organic chemistry 2: isomers
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
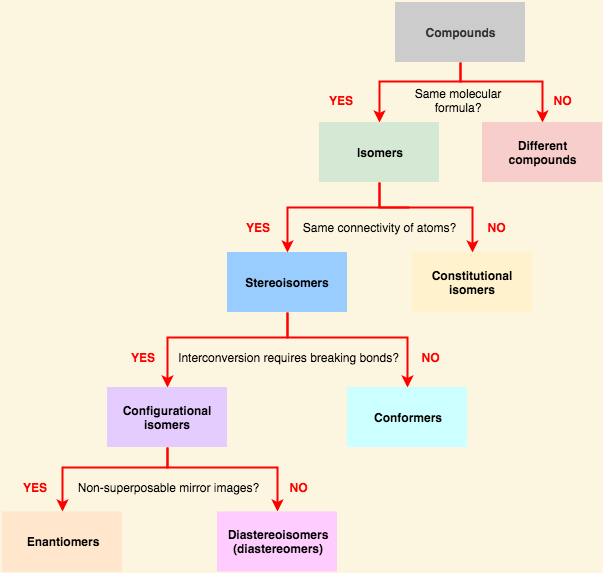
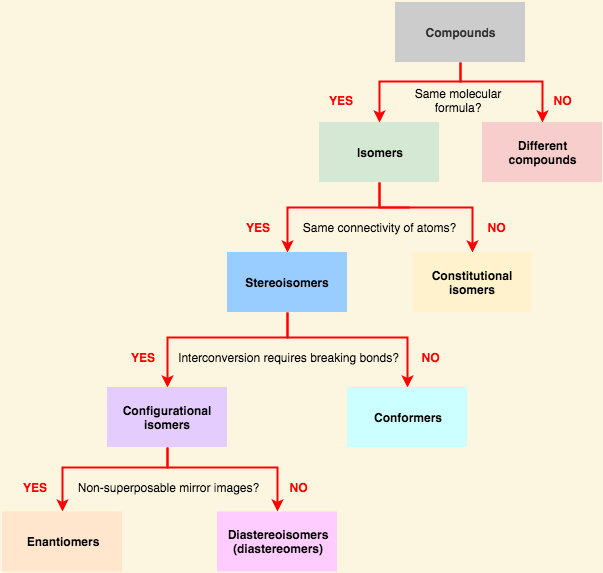
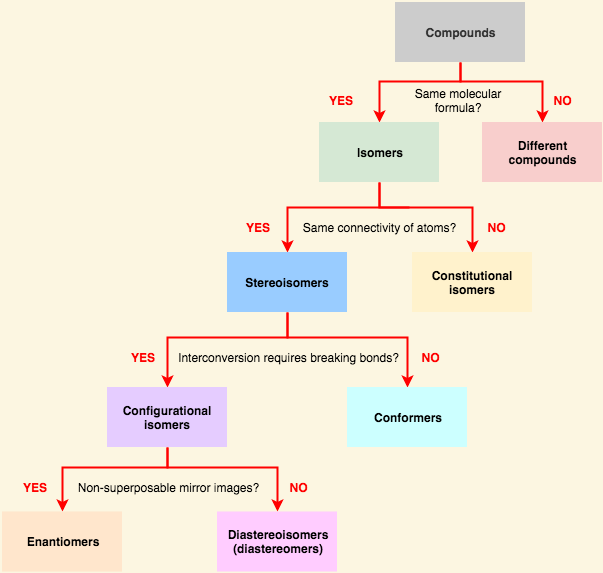
[...] have the same chemical formula but have a different stereochemical arrangement of their atoms
isomers
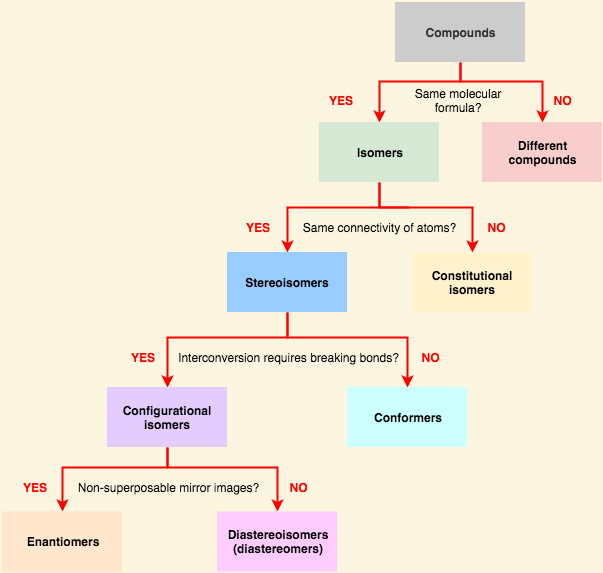
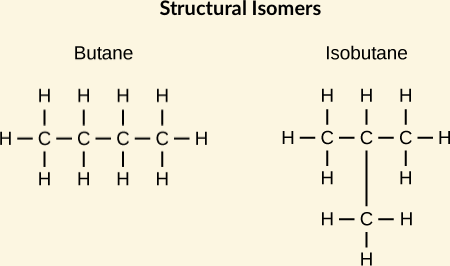
[... isomers] have identical chemical formulas but differ structurally
constitutional (structural) isomers '
the share only a molecular formula. have different physical and chemical properties
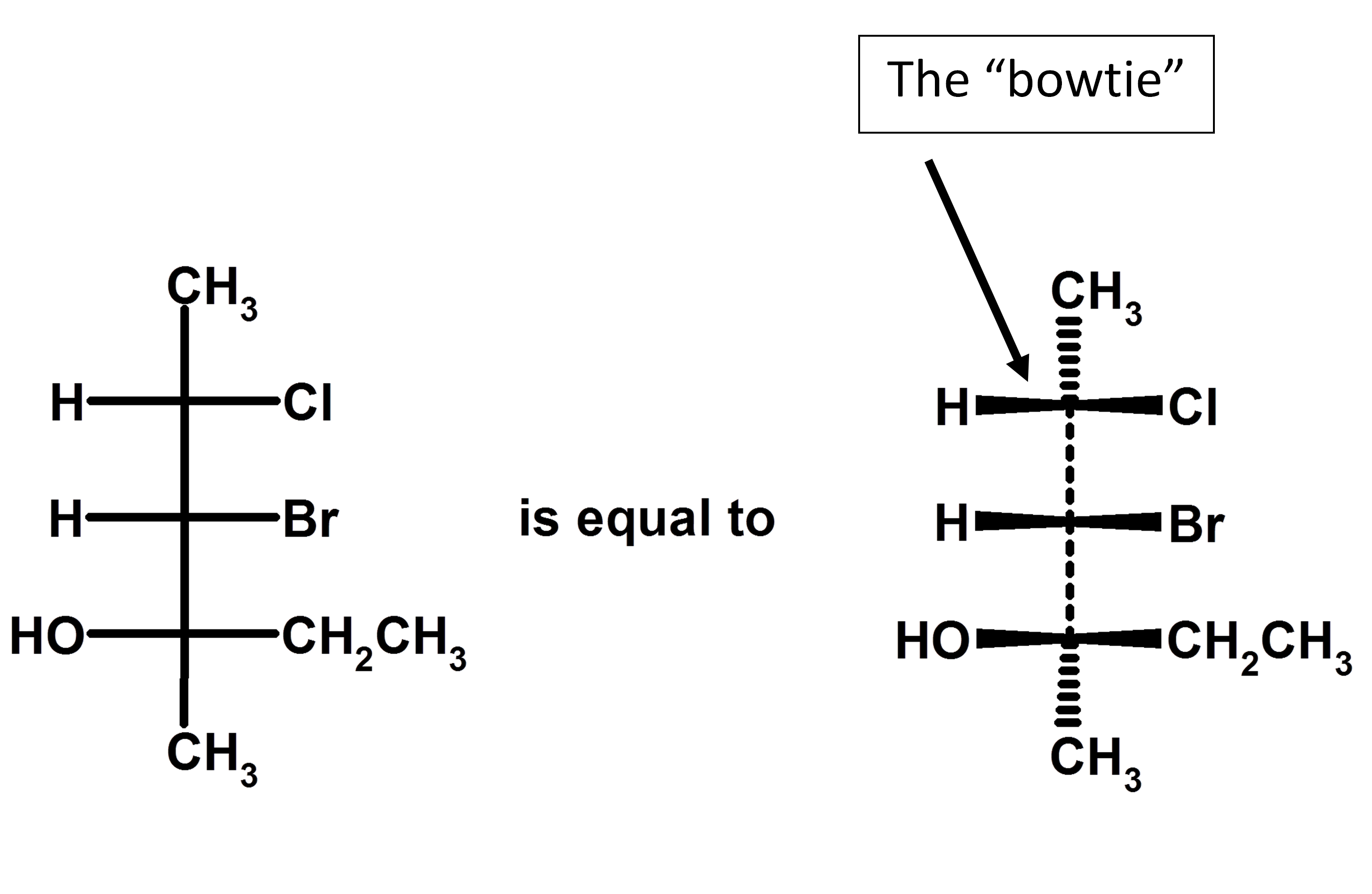
