Lecture 13: Gastrointestinal nematode parasites of swine
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Where do Ascaris suum worms reside in swine?
In the small intestine
What are the sizes of male and female Ascaris suum worms?
Males: 15-25 cm, Females: up to 45 cm
What is the global distribution of Ascaris suum?
Found worldwide, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and the U.S.
What is a distinguishing feature of the oral opening of Ascaris suum?
Three prominent lips
What type of life cycle does Ascaris suum have?
Direct life cycle
How many eggs can an adult female Ascaris suum produce per day?
Approximately 200,000 eggs/day
How long does it take for infective larvae to develop in an egg?
About 28 days under optimal temperature and humidity.
How long can Ascaris suum eggs persist in the environment?
up to 7 years
How does a susceptible host become infected with Ascaris suum?
By ingesting a larvated egg
Describe the migration route of Ascaris suum larvae in the host.
Ingested egg → hepatic blood supply → tracheal migration → lungs → swallowed → small intestine
What is the prepatent period for Ascaris suum?
about 8 weeks
What role do rodents play in the life cycle of Ascaris suum?
They can serve as paratenic hosts
What is the primary method of diagnosing Ascaris suum infection?
fecal flotation
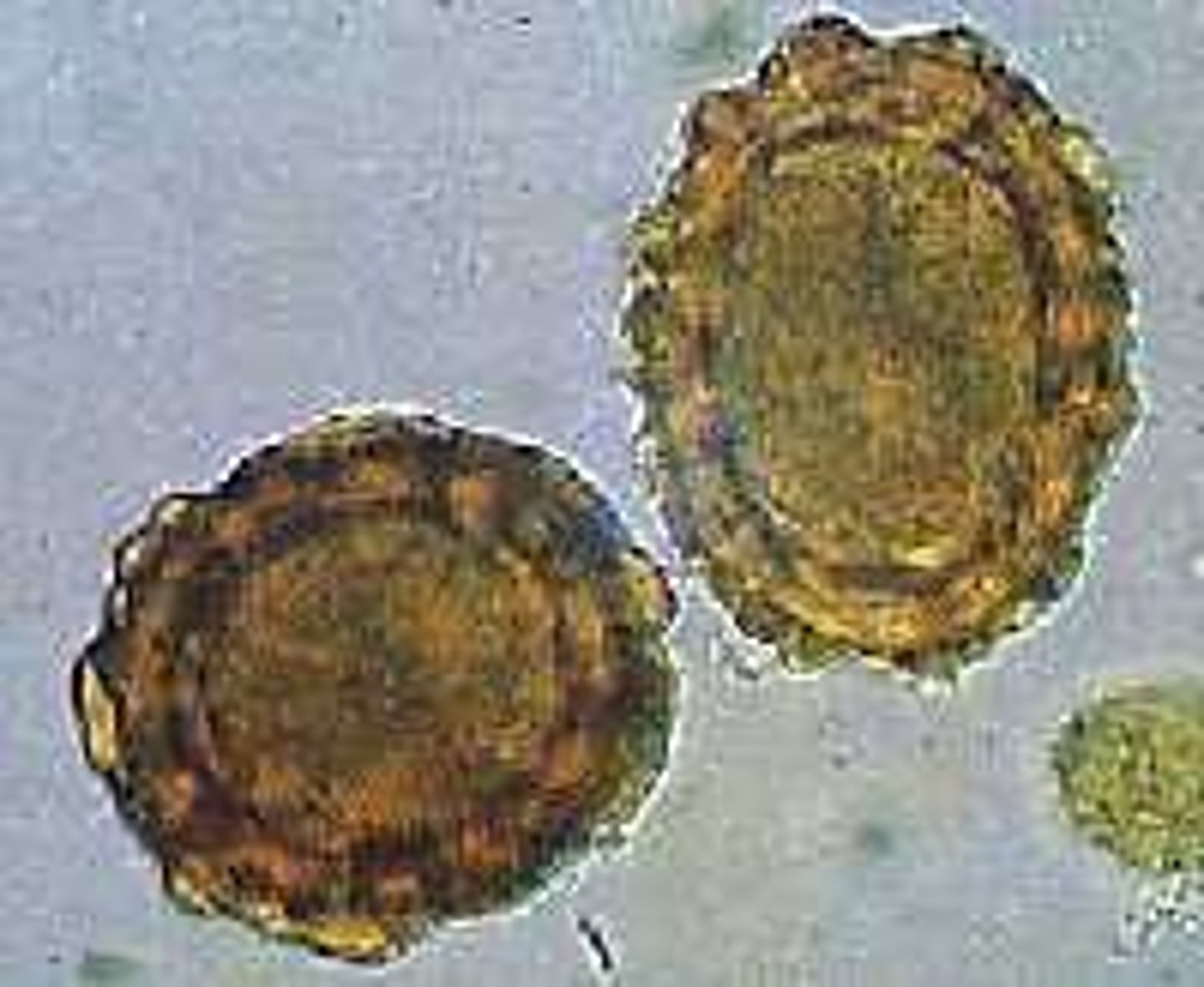
Describe the characteristics of Ascaris suum eggs
- Size: ~62 x 45 μm
- Thick, mammilated shell
- Golden brown color
- Single-cell (uninfective) when passed
- Sticky albuminous coat
How does Ascaris suum infection affect piglets?
Stunted growth, poor feed efficiency, and potential intestinal impaction.
What causes inflammation and hypoproteinemia in infected piglets?
Worm presence in the gut leading to nutrient consumption and immune response.
What is the risk for grower/finisher pigs on contaminated pastures?
High risk for disease due to lack of acquired immunity from previous exposure
How can Ascaris suum cause pneumonia and respiratory distress in pigs?
Through tracheal migration of larvae in the lungs.
