Inorganic: The Unit Cell
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
State
a physically uniform sample (density, flow, compressibility)
Phase
a chemically uniform sample (composition, structure)
London Forces
instantaneous dipoles (partial charges)
Dipole-dipole moment
permanent dipoles
Hydrogen Bonds
a particularly strong dipole (N, O, F)
Ion-dipole
ion is a full electrostatic charge
Ion-ion interactions
very strong networks formed
Crystalline
Well-ordered
Amorphous
Poorly ordered
Cubic Closest
ABC ABC ABC
Hexagonal Closest Packed
AB AB AB AB
Unit Cell
The smallest repeat unit in a 3-D lattice
Used to represent the entire lattice
Atom in body
1
Atom on edge
1/4
Atom on corner
1/8
Atom on face
1/2
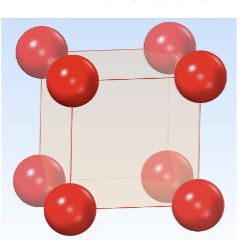
Primitive Cubic
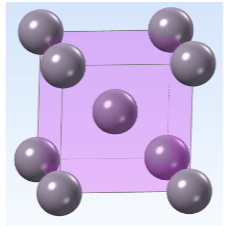
Body Centered Cubic 2 - atoms
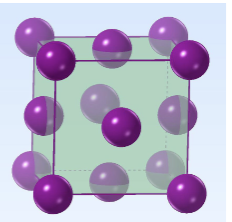
Face Centered Cubic (closest packed) - 4 atoms
Alloys
Compounds of ≥2 metallic elements
Metals have low________ hold electrons loosely
Zeff
Non-metals have high __________, hold electrons tightly
Zeff
In order to conduct, the valence electron orbitals must ________
overlap
the valence electrons are held very ___________due to the electropositive nature of metals
weakly
Metals with more electrons in __________ orbitals conduct better
valence
Diamond stucture
Half are filled in ½ of Td holes
Other half are in usual CCP formation
Conductor
band overlap
Semiconductor
no band overlap
Valence band
bonding orbital band
Conducting band
antibonding orbital band
Band gap
Energy gap between Fermi level and bottom of
conduction band
Intrinsic Semiconductor
Electrons are promoted: valence band to conduction band thermally
Conductivity increases with….
temperature
Extrinsic Semiconducting
Small, controlled amount of impurity introduced (doping)
N-type semiconduction
P has one extra electron, which lies in a higher energy orbital
and can become delocalized with very small energy input
P-type semiconduction
Al has one fewer electron, creating electron “holes”
that become delocalized with very small energy input
P-n Junction
One way gate for e- flow (diode)
Transistor
npn or pnp
Polarization does what
