Chapter 6 part 2 Homework
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
In glycolysis ___ moles of ATP and ___ moles of NADH are produced per one mole of glucose consumption.
1, 2
2, 2
2, 1
1, 1
2, 10
2, 2
The first committed step in glycolysis is mediated by ___________.
hexokinase
phosphofructokinase
triose phosphate isomerase
pyruvate kinase
phosphofructokinase
Which of the following features are common to all anabolic pathways?
They are oxidative.
Their overall free energy change is positive.
They require energy.
They break down complex molecules.
They require energy.
Which of the following is a method of directly regulating PFK-1?
Feedback inhibition by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.
Feed forward activation by phosphoenolpyruvate.
By its phosphorylation in response to glucagon signaling.
Allosteric activation by ADP.
Allosteric activation by ADP.
When the energetic level (glucose) of the cell low glycolysis is ___________ and when plasma glucose level is low gluconeogenesis is ___________.
activated; inhibited
activated; activated
inhibited; activated
inhibited; inhibited
none of the above
activated; activated
The reactions of glycolysis that are bypassed in gluconeogenesis are catalyzed by the enzymes ___________.
hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase
pyruvate carboxylase, aldolase, and phosphofructokinase
glucose-6-kinase, aldolase and enolase
glucose-6-phosphatase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, pyruvate carboxylase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
glucose-6-phosphatase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, pyruvate carboxylase, and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
In humans, which one of the following statements about gluconeogenesis is TRUE?
Can result in the conversion of protein into glucose
Helps to reduce blood glucose after a carbohydrate-rich meal
Is essential in the conversion of fatty acids to glucose
Requires the enzyme hexokinase
Can result in the conversion of protein into glucose
Which of the following statements regarding gluconeogenesis is TRUE?
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate activates gluconeogenesis.
It occurs actively in skeletal muscle during periods of exercise.
It is likely to occur when cellular ATP levels are high.
Gluconeogenesis is reciprocally regulated with glycogen synthesis.
The conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to 2-phosphoglycerate occurs in two steps.
It is likely to occur when cellular ATP levels are high.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, is a multi-subunit enzyme that requires which of the following vitamins and cofactors?
lipoic acid, thiamine, ferredoxin, vitamin D
thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoamide, nicotine adenine dinucleotide
thiamine, ascorbic acid, niacin, pantothenic acid
ferredoxin, thiamine, niacin, FMN
thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoamide, nicotine adenine dinucleotide
Which of the following is NOT a direct product of pyruvate metabolism?
A. Acetyl-CoA
B. Lactate
C. Oxaloacetate
D. Phosphoenolpyruvate
Both C and D are correct.
D. Phosphoenolpyruvate
The conversion of triacylglycerides into fatty acids for energy generation is an example of which of the following?
heterotropism
anaerobism
catabolism
anabolism
glycolysis
catabolism
Cells control or regulate the flux through metabolic pathways by means of
I.allosteric control of enzymes.
II.covalent modification of enzymes.
III.genetic control of the concentrations of enzymes.
IV.altering the ∆G value of reactions.
I, II, III
In the catabolic pathway, major nutrients are _____ broken down mainly resulting in more _____ metabolites.
exergonically; reduced
endergonically; reduced
exergonically; oxidized
endergonically; oxidized
endergonically; phosphorylated
exergonically; oxidized
The products of glycolysis include ATP, NADH, and
pyruvate
The enzyme ___ is the major control point for glycolysis.
phosphofructokinase
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to glucose?
hexokinase
phosphoglucose isomerase
glucose-6-phosphatase
phosphoglucose mutase
A transfer such as this does not occur in glycolysis.
hexokinase
Which is the net equation for aerobic glycolysis?
Glucose + 2 ATP → 2 lactate + 2 ADP + 2 Pi
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ → 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + + 2 H2O + 4 H+
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 lactate + 4 ATP + 4 H+
Glucose + 2 ATP + 2 NAD+ → 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 4 NADH + 4 H+
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ → 2 lactate + 4 ATP + 2 NADH + 4 H+
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ → 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + + 2 H2O + 4 H+
Of the reaction types listed below, which type of reaction is NOT used in glycolysis?
oxidation
phosphorylation
dehydration
isomerization
All are used in glycolysis.
All are used in glycolysis.
Select the enzyme from the list that would catalyze the reaction shown below.
hexokinase (HK)
pyruvate kinase (PK)
enolase
phosphoglucomutase (PGM)
G3P dehydrogenase (G3PDH)
hexokinase (HK)
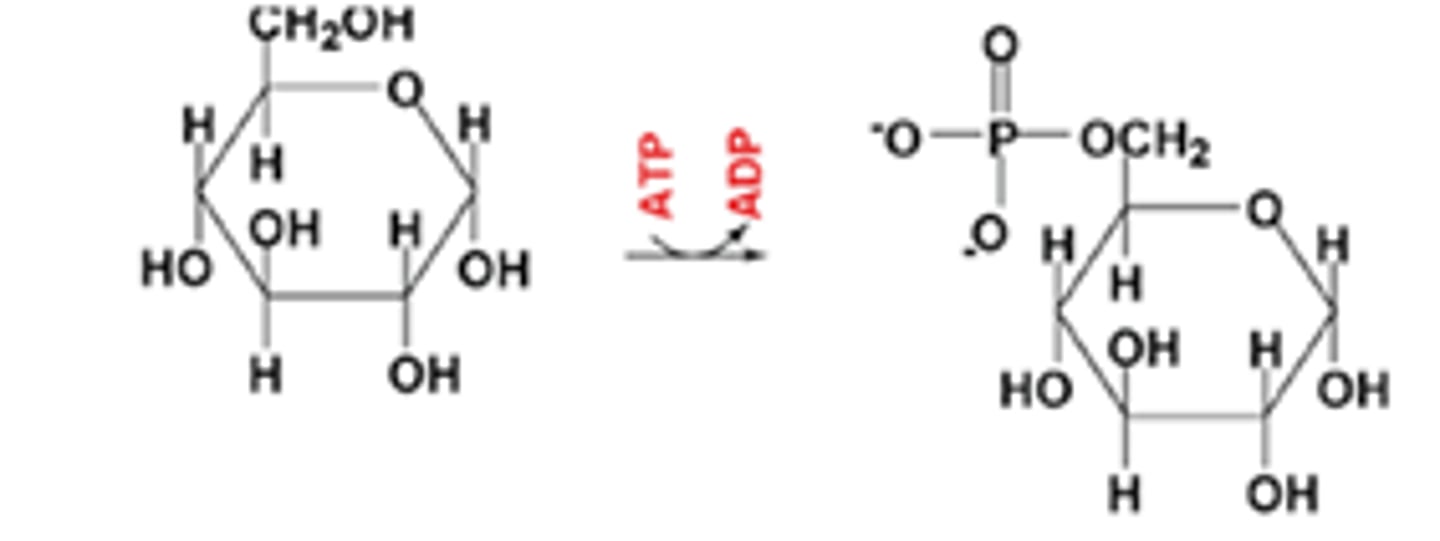
During reactions using the enzymes shown below, in which case(s) is ATP produced?