What is the economic impact of Ascaris suum in slaughtered pigs?
Liver condemnation due to granulomatous "milk spots" ($17/cwt loss)
How can piglets become infected from sows?
By ingesting eggs adherent to the sow's teat while nursing
What drug is effective for removing adult and immature Ascaris suum stages with no withdrawal time?
Fenbendazole (FBZ)
What drug can be given daily to prevent Ascaris suum larval migration?
Pyrantel (24-hour withdrawal time).
How can hygiene help prevent Ascaris suum infection?
Washing sows before farrowing
Providing clean nursing environments
Using slatted floors for confined growers
What condition has been reported in humans due to Ascaris suum?
Visceral larval migrans (VLM).
What clinical signs have been associated with human Ascaris suum infection?
Eosinophilic pneumonia and hepatic lesions.
Why is it difficult to differentiate human Ascaris from Ascaris suum?
They are morphologically indistinguishable and closely related at the molecular level.
What agricultural practice increases the risk of human Ascaris infections in some countries?
Using untreated (non-composted) swine manure as fertilizer
Where do Trichuris suis worms reside in swine?
in the cecum and large intestine
What are the sizes of male and female Trichuris suis worms?
Males: 30-50 mm, Females: 35-50 mm.
What is a distinguishing feature of Trichuris suis?
Stout body with a whip-like esophagus.
What is the global distribution of Trichuris suis?
Cosmopolitan distribution, present worldwide where swine production occurs.
What type of life cycle does Trichuris suis have?
direct life cycle
Where do adult Trichuris suis worms reside in the host?
cecum and large intestine
How long does it take for Trichuris suis eggs to become infective?
About 21 days under optimal temperature and humidity.
How long can Trichuris suis eggs persist in the environment?
up to 7 years
How does a susceptible host become infected with Trichuris suis?
By ingesting a larvated egg
Where do Trichuris suis larvae develop before migrating to their final location?
Beneath the epithelium of the small intestine
What is the prepatent period for Trichuris suis?
