unit 2 chapters 12,13,14 book anatomy
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
endocrine system
communicates by means of chemical messengers (hormones)secreted in the blood
nervous system
employs chemical (neurotransmitters) and electrical means to send messages from cell to cell.
sensory input
monitor internal and external stimuli.
integration
brain and spinal cord process sensory input and initiate responses
homeostasis
regulate and coordinate physiology
mental activity
conciousness, thinking, memory emotion
functions of nervous system
sensory input, integration, controls muscles and glands, homeostasis, mental activity.
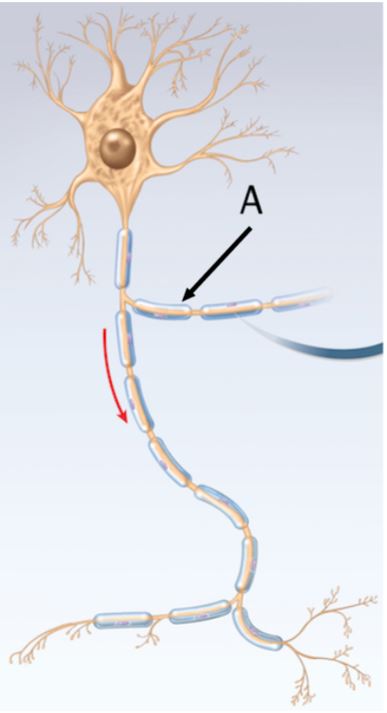
name the outer covering indicated by the arrow labeled A
myelin sheath
All characteristics of neuroglia
They protect the neurons and help them function, They bind neurons together and provide supportive scaffold
maintaining internal coordination
function of both endocrine and nervous system
excitability, conductivity, secretion
fundamental physiological properties of neurons
Astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes
Types of glial cells are found in the central nervous sytem
neurons classes
Sensory, inter, and motor, are the three classes of
Dendrites
The soma of a neuron gives rise to branch-like processes called what? They are the primary sites for receiving signals from other neurons.
Neuroglia
Which cells protect the neurons and help them function?
endocrine, nervous
Two organ systems are dedicated to internal coordination, communication between the other systems, and maintaining the overall homeostasis of the body. They are the ___system, which communicates by means of hormones, and the___system which sends quick electrical and chemical messages from cell to cell.
insulation
The myelin sheath is a spiral layer of___around a nerve fiber
satellite cells
In the PNS; surround somas of neurons in ganglia, provide electrical insulation, and regulate the chemical environment of neurons
Schwann cells
In the PNS; form neurilemma around all PNS fibers and myelin around most of them; aid in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers.
Ependymal cells
In the CNS; line cavities of the brain and spinal cord; secrete and circulate CSF
Microglia
In the CNS; phagocytize microorganisms, foreign matter, and dead nervous tissue
interneurons, sensory neurons, motor neurons
three functional classes of neurons
1:1
approximate ratio of glial cells to neurons
unmyelinated
An axon lacking a myelin sheath is said to be
Signal conduction will be faster
Which is true about a neuron with a large diameter, myelinated axon as compared to a neuron with a small diameter, unmyelinated axon?
lipids and protein
The myelin sheath is composed mostly of which of the folowing
in both the central and peripheral nervous systems
Where are unmyelinated axons found?
Large unmyelinated axon
Which of the following would have the fastest conduction speed?
Potential Energy
An electrical potential is a form of what type of energy?
True
Unmyelinated nerve fibers (axons) in the PNS are enveloped in Schwann cells.
True false question.
Potassium
The plasma membranes is most permeable to which of the following ions?
Endoneurium
Which of the following is required for nerve fiber regeneration?
Local potentials
Which term refers to decremental changes in electrical potential along a dendrite or the soma?
A form of potential energy that can produce current
Which best describes an electrical potential?
K+ is more concentrated in the ICF than in the ECF.
Which of the following contributes to the development of the resting membrane potential in neurons?
Presence of myelin, diameter of axon
All the factors that influence the speed of nerve signal conduction
grade, decremental
characterstics of local potentials
these events into the order in which they occur during a single action potential
local potential depolarizes membrane, threshold is reached, depolarization spike, repolarization, hyperpolarization
absolute
The refractory period in which no stimulus of any strength will trigger a new action potential is the______ refractory period.
Threshold
The minimum amount of voltage needed to open voltage-gated channels on an axon is called what?
refers to the period of time after a nerve cell has responded to a stimulus in which it cannot be excited by a threshold stimulus?
refractory period
presynaptic
At a synapse, the neuron that releases neurotransmitter is the ______ neuron.
Unmyelinated fibers have voltage-gated channels along their entire length.
A zone of depolarization excites voltage-gated channels immediately distal to the action potential.
Choose all of the following statements that are true about signal conduction along unmyelinated fibers.
A wave of depolarization opens more voltage-gated channels immediately distal to the action potential.
Which best describes signal conduction in unmyelinated axons?
Gap junctions
In electrical synapses, electrical signals move quickly from cell to cell through which of the following?
relative
The refractory period in which it is possible to trigger a new action potential, but only with an unusually strong stimulus is the ______ refractory period.
postsynaptic
The neuron that responds to the presynaptc neuron is called the
Postsynaptic neuron
In a chemical synapse, synaptic vesicles full of neurotransmitter are docked at release sites on the membrane of the presynaptic neuron, while neurotransmitter receptors are found on the membrane of the____ _____
Neurotransmitter is removed from synaptic receptors
Stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron will end when nerve signals stop arriving at the presynaptic axon terminal or when which of the following occurs?
synaptic cleft
Which term refers to the microscopic physical gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons at a chemical synapse?