[...] are connected in the same order but differ in 3D orientation
stereoisomers
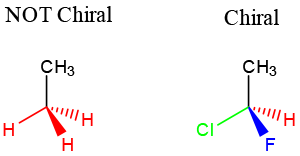
A/an [...] is when four different groups are attached to a central carbon
chiral center
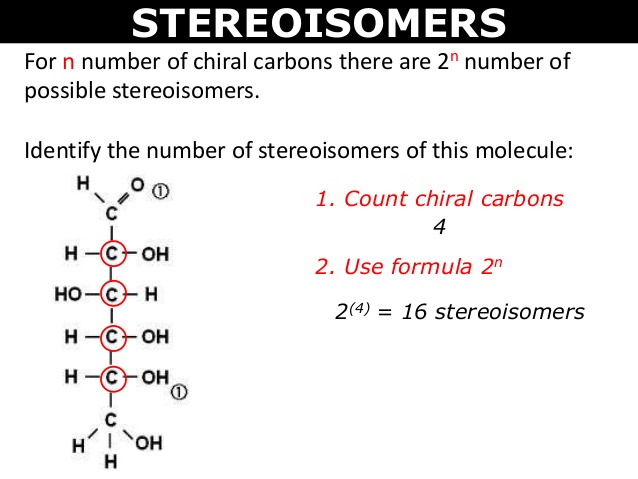
For n number of chiral carbons, there are [...] possible stereoisomers
2n
[... isomers] differ by rotation around a single σ bond
conformational isomers
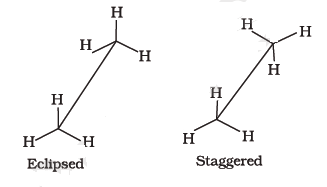
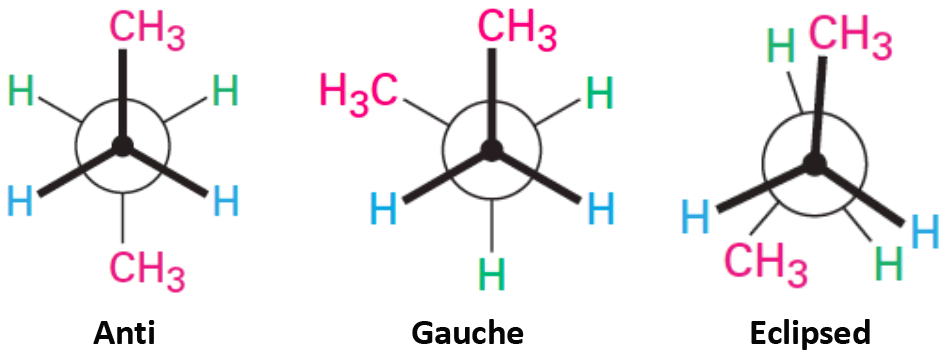
![<p><span>This Newman projection shows </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> conformation</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a916c56-0a06-4e82-9a59-809e4704bd34.png)