About 7-9 weeks
What is the primary method for diagnosing Trichuris suis infection?
fecal floatation
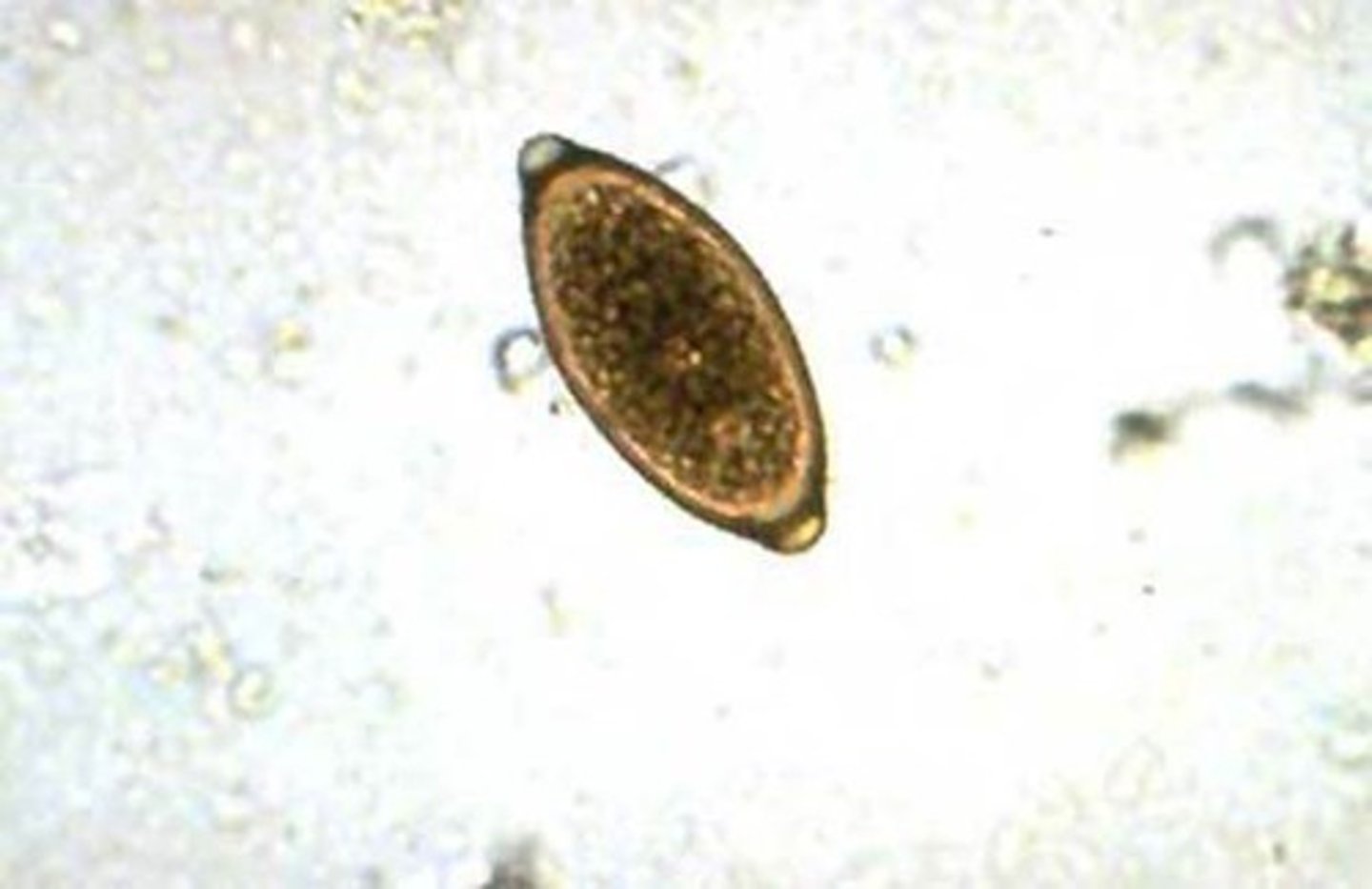
Describe the characteristics of Trichuris suis eggs.
