gastrointestinal tract
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lab practical
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
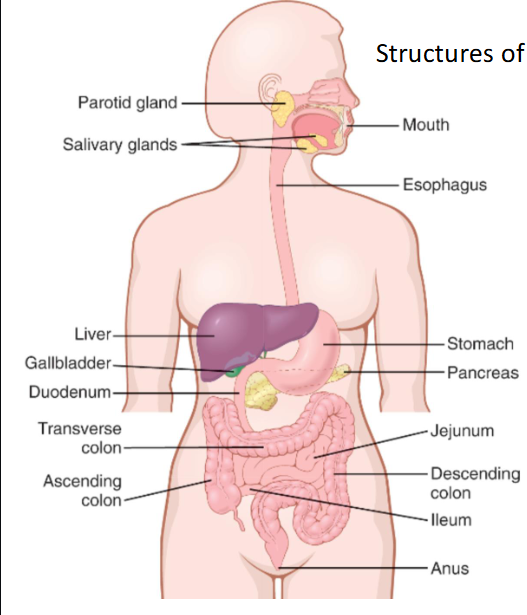
basics of GI
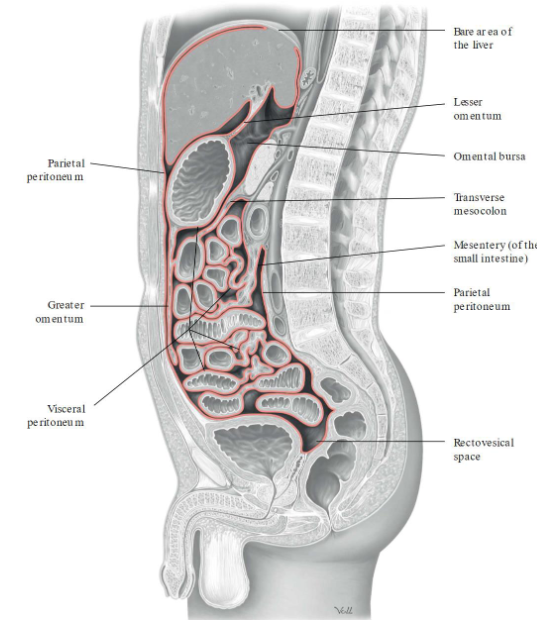
Peritoneum: serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity
Two layers
Parietal peritoneum: lines the internal surface of the abdominopelvic wall
Peritoneal cavity: space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum
Contains peritoneal fluid: water, electrolytes, substances similar to interstitial fluid
Visceral peritoneum: covers the intraperitoneal organs
Kidneys are retroperitoneal → behind the peritoneal cavity
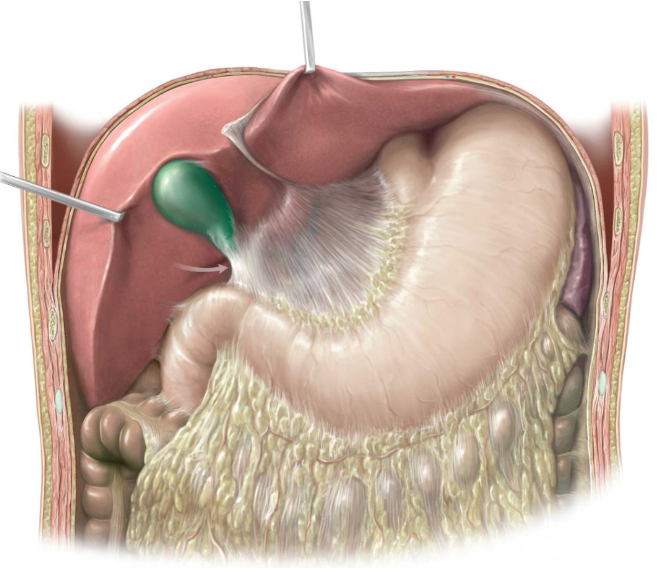
mesentery
Mesentery: serous membranes attached to the abdominal organs to hold them in place
Fat tissue → covers organs
Greater omentum: 4 layered mesothelium made up of simple squamous epithelium
Inferior to stomach
Go down towards the bladder