This Newman projection shows [...] conformation
anti
the carbons attachments are no opposite ends, 180 degrees apart
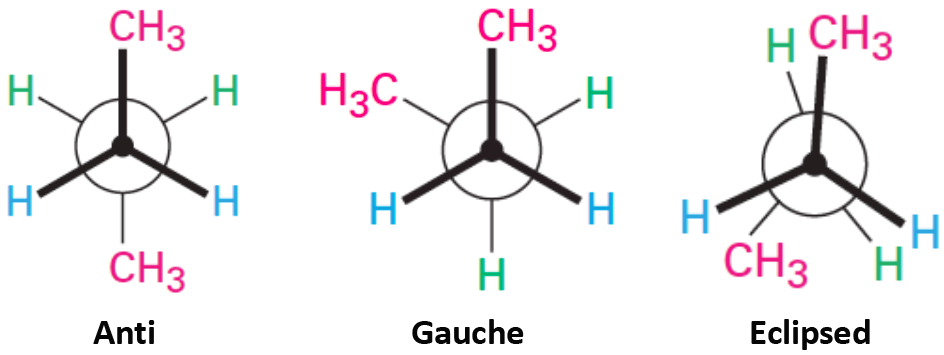
![<p><span>This Newman projection shows </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> conformation</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a30d9c5c-708e-4387-af35-0bc132a480de.png)
This Newman projection shows [...] conformation
gauche
the carbon attachments are 60 degrees apart
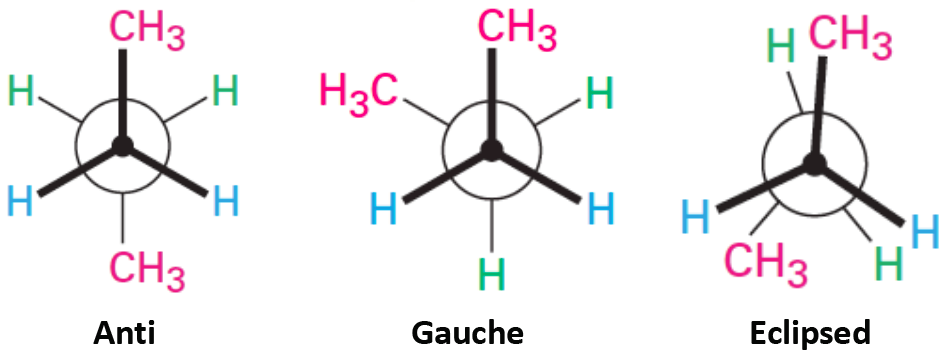
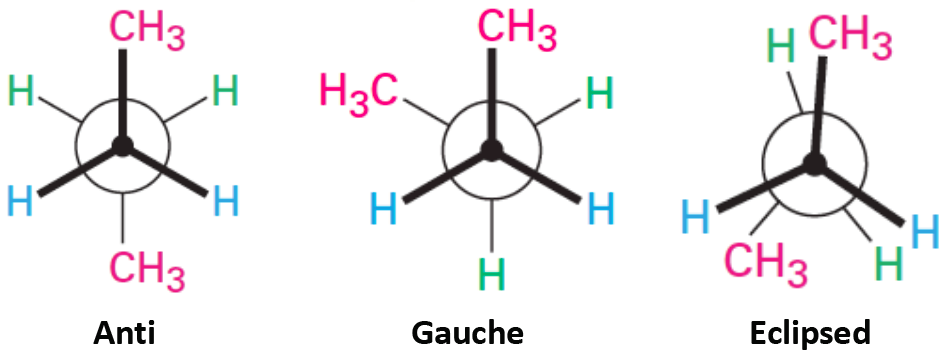