- Size: ~55 x 25 μm
- Elongate with distinct polar plugs
- Golden brown color
- Single-cell (uninfective) when passed in feces
What age group of piglets is most affected by Trichuris suis?
8 to 14 weeks old
What clinical signs are associated with Trichuris suis infection in piglets?
Stunted growth, poor feed efficiency, anemia, diarrhea, dehydration, dysorexia, and weight loss.
What pathological effects can adult Trichuris suis worms induce in the large intestine?
- Colitis
- Mucosal necrosis and edema
- Focal hemorrhage
Why is it difficult to distinguish human Trichuris from Trichuris suis?
They are morphologically indistinguishable, and their eggs are the same size on fecal examination.
What has recent molecular research suggested about Trichuris suis and human Trichuris?
They are closely related, with some suggesting they are the same species.
Is there evidence that Trichuris suis can cause disease in humans?
No, there is no evidence that transmissibility results in human disease.
What novel medical application has been explored using Trichuris suis in humans?
Induced infections as treatment for autoimmune disorders, such as Crohn's disease and autism spectrum disorders.
What is the "Hygiene Hypothesis" in relation to Trichuris suis?
The idea that microbes and parasites co-evolved with humans to regulate immune responses, preventing overactive inflammatory conditions.
How does Trichuris suis influence immune function?
It downregulates inflammatory and immune mechanisms, which may be beneficial in treating immune-mediated disorders.
Where do Oesophagostomum dentatum worms reside in swine?
in the large intestine
What are the sizes of male and female Oesophagostomum dentatum worms?
Males: 8-10 mm, Females: 11-14 mm.
What is a key morphological feature of Oesophagostomum dentatum?
A buccal capsule with a leaf crown
What is the global distribution of Oesophagostomum dentatum?
Cosmopolitan, found worldwide where swine production occurs
What type of life cycle does Oesophagostomum dentatum have?
direct life cycle
Where do adult Oesophagostomum dentatum worms reside in the host?
in the large intestine
How long does it take for infective larvae to develop on pasture?
Within 6 to 7 days under optimal temperature and humidity
What environmental factors affect the survival of Oesophagostomum dentatum larvae?
Larvae are susceptible to desiccation and temperature extremes
How does a susceptible host become infected with Oesophagostomum dentatum?
By ingesting the L3 larval stage
What happens after ingestion of Oesophagostomum dentatum larvae?
1. Larvae penetrate the intestinal wall and develop.
2. They return to the lumen as submature adults (L4 stage).
3. They mature into adult worms and reproduce.
What are the primary clinical effects of Oesophagostomum dentatum infection in piglets?
- Stunted growth and poor feed efficiency
- Nodule formation in the gut
- Enteritis
- Dysorexia
- Blood-stained feces
Why are grower/finisher pigs at significant risk for Oesophagostomum dentatum infection?
Because they are placed on contaminated pastures and do not develop acquired immunity from previous exposure.
What economic losses are associated with Oesophagostomum dentatum infection?
Condemnation of intestines used for sausage casings
What is the primary method for diagnosing Oesophagostomum dentatum infection?
