GHS Final Exam
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Attacks the immune system by destroying specialized white blood cells needed to fight infection
(THIS IS CONTAGIOUS)
AIDS
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Illnesses occurring due to the destruction of immune system cells by the HIV virus
(NOT CONTAGIOUS)
Common ways to get HIV/AIDS
HIV infection can be passed through
Blood
semen
vaginal fluids
breast milk
Sharing needles
Unprotected sex
Breastfeeding
Blood transfusions
Methods one can take to protect themselves from HIV/AIDS
Don’t share needles
ensure sterilized tattooing
Safe sex; condoms
Do not share hygiene products
HIV infection has 3 stages
Primary infection
Asymptomatic Period
Clinical latency
AIDS
How does COVID-19 impact a HIV+ person?
Health
Risk of dying from COVID-19 is double
Since HIV has more severe outcomes that compromise the immune system, resulting in higher simultaneous medical conditions
Beyond
COVID-19 lockdowns Disrupted testing
Steep drops in treatment diagnoses /referrals
Primary Infection of HIV
Commonly infection is not known right away
takes about 2-6 weeks after infection
Symptoms include:
Headache
Fatigue
Sore throat
Fever
Rash
Swollen Lymph nodes
Clinical Latency of HIV
Symptoms goes away but the virus remains in the body and can still be transmitted. This stage can last for several years.
During this time, the virus is killing CD4 cells and slowly destroying the immune system.
AIDS
CD4 T-cell number drops below 200
A person becomes at a higher risk of dying from another disease, such as the flu or cold, due to a compromised system.
Opportunistic infections
Infections that occur more often or are more severe in people with weakened immune systems
More than half of the current cases of HIV and half of new cases of HIV worldwide occur in females. Why
1. 2X as likely to acquire HIV from heterosexual sex
2. Women generally marry at younger ages
3. More likely to be the victims of sexual violence
Women tend to become infected with HIV at younger ages than men
What are the Prevention method
Enhanced WASH
Water treatment in risk areas
Hand washing
Vaccinate
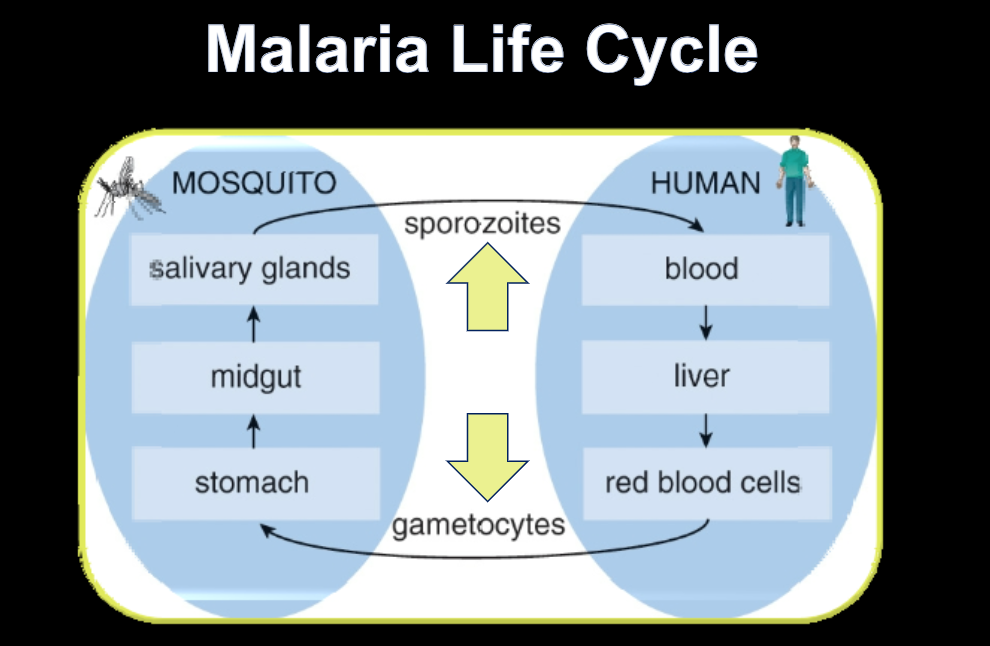
Sporozoites
Parasite stage that infects humans
Tuberculosis
A disease that typically affects the lungs
• Caused by bacteria
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
2 types of Tuberculosis
Pulmonary TB
Extrapulmonary TB
Pulmonary TB
Airborne
Released into the air
(cough, speak, sneeze)Nearby person breaths it in
Extrapulmonary TB
Typically, not infectious
• Hard to diagnose
Ways of Transmission Pulmonary TB
Speaking
Coughing
Singing
What is often a driver of TB transmission and why?
Poverty and economic status
How?
Poor living conditions with overcrowding (easy spread)
Lack of access to treatment
Poor nutrition
Latent Tuberculosis
When infected, the immune system will attack the bacteria by quarantining. If the quarantine is effective, the infection is then considered
Bacteria is inactive
No symptoms
Can’t spread TB
Will test positive for TB
How does TB attack?