Lesser omentum: connects the lesser curvature of the stomach and the proximal end of the duodenum to the liver and the diaphragm
Superior to stomach
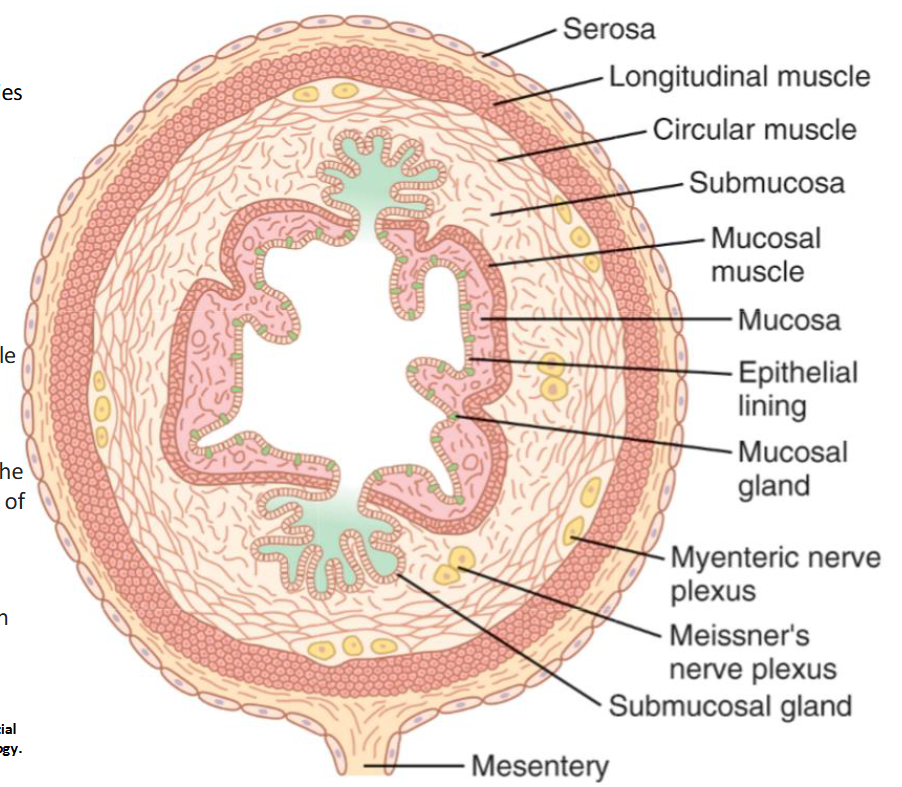
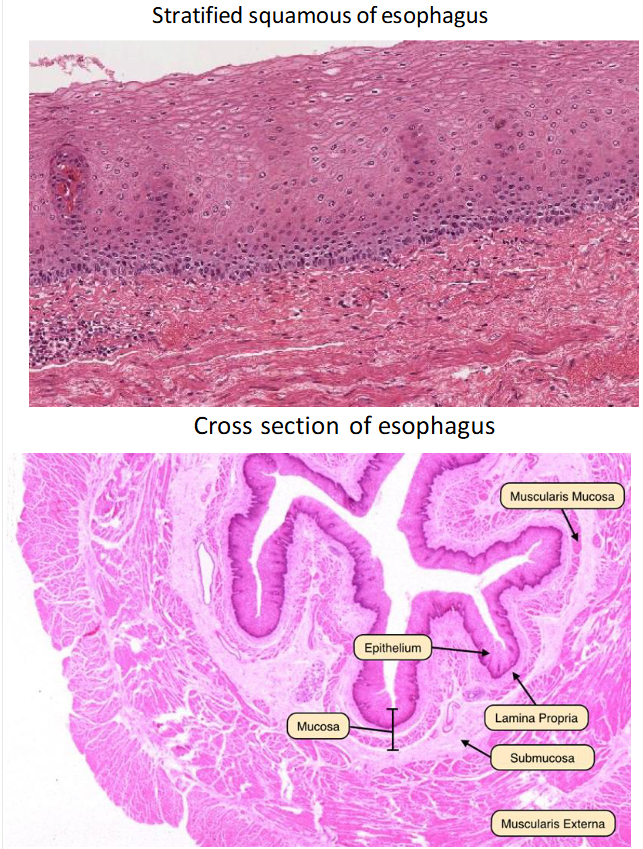
gastrointestinal tract cross section
Epithelial lining of the mucosa exposed to the lumen is stratified squamous
Same for any lining of the internal tubes (GI tract, anus, esophagus, etc)
The GI tract has its own nervous system
Myenteric plexus: controls main GI movements
Meissner’s plexus: inner plexus controlling GI secretions and local blood flow
Things move because there are muscles contracting
Slow waves: low electrical potential that occurs 24/7
Do not require an AP to occur
Generated and propagated by Interstitial cells of Cajal → spread to surrounding smooth muscle cells and control motility
Spike waves: initiated by APs in the smooth muscle
Promote motility → movement of contents through the GI tract
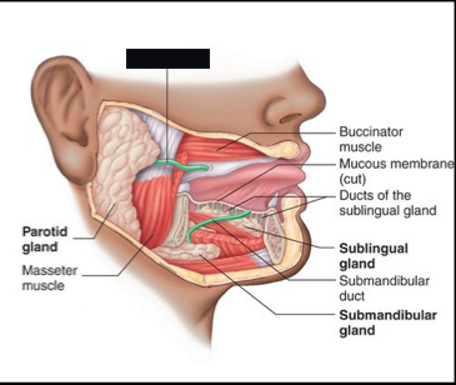
saliva
Saliva glands
Parotid gland
Sublingual gland
Submandibular gland
