Unit 2: Lecture 12: Neurophysiology Pt.3
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Action Potential
An electrical signal generated by neurons
occurs along the length of the axon
the ion channels that produce action potentials are mainly voltage-gated channels
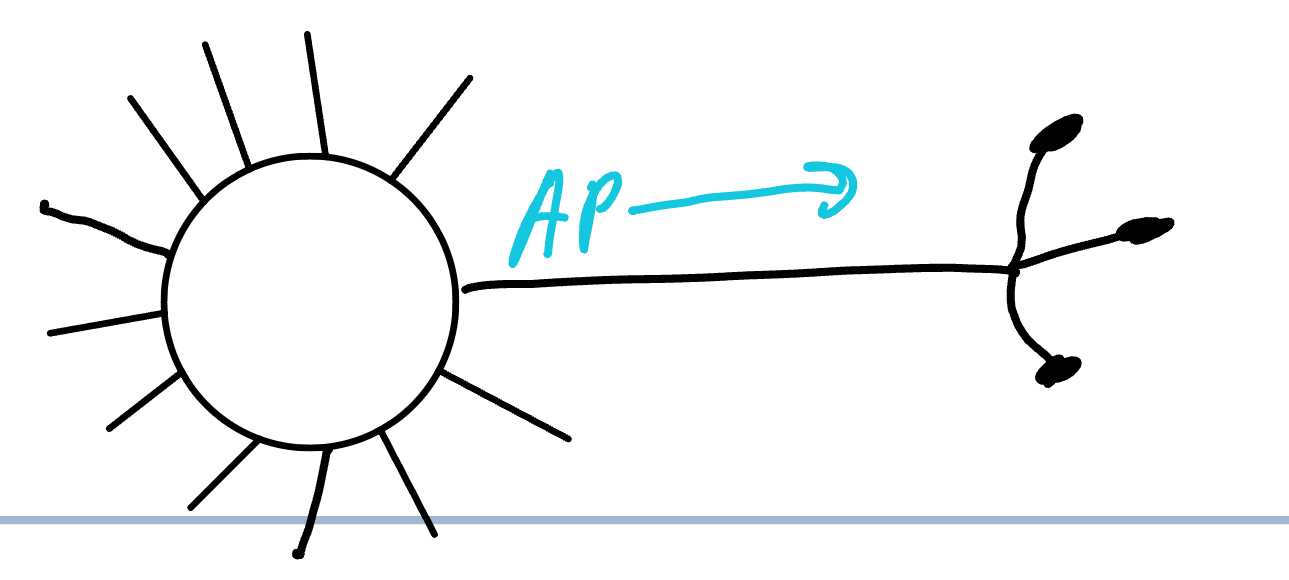
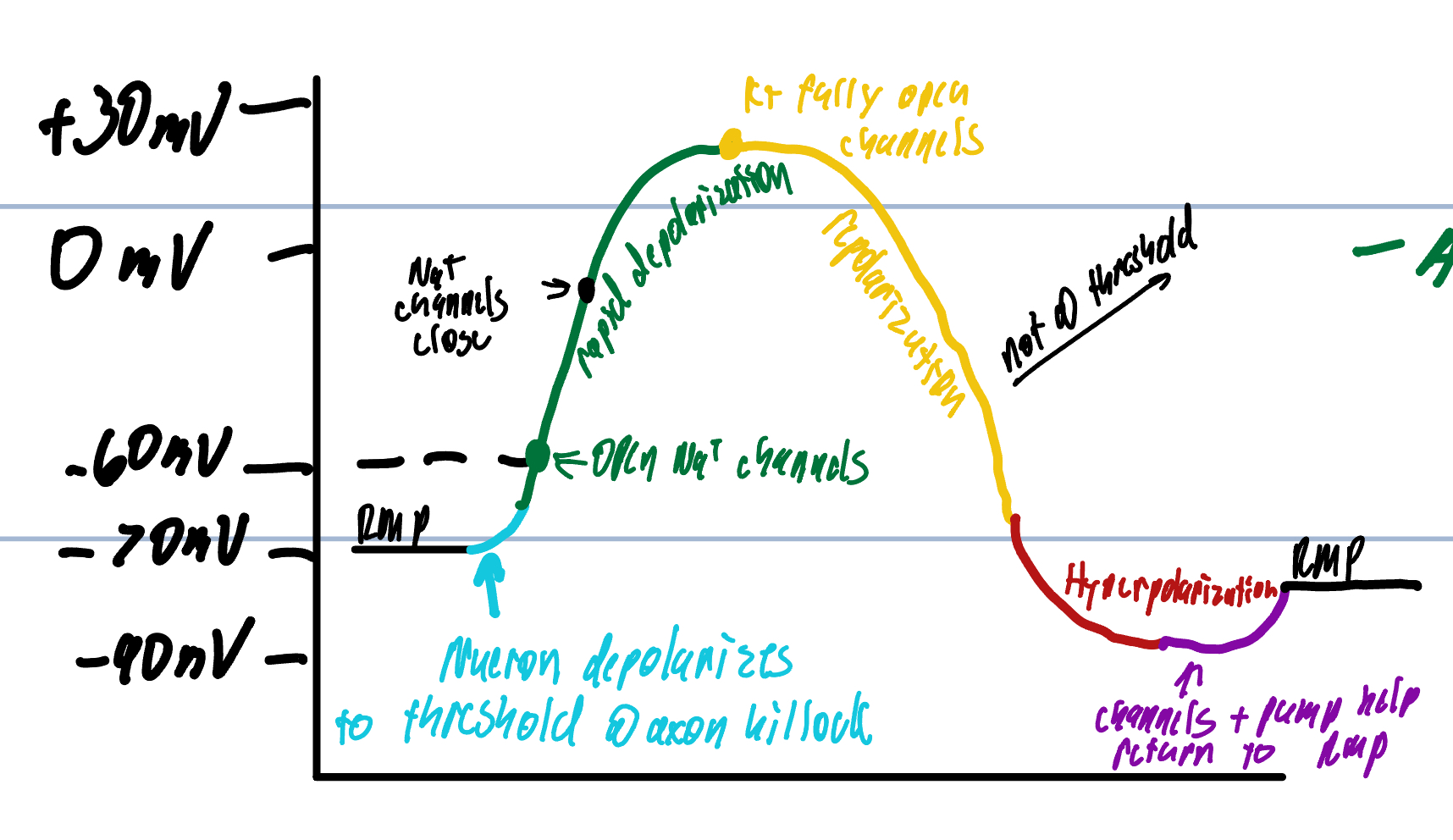