Provides transition between covalent and ionic spectrum
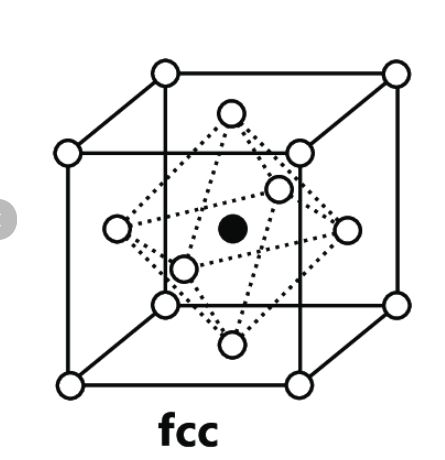
octahedral holes
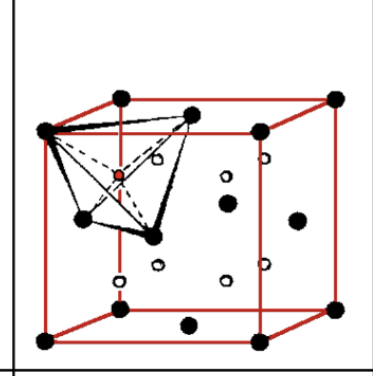
Tetrahedral holes in fcc
ratio of Td to Oh
2: 1
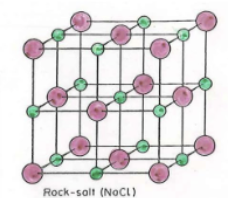
Rock salt
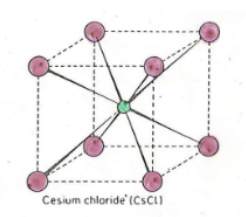
Cesium Chloride
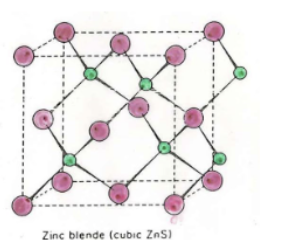
Zinc Blende
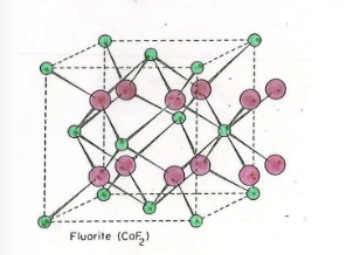
Fluorite
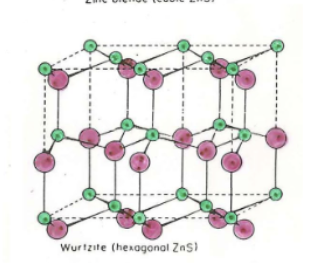
Wurtzite
Antifluorite
Madelung Constant
Energy between a single ion and every other ion in specific lattice pattern
(attractive or repulsive)
Born constant
Nuclei can’t be too close together w/o repulsion
ion
Large charges produce ________ lattice energies and ______ water solubilities
large; lower
Packing is ______ when ion sizes don’t match well, ________ solubility
poor; increases
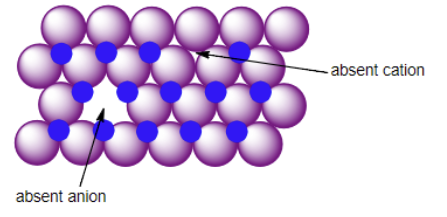
Schottky Defect
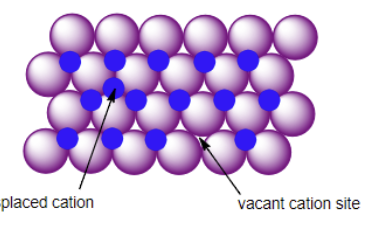
Frankel Defect
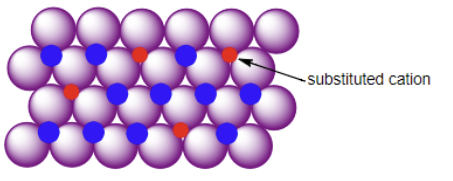
Substitition Defect
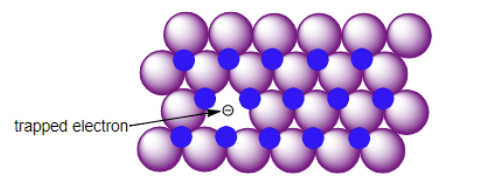
F-centers
What kind of solids are F-centers most likely to occur in?
Simple salts (NaCl)
Perovskites
Common mineral structure finding applications in superconductors, pizoelectronics, solar cells
True/False: you might need more than one cell to accurately represent a perovskite.
True
What holes are filled in Rock Salt (cation)?
All octahedral holes (both exchange off)
What holes are filled in Zinc Blende (cation)
Half of tetrahedral
What cation holes are filled in Wurtzite?
Half of tetrahedral
What holes are filled in ANION for Fluorite?
All tetrahedral
What cation holes are filled for anti-fluorite?
All tetrahedral holes
Holes filled in CsCl
Like BCC, One in middle (cation)?
CsCl formula
MX
Rock salt formula
MX
Zinc Blende formula
MX
Wurtzite Formula
MX
Fluorite Formula
MX2
Anti-fluorite formula
M2X
How many nearest neighbors for unary ccp/hcp?
12
How many nearest neighbors for unary bcc?
8
CsCl Anion/Cation CN (NN)
Anion: 8
Cation: 8
Rock Salt nearest Neighbors
Anion: 6
Cation: 6
Zinc Blende Nearest neighbors
Anion: 4
Cation: 4
Wurtzite Nearest Neighbors
Anion: 4
Cation: 4
Fluorite Nearest Neighbors
Anion: 4
Cation: 8
Antifluorite Nearest Neighbors
Anion: 8
Cation: 4