Contents of saliva
Lysozyme
Ptyalin or salivary amylase → breaks down carbs
Bicarbonate ions → buffer neutralizing acids
Immunoglobulins → prevent bacterial infections
Saliva protects the outer mucosa
Mucus protects the digestive tract from physical irritation
Lingual lipase helps begin lipid digestion
Increased salivation can be initiated by the facial nerve and the glossopharyngeal nerve
Protects epithelial cells from infection, dehydration, and physical or chemical injury
esophagus
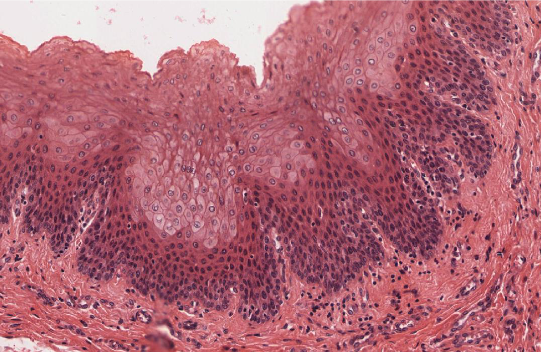
oropharynx
Oropharynx: starts from the mouth
Stratified squamous epithelium → non-keratinizing
Rests on a lamina propria
Contains a thick layer of longitudinally oriented elastic fibers
Lacks muscularis mucosae and submucosa
peristalsis
moves bolus toward the stomach
propulsion
moving food forward as in peristalsis
mixing
segmental contractions (non-propulsive)
No net movement forward
slow waves
