science earth and space yr 9 revision
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what are the layers of the earth
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
describe the crust
thinnest layer
avg thckness is 35 km
crust thicker on land than water
describe the mantle
contains higher amounts of iron, calcium and magnesium
2900km thick dense rock
areas flow like thick fluid
upper=plastic like
lower=rigid
describe the core of the earth
temp: 5200 degrees celcius
inner core solid because intense pressure of layers
made of iron and nickel
what are the main tectonic plates

Pacific, North American, Eurasian, African, Antarctic, Indo-Australian, and South American plates
what is continental drift
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface through geological time
what are continental shelves
gently sloping edge of a continent that extends from the shoreline to the continental slope
what is seafloor spreading (hess’s threory)
new oceanic crust formed at mid-ocean ridges during spreading

tectonic plate theory
the lithosphere of the earth (the crust and top of the mantle) is broken up into large pieces called tectonic plates that move over semi-molten asthenosphere (plasticy top part of mantle)
evidence supporting the theory of plate tectonics
how continents fit like puzzle pieces
identical fossils and rocks on different continents
distribution of volcanoes and earthquakes on boundaries
magnetic striping
similar geological sturctures
process of seafloor spreading
magma pushes up between two plates and then oozes out to solidify, which then creates a divergent boundary. the plates start to push apart due to the constant pressure from the magma, and sediments and rock aslo start to come along with them. the fault is where most of the newer rock is
how do plates move from convection currents in the earth’s mantle
when plates are dragged along the asthenosphere, and the magma rises up and then flows under plates, creating convection currents
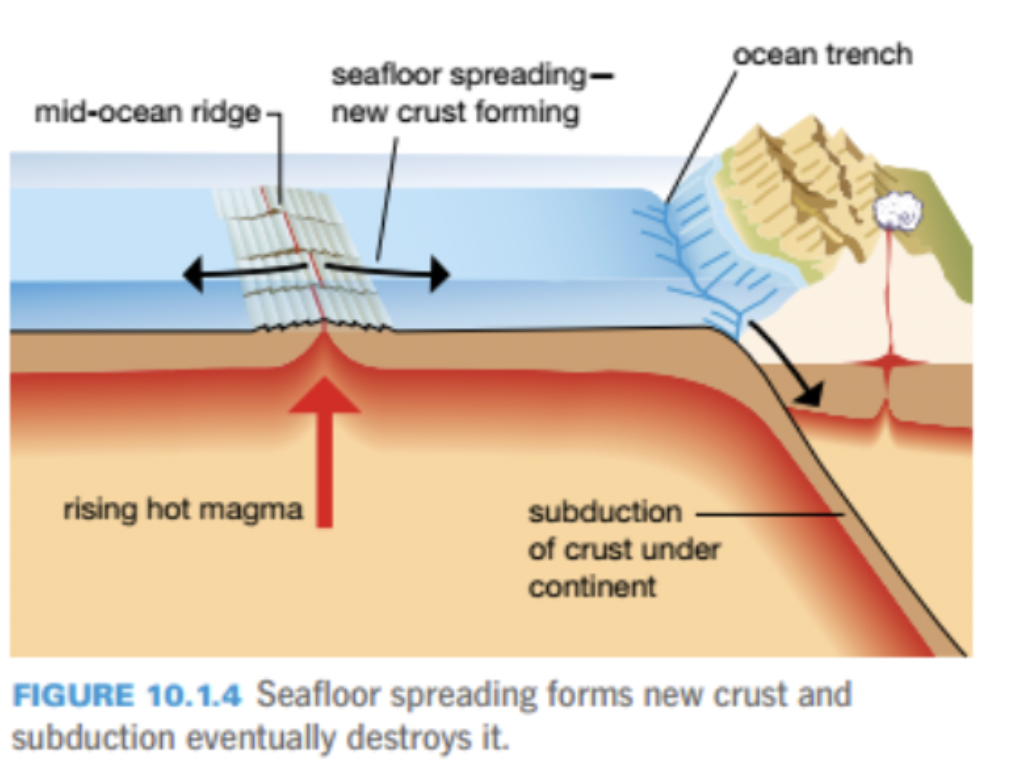
explain this image
the magma rises from the fault line and over time it moves to continental crust and subduct as it is being pushed apart towards the next continental crust. it then melts back to magma and resurfaces.
