Total Bio Final Review
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
steps of the scientific method
observation
ask question
form hypothesis
design controlled exp.
collect data
anylyze data
parts of an experiment
independent vs. dependent, control group vs. experimental group
Independent Variable
The variable you change on purpose
Dependent Variable
the variable you measure or observe
Control Group
all variables same as experimental except no independent variable
experiment group
all same control group except yes independent variable
Controlled experiment
experiment in which only one variable is changed
Qualitative data
qualities not numbers
quantitive data
numbers
Hypothesis
testable statement about how or why something happens
Theory
explains how or why something happens
the organelle involved in the process of photosynthesis
chloroplast
which stages happen in the parts of this organelle
Light-dependent reactions- thylakoid membrane
Light-independent reactions- stroma
the pigment involved in photosynthesis
chlorophyll
Know the products from photosynthesis that are important for cellular respiration
sugar and oxygen
Know aerobic vs. anaerobic
aerobic- needs oxygen
anaerobic- not need oxygen
how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are connected
products of photosynthesis are inputs of cellular respiration and products of cellular respiration are inputs of photosynthesis
different stages in the entire cell cycle
G1
G2
S Phase
G0
G1 Phase
Cell grows
S Phase
DNA copied
G2 Phase
Prepares for mitosis
G0 Phase
cell cycle paused
the phases of Mitosis
Prophase metaphase anaphase telophase
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nucleus dissolves, spindle forms
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Sister chromatids pull apart to opposite ends
Telophase
New nucleus reappears, chromosomes not visible
Cytokinesis
cell splits
Dominant gene
always Expressed when present
Recessive gene
only expressed when both alleles are recessive
Homozygous
Two of the same alleles
Heterozygous
One dominant, one recessive allele
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Genotype ratio
1 AA : 2 Aa : 1 aa
Phenotype ratio
3 dominant : 1 recessive
meiosis Prophase I
spindles form, chromosomes form, nucleus disappears, homologous chromosomes pair up, crossing over can occur
what is crossing over
homologous pairs swap genes
meiosis Metaphase I
chromosomes line up down the middle, lined up as homologous pairs
meiosis anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separate to opp. sides of cell
meiosis Telophase I/cytokenesis
nucleus reforms, chromosomes not visible, pinching for cytokenesis, spindles disappear, chromosomes now seprated in diff. cells and are not pairs making 2 haploid cells for m2
meiosis Prophase II
2 haploid daughter cells go through this process, spindle fibers form, chromosomes become visible, nucleus disappears
meiosis metaphase II
chromosomes line up, spindles attach to sister chromatid
meiosis anaphase II
sister chromatids seperate and go to opp sides
meiosis telephase II
spindle disappear, chromosomes not visible, nucleus reappears, pinching, end w/ 4 haploid cells
Diploid (2n)
Full set of chromosomes (body cells)
Haploid (n)
Half set (gametes/sex cells)
the parts of a nucleotide
Sugar (deoxyribose)
Phosphate
Nitrogen base (A, T, C, G)
the parts of a DNA molecule such as the different bonds involved
Hydrogen bonds: between base pairs (A-T, C-G)
Covalent bonds: between sugar and phosphate backbone
the enzymes involved in replication
helicase, DNA polymerase, ligase
DNA Helicase:
unzips DNA - breaks H bonds
DNA polymerase
adds new nucleotides for new strand
DNA Ligase
seals gaps between okazaki fragments
the differences between DNA and RNA
DNA-double strande d, thymine, deoxyribose
RNA- single stranded, uracil, ribose
what happens in transcription
mRNA copies the DNA - tRNA carries the DNA to cytoplasm rRNA which makes the protien
Codon
3-letter sequence on mRNA
Anticodon
3-letter match on tRNA
Point mutation
one amino acid is changed
Frameshift
insertion or deletion (more damaging)
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Species evolve over time by natural selection
natural selection and how this process occurs
Traits that help survival are selected for
Organisms with beneficial traits live longer & reproduce more
RNA primase
adds RNA at beginning so polymerase knows where to start
topoisomerase
unwinds dna double helix
how does dna replication work
semi conservative- old dna strand used to make new DNA strand they go to together
What are the stages of cellular respiration and what order do they occur in?