![<p><span>This Newman projection shows </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> conformation</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5fda3ba7-23d7-4618-a06d-ae577cb11810.png)
This Newman projection shows [...] conformation
eclipsed
less favorable because it fores more interactions between the front and back attachments, creating more strain
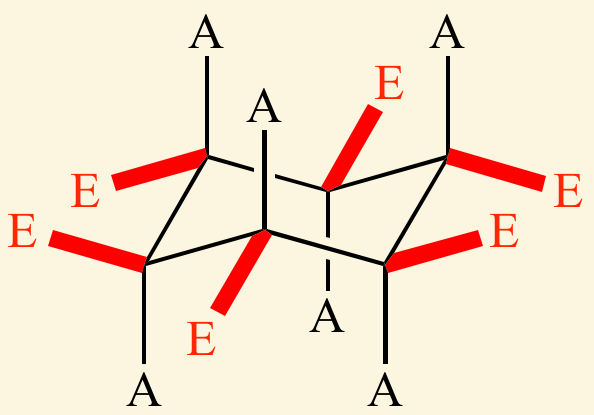
An [... bond] is a bond which is perpendicular to the axis of the ring
equatorial bond
the bond lies along the equator of the chair
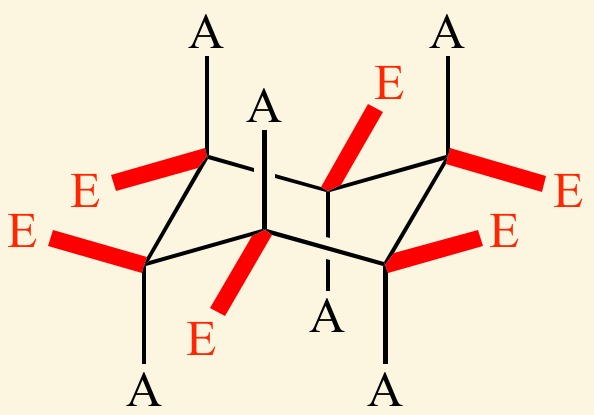
