Chapter 9: Articulations (Joints)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Joint (articulation)
•any point where two bones meet, whether or not the bones are movable at that interface
Arthrology
science of joint structure, function, and dysfunction
Kinesiology
study of musculoskeletal movement
-A branch of biomechanics, which deals with a broad variety of movements and mechanical processes
There are many different types of joints; we will discuss the following 3:
-Fibrous joints
-Cartilaginous joints
-Synovial joints
Fibrous Joint
adjacent bones are bound by collagen fibers that emerge from one bone and penetrate into the other
Other terms for fibrous joint
synarthrosis or synarthrodial joint)
3 types of fibrous joints
-Sutures (i.e., in skull)
-Gomphoses (i.e., tooth socket)
-Syndesmosis (eg., radio-ulnar, tibio-fibular)
sutures (fibrous joints)
immobile or slightly mobile fibrous joints in which short collagen fibers bind the bones of the skull to each other
Gomphosis (fibrous joint)
attachment of a tooth to its socket
- attached via short connective tissue fibers
Syndesmosis (fibrous joint)
a fibrous joint at which two bones are bound by long collagen fibers
Other terms for Cartilaginous joint
amphiarthrosis or amphiarthrodial joint
cartilaginous joint
two bones are linked by cartilage
-Examples include pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs
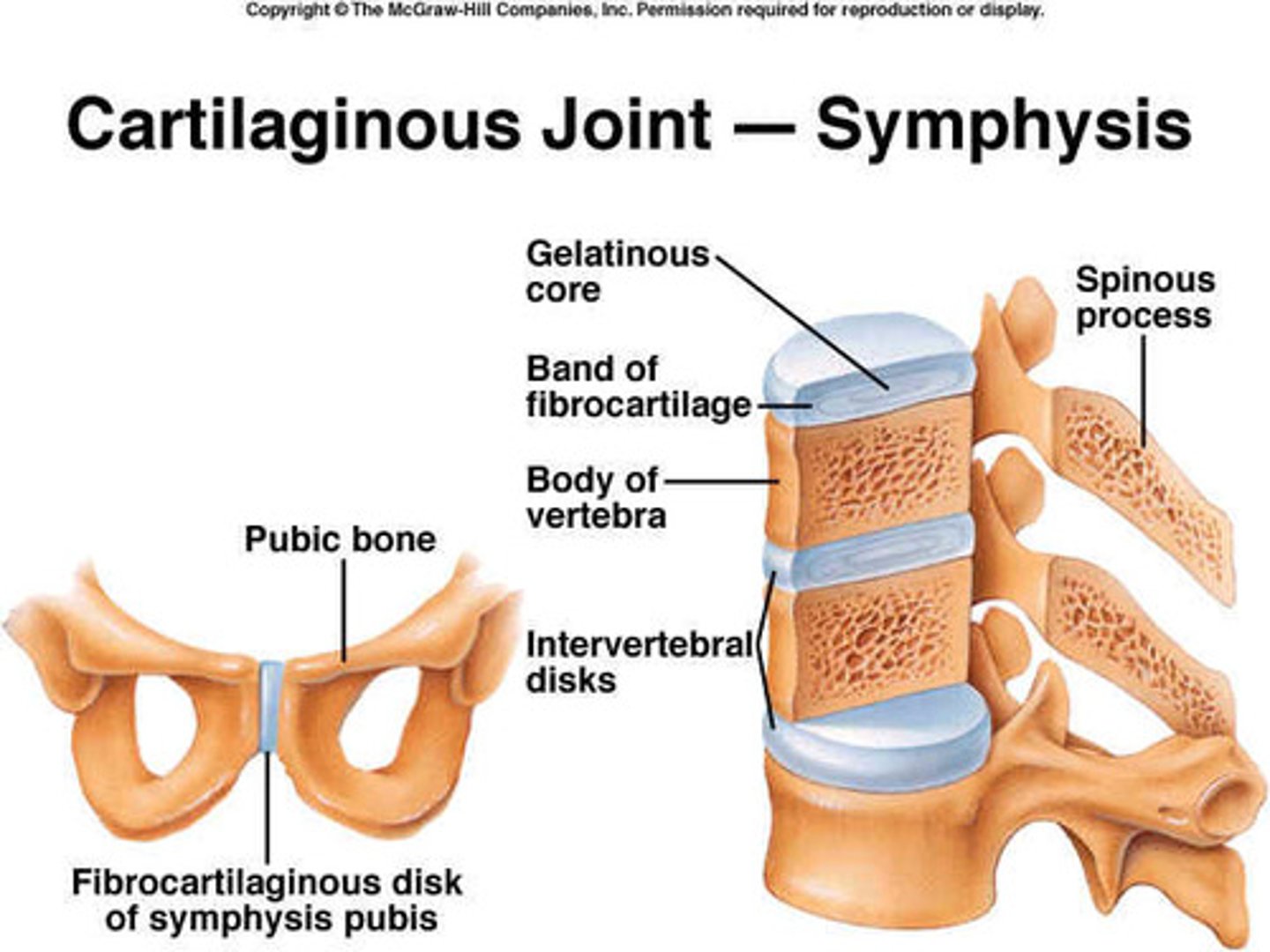
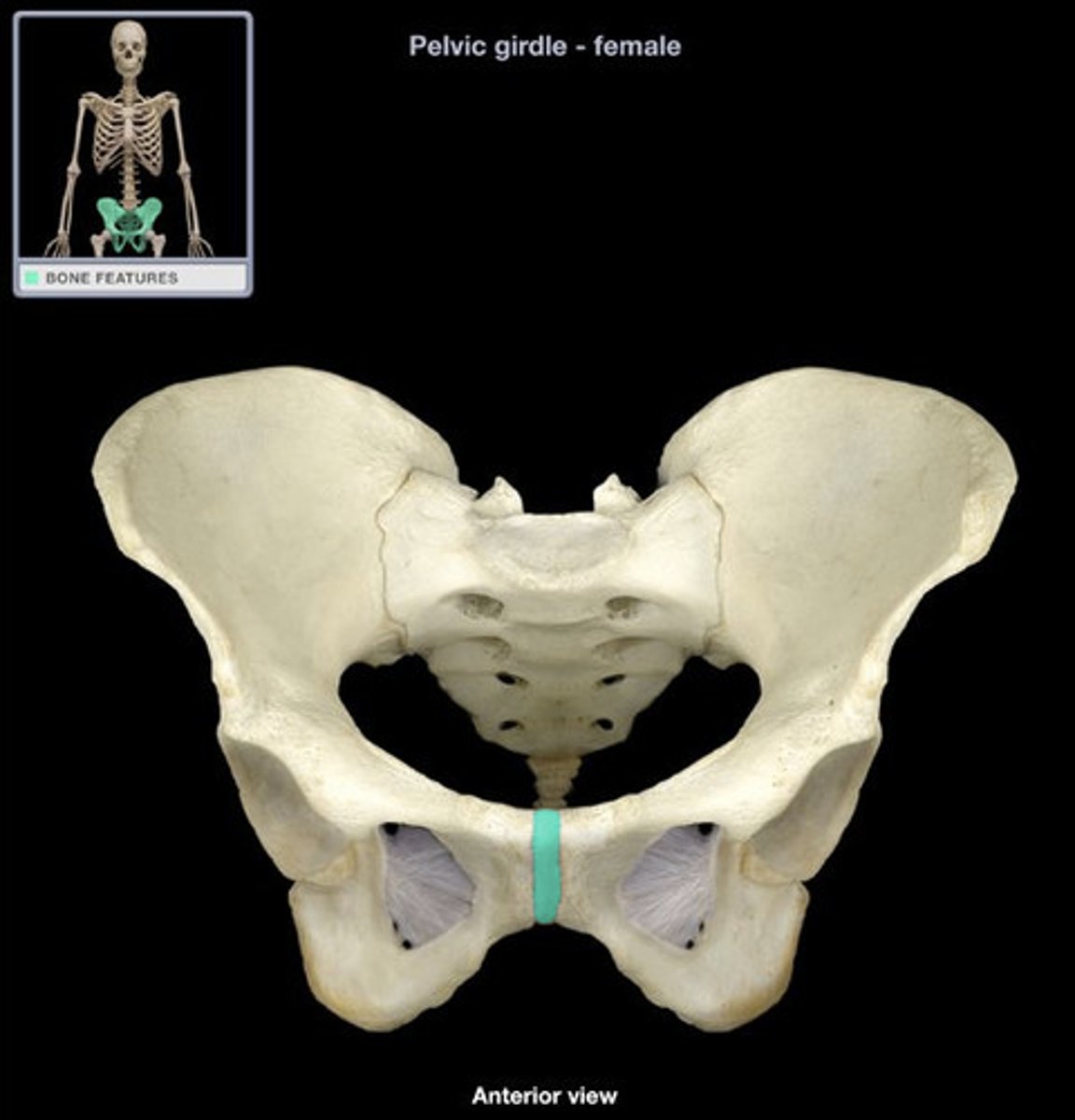
pubic symphysis
joins right and left pubic bones with interpubic disc
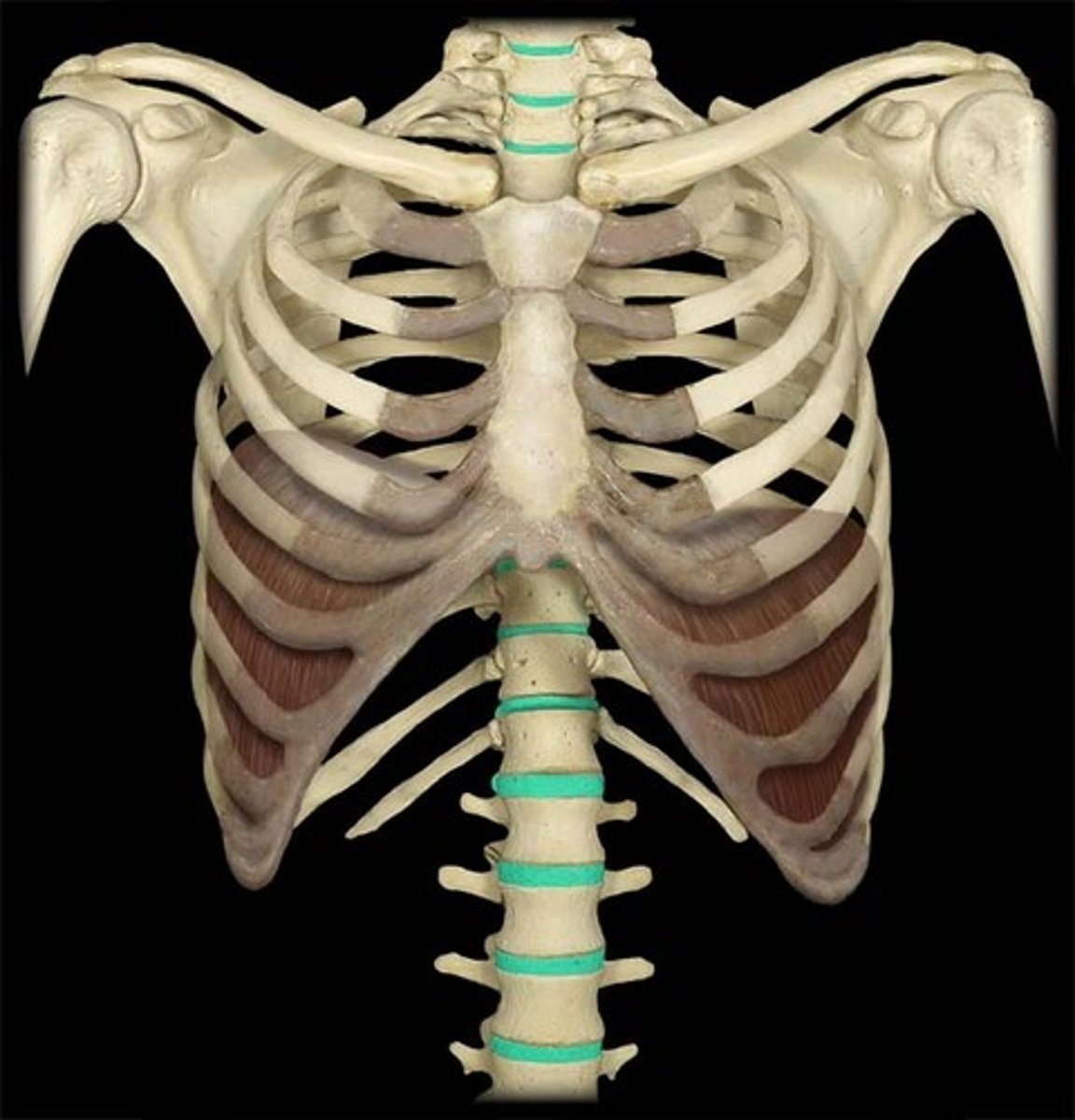
Bodies of vertebrae joined by ________
