PULM/HEME EXAM 2 🫁
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
What regulates bronchodilation in airway smooth muscle?
The sympathetic (adrenergic) nervous system.
Which receptors mediate bronchodilation, and what activates them?
β2-adrenergic receptors; activated by epinephrine.
What regulates bronchoconstriction in airway smooth muscle?
The parasympathetic (cholinergic) nervous system.
Which receptors mediate bronchoconstriction, and what stimulates them?
Muscarinic M3 receptors; stimulated by acetylcholine.
What other fibers regulate bronchial smooth muscle tone besides adrenergic and cholinergic systems?
Nonadrenergic, noncholinergic (NANC) fibers in the respiratory tree.
Which mediators act as bronchoconstrictors from NANC fibers?
Neurokinin A, calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P, bradykinin, tachykinin, neuropeptide Y.
Which mediators act as bronchodilators from NANC fibers?
Nitric oxide (NO)
Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)
Which interleukin induces eosinophil proliferation and survival?
IL-4.
Which interleukin recruits eosinophils?
IL-5.
Which interleukin activates eosinophils?
IL-33.

Which interleukin stimulates TH2 & ILC2 function?
IL-25.
Which interleukin chemoattracts TH2 cells?
IL-33.
Which cytokine activates DCs to promote TH2 differentiation?
TSLP.
Which interleukin induces B cells to produce IgE?
IL-4.
👉 Why? IgE is what arms mast cells against allergens — when allergens show up, mast cells dump histamine and leukotrienes, causing bronchoconstriction. At the same time, IL-4 keeps eosinophils alive to prolong the attack.
Which interleukin induces goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus production, and smooth muscle hyperplasia?
IL-13.
👉 Why? IL-13 makes airways clogged with mucus and thickened with extra smooth muscle. This means air can't flow normally → wheezing, coughing, and harder-to-treat asthma.
Which interleukins initiate macrophage switch to M2?
IL-4 & IL-13.
What is the role of airway epithelial cells in immunity?
First line of innate immune sensing; produce cytokines (IFN-α, β, γ, IL-33, IL-25, TSLP, CCL2, CCL20).
What do Toll-like receptors (TLR) recognize?
Nucleic acids (TLR3, TLR7, TLR9) and lipopolysaccharide (TLR4).
What do RIG-like receptors (RLR) recognize?
Replicating RNA viruses.
What do protease-activated receptors (PAR) detect?
Nonfungal allergens; elicit allergic airway inflammation in response to proteolytic allergens.
Allergens (like P for Pollen)
What do NOD-like receptors (NLR) detect?
Bacterial peptidoglycans.
Bacteria
What do C-type lectin receptors detect?
Fungal patterns.
Fungus
Where are dendritic cells located in the airway and what do they do?
On the basolateral side of the epithelium; sample antigens with pseudopodia and express pattern recognition receptors.
What are cDCs (conventional dendritic cells)?
Finish development in the lung; can induce TH2 & TH17 helper cells OR TH1, TH2, T cytotoxic, and Treg cells depending on subtype.
Conventional found in the lung
What are pDCs (plasmacytoid dendritic cells)?
Fully develop in bone marrow; maintain tolerance to harmless antigens and drive antiviral responses.
What are moDCs (monocyte-derived dendritic cells)?
Present in steady-state lungs; important in antiviral responses and can contribute to pulmonary immunopathology.
be MINDFUL of these
Both alveolar and interstitial macrophages are ________
fetal yolk-sac derived and express pattern recognition receptors.
What are the key functions of alveolar macrophages (AM)?
Sit at the frontlines of alveoli → must clean up inhaled debris (phagocytosis), present antigens to T cells, and balance between defense (inflammation) vs. tolerance (activate Tregs).
Their M1/M2 switch lets them go pro-inflammatory or repair mode depending on signals.
Interstitial macrophages
Deeper in parenchyma → act as "regulators" of lung environment.