interstitial cells of Cajal of the myenteric plexus forms specialized pacemaker cells that promote rhythmic contractions of smooth muscle throughout the gastrointestinal tract
motility
contraction of smooth muscle along the G.I. tract and moving it contents along with it
spike waves
true action potentials
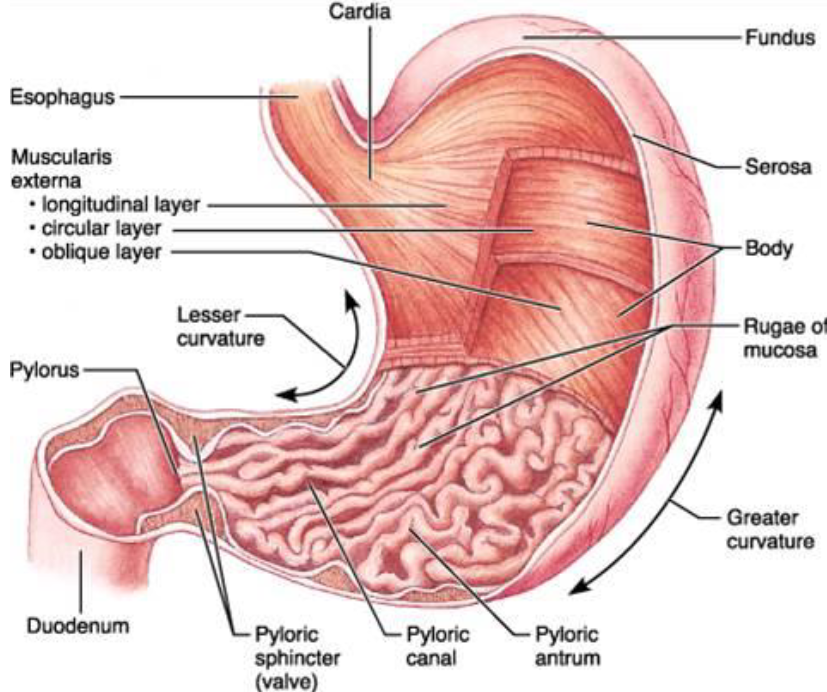
stomach
Food first enters the fundus
Muscles relax → allow for stretching of the stomach
“Vagovagal reflex” results from the stretching of the stomach
Signal travels from stomach to the brainstem → reduces the tone in the muscular wall of the stomach body
Accommodates greater amount of food
Food in the stomach mixes with stomach secretions → what flows down the gut is chyme
Stomach emptying: pushing of food into the duodenum
Duodenum: breaks down food
Pyloric sphincter holds food in the stomach until duodenum is clear
Both the gastroesophageal and the pyloric sphincter control the movement of the food in and out of the stomach
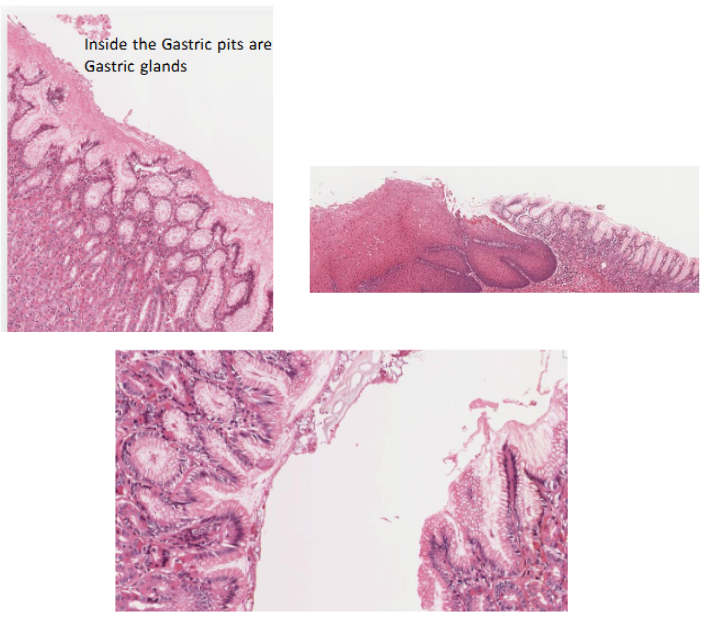
hydrochloric acid production
CO2 and Cl- diffuse from the blood into the stomach cell