intervertebral discs
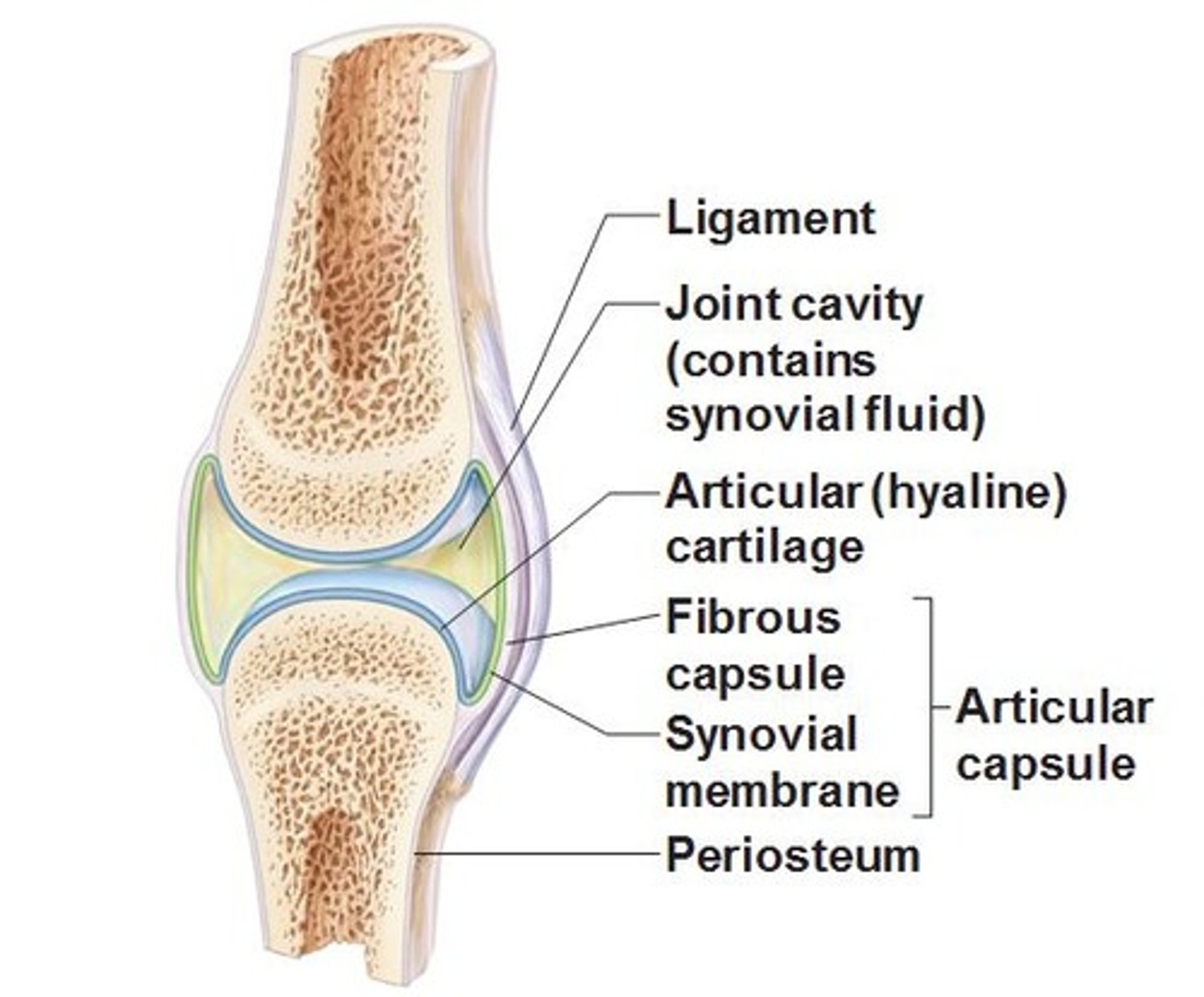
Synovial joint
joint in which two bones are separated by a joint cavity
Other terms for synovial joint
diarthrosis, or diarthrodial joint
what feature of synovial joints makes them important to quality of life?
their mobility
articular cartilage
layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the facing surfaces of two bones
Joint cavity
separates articular surfaces
outer fibrous capsule
continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones
inner, cellular, synovial membrane
composed mainly of fibroblast-like cells that secrete synovial fluid and macrophages that remove debris from the joint cavity
synovial fluid
slippery lubricant in joint cavity
Purpose of synovial fluid
- Rich in albumin and hyaluronic acid
- Nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste
- Makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free
Joint (articular) Capsule
connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid
In a few synovial joints, _________ grows inward from the joint capsule, forming a ___________.
*fibrocartilage
*meniscus
Meniscus (specialized synovial joint)
-Moon-shaped fibrocartilage in knee
-These cartilages absorb shock and pressure
-Guide bones across each other and improve their fit together
-Stabilize the joints, reducing the chance of dislocation
Tendon
strip of collagenous tissue attaching muscle to bone
Ligament
strip of collagenous tissue attaching one bone to another
Bursa
fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid, located between muscles, where tendons pass over bone, or between bone and skin
How does exercise affect synovial fluid?
It warms the synovial fluid, making it less viscous and more easily absorbed by cartilage.
What happens after exercise causes synovial fluid to warm up?
Cartilage then swells and provides a more effective cushion.
What is the result of repetitive compression of nonvascular cartilage during exercise?
Fluid and metabolic waste is squeezed out of the cartilage.
what happens to cartilage when weight is removed after exercise?
cartilage absorbs synovial fluid like a sponge taking in oxygen and nutrients to the chondrocytes
What happens to cartilage without exercise?
it deteriorates more rapidly from inadequate nutrition and waste removal
Muscles attach to bones via _________.
tendons
To allow movement, muscles MUST.....