An [... bond] is a bond which is parallel to the axis of the ring
axial bond
straight up and down
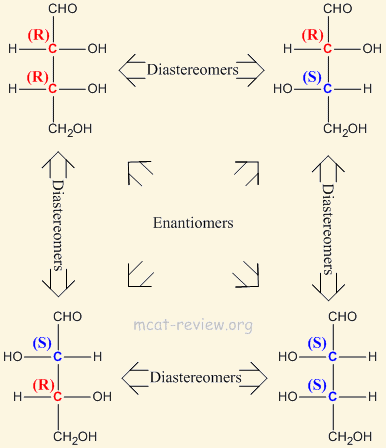
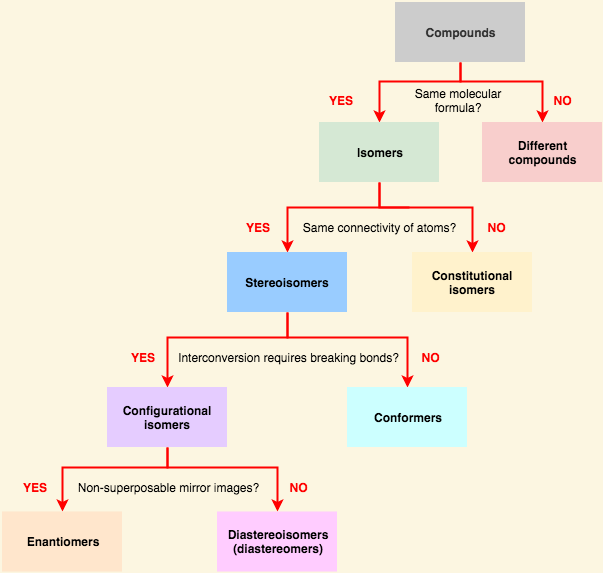
The two categories of [... isomers] are enantiomers and diastereomers
configurational isomers
can only change from one form to another by breaking and reforming bonds
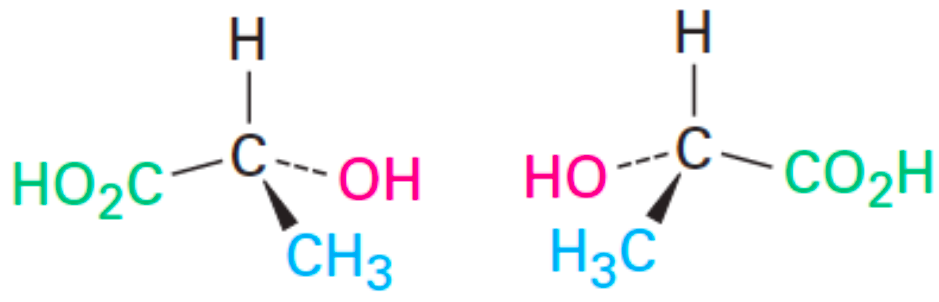
[...] are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable and are mirror images of each other
enantiomers
same chemical and physical properties, expect for rotation of plane polarized light
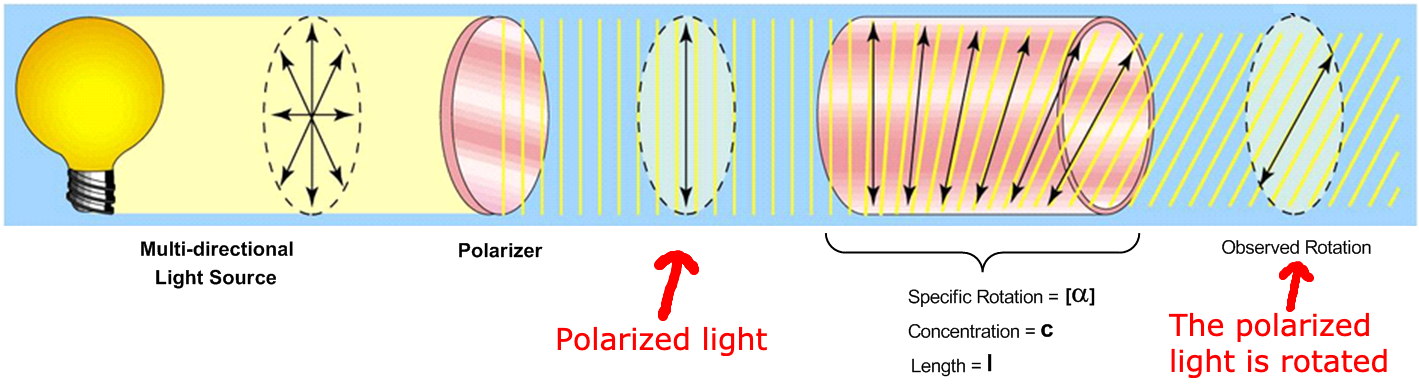