Step 1 of Action Potential
cell starts at -70 mv= RMP
local potential at axon hillock increases until it rises to threshold=-60 mv
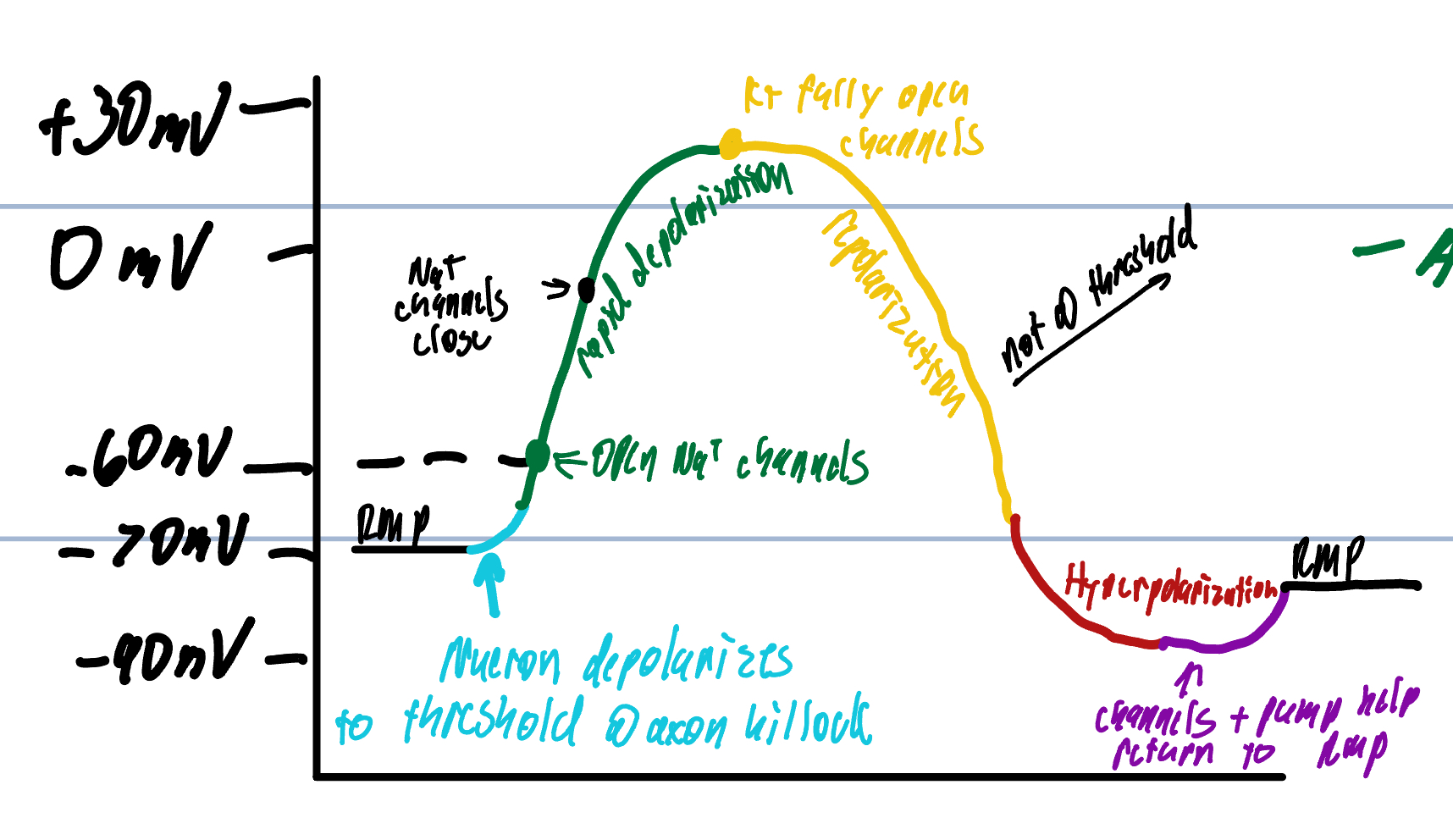
Step 2 of Action Potential
Neurons produce AP
voltage-gated Na+ channels open more and more
More Na+ enters the cell
K+ channels open very slowly when threshold is reached
rapid depolarization
