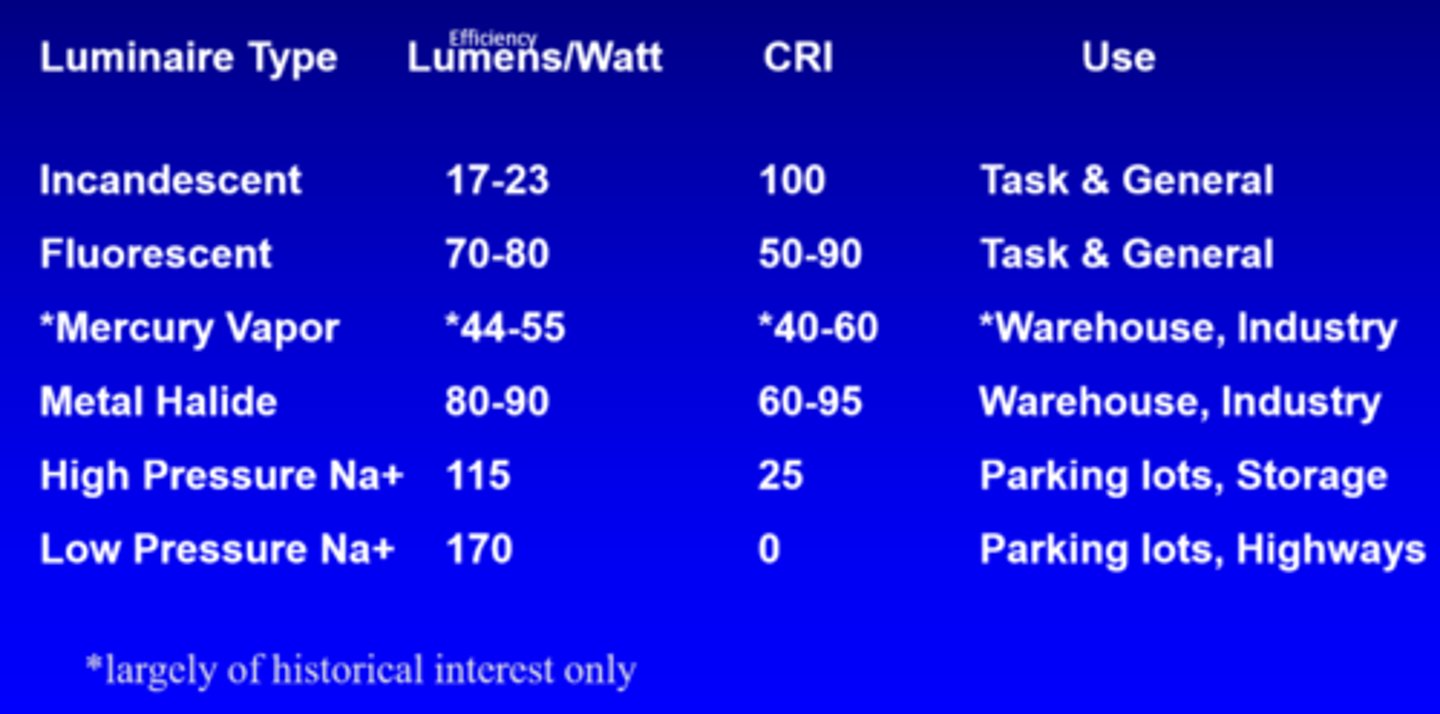
What is the CRI of metal halide lights?