Optical activity is the ability of a molecule to [...] plane-polarized light
rotate
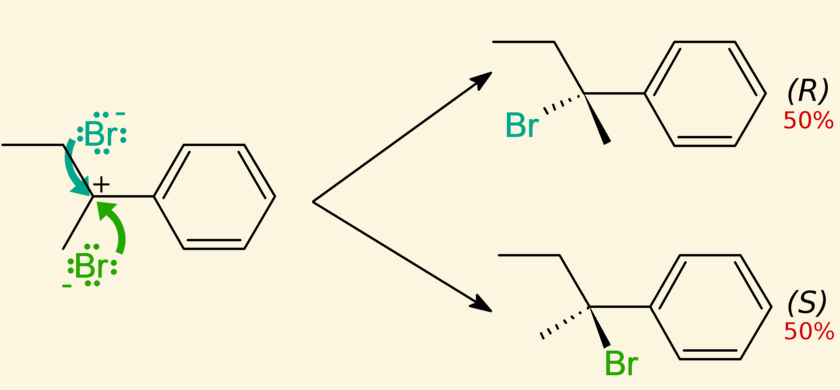
A/an [...] mixture is a 50:50 mixture of two enantiomers
racemic
not optically active because the light rotations cancel out
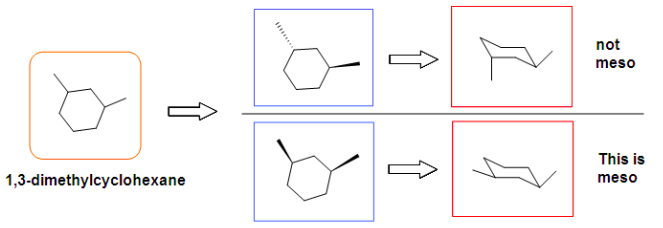
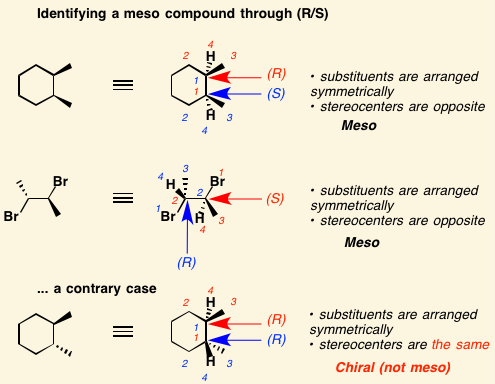
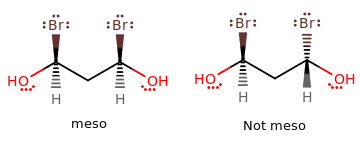
[...] have an internal plane of symmetry
meso compounds
will be optically inactive because the two sides of the molecule cancel each other out
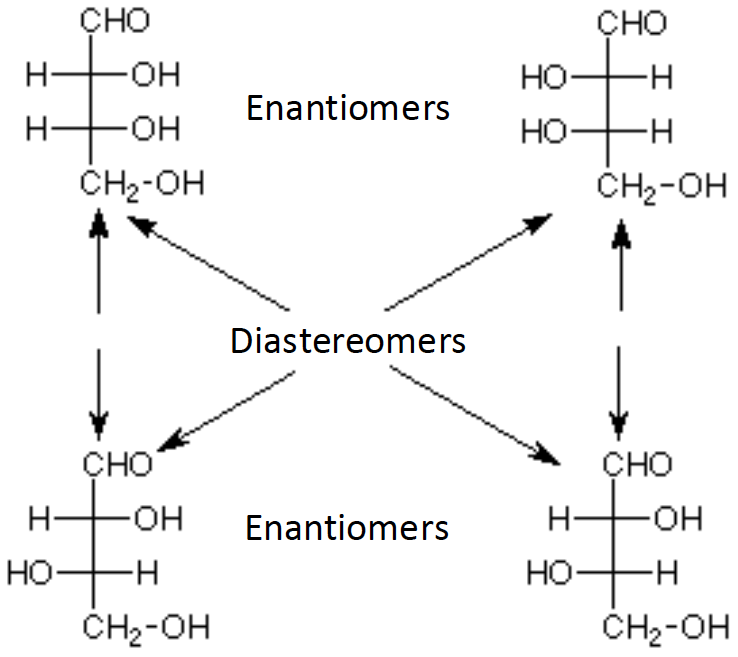
[...]are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable and are not mirror images of each other
