ANSC356 - Reproduction and Incubation
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1) ovary
2) infundibulum
3) magnum
4) isthmus
5) uterus
6) vagina
7) cloaca
List the 7 parts of the hen’s reproductive tract
ovary
location of follicles
infundibulum
catches ovum at ovulation
magnum
deposits egg white proteins
isthmus
location fluid is added
uterus
deposits membranes & shell
vagina
stores sperm
cloaca
expels urine, feces, & egg; site of insemination
23-25 hours
Time it takes for an egg to develop
300 eggs
Modern hens lay about how many eggs per year?
12 eggs
The red jungle fowl (modern hen ancestor) lays about how many eggs per year?
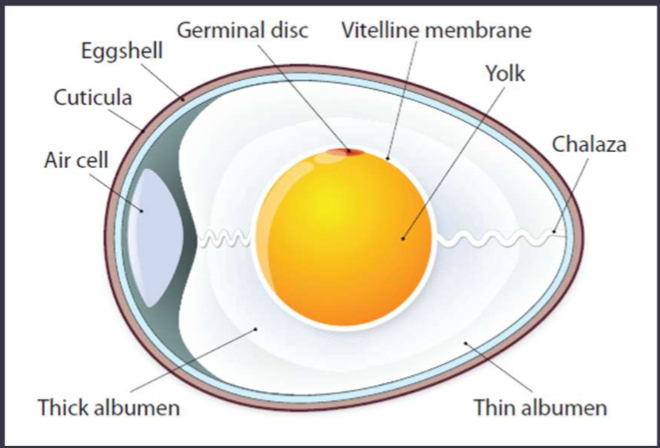
Label the parts of the egg
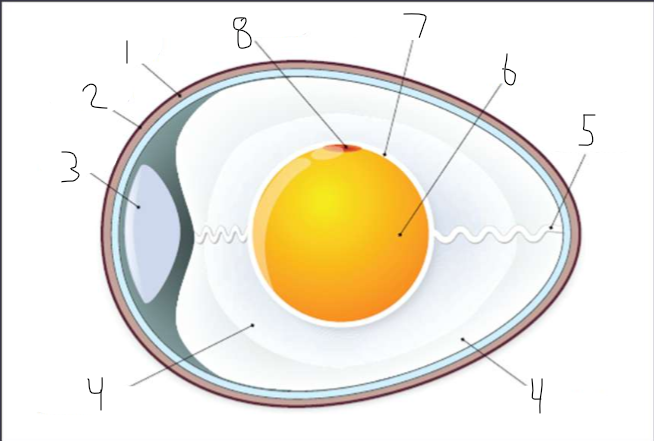
shell
hard, porous, protective structure around the egg
yolk
a structure full of nutrients which feeds the embryo
albumen
protein-rich egg white
germinal disc
region that contains embryonic cells, organelles, and RNA
air cell
formed when the cooling egg contracts and pulls the inner and outer shell membranes apart
vitelline membrane
membrane around the yolk
chalaza
spiral bands of tissue that suspend the egg yolk in the albumen
cuticula
protein-based membrane around the eggshell that protects against bacteria
pores
very small holes invisible to the naked eye
calcium
Egg shell is made mostly of what?1)
1) water
2) carbon dioxide
3) oxygen
4) bacteria
What 4 things can move through the egg shell pores?
shell
The ___ temp. is used to determine the embryo temp.
Salmonella
Common bacteria that colonizes egg shells
day 12
Growth hormone is produced by the embryo at what day in development?
Yolk
Color of this structure is determined by the hen’s diet
1) beta-carotene
2) lutein
2 compounds that determine egg yolk color
ovalbumin
Main protein found in albumen
Liquifies
The albumen _______ when refrigerated
basic
When the albumen liquifies the pH becomes more?
germinal disc
fertilization by a sperm cell occurs here
candling
process used to determine the size of the air sac
air sac
used to determine if humidity levels are incorrect during incubation
protein
The chalaza is made up of what?
cuticula
noncalcified, protein protective layer that covers the egg
1) Hen sitting (natural)
2) Artificial
2 processes of incubation
hatchability
number of eggs hatched divided by the number of eggs set
(chicks hatched/fertile eggs) * 100
hatchability percentage equation
83%
average hatchability in the USA
1) temp.
2) humidity level
3) position
4) oxygen level
5) carbon dioxide level
5 critical parameters for incubation & hatch
99.8°F
Ideal temp. day 1-19 of embryonic development
98.8°F
Ideal temp. day 19-hatch
< 96°F
> 103°F
2 temps. embryos will die at
50% to 55%
Ideal humidity percentage day 1-19
70%
Ideal humidity percentage day 19-hatch
small air sac
high humidity = ____ air sac
large air sac
low humidity = ___ air sac
3 to 5 times
Ideal number of times egg should be turned from day 2-18
1) prevents embryonic membranes from adhering to the shell membrane
2) aids in air circulation in the incubator
2 reasons eggs should be turned during embryo development
large end up or on their side
2 egg positions that are correct for embryo development
day 15 or 16
Day the embryo’s head is near the air sac
21%
Ideal percentage of oxygen in egg during embryo development
0.5%
Ideal percentage of carbon dioxide in egg during embryo development