60-95
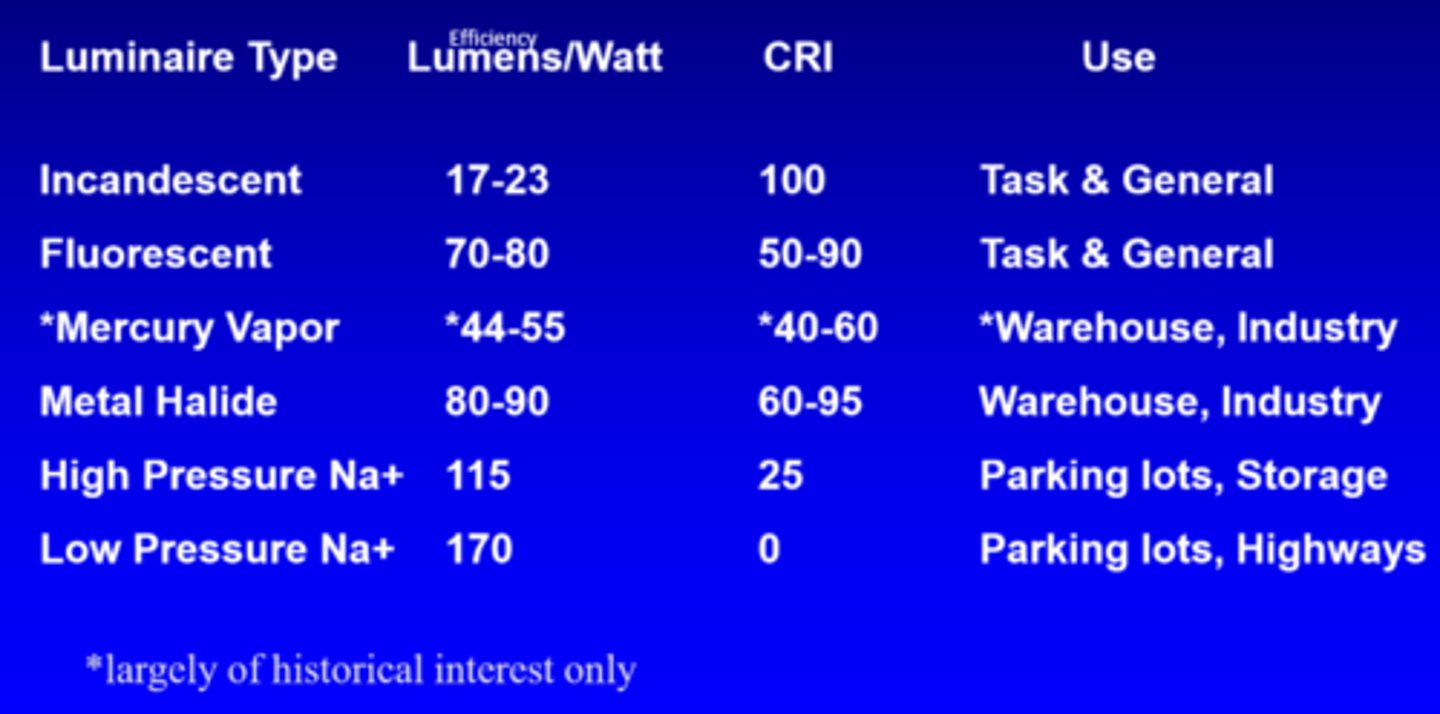
What is the CRI of high pressure Na+ lights?
25
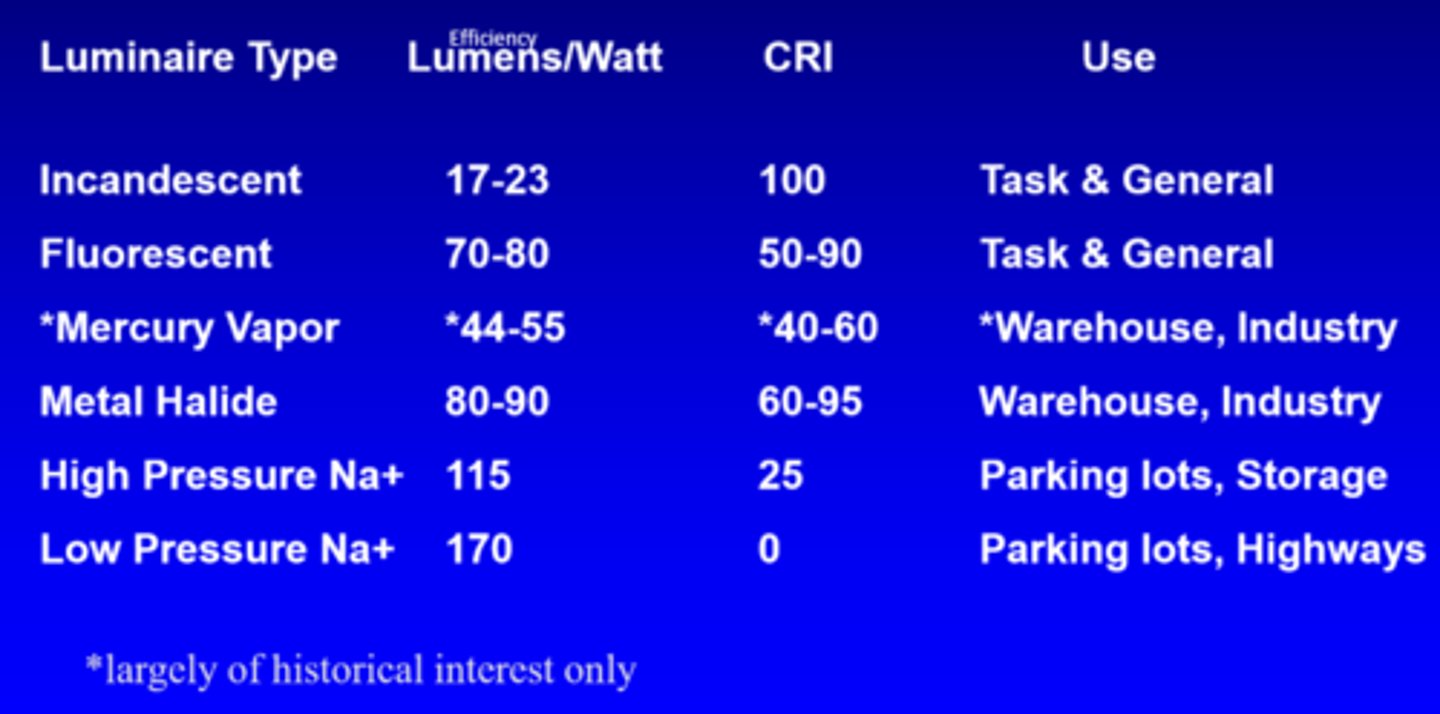
