Exam 3 - Deuterostomes, Animal Evolution, Reproduction Speciation
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
all animals in the chordate phylum share these characteristics that appear at some stage during their development:
notochord
dorsal hollow nerve cord
pharyngeal gill slits
post-anal tail
endostyle/thyroid gland
class asteroidea
sea star
class ophiuroidea
brittle stars
echinoidea
sea urchins, sand dollars
crinoidea
sea lilies
holothuroidea
sea cucumbers
5 classes under the echinoderm phylum
asteroidea
ophiuroidea
echinoidea
crinoidea
holothuroidea
adult echinoderms have _________ symmetry
pentaradial
larval forms of echinoderms exhibit _______ symmetry
bilateral
echinoderms
capable of regeneration
water vascular system
lack a head region, but do have a nerve ring
binary fission
occurs in prokaryotic microorganisms and in some invertebrate organisms; after a period of growth, an organism splits into two separate organisms
budding
results from the outgrowth of a part of a cell or body region leading to a separation from the original organism into two individuals
fragmentation
the breaking of the body into two parts with subsequent regeneration.
budding occurs commonly in invertebrate animals such as:
corals and hydras
parthenogensis
an egg that develops into a complete individual without being fertilized. the resulting offspring be either haploid or diploid, depending on the process and the species
deuterostomes
anus forms first
chordates have _____ symmetry
bilateral
unochordata
turnicates
tunic
cellulose-like carbohydrate material that covers the whole body
adult turnicates are:
sessile
