Gleim Stage 1 Study questions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the purpose of wing flaps?
To enable the pilot to make steeper approaches to a landing without increasing the airspeed.
2 multiple choice options
One of the main functions of flaps during approach and landing is to?
Increase the angle of descent without increasing airspeed
2 multiple choice options
What is the purpose of the rudder on an airplane?
To control yaw.
The rudder controls the aircraft around the vertical or yaw axis.
2 multiple choice options
What are the three primary flight controls?
Ailerons, Rudder, Elevator
The elevator controls movement around which axis?
Lateral
2 multiple choice options
Which Statement is true concerning primary flight controls?
The effectiveness of each control surface increases with speed because there is more airflow over them
2 multiple choice options
Trim systems are designed to do what?
They relieve the pilot of the need to maintain constant back pressure on the flight controls.
The four forces acting on an airplane in flight are?
Lift, weight, thrust, and drag
When are the four forces that act on an airplane in equilibrium?
During unaccelerated level flight
What is the relationship to lift, drag, thrust, and weight when the airplane is in straight and level flight?
Lift equals weight and thrust equals drag
Which statement relates to Bernoulli's principle?
Air traveling faster over the curved upper surface of an airfoil causes lower pressure on the top surface.
The acute angle A is the angle of?
attack
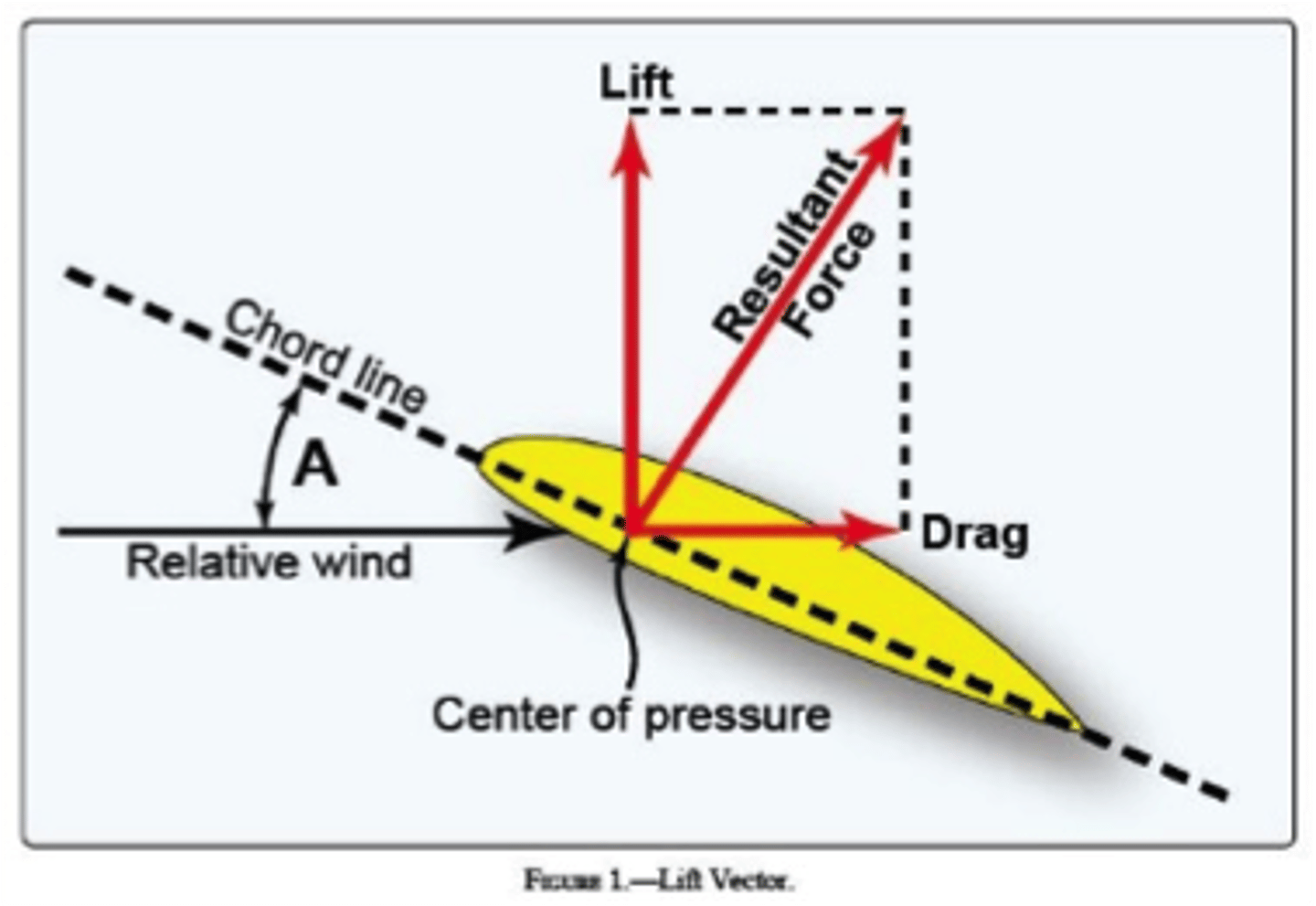
Angle of attack is defined as the angle between?
