ch.15 Organs of the digestive system.
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards focusing on key concepts of the digestive system anatomy and functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are the main organs of the digestive system?
Parotid gland, submandibular gland, esophagus, mouth, pharynx, liver, stomach, pancreas, duodenum, colon, jejunum, ileum, rectum, appendix, anal canal.
What is the gastrointestinal (GI) tract?
A long tube that is open at both ends for the transit of food, including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum.
These structures are all part of the _______ canal.
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Anal canal
Alimentary
What are accessory structures in the digestive system?
Structures that are not part of the GI tract but contribute to food processing, including teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
What are the six basic processes involved in digestion?
Ingestion, secretion, motility, digestion, absorption, and defecation.
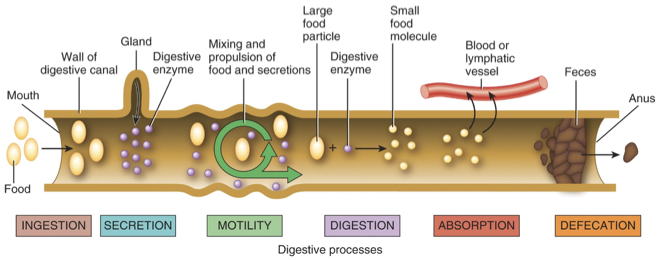
What layers are found in the GI tract?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, and serosa.
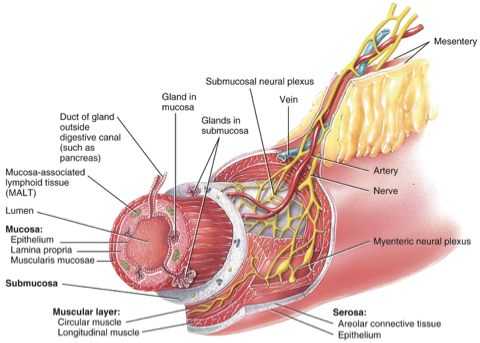
What is the role of the enteric nervous system in digestion?
It includes the submucosal plexus and myenteric plexus that regulate GI secretion and motility.
What is the purpose of the GI reflex pathways?
To regulate GI secretion and motility in response to stimuli within the GI tract.
What does Retroperitoneal mean?
Organs such as the pancreas and kidneys that lie posterior to the peritoneal membranes.
What is the peritoneum?
The peritoneum is the largest serous membrane in the body that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the abdominal organs. Composed of 2 membranes and a cavity between.
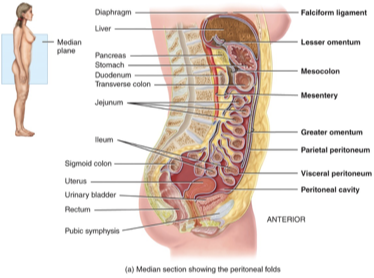
The Greater Omentum (fatty apron)
is a large fold of peritoneum extending from the stomach to cover the intestines, providing cushioning and supporting immune functions.
Lesser Omentum
two folds that suspend the stomach and duodenum from the liver
What is the Mesentary?
It is a fan-shaped tissue that connects the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall and helps hold them in place while supplying them with blood.
Mesocolon
Binds large intestine to the posterior abdominal wall; carries blood and lymph vessels to the intestines.
Parasympathetic innervation of the digestive system
part of the autonomic nervous system- it stimulates digestive processes, such as increasing movement of food through your digestive tract + secretion & absorption.
Sympathetic innervation of the digestive system
digestion slows down
The plexuses (enteric nervous system)
known as the "second brain," it controls digestive functions independently of the central nervous system, coordinating actions such as peristalsis and secretion.