Slowly destroys the tissues and leaves in their place a thick cheesy substance
- If in the lungs it will causes holes
What is the link between TB and HIV
TB is the leading cause of death in people w/HIV
HIV+ are 30x more likely to develop TB
What is TB an example of?
An opportunistic infection
What is another name for TB Disease?
Wasting disease; the disease is wasting away of the body
What is the main symptom of Cholera?
Acute watery diarrhea (Rice Water Diarrhea)
Cholera
the bacteria doesn’t directly attack but instead releases toxins
What is the recipe for ORS?
6 teaspoons of sugar
A half teaspoon of salt
1 liter of water
What place has Malaria disproportionately affected globally?
Africa, with 90% of all cases & deaths occur in sub-saharan Africa
Gametocytes
Parasite stage that mosquitoes take in
How to tell if a mosquito is a malaria mosquito vector?
First, identify the gender; this is done by looking at the antenna (Males have bushy antennas, whereas females don’t)
The female transmits the disease.
Palps
The length of the palps are the same length as the mouthparts
Resting Stance
Rest at a 45-degree angle
Butt pointed towards the sky
What groups or demographic are at the highest risk for severe malaria complications and/or death?
Children Under 5 & Pregnant Women
Interventions for Malaria
Artemisinin
From the Sweet wormwood plant
Long-Lasting Insecticide-treated Nets
Typically lasts up to 3-5 years
Not a definite answer, but a solid temporary solution
Indoor Residual Spraying
Coating walls/other surfaces of a house with a residual insecticide
What is the most common cause of malaria?
P vivax
P.vivax (and P.ovale also) results in
relapsing malaria
Relapsing malaria
After recovery from malaria, it returns and causes additional attacks without reinfection
can happen months/years later
can happen several times
Neglected Topical Diseases (NTDS) derive from
Bacteria
Viruses
Parasites
Two types of disease-causing parasites
Protozoa
Single-celled organism
Often lives in water
Helminth
multicellular worm that lives inside the body of its host
What disease is Protozoan
Malaria
Helminth Location
Definitive host
• Animal host in which a parasite
reaches sexual maturity and
reproduces.
This is the parasites “goal”
ntermediate host
• Animal host in which an
immature parasite develops but
does notdoes not reach sexual maturity
Vectorborn Infection a result og
Human → Insect → human cycle
or
Animal → insect → animal cycle
Flaviviruses
RNA viruses found in arthropods
(primarily ticks and mosquitoes) can infect humans
Romana’s sign
Swelling in eyelid
Chagastic Megacolon
Extreme bloating of the colon; contispation which
Dengue fever (DF) is also known as
break-bone fever
due to extreme pain in joints
2 main mosquitos transmit this virus
Aedes aegypti
Aedes albopictus (Also known as the Asian tiger mosquito)
Aedes albopictus (Asian tiger mosquito) are most active
diurnal - active during the daylight hours
4 serotypes (strain)
1st infection - Symptoms
2nd infection - Often severe Dengue
Death (hemorrhagic fever, shock)
West Nile Virus
Typically a disease in birds but can and will effect humans
Most people asymptomatic:
Severe: encephalitis
weakness
coma
vision loss
death
Lymphatic Filariasis
Transmitted by mosquitoes which transmit microscopic roundworms (filarial Nematodes)
Immense swelling in legs
Immense swelling in the scrotum for men
Two different types of Trypanosomiasis
1. HAT (African Sleeping Sickness)
Chagas Disease
HAT (Human African Trypanosomiasis)
Also known as Sleeping Sickness
Symptoms of the 1st stage
Fever
severe headaches/fatigue,
swollen lymph nodes
aching muscles and joints
Symptoms of the 2nd stage
invades the central nervous system
- Confusion, personality changes, other neurologic
Two key eye worm diseases
Onchocerciasis
Loa Loa
Chagas Disease
Triatomine Bug defecates
Signs
Ramona’s sign
Diseases of poverty
Symptoms: Initially mild and become
chronic and deadly after many years
- Heart rhythm abnormalities; sudden death
- A dilated heart that doesn’t pump blood well
- A dilated esophagus or colon (megacolon)
Onchocerciasis
Big lumps in skin; produce juvenile worms called Microfilaria
Intense itching which may change the appearance of the skin
(kinda like a vitiligo effect) leopard skin
lumps
If enter eyes, may cause blindness
Treatment
Ivermectin (3mg)
Loiasis (Loa Loa)
Transmitted by deer fly
Symptoms
Intense itching
Painful swelling
If enter eyes, may lead to blindness
Treatments
DEC
Dracunculiasis
Transmitted by drinking water with infected copepods (water bugs)
Treatment
Only way to remove is to twist slowly with a stick
Zika Virus
transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes
can also be sexually transmitted
mainly affects mothers and their infants
linked to microcephaly (decrease in head shape)
Yellow fever
Spread by infected aedes mosquitos
Named after the jaundice (yellow color of the skin) from an infection
Two Cycles of Yellow fever
Urban- spread between humans and mosquitoes in populated areas,
Sylvatic- spread between mosquitoes and wild animals, generally in monkeys
Neonate
a newborn within first 28 days after birth
Infant
a baby between birth and their 1st birthday
Preterm birth
the delivery of a baby before the 37th week of pregnancy
A typical pregnancy is about 40 weeks long
In resource-limited settings, survival
of preterm babies is enhanced by?