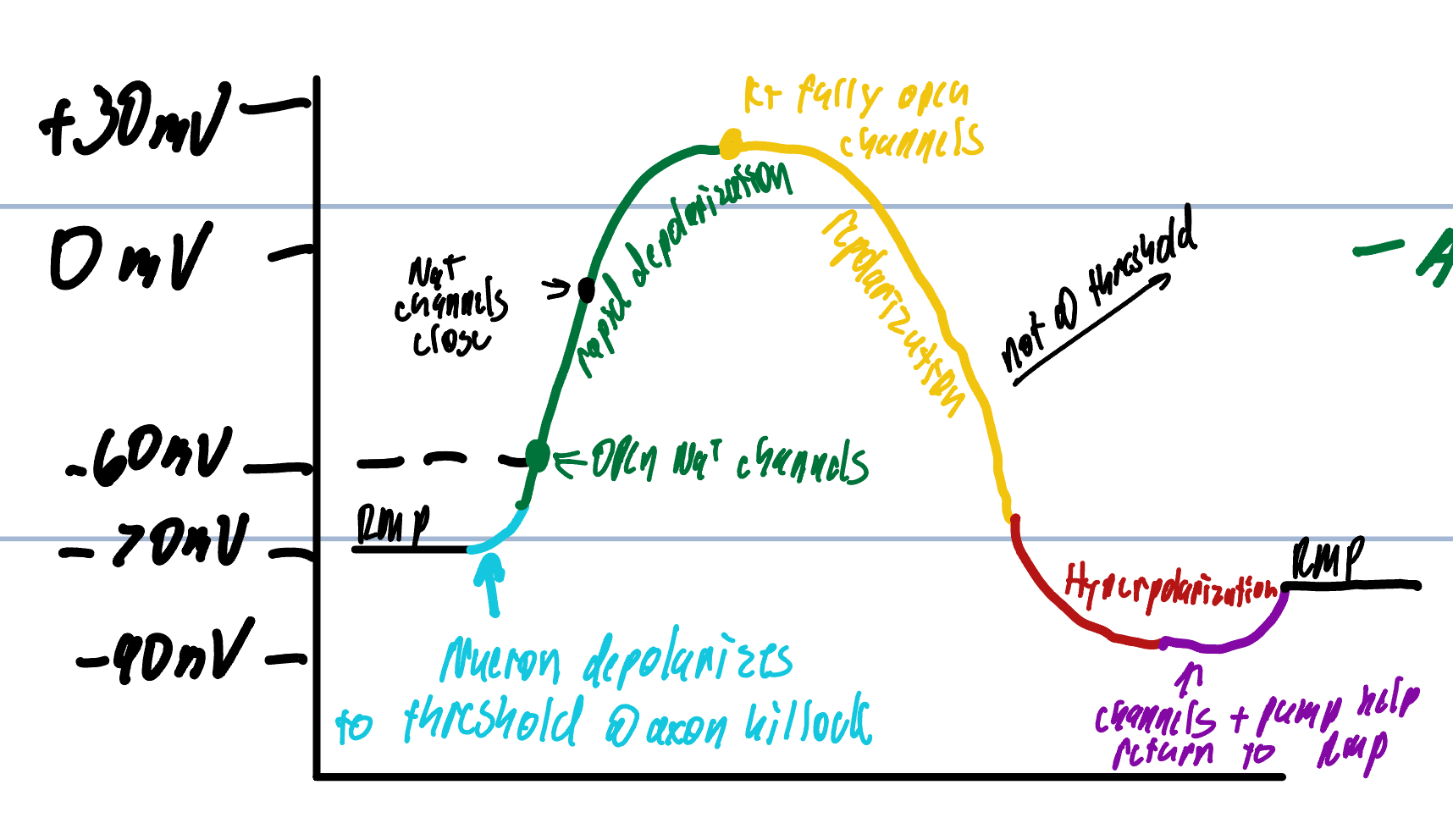
Step 3 of Action Potential
Rush of Na+ ions enter to depolarize
Voltage peaks at approx +35 mv
K+ voltage gated channels are becoming fully opened
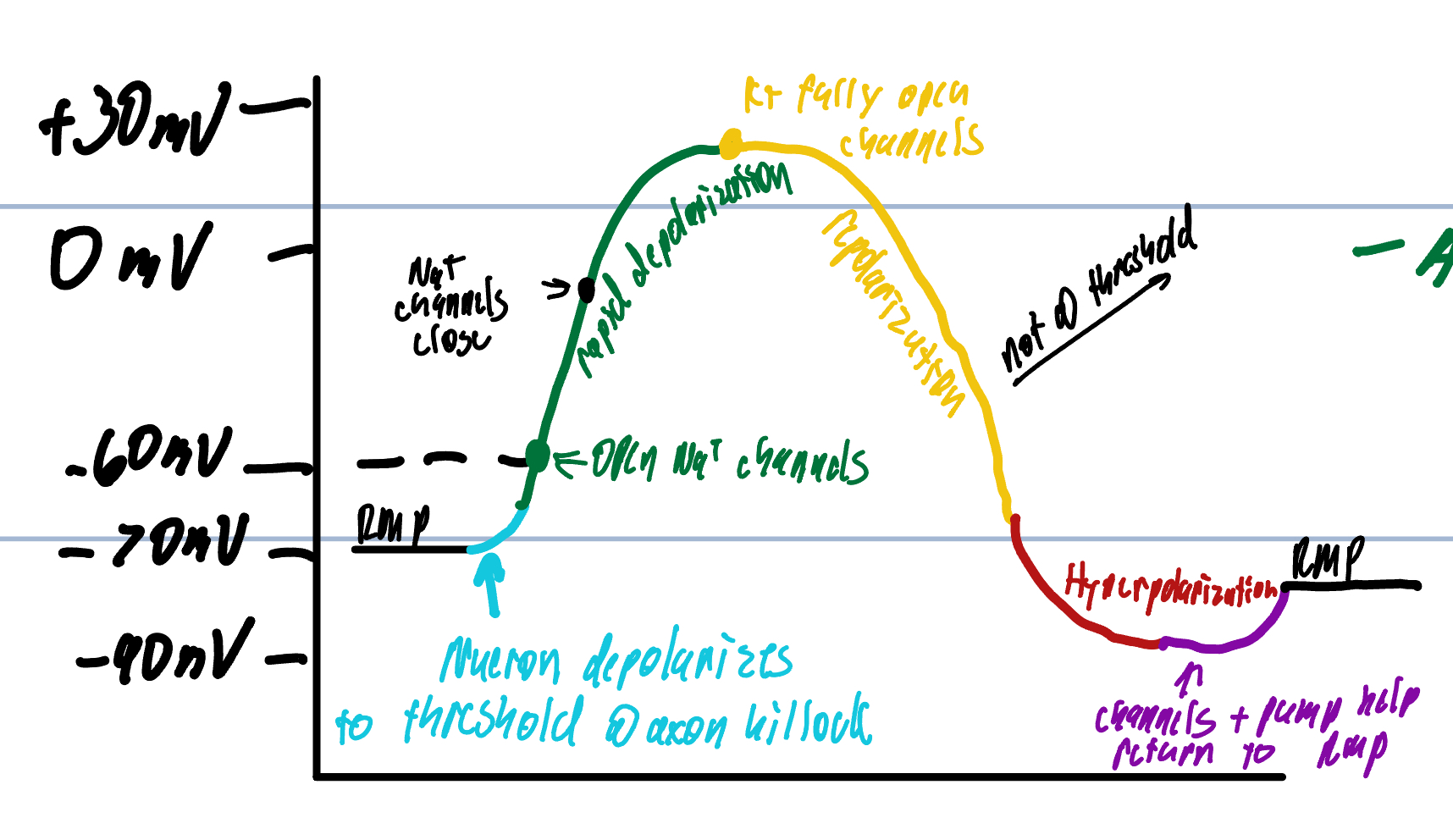
Step 4 of Action Potential
K+ leaves the cell repolarizing the membrane
causes a shift back to negative inside and positive on the outside of the cell