fecal floatation
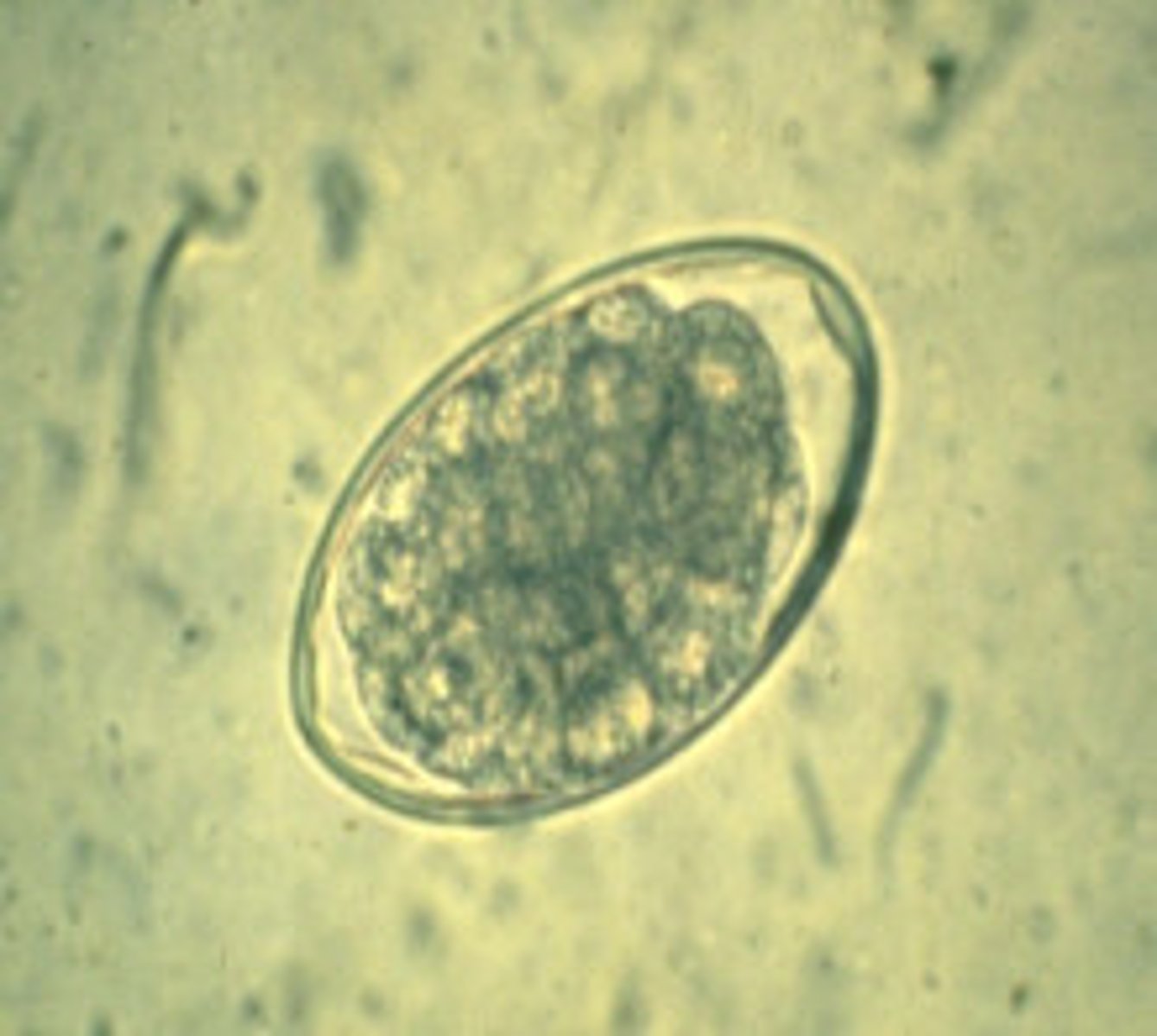
Describe the characteristics of Oesophagostomum dentatum eggs.
- Size: 60-80 μm x 35-40 μm
- Thin-shelled morula
- Uninfective when passed in feces
Is Oesophagostomum dentatum known to be zoonotic?
No, it is not considered zoonotic
What species of Oesophagostomum infects African primates?
African primates have their own species of Oesophagostomum
Can humans be infected with Oesophagostomum species?
Yes, but only occasionally, and they experience similar disease sequelae as other animal hosts.
Where do Stephanurus dentatus worms reside in swine?
Around the kidneys and ureters.
