Computer Science - OCR GCSE - 1.3.2 Network Topologies, Protocols And Layers
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is Ethernet?
Ethernet is a set of protocols and associated hardware which are commonly used in wired local area networks.
It provides a simple interface for connecting multiple devices, such computers, routers, and switches.
With a single switch and a few Ethernet cables , you can create a LAN, which allows all connected devices to communicate with each other
Describe the different types of Ethernet cables:
Category | Bandwidth/ How much data can be sent at a given period of time/ per second |
3 | Up to 10Mbps |
4 | Up to 16Mbps |
5 | Up to 100Mbps = CAT 5 Up to 1Gbps = C |
6 | Up to 10Gbps |
Using Ethernet, data is sent around a network using the concept of “frames”.
What is an Ethernet frame?
Messages are broken down into conveniently sized packets which are called frames. They contain for example, the source and destination MAC address of the data.
An Ethernet frame contains different pieces of data. Label the contents of the Ethernet frame below using the terms given:
Ethernet Frame | |||||
A | B | C | D | E | F |
7 bytes | 1 byte | 6 bytes | 6 bytes | 2 bytes | 42-1500 bytes |
Frame Section | Contents |
A | Preamble (identifies that this is an ethernet frame) |
B | SFD - Start Frame Delimiter (beginning of the frame) |
C | Destination MAC address |
D | Sender MAC address |
E | Payload (part of the actual message being sent) |
F | Checksum CRC |
Describe the features of Ethernet:
Stable connection
Reduced possibility to be hacked
More secure
Wider bandwidth
Describe the features of Wi-Fi
Cheap set-up costs
More vulnerable to hacking
The signal quality will reduce through walls or obstructions
Interference can occur
Generally will have a good quality signal
Less disruption to the building due to no wires being installed
User not tied down to a specific location
Can connect multiple devices without the need for extra hardware
May not be able to receive a signal
The connection can “drop off”
Tend to have slower transfer speeds
Give a diagram for the old style “bus” ethernet network:
This:
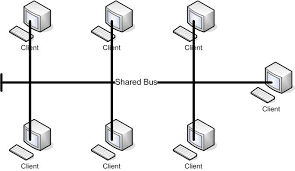
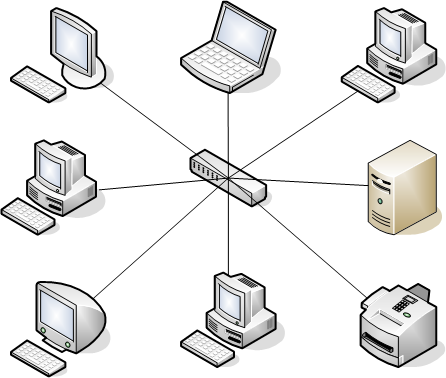
Give a diagram for the star ethernet network:
This:
What does WiFi stand for and what does it mean?
Wireless Fidelity - Wireless connections on a LAN using radio waves
What equipment is needed to connect a device to a Wi-Fi network?
Wireless Access Point - Receives data from a network via a physical connection
Integrated Wireless Network Card/Wireless Adapter - Allows device to connect to network
What is the role of a Wireless Access Point (WAP)?
Receives data from a network via a physical connection
Creates an area of connectivity called a hotspot
Allows wireless enabled devices to communicate with it at frequency of 2.4GHz or 5GHz
Allows wireless access devices to connect to the wired network by connecting the WAP to a switch and access resources such as server, printers, file shares
The WAP may be connected to a router thus providing an internet connection
A WAP allows users to send and receive data on a LAN
Diagram for Wireless Network:
This:
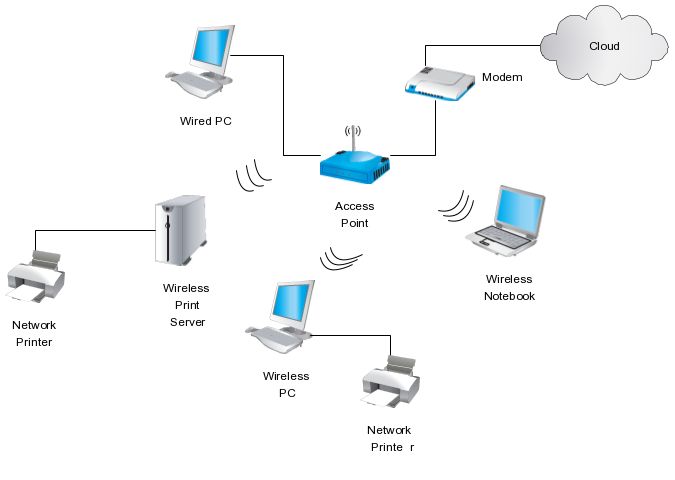
Give three reasons why wireless networking is less beneficial than wired networking:
Limited Range
More vulnerable to hacking
Bandwidth stealing
Give three reasons why wireless networking is more beneficial than wired networking:
Cheap set-up costs
Good quality signal
No wires
Easier to add new devices
Easier to set up
Portability and Convenience
Give three ways in which wireless networks can be made more secure:
Encrypt data - Ensures that data transferred over a wireless connection is less likely to be intercepted and readable
Password protection
Restricting the number of devices that can connect to a WAP - by their MAC address
Disable SSID (i.e. the name of their wireless network) to make it more difficult to locate
State three applications of Bluetooth:
Connecting I/O devices to a computer e.g. Keyboard, Headphones
Transferring files e.g. downloading photos, video and contacts from a phone or digital camera between devices
Linking a hands-free headset to a smartphone e.g. making it possible to talk and drive at the same time
Complete the table below to compare WiFi with Bluetooth:
WiFi | Bluetooth | |
Range | Both are affected by obstacles, up to around 100m | Usually about 10m to 20m |
Typical Bandwidth | Around 1Gbps | About 2Mbps |
Power Consumption | More than Bluetooth | Less than Bluetooth |
Security | Encrypted | Encrypted |
What is encryption?