K+ channels remain open a little longer than the Na+ channels
More K+ ions leave the cell than Na+ ions causing hyperpolarization
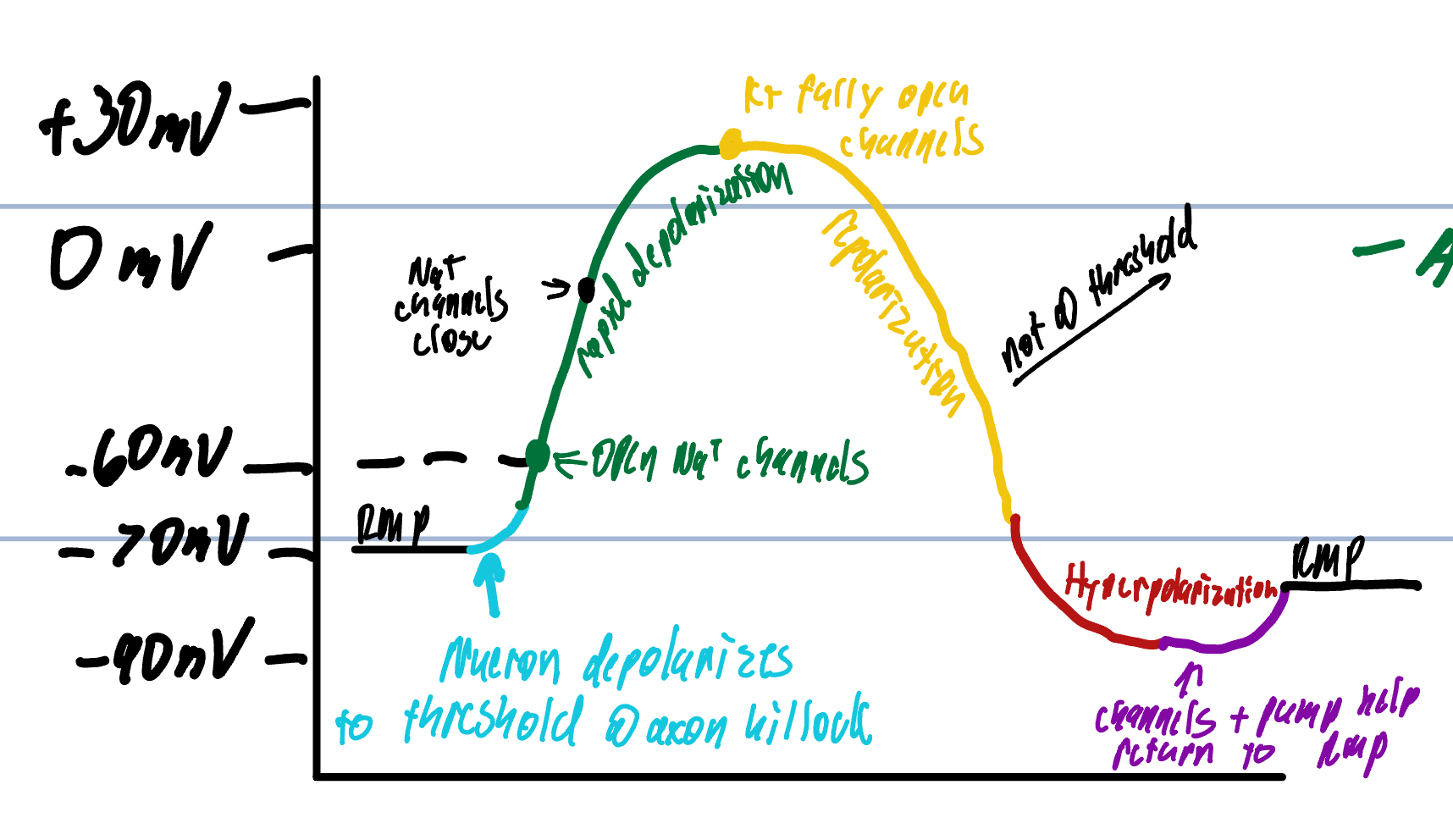
Step 5 of Action Potential
Na+/K+ ATPase pump helps to restore cell to RMP
removes excess Na+
Gain the loss of K+
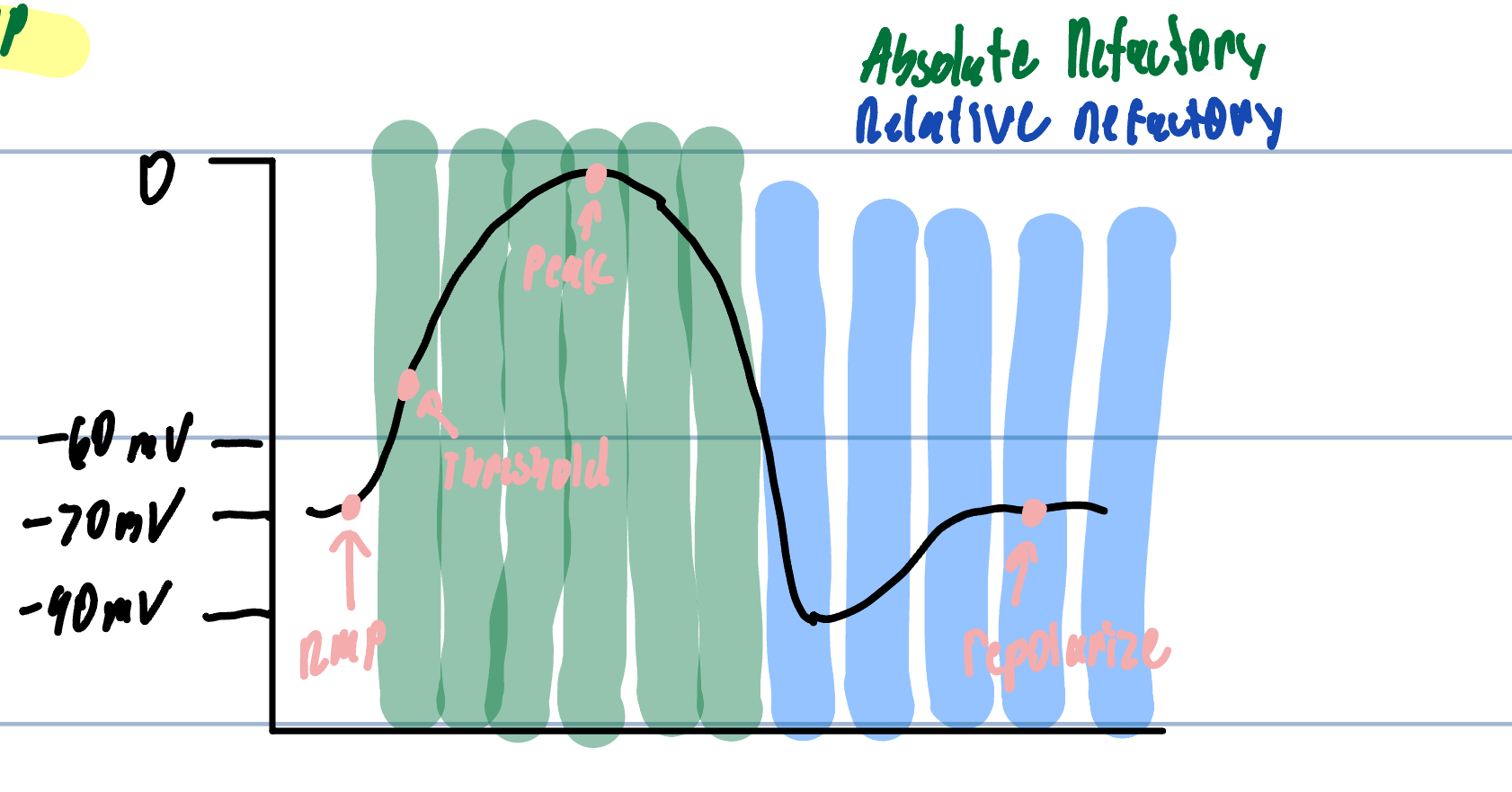
