Quantitative Chemistry in AQA GCSE Chemistry
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Law of conservation of mass
No atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction so the mass of the products = mass of the reactants.
Mass changes with gas reactants/products
If a reaction appears to involve a change in mass, check to see if this is due to a reactant or a product as a gas.
Example of mass change
When a metal reacts with oxygen: mass of metal oxide product > mass of metal.
Chemical measurements uncertainty
Whenever a measurement is made there is always some uncertainty about the result obtained.
Moles
Chemical amounts are measured in moles. The symbol for the unit mole is mol.
Mass of one mole
The mass of one mole of a substance in grams is numerically equal to its relative formula mass.
Example of mass of iron
The Mr of iron is 56, so one mole of iron weighs 56g.
Example of mass of nitrogen gas
The Mr of nitrogen gas, N2, is 28 (2 x 14), so one mole is 28g.
Particles in one mole
One mole of a substance contains the same number of the stated particles, atoms, molecules or ions as one mole of any other substance.
Converting between moles and grams
You can convert between moles and grams by using the equation: mass = moles x molar mass.
Example of moles calculation
How many moles are there in 42g of carbon?
Moles
Mass / Mr = 42/12 = 3.5 moles
Avogadro constant
The number of atoms, molecules or ions in a mole of a given substance is 6.02 x 10^23 per mole.
Masses of reactants & products
Can be calculated from balanced symbol equations.
Chemical equations interpretation
Chemical equations can be interpreted in terms of moles.
Example of chemical reaction
Mg + 2HCl -> MgCl2 + H2 shows that 1 mol Mg reacts with 2 mol HCl to produce 1 mol MgCl2 and 1 mol H2.
Total moles conservation
Total moles of one element must be the same on both sides of the equation.
Balancing numbers in equations
Balancing numbers in a symbol equation can be calculated from the masses of reactants and products.
Converting masses to moles
Convert the masses in grams to amounts in moles.
Limiting reactants
In a chemical reaction with 2 reactants, one is used in excess to ensure that all of the other reactant is used.
Limiting reactant
The reactant that is used up / not in excess (since it limits the amount of products).
Product produced
If a limiting reactant is used, the amount of product produced is restricted to the amount of the excess reactant that reacts with the limiting one.
Concentration of a solution
Can be measured in mass per given volume of solution, e.g., grams per dm³ (g/dm³).
Mass of solute
To calculate mass of solute in a given volume of a known concentration, use mass = conc x vol, i.e., g = g/dm³ x dm³.
Higher concentration
A smaller volume or larger mass of solute gives a higher concentration.
Lower concentration
A larger volume or smaller mass of solute gives a lower concentration.
Percentage yield
Percentage yield = (Amount of product produced / Maximum amount of product possible) x 100.
Yield
Amount of product obtained.
Theoretical mass of a product
To calculate the theoretical mass of a product from a given mass of reactant and the balancing equation for the reaction.
Moles of reactant
Calculate mol. of reactant by using mol. = mass / molar mass.
Balancing numbers
Use balancing numbers to find mol. of product.
Atom economy
A measure of the amount of starting materials that end up as useful products.
High atom economy
Important for sustainable development and for economic reasons to use reactions with high atom economy.
Atom economy formula
Atom economy = (Mr of desired product from reaction / sum of Mr of all reactants) x 100.