Interstitial macrophages have a high _______ baseline that makes them immunosuppresive, preventing overreaction.
IL-10/IL-6/IL-1ra
Interstitial macrophages also respond to _______
hypoxia, important for lung tissue repair and vascular balance.
M1/M2 and IM1/IM2 diversity
Reflects macrophages' ability to polarize → either drive inflammation (M1/IM1) or promote tissue repair/tolerance (M2/IM2).
What are the 3 subsets of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in the airway?
ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3.
What do ILC1 cells do?
Include NK cells; release IFN-γ and TNF-α; increase in lung pathology.
What do ILC2 cells do?
Produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-13; activated by IL-25 and IL-33; increase with allergic lung inflammation.
What do ILC3 cells do?
Produce IL-22 and/or IL-17 in response to IL-23; help develop secondary lymphoid tissue; may contribute to COPD.
What do Tc (cytotoxic T cells) do?
CD8+ effector cells; kill virally infected or transformed (tumor) cells.
What do Th (helper T cells) do?
CD4+ cells that direct immune responses.
What do Th1 cells do?
Produce IFN-γ, IL-2, TNF-α; promote cellular responses with Tc and Th cells.
What do Th2 cells do?
Guide antibody production (allergy/parasite).
Produce IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-13
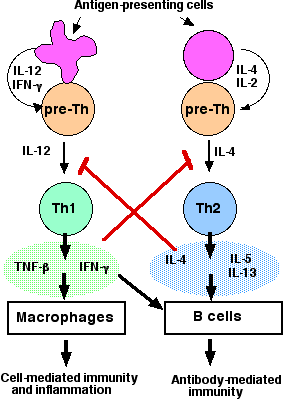
What do Th17 cells do?
Promote neutrophil migration, chemokine secretion, enhance Th2 responses.
Produce IL-17
What is the Hygiene Hypothesis (Missing Old Friends Hypothesis) of Allergy?
Lack of infection or exposure to microbes humans co-evolved with favors allergic disease.
What infections are key in this hypothesis for restoring immune balance?
Mycobacteria and helminths → stimulate TH1 responses and regulatory mechanisms.
How do multiple/repetitive infections during development affect allergy/asthma risk?
Shape the immune system and reduce risk of allergic disease.
What role do nonpathogenic organisms play?
Help regulate the immune system (e.g., Prevotella copri).
_____ asthma is IgE mediated and also called “allergic asthma.”
Extrinsic (Type 2)
In intrinsic (non-allergic) asthma, serum IgE levels are ______.
normal or low
Intrinsic asthma is also called ______ asthma.
Type 1/17
Intrinsic asthma often has later onset and shows ______ predominance.
female
The precipitating factor for intrinsic asthma is often ______.
unknown (may be environmental, stress, or hormones)
Occupational asthma requires ______ to a specific chemical (e.g., isocyanates, flour, latex, glue).
sensitization
______-induced occupational asthma develops after a single, very high exposure to an irritant chemical and is not immune related.
Irritant
In intrinsic (non-allergic) asthma, serum IgE levels are ______.
normal or low
Intrinsic asthma is also called ______ asthma.
Type 1/17
Intrinsic asthma often has later onset and shows ______ predominance.
female
What causes airway narrowing in asthma?
Bronchospasm, mucosal edema, mucus plugging
What causes hyperinflation in asthma?
Functional residual capacity rises; helps keep airways open
What happens to the accessory muscles during asthma?
Accessory muscles used to maintain hyperinflation
What happens to gas exchange during asthma?