What is the CRI of low pressure Na+ lights?
0
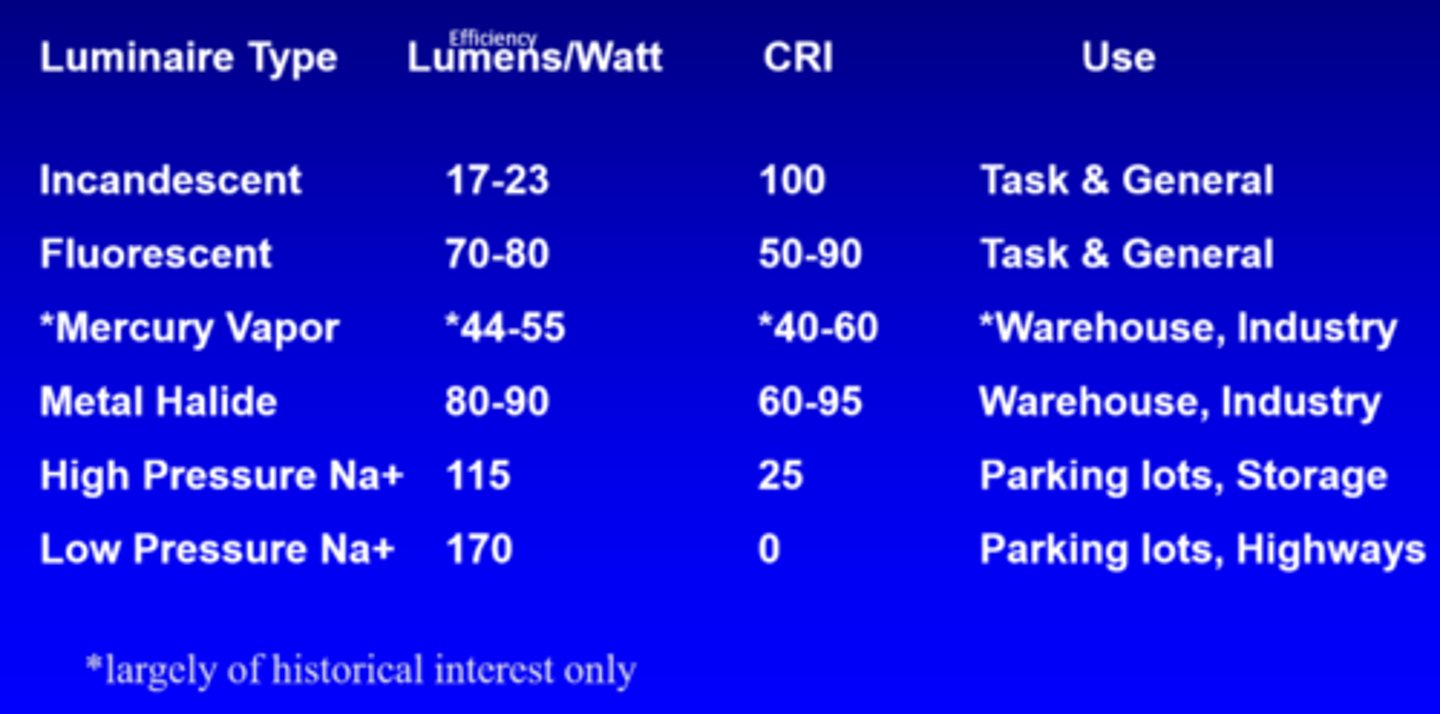
What is the use of incandescent and fluorescent lights?