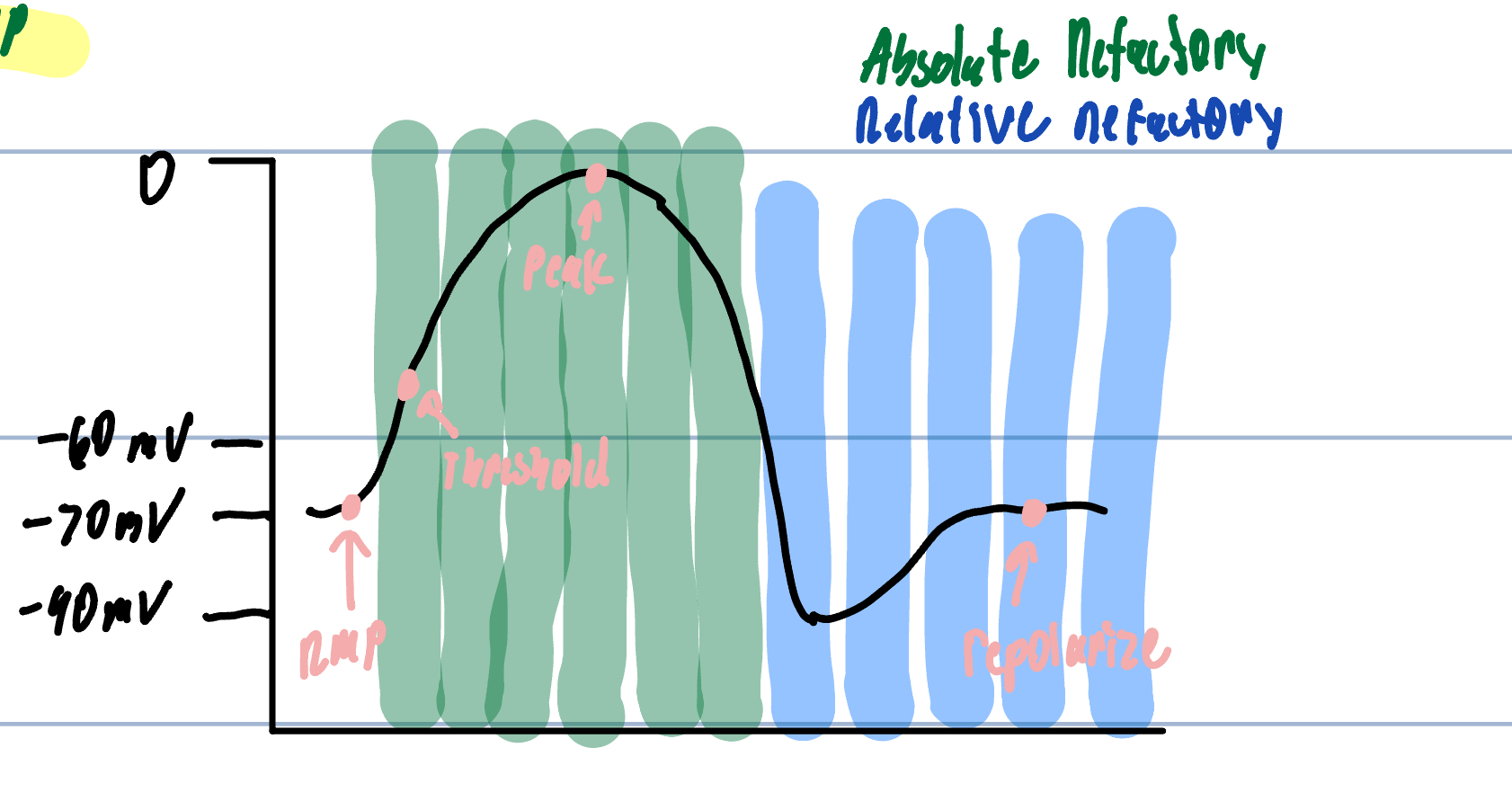
Absolute Refractory Period
Impossible to make another AP on a membrane segment
Threshold at +35 mv
All or None Principle
threshold met= AP will occur
threshold not met = No AP
Irreversible
Relative Refractory Period
Difficult to make an AP membrane segment
Can generate another AP but requires STRONG stimulus