Cross one or more joints
Muscles actively ________ and passively ________.
shorten, lengthen
- They cannot exert force by lengthening
Long bones act as levers to enhance what?
the speed or power of limb movements
Lever
any elongated, rigid object that rotates around a fixed point called a fulcrum
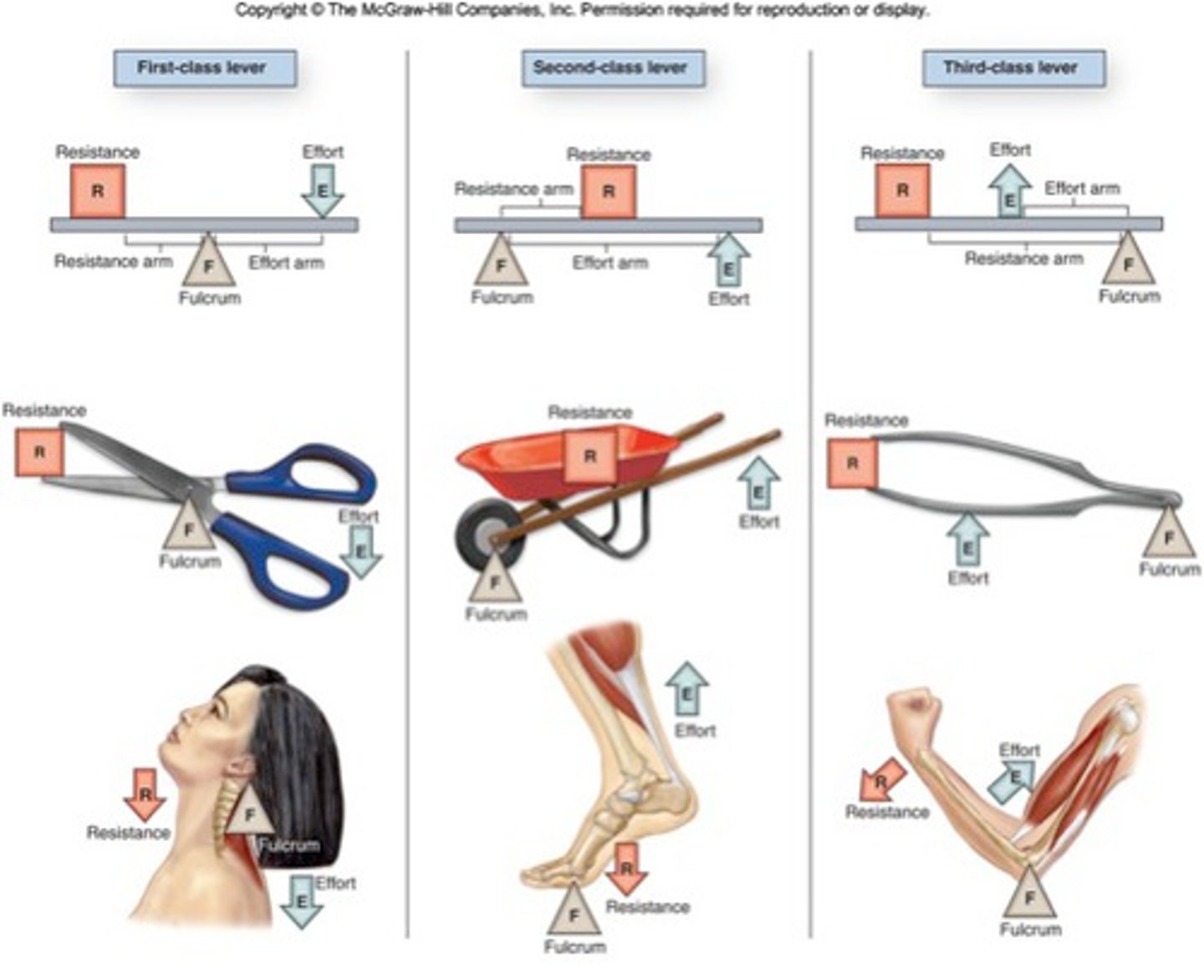
•Two kinds of advantage conferred by a lever
- exerting more force
- moving the resisting object farther or faster. Ex: movement of a rowing boat
Mechanical advantage (MA) of a lever
the ratio of its output force to its input force
arthritis
a broad term for pain and inflammation of a joint
Osteoarthritis (OA)
most common form of arthritis
-"Wear-and-tear arthritis"
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
-This is an autoimmune disease, in which the immune system attacks the joints.