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs cycle
3. Electron Transport Chain
Where does glycolysis occur?
in cytoplasm (outside of mitochondria)
Where does the Krebs cycle occur?
mitochondrial matrix
Where does electron transport chain occur?
inner membrane of mitochondria
What are the reactants and products of glycolysis?
reactants: 1 glucose and 2 ATP
products: 2 pyruvate and 2 NADH
What are the reactants and products of the krebs cycle?
reactants: 2 pyruvate molecules (one per turn)
products: 6 CO2, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2 (2 ATP?) (half per one turn)
What are the reactants and products of the electron transport chain?
Reactants: NADH, FADH2, O2
Products: H2O, 26-38 ATP
How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration relate to each other?
The oxygen and glucose made in photosynthesis are used in cell respiration. The carbon dioxide and water produced in cellular respiration are then used in photosynthesis to create glucose and oxygen. The cycle then repeats!
Order of the cell cycle? What happens in interphase vs M phase?
Interphase
- G1
- G0
- S Phase
- G2 Phase
M Phase
- Mitosis
- Cytokinesis
What happens in G1?
Cell growth
What happens in S Phase?
DNA replicates
What happens in G2?
Cell preps for mitosis
What happens in G0 Phase?
It's a branch off of G1 where cells with problems go and divison is paused dividing. This can be permanent or temporary
What happens in mitosis?
PMAT
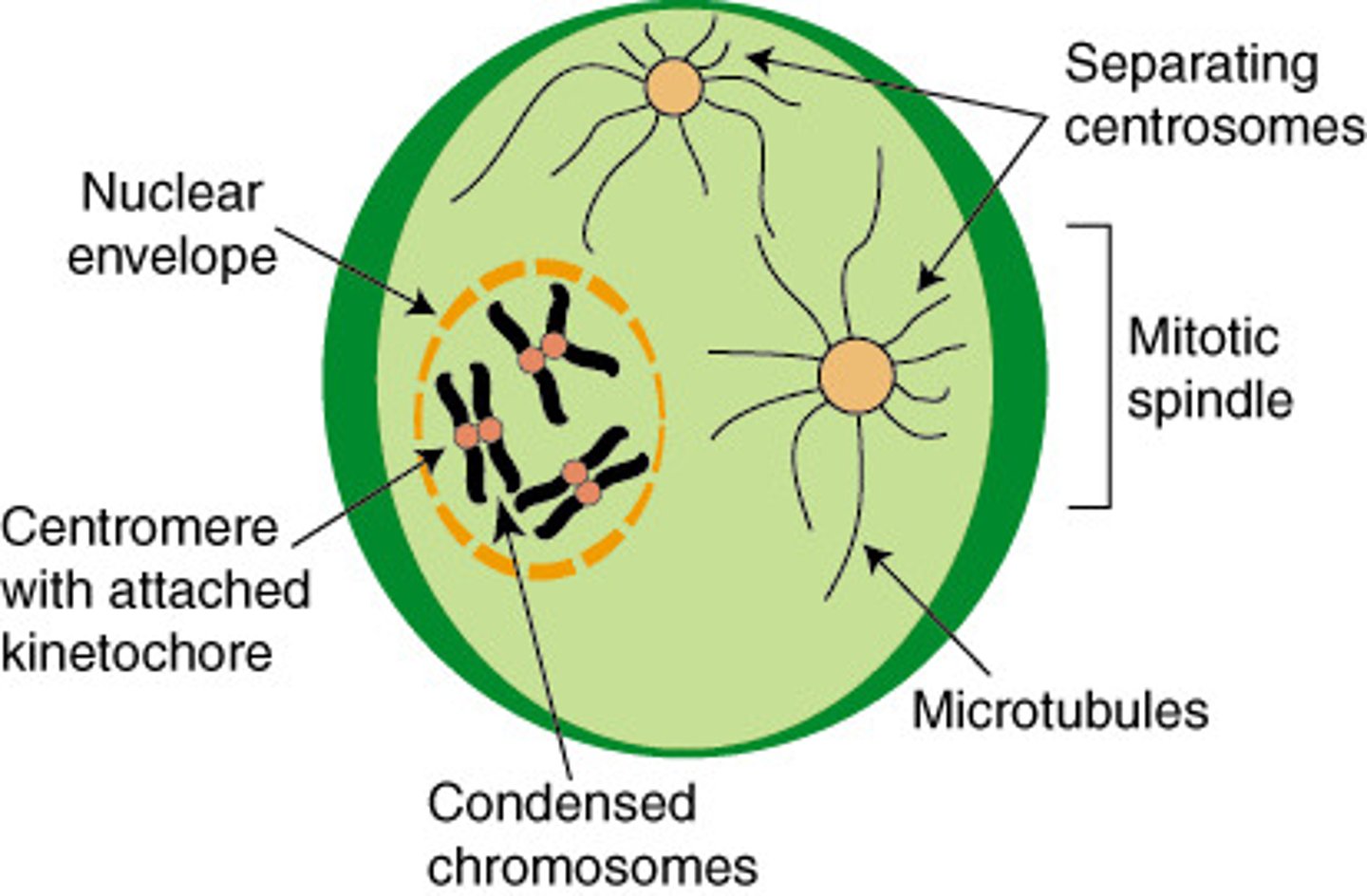
What happens in Prophase? 3
Nucleus disappears, chromosomes condense and are visible, spindle fibers form
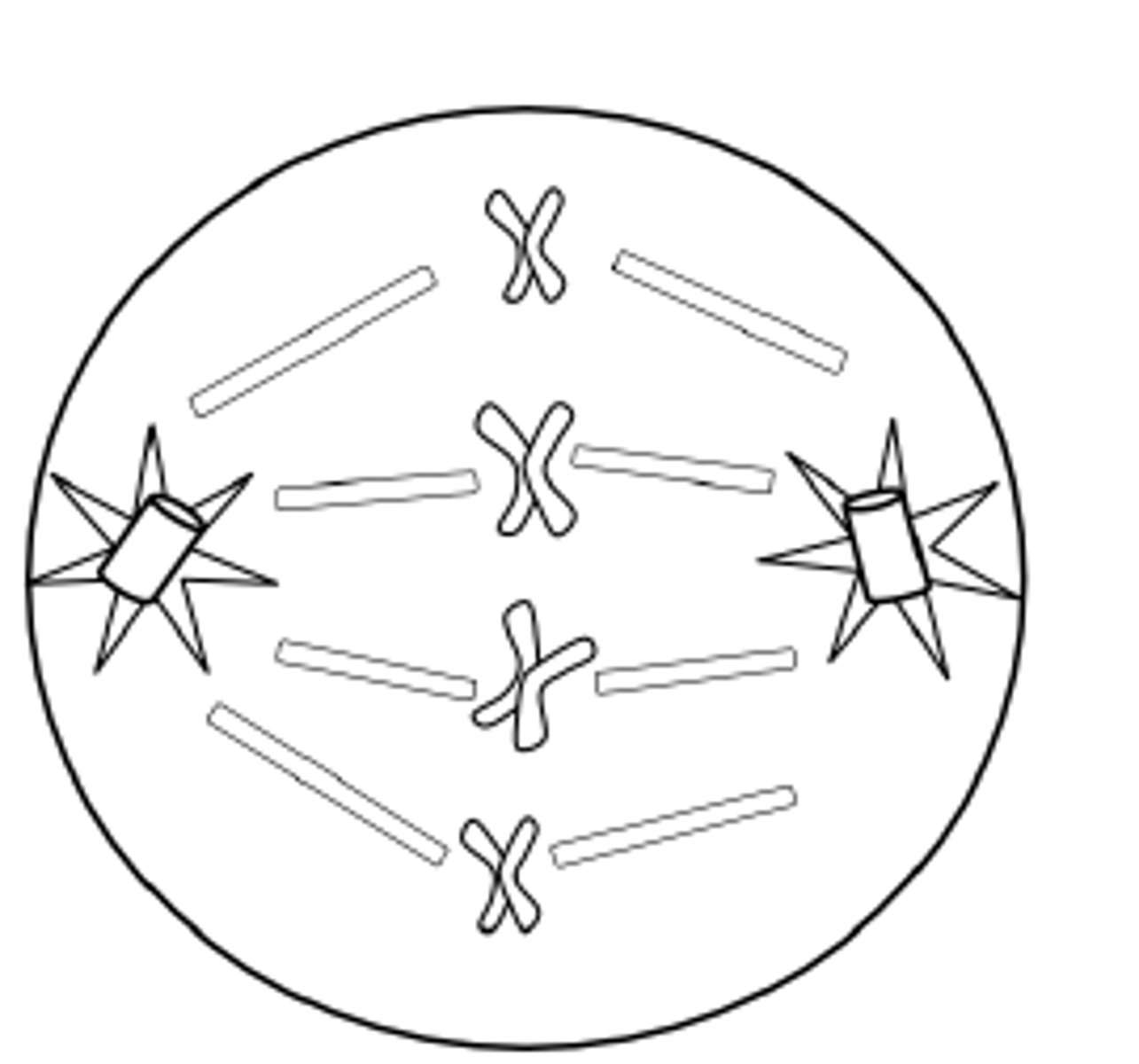
What happens in Metaphase? M for? 2
Middle.
