Chapter 3 | Water and Life
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds that form between the partial positive charge of a hydrogen atom in one molecule and the partial negative charge of an oxygen atom in another molecule
Polarity of Water
Water molecules have a partial negative charge around the oxygen atom and partial positive charges around the hydrogen atoms. This polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other
Cohesion
The tendency of water molecules to stick to each other due to hydrogen bonding. This property allows water to form droplets and maintain surface tension
Adhesion
The tendency of water molecules to stick to other substances, especially those that are hydrophilic (polar molecules). This property is responsible for water’s ability to climb up plant stems through capillary action
High Surface Tension
The strong cohesive forces between water molecules at the surface, which makes it difficult to break through the surface layer. This is why water striders can walk on water and why water droplets retain their shape
High Specific Heat
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius. Water has a high specific heat, meaning it absorbs and releases heat more slowly than many other substances
Evaporative Cooling
The process by which the evaporation of water removes heat from the surface, cooling the surrounding area (e.g., sweating)
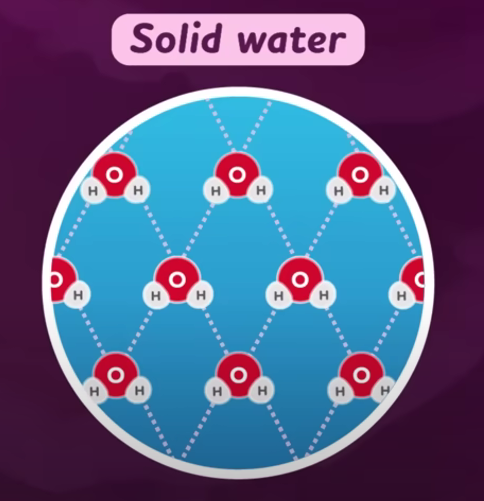
Ice Floats
When water freezes, its molecules form a crystalline structure with more empty space, making it less dense than liquid water
Solution
A homogenous mixture of two or more substances
Solvent
The substance that dissolves other substances (in most cases, this is water)
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in the solvent
Hydrophilic
Substances that are attracted to water and can dissolve in it (e.g., salts, sugars)
Hydrophobic
Substances that repel water and do not dissolve in it (e.g., oils)
Acid
A substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution, resulting in a pH less than 7. Example: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissociates into H⁺ and Cl⁻
Base
A substance that decreases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in a solution, resulting in a pH greater than 7. Example: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) dissociates into Na⁺ and OH⁻
Hydronium Ion (H₃O⁺)
Formed when a hydrogen ion (H⁺) associates with a water molecule
Hydroxide Ion (OH⁻)
Formed when a base dissociates in water
pH Scale
A scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic), with 7 being neutral