needs to reach threshold with K+ leaving but greater force of Na+ entering
Sodium Voltage Gated Channels
RMP
Threshold
Peak
Repolarize
activation gate= outside of cell
inactivation gate= inside of cell
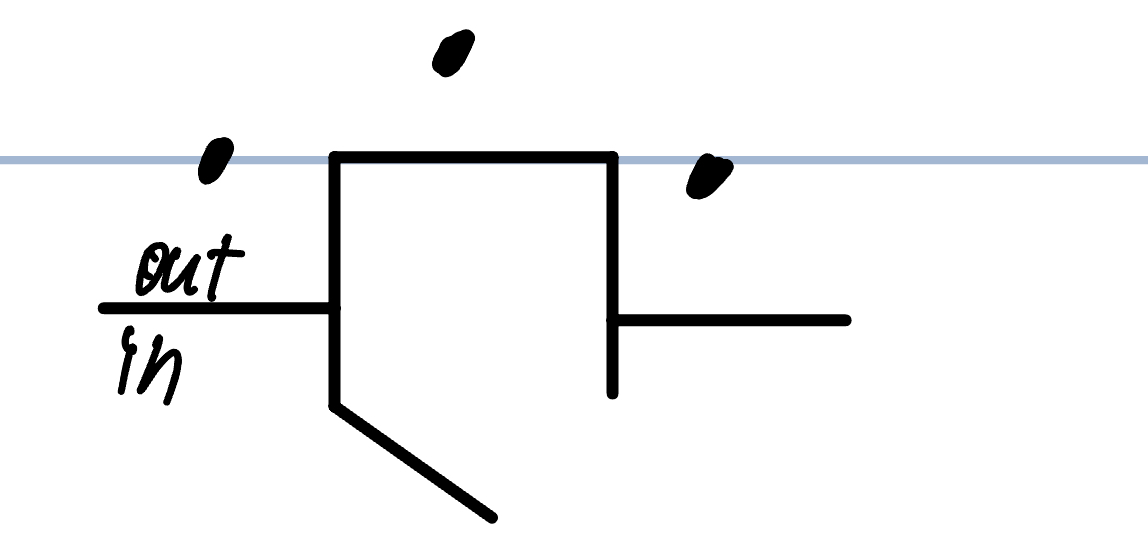
RMP voltage gate
-70 mv
Activation gate closed
inactivation gate opened
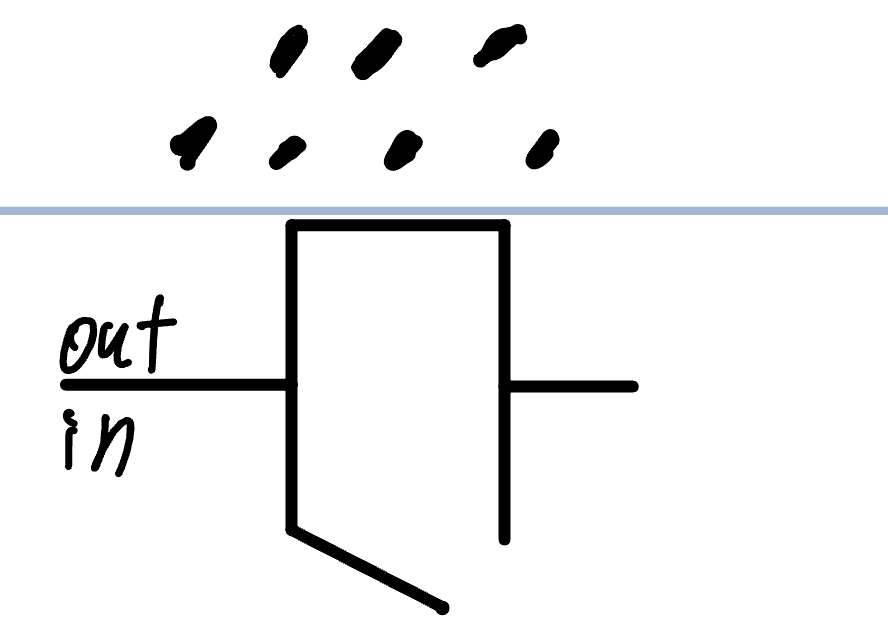
Threshold voltage gate