diastereomers
not mirror images
Cis functional groups are on [...] side
Trans functional groups are on [...] sides
the same sides
opposing sides
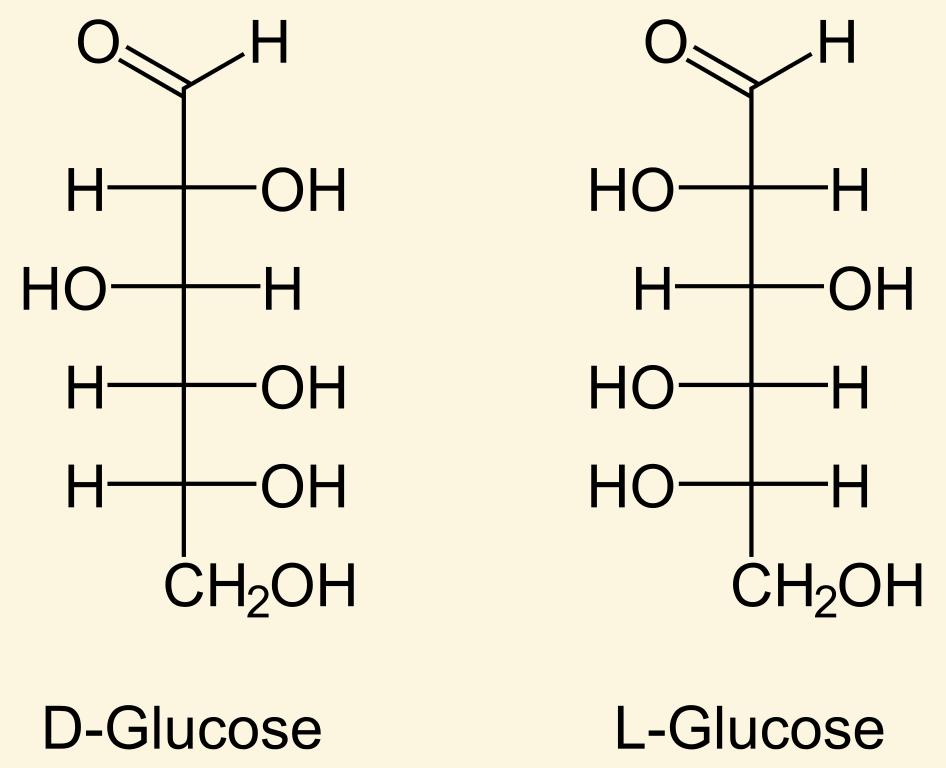
[.. configuration] gives the stereochemistry of a compound relative to the D- and L- forms of glyceraldehyde
relative configuration
in a fischer projection, look at the highest numbered chiral carbon
if -OH is on the right then its a D-sugar. If -OH is on the left then it is an L-Sugar
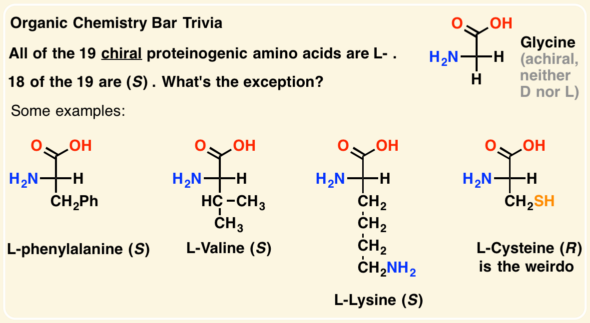
The stereochemistry of the α-carbon in all eukaryotic amino acids (except glycine) is [...]