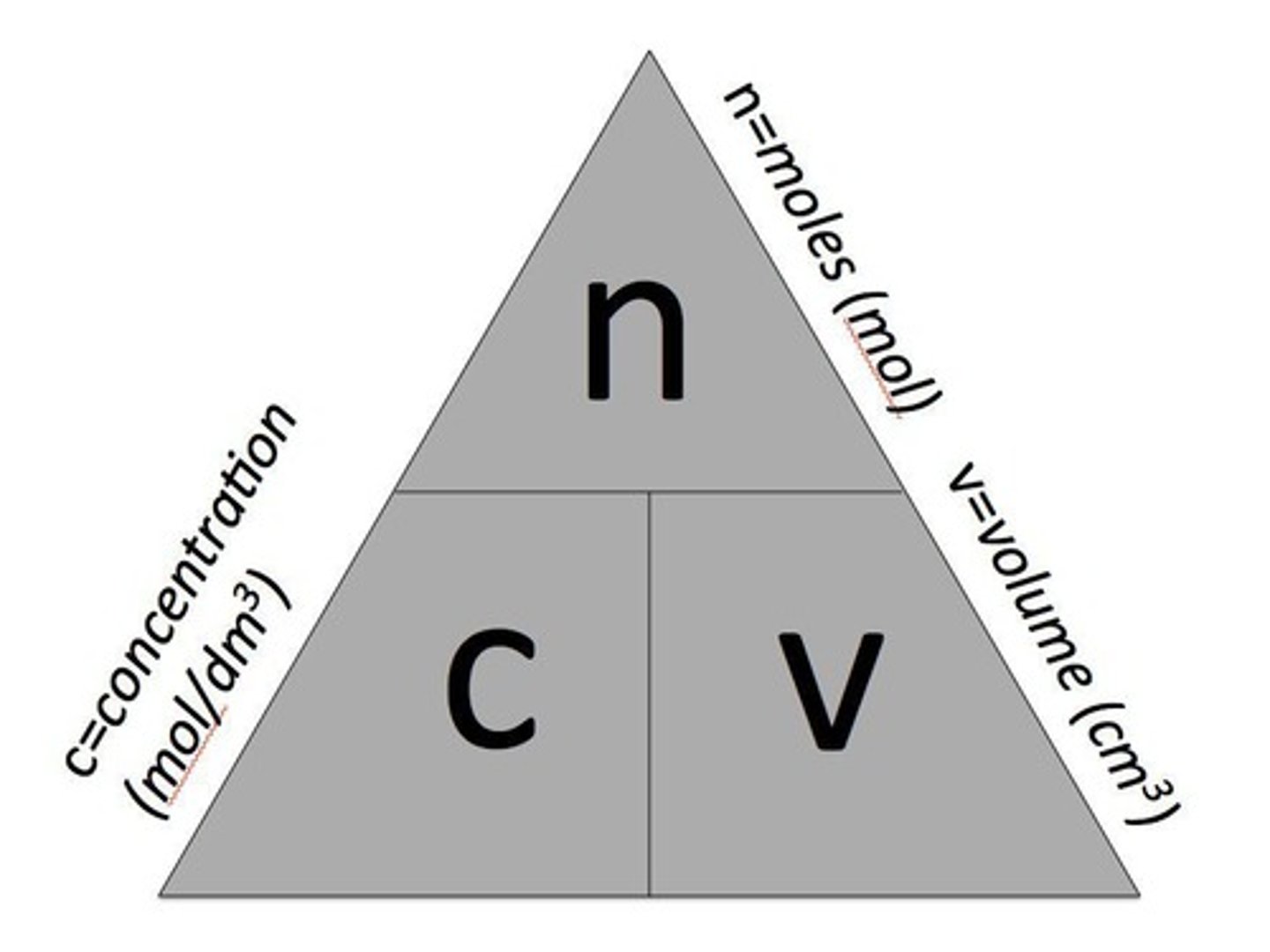
Concentration in mol/dm³
Concentration of a solution can be measured in mol. per given volume of solution, e.g., mol. per dm³ (mol./dm³).
Moles from concentration
Mass of a solute and the volume of a solution are related to the conc. of the solution through the equation moles = concentration x volume.
Volume of gas
Equal amounts (in mol.) of gases occupy the same volume under the same conditions of temperature and pressure (e.g., RTP).
Volume of 1 mol of gas
Volume of 1 mol of any gas at RTP (room temperature and pressure: 20 degrees C and 1 atmosphere pressure) is 24 dm³.
Gas volume equation
Volume of gas (dm³) at RTP = Moles x 24.
Calculating gas volume
Using the gas volume equation, if the reaction is at RTP, you can calculate moles of a gas produced and then x24 to get volume produced.