-60 mv
activation gate opened
inactivation gate opened
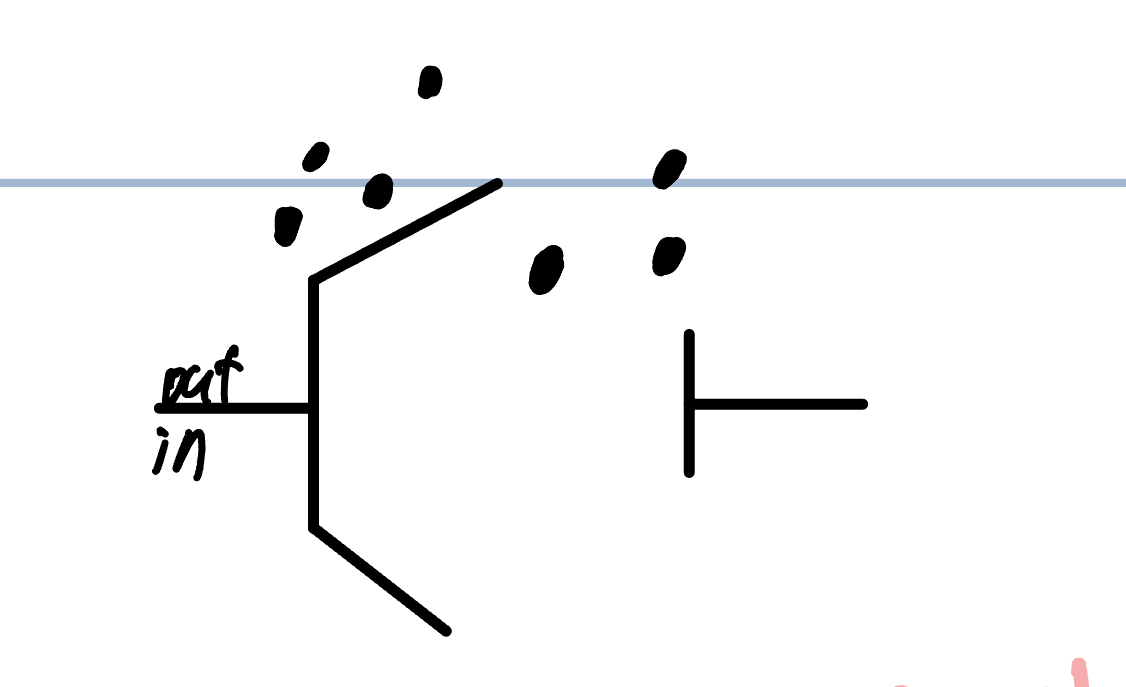
Peak voltage gate
+35 mv
activation gate opened
inactivation gate closed
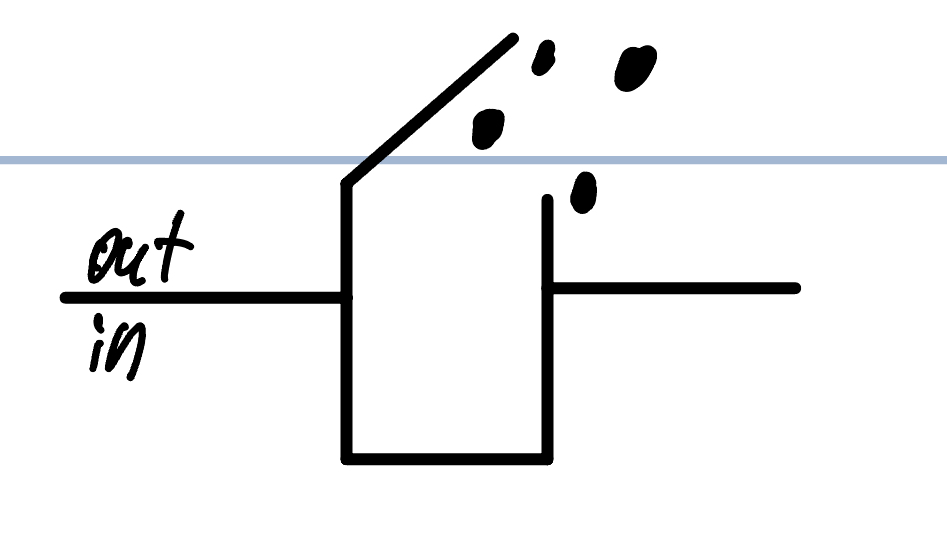
Repolarize voltage gate
-50 mv
activation gate reclosed
Inactivation gate reopens
Propagation
Continuous
Saltatory
Continuous Propagation
unmyelinated axons
AP spreads to the next segment
Saltatory Propagation
myelinated axons
Salt=Skip
Does not have to propagate every single segment of the axon
This allows for much faster APs
Axon Diameter
Large Diameter= faster propagation
Smaller diameter= slower propagation
Type A= largest + myelinated
Type B= medium+ myelinated
Type C= Smallest + unmyelinated