L
[... configuration] gives the stereochemistry of a compound without having to compare to other compounds
absolute configuration
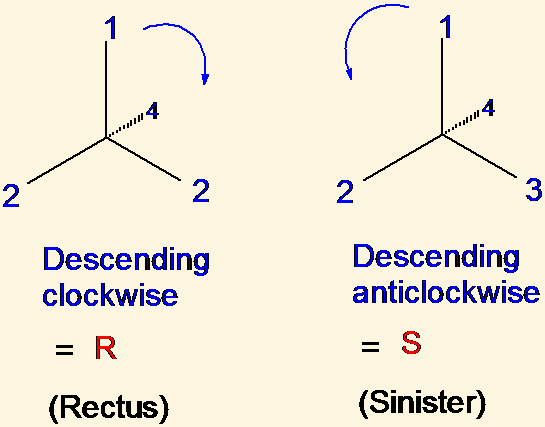
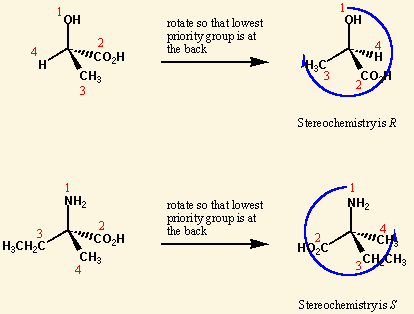
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules are rules for [...]
naming stereoisomers
priority is given by looking at atoms connected to the chiral carbon or double-bonded carbons. whichever has the highest atomic # gets highest priority
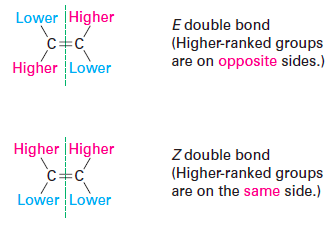
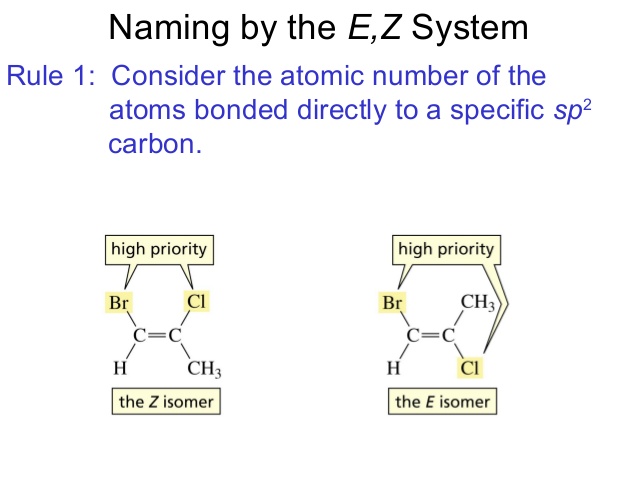
In the E-Z naming system for alkenes:
(Z) has the highest priority on [...] side(s)
(E) has the highest priority on [...] side(s)
the same
opposite
![<p>In Fischer projections:</p><p><strong><u>Vertical</u></strong> lines go to <span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span> of the page</p><p><strong>Horizontal</strong> lines <span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span> page</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c1d7c0c7-2ab3-4989-b263-ef2047818dca.png)
In Fischer projections:
Vertical lines go to [...] of the page
Horizontal lines [...] page
vertical lines go back of the page
horizontal lines come out of the page
vertical lines are like dashes
horizontal lines are like wedges