Hypoxemia due to V/Q mismatch during severe attacks
Late Phase Asthma Response
Inflammatory cascade causing persistent obstruction
Modifiable Factors that can lead to Severe Asthma
Uncontrolled asthma symptoms
High SABA use (≥3 canisters/year)
Poor adherence to ICS
Incorrect inhaler technique
Smoking
Allergen exposure
Air pollution
Physiological Factors that can lead to Severe Asthma
Low FEV1 (<60% predicted)
High bronchodilator response
Elevated eosinophils
High FeNO
Comorbidities which can contribute to asthma severity
Obesity, rhinosinusitis, GERD, food allergy, pregnancy
Medical History which can lead to Severe Asthma
Prior ICU/intubation
≥1 severe exacerbation in last 12 months
Medication risks that can lead to severe Asthma
Frequent oral corticosteroids
Long-term high-dose ICS (esp. with CYP450 inhibitors)
Developmental Risks which can lead to worse Asthma
Preterm birth, low birth weight, chronic mucus hypersecretion
Symptoms characteristic of asthma
Multiple: wheeze, shortness of breath, cough, chest tightness
Worse at night/early morning
Variable over time/intensity
Triggers: viral infections, exercise, allergens, weather changes, cold air, laughter, irritants (smoke, exhaust, strong smells)
SABA (albuterol, levalbuterol) MOA
β2 agonist → bronchodilation
SABA (albuterol, levalbuterol) ADR
Tremor, tachycardia, hypokalemia
Fastest onset, preferred reliever
SABA
Anticholinergic (ipratropium) MOA
Blocks M3 receptors → ↓ bronchoconstriction
Anticholinergic (ipratropium) ADRs
Dry mouth, blurred vision
ICS ADR
Thrush, dysphonia, systemic effects (high dose)
ICS MOA
↓ airway inflammation
LABA ADR
Tremor, tachycardia
LABA MOA
Long β2 agonism
LABA (formoterol, salmeterol, vilanterol) are always combined with what?
ICS
Systemic steroids (prednisone, methylprednisolone) MOA
Broad anti-inflammatory
Systemic steroids (prednisone, methylprednisolone) ADRs
Hyperglycemia, mood changes, Cushing’s (chronic use)
Leukotriene modifiers (montelukast, zafirlukast, zileuton) MOA
Block leukotriene signaling
Leukotriene ADRs
Neuropsychiatric (montelukast), hepatotoxicity (zafirlukast, zileuton)
Theophylline MOA
PDE inhibition, ↑ cAMP
Theophylline ADRs
Nausea, arrhythmias, seizures
Note for Theophylline
Narrow therapeutic index
Biologics for Asthma MOA
Target IgE, IL-5, IL-4R, TSLP
Biologics for Asthma ADR
Hypersensitivity, eosinophilia
LAMA (tiotropium) MOA
Block M3 receptor
LAMA (tiotropium) Common ADRs
Dry mouth, headache
Airsupra®
Budesonide/Albuterol → ICS + SABA
Symbicort®
Budesonide/Formoterol → ICS + LABA
Advair
Fluticasone/Salmeterol → ICS + LABA
Dulera®
Mometasone/Formoterol → ICS + LABA
Breo Ellipta®
Fluticasone/Vilanterol → ICS + LABA
Trelegy Ellipta®
Fluticasone/Vilanterol/Umeclidinium → ICS + LABA + LAMA
Breztri Aerosphere
Beclomethasone/Formoterol/Glycopyrrolate → ICS + LABA + LAMA
Chronic (Stepwise, GINA 2024) Asthma Treatment
Step 1-2: AIR only (budesonide-formoterol or budesonide-albuterol) PRN
Step 3: Daily low-dose ICS-formoterol + PRN
Step 4/5: Higher-dose ICS-formoterol, add-ons (LAMA, biologics)
Acute Exacerbation Asthma Treatment
Early ↑ reliever (SABA/ICS-formoterol)
Add oral steroids 5–7 days if moderate-severe
Remove trigger, monitor PEF
Discharge: ICS optimization, follow-up in 2–7 days
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm (EIB)
Regular ICS helps prevent
Pretreat with SABA or low-dose ICS-formoterol before exercise
What are the brand names of albuterol?
ProAir®, Ventolin®, Proventil®
What is the brand name of levalbuterol?
Xopenex®