CO2 combines with H2O to form H2CO3
H2CO3 dissociates into bicarbonate (HCO3-) and H+
ATP pump is necessary to pump the H+ and Cl- into the duct since the concentration of HCl- is about a million times more concentrated in the duct than in the cytosol of the cell
H- combines with Cl- in duct of gastric gland to form HCl-
Now you have stomach acid
HCO3- goes to the respiratory system to expel CO2
gastrin
source: stomach
stimulus: stretches walls of stomach
response: increase secretion of HCL (hydrochloric acid)
cholecystokinin
source: small intestine
stimulus: fatty acids and pepties
response:
stimulates pancreatic enzyme, pancreatic bicarbonate secretion,
gallbladder contraction
growth of exocrine pancreas
inhibits gastric emptying
ghrelin
source: stomach
stimulus: empty stomach
response:
stimulates appetite
increases food intake
promotes fat storage
intrinsic factor
source: parietal cells of stomach
response: necessary for B12 absorption
secretin
source: duodendum
stimulus: acidity of chyme
response:
decreases gastric secretion
stimulates pancreas secretion of bicarbonate ions
pepsin
source: stomach
stimulus: presence of pepsinogen
response:
HCL and pepsin converts pepsinogen → pepsin
(pepsin is a protein)
GIP
source: duodenum
stimulus: fat and glucose levels
response:
stimulates insulin release
inhibits gastric acid secretion
motilin
source: duodenum
stimulus: fatty acids
response: stimulates gastric and intestinal motility
pancreatic amylase
source: pancreas
stimulus: digestion in small intestine
response: breakdown of carbohydrates
nuclease
source: pancreas
stimulus: digestion in small intestine
response: breakdown of nucleic acids
trypsin
source: pancreas
stimulus: digestion in small intestine
response: breakdown of proteins
peptidase
source: pancreas
stimulus: digestion in small intestine
response: breakdown of amino acids
gastric lipase
source: pancreas
stimulus: digestion in small intestine
response: breakdown of lipids
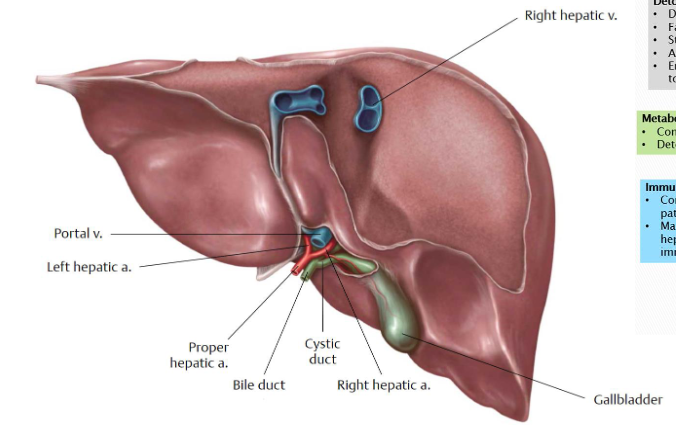