do not possess a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, or post-anal tail
the “tadpole” larval form of turnicates:
possess all structures of a chordate
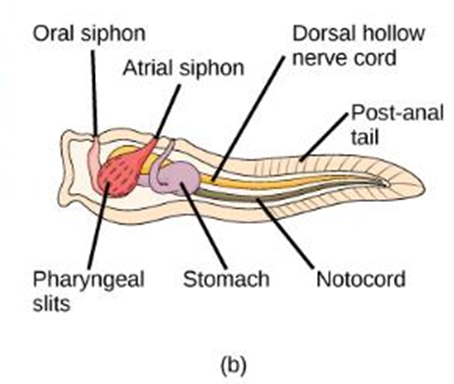
turnicate larva/ “tadpole”
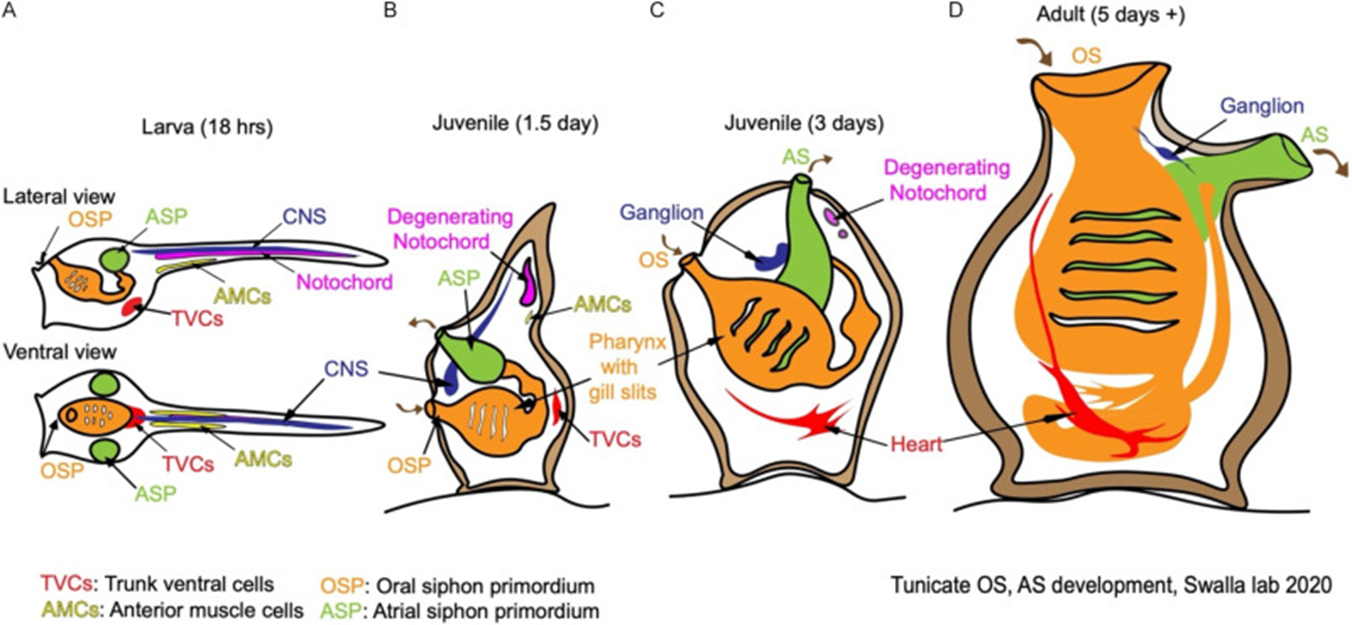
turnicate development
some tunicate species may reproduce by:
budding
gnathostomes
“jawed mouth”, fish and tetrapods
tetrapod
“four-footed” amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
agnathan
jawless
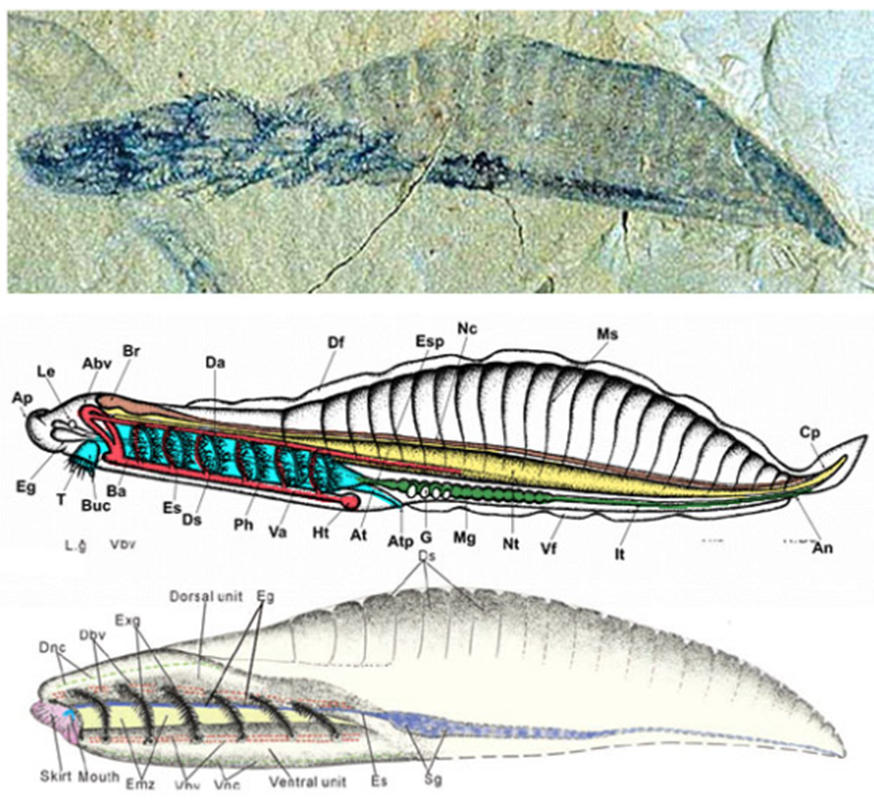
haikouella
haikouella
chordate, has some advanced cephalization, craniate-like
hagfish
chordate with a head but no jaw
sexual reproduction
allows genetic variation
asexual reproduction
genetically identical to the parent
external fertilization
can result in a greater mixture of genes within a group
offspring produced must mature rapidly
survival rate of eggs is low
internal fertilization
protects the fertilized egg from predation or dehydration
fewer offspring
higher survival rate
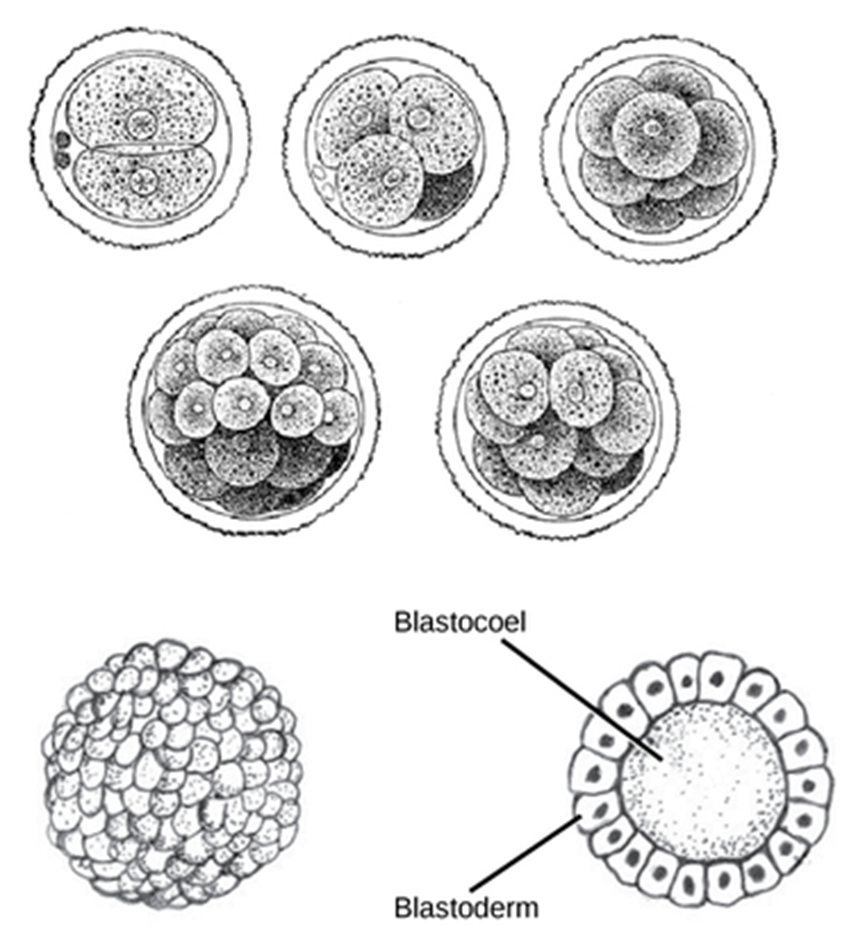
zygote to blastula
gastrulation
blastula folds upon itself to form the three layers of cells
endoderm
internal layer; lung, thyroid, and digestive cells
mesoderm
middle layer; muscle cells, red blood cells, and tubule cells of the kidney
endoderm
external layer; skin cells of epidermis, neurons
organogenesis
organs form from the germ layers through the process of differentiation
differentiation
when the embryonic stem cells express specific sets of genes which will determine their ultimate cell type
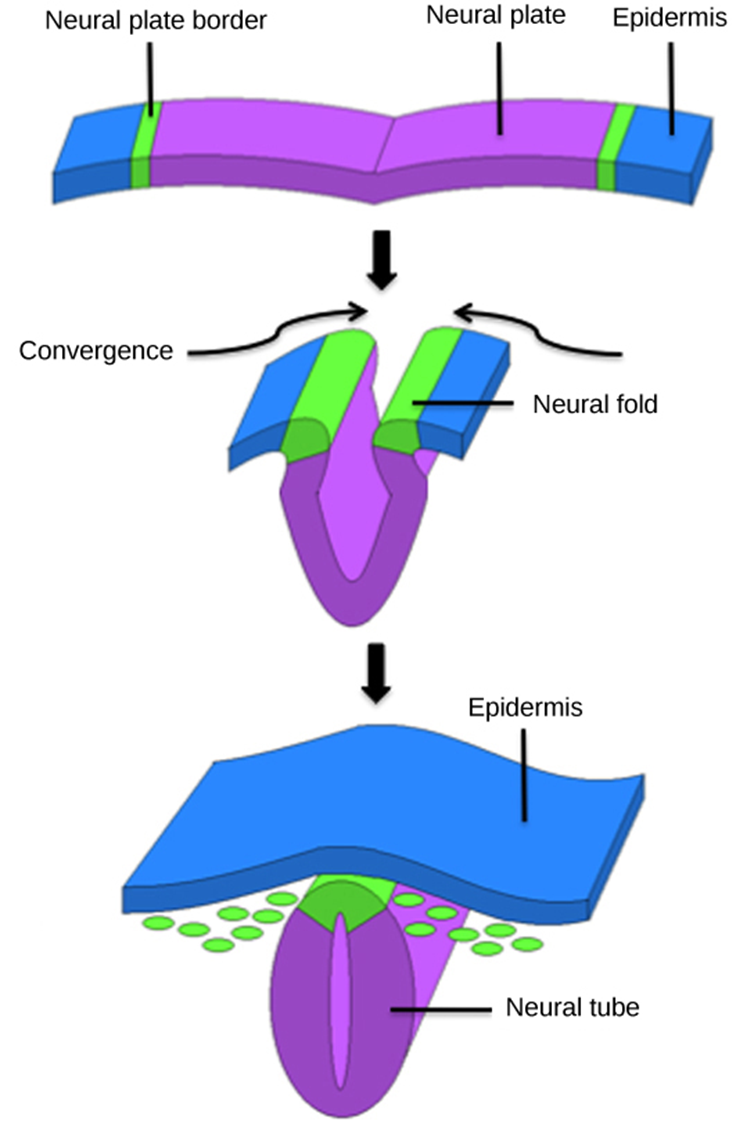
formation of the neural tube