A chord line of the wing and the relative wind
The angle of attack at which an airplane wing stalls will?
Remain the same regardless of gross weight
As altitude increases, the indicated airspeed at which a given airplane stalls in a particular configuration will
Remain the same regardless of altitude
All the performance factors of an airplane are dependent upon air density. As air density decreases, the airplane stalls at a higher true airspeed. However, you cannot detect the effect of high density altitude on your airspeed indicator. Accordingly, an airplane will stall in a particular configuration at the same indicated airspeed regardless of altitude
In what flight condition must an aircraft be placed in order to spin?
Stalled
During a spin to the left, which wing(s) is/are stalled?
Both wings are stalled
What is ground effect?
The result of the interference of the surface of the Earth with the airflow patterns about an airplane.
Floating caused by the phenomenon of ground effect will be most realized during an approach to land when at
Less than the length of the wingspan above the surface
What must a pilot be aware of as a result of ground effect?
Induced drag decreases; therefore, any excess speed at the point of flare may cause considerable floating
What makes an airplane turn?
The horizontal component of lift.
What determines the longitudinal stability of an airplane
The location of the CG with respect to the center of lift
Positive stability is attained by having the center of lift behind the center of gravity. Then the tail provides negative lift, creating a downward tail force, which counteracts the nose's tendency to pitch down
An airplane said to be inherently stable will
require less effort to control.
A stable airplane will tend to return to the original condition of flight if disturbed by a force such as turbulent air and requires less effort to maintain control.
An aircraft leaving ground effect during takeoff will
Experience an increase in induced drag and a decrease in performance
Changes in the center of pressure of a wing affect the aircraft's
Aerodynamic balance and controllability
CP (center of pressure) is the imaginary but determinable point at which all of the upward lift forces on the wing are concentrated. At high angles of attack the CP moves forward while at low angles of attack the CP moves aft. The relationship of the CP to center of gravity (CG) affects both aerodynamic balance and controllability
An airplane has been loaded in such a manner that the CG is located aft of the aft CG limit. One undesirable flight characteristic a pilot might experience with this airplane would be?
difficulty in recovering from a stalled condition
What causes an airplane to pitch nose down when power is reduced and controls are not adjusted?
The downwash of the elevators from the propeller slipstream is reduced and elevator effectiveness is reduced.
The relative wind on the tail is the result of the airplane's movement through the air and the propeller slipstream. When the slipstream is reduced, the horizontal stabilizer will produce less negative left and the nose will pitch down.
What is the effect of advancing the throttle in flight?
Both aircraft groundspeed and angle of attack will increase
When advancing the throttle, initially the groundspeed increases due to the corresponding increase in airspeed. This causes the aircraft to pitch up, increasing the angle of attack. Airspeed and lift continue to increase until the opposing forces equalize.
Loading an airplane to the most aft CG will cause the airplane to be
less stable at all speeds
Airplanes become less stable at all speeds as the center of gravity is moved backward. The rearward center of gravity limit is determined largely by considerations of stability
An airplane loaded with the Center of Gravity (CG) rear of the aft CG limit could
Increase likelihood of inadvertent overstress
Tail-heavy loading produces very light control forces, which makes it easy for the pilot to inadvertently overstress the aircraft
In what flight condition are torque effects more pronounced in a single-engine airplane?
Low airspeed, high power, high angle of attack.
the effect of torque increases in direct proportion to engine power and inversely to airspeed. Thus, at low airspeeds, high angle of attack, and high power settings, torque is the greatest.
The left tending turning tendency of an airplane caused by P-factor is the result of the?
Propeller blade descending on the right, producing more thrust that the ascending blade on the left.
When does P-factor cause the airplane to yaw to the left?
When at high angles of attack
P-factor occurs when an airplane is flown at a high angle of attack because the downward-moving blade on the right side of the propeller has a higher angle of attack which creates higher thrust than the upward-moving blade on the left. Thus, the airplane yaws around the vertical axis to the left
Which basic flight maneuver increases the load factor on an airplane as compared to straight-and-level flight?
Turns
Turns increase the load factor because the lift from the wings is used to pull the airplane around a corner as well as to offset the force of gravity. The wings must carry the airplane's wight plus offset centrifugal force during the turn. For example, a 60° bank results in a load factor of 2 and the wings must support twice the weight they do in level flight
If an airplane weighs