The mouth
It is formed by the cheeks, hard and soft palates and tongue

The Salivary glands
They secrete saliva to the oral cavity. Saliva softens, moistens, and lubricates food, as well as containing enzymes like salivary amylase. (chemical digestion)
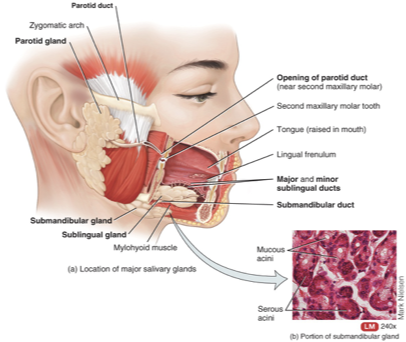
The 3 salivary glands
parotid
submandibular
sublingual
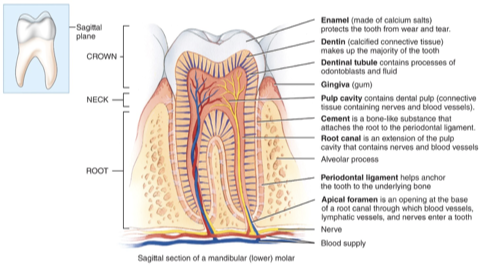
What role do the teeth play in the digestive system?
They break down food (mastication) into smaller and easier to swallow pieces by mechanical digestion.
Extrinsic tongue muscles
Move tongue from side to side and in and out, aiding in manipulation of food during chewing and swallowing.
Intrinsic tongue muscles
Alters shape of tongue, they help with speech and swallowing.
Taste buds
Function in enabling the perception of different flavors and contributing to the overall sensory experience during eating.
Lingual glands
Secrete lingual lipase- contribute to the digestion of fats in the mouth.
The Pharynx
A funnel shaped tube composed of skeletal muscle and lined with mucous membrane. It connects the mouth and nasal cavity to the esophagus and larynx, playing a crucial role in both the digestive and respiratory systems. It is divided into 3 main sections (Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx)
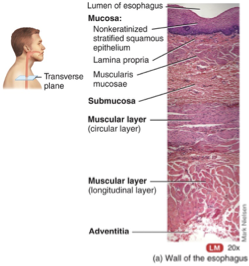
Esophagus
A collapsible, muscular tube that lies posteriorly to the trachea and connects the pharynx to the stomach.
The stomach and it’s function
A muscular organ that stores and mixes food, secretes digestive acids and enzymes. It is located superior to Pancreas and transverse colon, & inferior to diaphragm
What is deglutition?
The process of swallowing.
What cells are found in the gastric glands of the stomach?
Surface mucous cells, mucous neck cells, parietal cells, chief cells, and G cells.
What are the 3 major hormones that control digestion?
Gastrin- promotes secretion of gastric juice, gastric motility
Secretin- stimulates the pancreas to release bicarbonate and inhibits gastric acid secretion.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)- stimulates gallbladder contraction and promotes the release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
What causes gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
A failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to close properly after food enters the stomach- resulting in heartburn feeling.
What are the 3 phases of digestion?
Cephalic phase- stimulates gastric secretion & motility
Gastric phase- neural and hormonal mechanisms
Intestinal phase- Neural and hormonal mechanisms
Bariatric surgery
A type of surgery that helps with weight loss by making changes to the digestive system, often by reducing the size of the stomach. 3 common methods; gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, & gastric bypass.
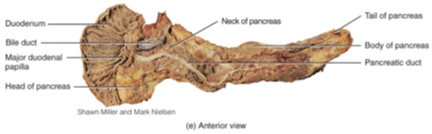
The Pancreas
A gland that lies posterior to the stomach, it produces enzymes that digest carbs, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids. And empties its contents into the duodenum ( first part of the small intestine).
Gallbladder
A small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile produced by the liver, releasing it into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats.
Small intestine
The portion of the digestive tract where most of the digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs, consisting of three parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum!!
Large intestine
The final section of the digestive tract, responsible for the absorption of water and electrolytes, as well as the formation and elimination of feces. Consisting of three parts : cecum, colon, and rectum!!