Chromosomes line up single file down middle of cell. Spindles attach to the centrioles of the chromosones
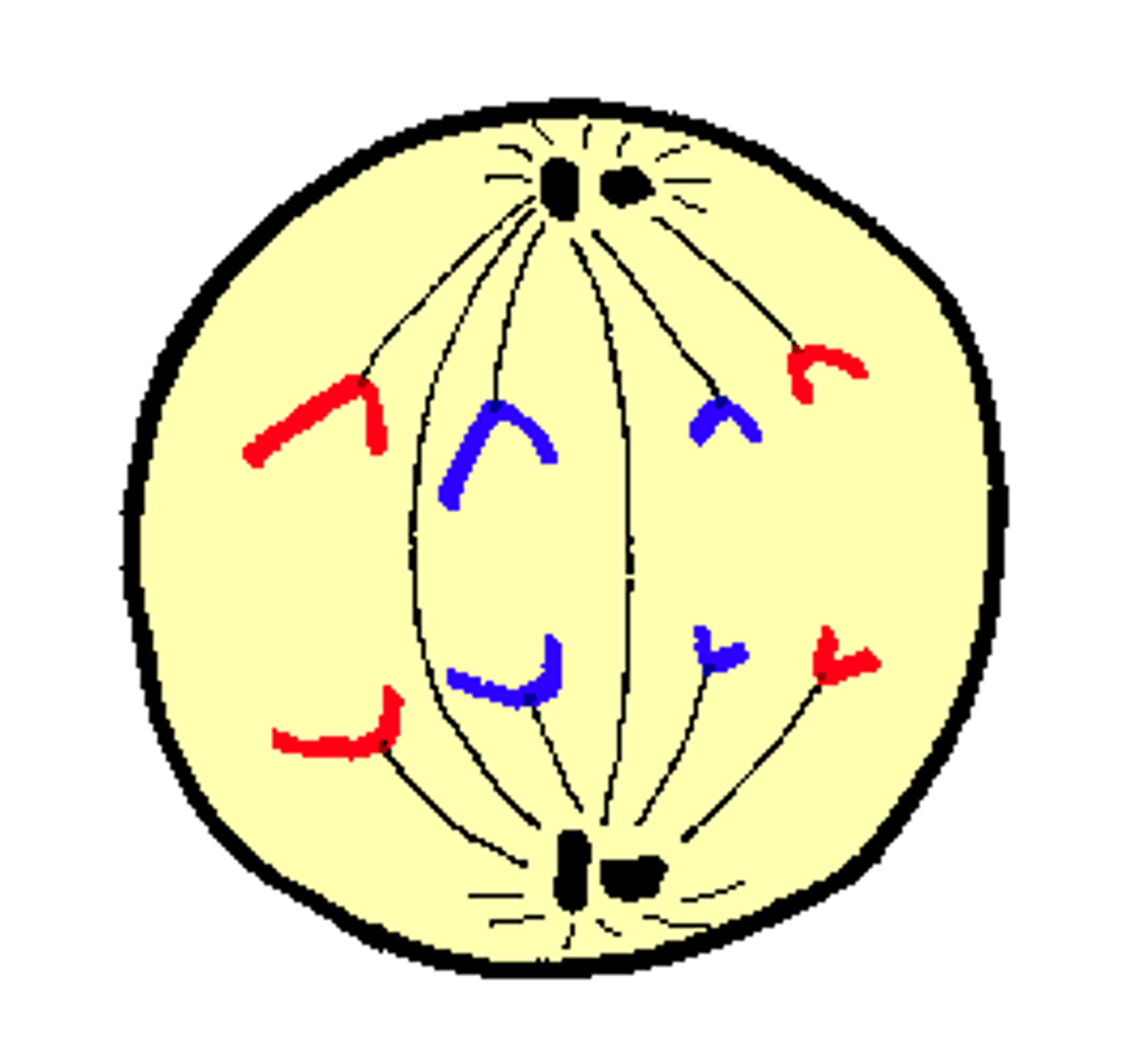
What happens in Anaphase? A for? 1
Away.