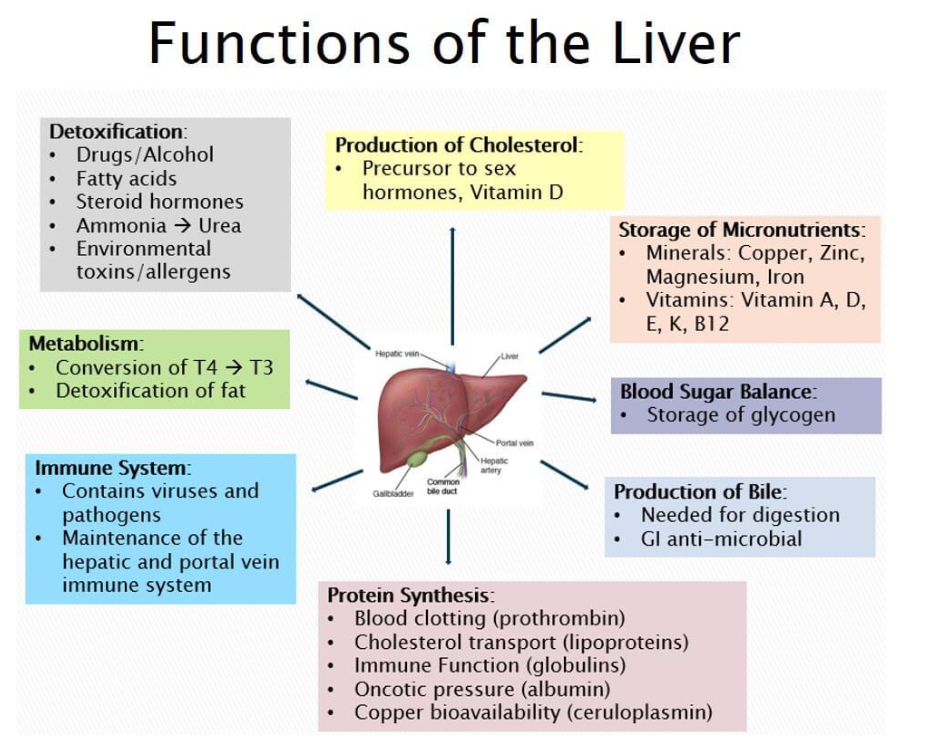
liver
Food does not go through the liver
Can regenerate itself
Functions
Manufactures bile
Stored by the gallbladder
Is a detergent
Opens up a molecule → breaks down bonds that are in the way
So that enzymes can reach/bind to the active site of the molecule
Protein synthesis
Immune system
Metabolism
Detoxification of chemicals and bacteria
Production of cholesterol
Storage of micronutrients
Blood sugar balance
Produces blood proteins
Filters blood
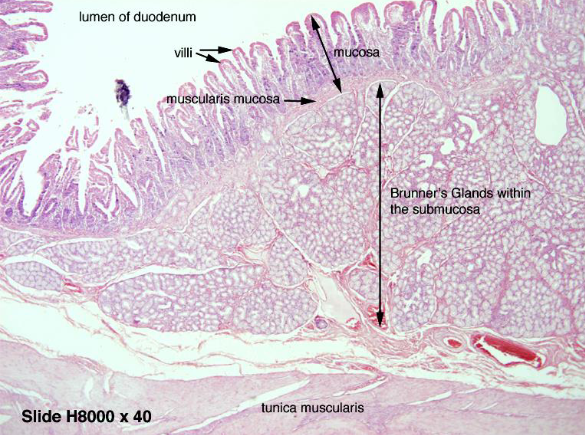
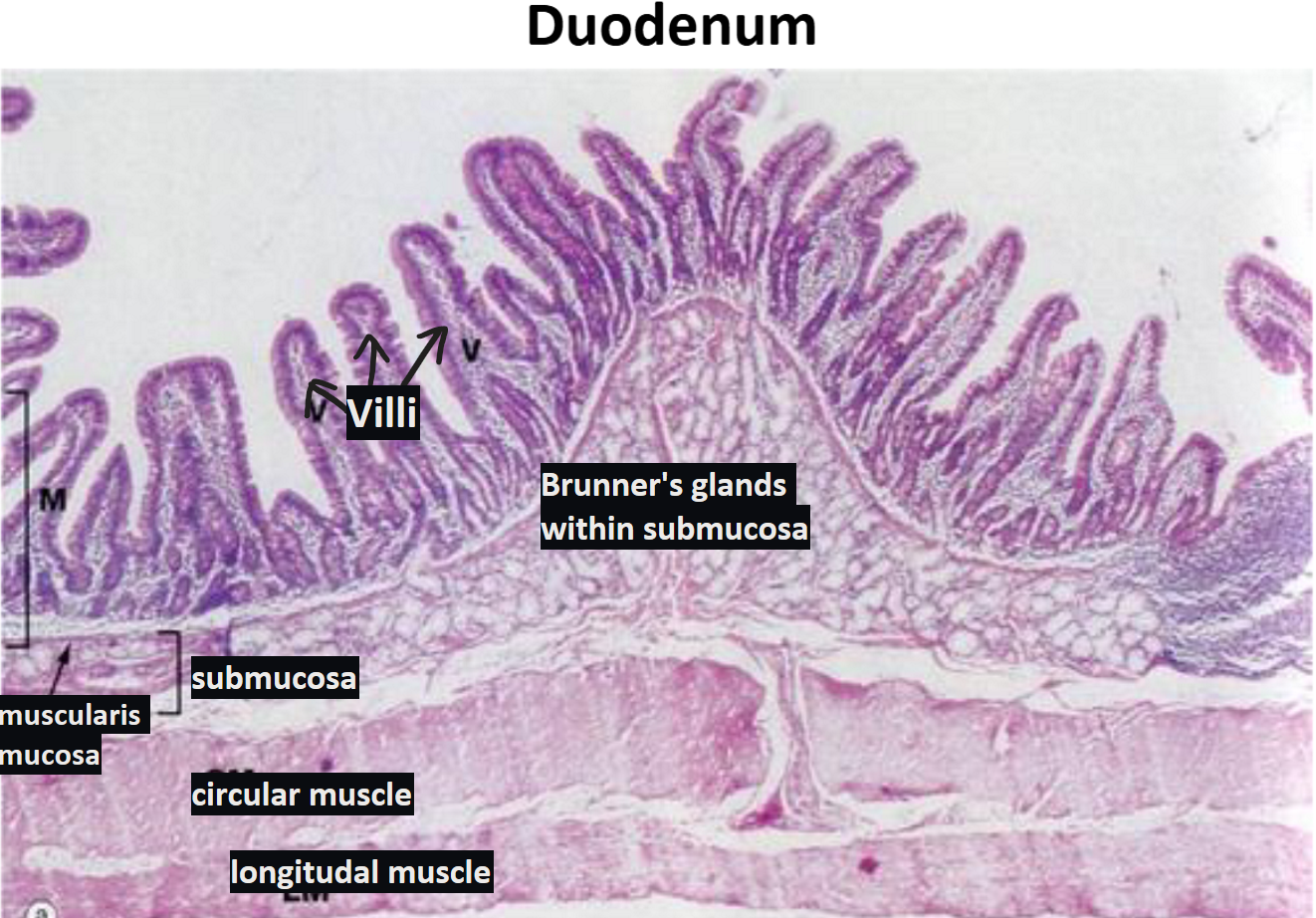
duodenum
Epithelial tissue faces the lumen ALWAYS → here its columnar cells
Layers in order
Simple columnar with microvilli lining the mucosa
Lamina propria (CT)
Muscularis mucosa (submucosa) → with Brunner's glands
Secretes mucus
Coats the duodenal epithelium to protect it from stomach acids
Empty into the intestinal glands
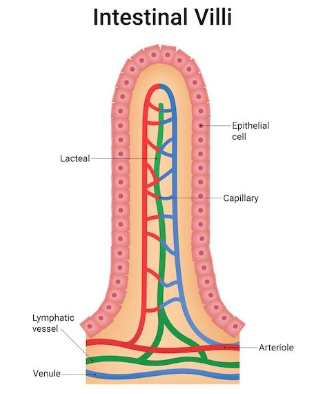
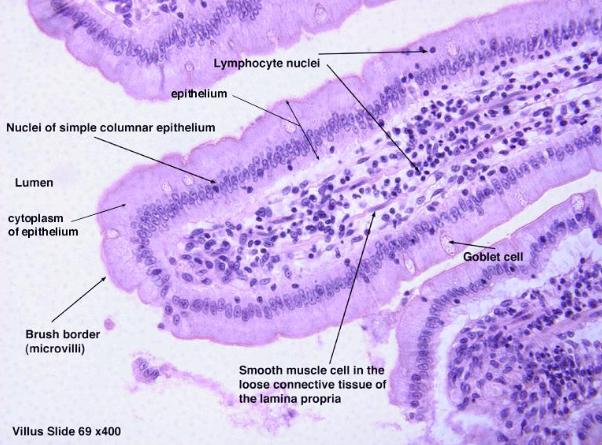
intestinal villi