diverging boundary and give example
tectonic plates are moving apart from each other
eg,
mid atalantic ridge is when north american and Eurasian plates split apart (oceanic)
east african rift between nubian and somali plate
converging boundary and examples
plates collide with each other
continental 2x: Himalayas- eurasian and Indian plates
oceanic continental: andes mountains- nazca subducts under north American plate
ocenanic 2x: maraina trench subducts pacific and phillipine sea plate
transform boundaries and example
plates that slip past each other
Alpine fault between pacific and Australian plate
subduction
an oceanic plate sinking under a lighter continental plate and become distorted forming fold mountains and volcanoes
fault
a fracture or zone of fractures in the Earth's crust where rocks have moved past each other, causing a displacement
rift valley
an area where the earth’s crust is splitting apart
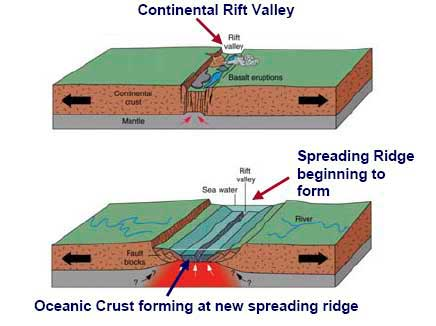
mid ocean ridge
a continuous undersea mountain range formed at a divergent tectonic plate boundary where new oceanic crust is create
what do each of the boundaries create
Divergent: mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys
Convergent: mountain ranges, volcanoes, and trenches
Transform: earthquakes and feature valleys/block mountains
causes of earthquakes
sudden release of energy form the movement of tectonic plates along faults of boundaires
methods of detecting earthquakes
seismometer detect earthquakes. the machine uses inertia to stabilise the pen and the rest of the machine moves with the vibrations of the Earth
p-waves(primary waves)
longitduinal waves (back and forth)
fastest wave
weakest wave
s-wave (secondary wave)
transverse waves (up and down)
slower than p-waves
stronger than p-waves
surface waves
slowest
most destructive
travel along the earth;s surface
focus
place where the quake starts
100’s km deep in the Earth
epicentre
surface directly above the focus
buildings near it would be damaged
oceanic crust
found on ocean floor
thinner
denser (iron+magnesium)
continental crust:
crust forming continents rising above sea level
thicker
lighter (aluminium+silicon)
where and how volcanoes form: divergent, convergent
divergent plate: magma rises to fill fault line, cools + hardens, creating new crust. slowly builds up into mountain that has a way to spew magma
convergent: sub ducting, oceanic plate melts from high pressure and makes less dense magma, which then resurface as an eruption from a volcano
where and how are earthquakes formed: convergent and diverent
convergent:
most and strongest earthquakes are from convergent boundaries
when the plates collide, the stress builds up and it releases seismic waves through the ground, causing an earthquake
divergent:
plates move out causing sudden slips in between tectonic plates
destructive landforms with divergent boundaries
mid-ocean ridges: plates in ocean pull apart then magma fills the gap making underwater mountain ranges
rift-valleys: the stretched crust creates a valley
Volcanic islands: magma constantly spewing out to create a volcano that has a bigger base that it creates an island
destructive landforms woth convergent boundareis
fold mountains:plates push upwards to make mountain slowly
trenches: subducted plates creates depressions on the sea floor
volcanic arcs: product of oceanic floors subducting pushing magma up to create a chain of volcanoes parallel to each other