Postsynaptic potentials
ESPSs and IPSPs are examples of
The type of receptors on the postsynaptic cell
Some neurotransmitters can have either excitatory or inhibitory effects depending on which of the following?
Choose all that would cause postsynaptic stimulation to end.
Reuptake of neurotransmitter into the presynaptic knob
Diffusion of neurotransmitter from the synaptic cleft into extracellular fluid
Cessation of signals in the presynaptic nerve fiber
Enzymatic degradation of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft
In the axon terminal
In a synapse, where are synaptic vesicles located?
Chemical synapses
Which are the sites of learning and memory?
-70 mV
Which numerical value is most likely to be the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
All statements that are true regarding postsynaptic potentials?
They include EPSPs and IPSPs.
They are changes in the membrane potential of the postsynaptic terminal of a chemical synapse.
They are caused by neurotransmitters
They are inhibitory.
Their actions depend on their receptors.
They are excitatory.
All that are true of neurotransmitters
EPSPs
Sodium ions flowing into a neuron cell membrane are most likely to produce what?
-55
Which is most likely to be the threshold potential for neuron
Postsynaptic potentials
Neural integration is based on the combining together of which of the following?
All of the following that may be the result from inhibitory postsynaptic potentials
Opening Cl- channels
Opening K+ channels
Sodium
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are usually due to the entry of which type of ion?
Chloride or potassium
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials is usually is usually due to to the opening of which type of ion channels?
When sodium channels open
When do EPSPs usually occur?
Which neurotransmitters are excitatory to some cells and inhibitory to others, depending on the type of receptors on the target cells?
Acetylcholine
Norepinephrine
oligodendrocytes
myelin sheaths are created by___in the central nervous system
axon
___is the cellular process that carries the impulse away from the neuron cell body
neurons, glial
Two cell types of nervous tissue are the__,and___
schwann cells
myelin sheaths are created by___in the peripheral nervous system
dendrites
___are the cellular processes of the neuron that receive the input
axon to dendrite
In which direction does the neurotransmitter cross a synapse?
On the axon
Where is the synaptic knob located?
multiple dendrites and one axon
multipolar neurons have
sensory or afferent neurons
Unipolar neurons generally function as
soma
The cell body is also known as the
axon neuron
Which part of a neuron carries the impulse away from the cell body?
microglia
Derived from white blood cells, these cells in the central nervous system are often found at the site of injury of brain tissue.
ependymal cells
Which type of neuroglial cells produces cerebrospinal fluid?
Schwann cells form a myelin sheath around a portion of only one axon, while oligodendrocytes can surround portions of several axons.
Schwann cells differ from oligodendrocytes in which of the following ways?
sodium ion
What ion is found on the outside of the neuron membrane that is a major contributor to the resting membrane potential?
after repolarization
potassium ion channels close
repolarization of the neuron
Opening of potassium ion channels typically leads to
sodium-potassium pump and leaky potassium ion channels
What maintains the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
resting membrane potential
The sodium/potassium pump is primarily responsible for the
All that are functions of spinal cord
Locomotion, conduction, reflexes
foramen magnum
What structure marks the superior end of the spinal cord?
Anterior median fissure
A longitudinal groove on the ventral surface of the spinal cord is which fissure
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral
all regions of the spinal cord
For the level of vertebral column from which its spinal nerves emerge.
How are the spinal cord regions named?
medullary cone
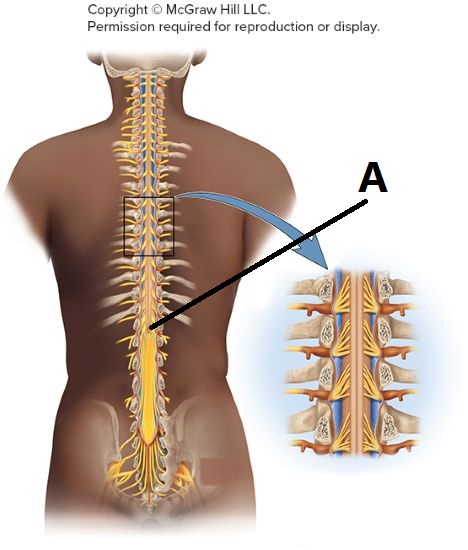
The foramen magnum
Where does the spinal cord arise from the medulla oblongata?
The longitudinal groove on the dorsal surface of the spinal cord
What is the posterior median sulcus of the spinal cord?
cauda equina nerve bundles
The bundle of nerves inferior to the medullary cone of the spinal cord is called the ____ ____
meninges
Which are a series of fibrous connective tissue membranes covering the central nervous system?
posterior
The____ median sulcus is a longitudinal groove on the dorsal surface of the spinal cord.
Dura
The dural sheath around the spinal cord is formed from the____mater
A bundle of nerve roots occupying the vertebral canal from L2 to S5
What is the cauda equina?
epidural
the____space is located between the vertebrae and the dural sheath around the spinal cord.