task, general
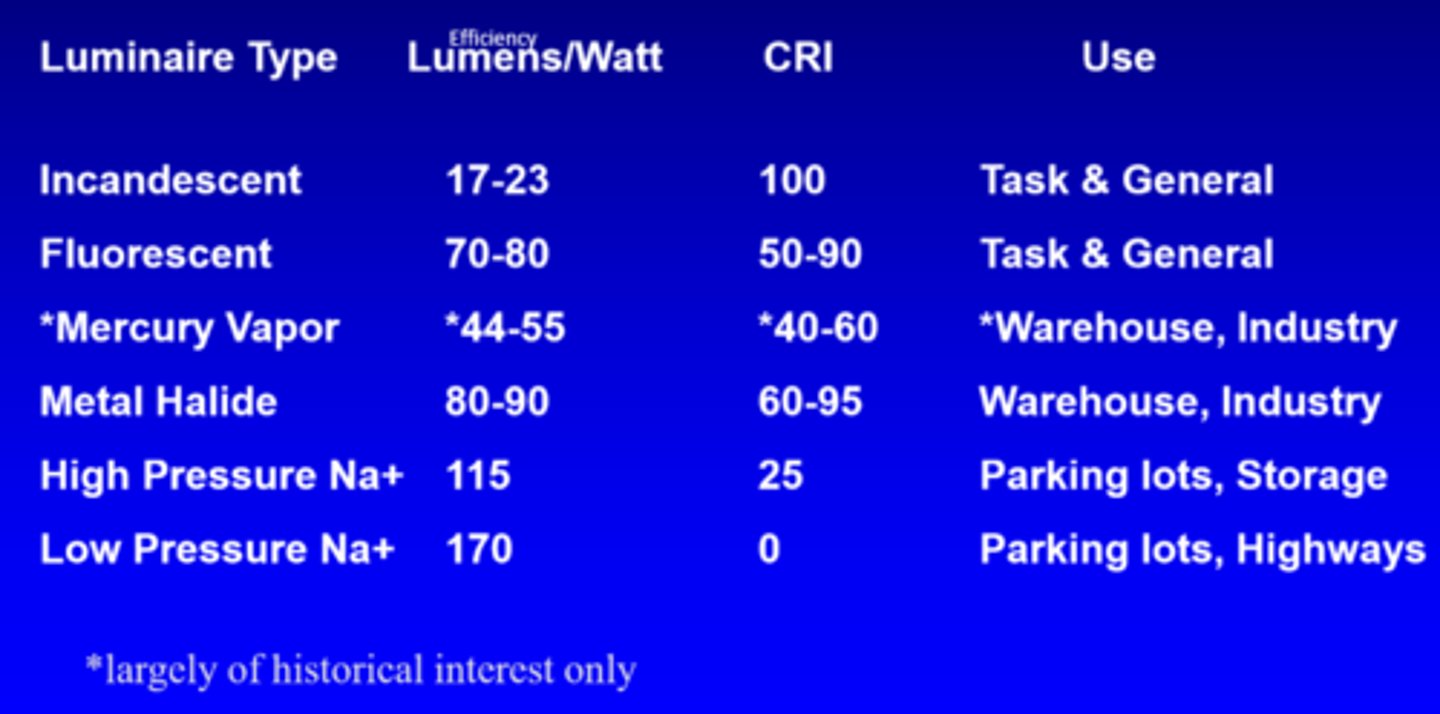
What is the use of mercury vapour and metal halide lights?