What are the sizes of male and female Stephanurus dentatus worms?
Males: 20-30 mm
Females: 30-45 mm
What is a key morphological feature of Stephanurus dentatus?
A well-defined buccal capsule.
Where is Stephanurus dentatus commonly found?
Worldwide in swine production, especially in backyard/dirt lot operations.
What type of life cycle does Stephanurus dentatus have?
Direct life cycle (Facultative indirect)
Where do adult Stephanurus dentatus worms reside?
In the ureters
How are Stephanurus dentatus eggs excreted from the host?
Eggs are passed in urine
How long does it take for infective larvae of Stephanurus dentatus to develop on pasture?
Within 4 days under optimal temperature and humidity.
What environmental factors affect the survival of Stephanurus dentatus larvae?
Larvae are susceptible to desiccation and temperature extremes.
What are the three ways a susceptible host can become infected with Stephanurus dentatus?
1. Ingestion of L3 larvae
2. Skin penetration
3. Ingestion of an earthworm (paratenic host)
Describe the migration pathway of Stephanurus dentatus larvae.
1. Larvae penetrate the stomach wall and enter the hepatic blood supply.
2. Undergo extensive and destructive systemic migration (3-9 months).
3. Reach the kidneys and ureters, where they mature and reproduce.
What is the prepatent period of Stephanurus dentatus?
9-16 months
What is the primary pathology caused by Stephanurus dentatus?
Extensive and destructive migration, affecting:
- Liver capsule
- Peritoneal cavity
- Perirenal tissues
What are the main clinical signs of a herd-wide Stephanurus dentatus infection?
- Liver cirrhosis
- Stunted growth, poor feed efficiency
- Dysorexia & emaciation
What parts of the pig are condemned at slaughter due to Stephanurus dentatus?
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Pork loin and other choice cuts
What management strategies help prevent Stephanurus dentatus infections?
Attention to hygiene to avoid infection sources
Gilts-only breeding (keeping for one season only)
What is the primary diagnostic test for Stephanurus dentatus?
Identification of eggs in a clean-catch urine sample (if adults are present).
What are the characteristics of Stephanurus dentatus eggs?
Size: 90-120 μm x 43-70 μm
Thin-shelled morula
Uninfective when passed in urine
Why is Stephanurus dentatus often diagnosed at necropsy?
Because its pathology primarily affects internal organs (liver, kidney, ureters), and urine-based diagnosis is less commonly performed.
Is Stephanurus dentatus known to be zoonotic?
No, it is not considered zoonotic.
Why might Stephanurus dentatus be found in commercial meat cuts?
Wandering larvae migrated to peri-renal fat.
Considered indicative of poor butchering technique.
Where do adult Strongyloides ransomi worms reside in swine?
in the small intestine
Which gender of Strongyloides ransomi is parasitic?
Only females are parasitic
What two life cycle types does Strongyloides ransomi have?
Homogonic life cycle - direct development to infective larvae.
Heterogonic life cycle - free-living adult stages.
What type of immunity develops in adult sows against Strongyloides ransomi?
age-associated immunity
How are neonatal piglets infected with Strongyloides ransomi?
By hypobiotic larvae via the lactogenic route.
What is the prepatent period of Strongyloides ransomi?
~7 days (extremely short!).
Why is Strongyloides ransomi highly pathogenic in sucking pigs?
It causes:
- Diarrhea
- Anemia
- Emaciation
What are the other possible routes of Strongyloides ransomi infection besides lactogenic transmission?
1. Ingestion of L3 larvae
2. Percutaneous penetration
What is the clinical significance of Trichinella sp. in swine?
Zoonotic disease in humans.
How is Trichinella sp. traditionally transmitted to humans?
By ingestion of pork from infected domestic swine.
Why has Trichinella sp. become less common in domestic pigs?
Due to total confinement-based production, reducing exposure
What is the primary source of Trichinella infections in humans today?
Wild game meat (e.g., bear meat)