Increase surface area (SA)
Contain goblet cells: secrete mucus
On top of each villus is microvilli: one of the brush borders
Increase surface area to absorb nutrients
Have a blood supply to receive nutrients into the bloodstream
jejunum
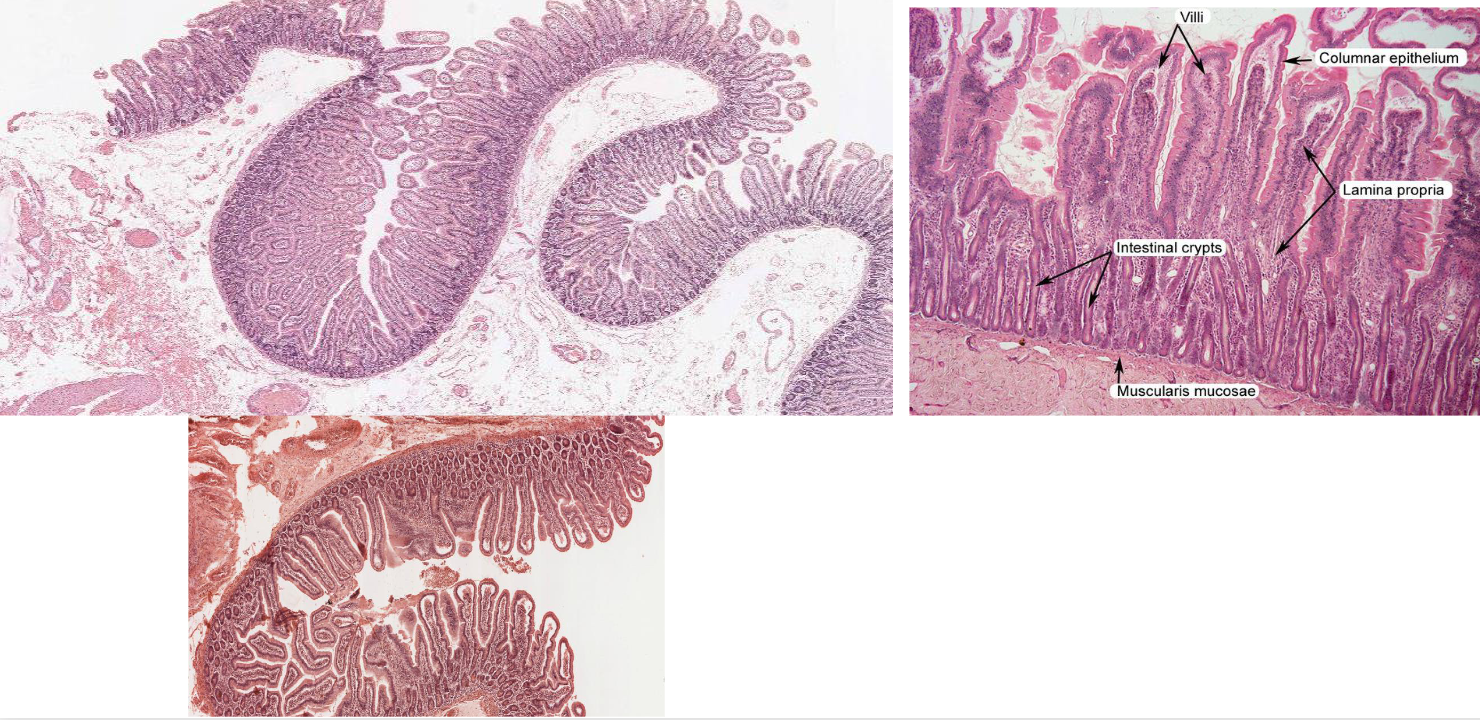
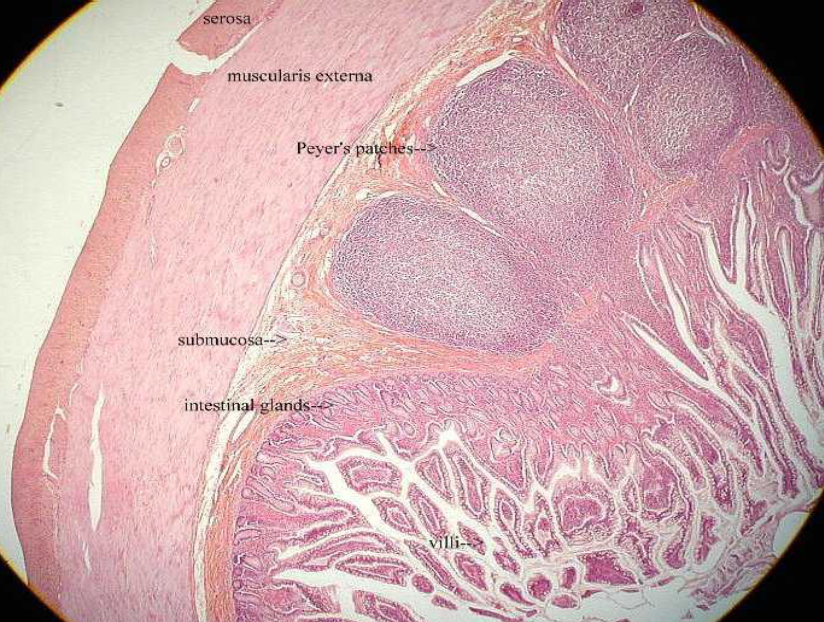
ileum of small intestine
crypts (i.e, mucosal glands) of the ileum of the small intestine lie within a lamina propria
rich in lymphocytes, eosinophils, and plasma cells
Peyer’s patches: lymph nodules found in the ileum of the small intestine
Part of the immune system
Have different immune cells: B and T lymphocytes
Not a lot of nutrient absorption occurs here
Main function in immune system → instead protection from microorganisms
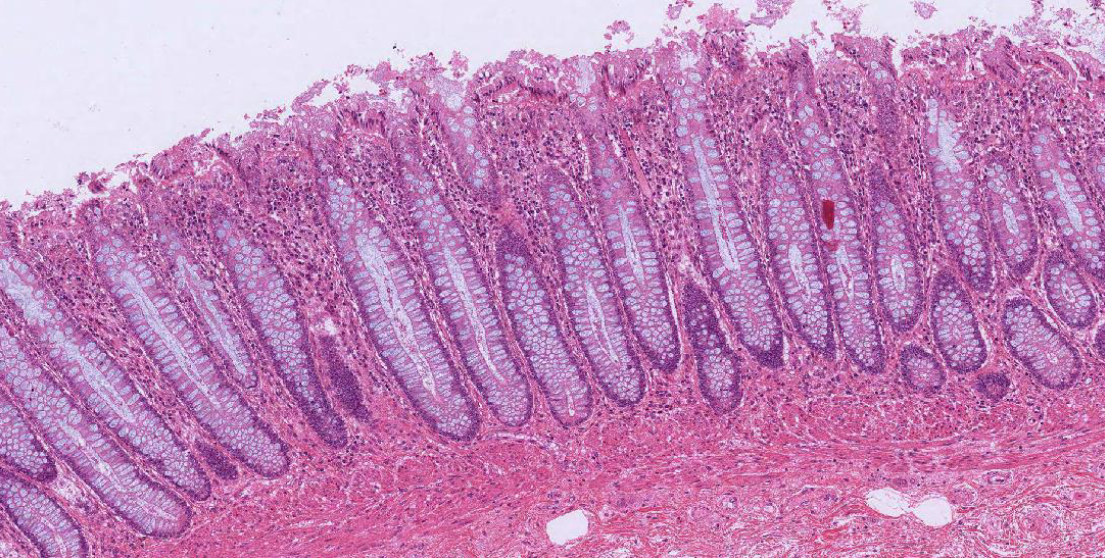
large intestine
Feces consists of water, undigested food (cellulose), microorganisms, sloughed-off epithelial cells
Good bacteria
Break down carbs
Involved in immune response
Produce vitamin K → absorbed
Mucus provides protection