warehouse, industry
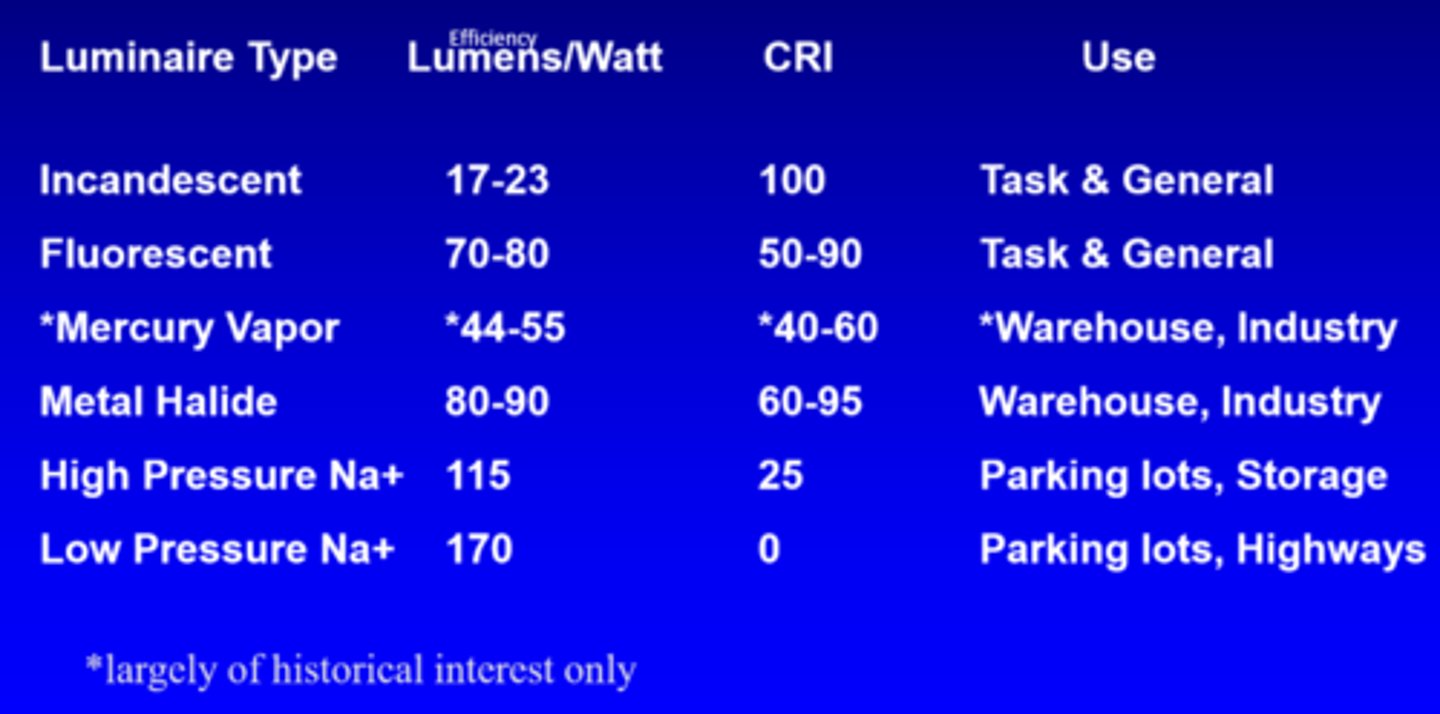
What is the use of high and low pressure Na+ lights?
parking lots, storage, highways