9. Esters
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
What are the properties of Esters?
Have distinct smells (fruits & perfumes)
Used in processed foods
cannot H bond so very insoluble
Can also be used in medications, solvents and explosives
can be separated by distillation
How do you name Esters?
First name comes from the alcohol (does not have the carbonyl
take the name of the alcohol and change ending to -yl
Second name: carboxylic acid
take name of acid and change ending to -anoate
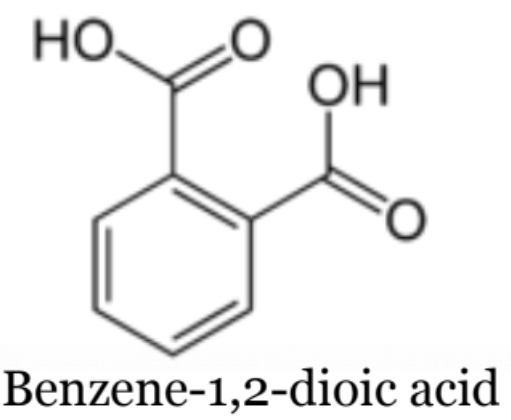
What is Esterfication?
the condensation reaction that forms an ester; an alcohol combining with a carboxylic acid and creating a water molecule
Reaction of Esters: Hydrolysis
reverse of esterfication
ester mixed acid or base will back into alcohols and carboxylic acids
Real example: fats and oils are esters from long-chain acids. When heated with a base, hydrolysis happens and makes soap.