Sister chromatids get pulled apart and moved to the opposite sides of cells by the spindles
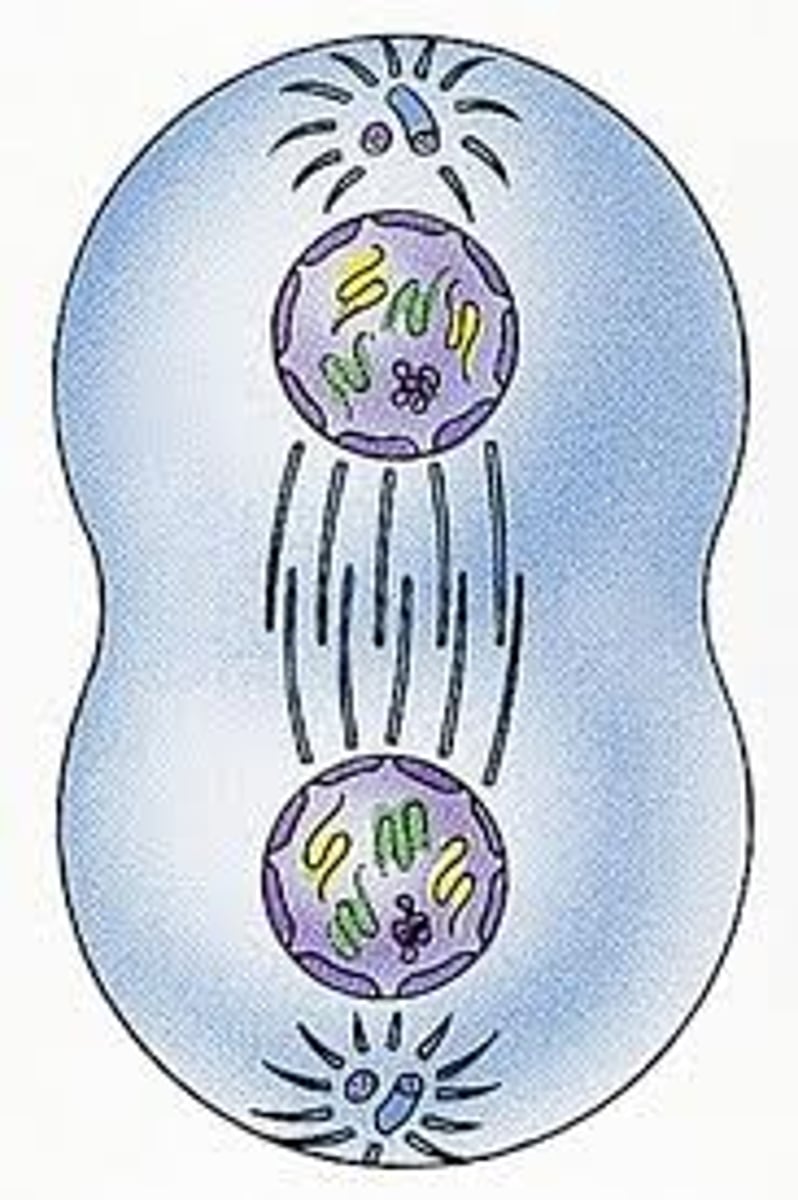
What happens in telephase? T for? 3
Two.
Nucleus reforms, spindles fibers disapear, chromosomes start to no longer be visible
What happens in Cytokynesis?
Cytoplasm divides to create to identical daughter cells. Cell membrane pinches and causes clevage until fully apart and now 2 cells
What happens in a plant cell division?
Can't pinch due to cell wall, cell plate forms down middle and will turn into new cell wall for 2 new cells?
Why do cells divide?
To help repair the body and for general maintenance of body tissue. To make new cells to repair damaged ones.
What is a cyclin? When does it show?
A protein that helps regulate the cell cycle. Only when needed at checkpoints
What is CDK?
Enzyme that is always present but only works when cyclin needed is present. Regulates cell cycle
What do CDK and cyclin do together?
Manage checkpoints
How do the dependent and independent reactions relate and work together in photosynthesis?
They work together to create sugar for the plant.
- the light dependent creates ATP and NADPH which the Calvin Cycle uses to create sugar(gluclose)
What is the job of photosystem II in the electrons transport chain? 2 main things
- absorbs sunlight energy, which charges the electrons
- it splits H2O molecules, releasing oxygen (and hydrogen ions)
What happens in photosystem I in the electron transport chain? 1 thing photosynthesis
- electrons are recharged (in the same way as photosystem II)
What is the overall goal of the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH
What is the energy source in the light dependent reaction?
Sunlight
What are the products from the light dependent that go in the light independent reaction?
ATP and NADPH
natural selection
nature/ environment an organism is in will determine what traits are favorable + survive
artificial selection
humans choose + breed what trains they find favorable in an organism