why is exposure to toxins especially dangerous during the first trimester?
all of the organ systems are in their initial development stages
adaptation
a heritable trait that helps an organisms survival and reproduction
divergent evolution
2 species that evolve in diverse directions from a common point
gene pool
shared pool of DNA information among organisms able to produce viable offspring together
reproductive isolation
driver for divergent evolution or differences in lineages
types of reproductive isolation
prezygotic v.s postzygotic barriers
prezygotic barrier
before mating/fertilization
postzygotic barrier
after fertilization
how can a postzygotic barrier occur?
embryo doesn’t survive
if embryo survives, adult may be sterile (ex: mule)
prezygotic barrier types
habitat
temperate
behavioral
mechanical
behavioral isolation
when the presence or absence of a specific behavior prevents reproduction
species
group of individual organisms that interbreed and produce fertile, viable offspring
why are tunicates classified as chordates?
at some point in their lives, they have a dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail
what adaptations permitted the transition from water to land?
limbs and digits and having lungs
stages of development:
fertilization > cleavage > gastrulation > neurulation > organogenesis > growth
which germ layer will form the skin cells of the epidermis and the neurons of the brain?
ectoderm
which germ layer will form the dermis of the skin and muscle?
mesoderm
broadcast spawning
mechanism for fertilization and colonization of new environments for sessile aquatic organisms (ex: sponges)