Before Transmission - Data is scrambled/encrypted using a key into ciphertext
During Transmission - If intercepted, the ciphertext is meaningless/unreadable without the key
After Transmission - Data is decrypted/unscrambled from ciphertext back into a readable form, using the key
This is Symmetric encryption:
This is Asymmetric encryption:
What is an IP address?
Internet Protocol - An IP address is a unique address allocated to nodes on the internet that identifies a device on the internet or a local network, it changes as it moves location.
The address is allocated by an internet provider/ router/ server and can change
Used by routers on the internet to send data packets to the correct destination
Write down an example IP address
IPv4 → 65.123.217.14
IPv6 → BC43:71A9:0000:044c:3879:0000:55FD:286B
Explain the following terms relating to an IP address:
octet
0 to 255
ipv4
ipv6
Octet →A number that can represented by 8 bits
0-255 → The range of denary values that can be displayed in an octet in IPv4
IPv4 → Written in denary, 32bit address, formed by 4 decimal numbers separated by full stops
IPv6 → Written in hexadecimal, a 128 bit address, formed by 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits, separated by colons
What is a MAC address?
A unique address allocator to nodes on a LAN
Physically embedded on the Network Card by the manufacture, making it permanent
Switches route data on a LAN using MAC addresses
How are MAC addresses composed and how do they relate to binary numbers?
Written in 12 Hexadecimal Characters which are represented by a 48 bit Binary Number
How could a MAC address be used in network security?
Only certain MAC addresses are allowed/ not allowed to connect to a switch or router
Why are MAC addresses not used for sending data packets over the internet?
MAC addresses are used on LANs. IP addresses are used to send packets over the internet
Complete the table below to compare/contrast IP and MAC addresses
IP Address (IPv4) | MAC Address | |
How it is allocated to a node | By an ISP/ Router/ Server | By the manufacturer of the NIC |
Permanency | Changes with the device’s network | Permanent |
Number System | Decimal/ Denary | Hexadecimal |
Number of bits | 32 (IPv4) 128 (IPv6) | 48 |
Main use | Routing data packets to the correct nde over the internet | Routing data frames to the correct route node over a LAN |
What are network standards?
Standards are a set of specifications for hardware or software that make it possible for manufacturers and producers to create products and services which are compatible with each other. Without standards most devices wouldn't be able to communicate with each other.
Give examples of some standards related to Computing:
ASCII/UNICODE
IEEE
HTML
Document, image and sound standards
What is a network protocol?
Network protocols are a set of rules or conventions which control the communication between divides on a network.
What do protocols specify?
Data Packets format
Addressing system being used eg IPv4 or 6
Transmission Speed
Error checking procedures
For the next slides:
Full Name, What it does, When would it be used
TCP/
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TCP:
Breaks data down into packets at sender’s end
Gives each packet a sequence number
Packets are reassembled and resequenced at the receiving node
Lost/damaged packets are detected and resent
IP:
A destination and source IP addresses are assigned to each data packet
Routers send data to the correct destination by inspecting the packets destination address
Anytime data is transferred across the internet
HTTP
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Use for accessing and receiving web pages in the form of HTML. The protocol requests a web server to provide a certain web page to the user’s web browser for viewing.
When requesting a website to be viewed.
HTTPS
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure
An extension of HTTP where any information transferred between a web browser and a web server is encrypted.
When accessing a webpage/website where you may want to encrypt data – e.g. a Bank website.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol
Allows the transfer of files between local client computers and remote servers on the internet.
To publish website files from a local computer to a remote live web server. For example, updating the live website.
POP
Post Office Protocol
Email messages are downloaded from the mail server. POP creates local copies of emails and deletes the originals from the mail server
Viewing Emails
IMAP
Internet Messaging Access Protocol
Email messages are stored on the mail server and viewed/deleted on the server itself. No local copies of emails are made.
When email is being accessed by multiple clients simultaneously, or email is being accessed on multiple
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Used for sending email messages between clients and mail servers
When sending an email
What is meant by the concept of “layering” in computer networks?
Layering in a computer network is defined as a model where a whole network process is divided into various smaller sub-tasks. These divided sub-tasks are then assigned to a specific layer to perform only the dedicated tasks.
Why do computer networks use layers?
Reduces complexity of network into subprograms
Products from different vendors work together
Devices can be manufactured to work at a particular layer
Complete the table below which describes the layers used in the TCP/IP protocol:
Layer | Function |
Application Layer | Encodes data so that it will be understandable by the recipient. Formats data as required using protocols such as HTTP |
Transport Layer | Splits data into packets and adds information to these such as sequence numbers. Managed by the TCP protocol |
Internet/Network Layer | Adds source and destination IP address to packets. Routers operate at this layer. |
Link Layer | The MAC address of the recipient/sender is added so that the packet can be directed to the correct recipient on the LAN |
Difference between POP3 vs IMAP:
POP3 | IMAP4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|