Skin-so-skin contact of mother/newborn
- Frequent breastfeeding
- Early discharge from the hospital
Breastmilk contains
Colostrum
which all needed nutrients, water, digestive enzyme
Neonatal Survival
Beings with universal access to prenatal care
Labor and delivery care should be provided by skilled birth attendants
After birth, routine care for newborns
Clinical treatment for breathing difficulties, signs of infection, jaundice, other problems
Reproductive rights
The freedom of women & their partners to decide how many children they want
Without interference from governments/others
1st Trimester
Hyperemesis gravidarum
severe nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy that causes severe dehydration & significant weight loss
Ectopic pregnancy
fertilized egg implants in fallopian tubes/another location outside the uterus
2nd/3rd Trimester
Placenta previa
the placenta covers
part/all of the cervix, causing bleeding
Placental abruption
placenta separates
from the uterine wall prior to delivery
Causes of Maternal Mortality
Preeclampsia
Worsening hypertension in the final months of pregnancy
Family Planning
The process by which both
women/men make informed decisions about
How many children they want to have
How many years apart they want pregnancies
Actions they will take to achieve these goals
Family Planning Methods
Abstinence- refraining from sexual contact
Contraception - intentional prevention of pregnancy through a variety of measures
Fertility Treatment - mechanisms that assist the pregnancy process (conception/infertility)
Birth spacing
time period after the birth
of a child before conceiving the next child
What is the optimal time period between childbirth (for birth spacing)
two years
Spacing Benefits
Women/Children are usually healthier
when women have fewer pregnancies
Malnutrition from weaning (older child)
Increased risk of low birthweight
as well as preterm birth (younger child)
Economic benefits as well
Work productivity → resources
What is the correlation between gross national income per capita and % of deaths from NCDs
Higher gross national income per capita is
associated with a higher % of deaths from NCDs
Based on the diseases who do you think is most at risk for death NCDs?
Older population
70 and older
Is this true for low income countries (yes because people typically build immunity from communicable diseases and will most likely die from )
The risk of NCD is
most common cause of death for older adults in every country
Example of NCDs
Heart disease / other cardiovascular diseases
Cancers
Chronic respiratory diseases
Diabetes
NCDs also called
“Diseases of affluence”
Diseases of affluence is contrast to
“Diseases of poverty”
Infectious diseases/undernutrition
Lifestyle diseases
disease that can be prevented through the behavior change
Behavior change
Process of adopting healthier habits & maintaining the practices
Diabetes
chronic condition that affects how your body turns food into energy
Insulin
Allows glucose (sugar) into cells
lack of insulin results in Sugar staying in your bloodstream
3 types of diabetes
Type 1
Not preventable
Body does not create enough insulin
Type 2
Preventable
Body does not create enough insulin OR develops insulin resistance
Gestational
Pregnancy related
Treatment?
Have the baby
Resolves after delivery
Diabetes Results
Heart disease
Kidney disease/failure
Blindness
Nerve damage
Diabetic neuropathy
Foot ulcers
May lead to amputation
Common CVDs
Heart attacks
Strokes
Arrhythmia
Hypertension
Where is the Overall CVD mortality rate highest and why?
In high-income countries.
WHY?
- Have the highest proportion of older adults
Ischemic heart disease and it’s effects
Ischemia is a reduced supply of oxygenated blood
Often a result of atherosclerosis
Thickening of the artery walls which carry blood from the heart to the heart muscle
Stroke
brain cells die from lack of oxygen
2 common causes of strokes
Ischemia (reduced blood flow to brain)
Hemorrhage
Symptoms of Stroke
Weakness on 1 or both sides of the face/body
Vision issues, loss of balance, severe headache
Trouble speaking/understanding
Confusion
Cancer
abnormal cells reproduce
uncontrollably within the body
• Often invading nearby tissues and
spreading to other parts of the body
Apoptosis
Cell programmed death
This is what normal cells go through to eliminate the chance of cancer
Cancer cells vs Normal Cells
Normal cells are genetically stable and will die after some time (Apoptosis)
Cancer cells are genetically UNSTABLE & undergo unlimited reproductive cycles
(no apoptosis)
Risk factors for Cancer
Tobacco use increases risk of cancers
Environmental hazards induce cellular damage
Air pollution, residential radon, arsenic, etc.
Occupational exposure to
carcinogens damages cellsUnhealthy diet, obesity,
physical inactivity may
impair cellular function
Cancer Prevention
Detection at an early stage through screening
What virus did we skip over in the Spillover documentary?
Nipah virus