I.phosphofructokinase (PFK)
II.phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK)
III.pyruvate kinase (PK)
II, III
In which of the following metabolic conversions is ATP required during glycolysis?
I.fructose-6-phosphate → fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
II.glucose → glucose-6-phosphate
III.fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
IV.glucose-6-phosphate → fructose-6-phosphate
I, II
The process of _____ converts glucose into _____.
electron transport; CO2
glycolysis; pyruvate
glycogenolysis; glycogen
gluconeogenesis; glycogen
glycogen synthesis; pyruvate
glycolysis; pyruvate
Hexokinase is an example of a(n) _____ enzyme.
ligase
hydrolase
transferase
lyases
isomerase
transferase
Which enzyme is responsible for splitting a hexose into two trioses?
enolase
phosphoglycerate mutase
phosphofructose isomerase
triose phosphate isomerase
aldolase
aldolase
Which of the following is a potent activator of phosphofructokinase in mammals?
fructose-6-phosphate
glucose-6-phosphate
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
The active site of aldolase contains a Lys residue that forms a(n) _____ and a(n) Asp residue that participates in _____ reactions.
amide; acid-base
Schiff base; acid-base
secondary amine; acid-base
amide; isomerization
Schiff base; isomerization
Schiff base; acid-base
Triose phosphate isomerase catalyzes a reaction that is most like that of _____.
phosphoglycerate mutase
phosphoglucose isomerase
hexokinase
aldolase
enolase
phosphoglucose isomerase
Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 is oxidized to _____, which can transfer a phosphate to _____.
phosphoenolpyruvate; ADP
phosphoenolpyruvate; AMP
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; ADP
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; AMP
3-phosphoglycerate; ADP
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; ADP
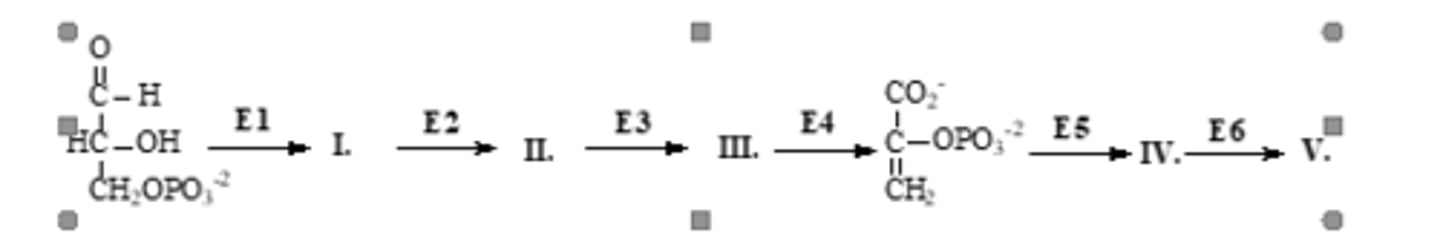
Consider the following portion of the glycolytic sequence catalyzed by the enzymes above the arrows. Which products(s) will produce ATP?
I, IV
II, IV
II only
III, IV
IV only
II, IV
Why is phosphoglycerate kinase still considered a kinase even though ADP is converted to ATP?
The enzyme is freely reversible.
ATP is the ultimate source of the phosphate that is transferred to ADP.
The phosphate is transferred in conjunction with an oxidation reaction.
The reaction is metabolically irreversible.
None of the above
The enzyme is freely reversible.
In which reaction below is ATP required?
I.1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) → 3-phosphoglycerate(3PG)
II.Glucose → glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
III.2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) → 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
IV.Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
V.Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) → fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
II only
Which reaction below is an oxidation reaction?
I.1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) → 3-phosphoglycerate(3PG)
II.Glucose → glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
III.2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) → 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
IV.Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
V.Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) → fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
IV only
In which reaction below is at least one NADH formed?
I.1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) → 3-phosphoglycerate(3PG)
II.Glucose → glucose-6-phosphate (G6P)
III.2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) → 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG)
IV.Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
V.Glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) → fructose-6-phosphate (F6P)
IV only
What type of enzyme is enolase, which catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate and water?
transferase
hydrolase
ligase
lyase
oxidoreductase
lyase
What sort of activity does fructose-1,6-bisphosphate have on pyruvate kinase?
no effect
competitive inhibitor
noncompetitive inhibitor
allosteric inhibitor
activator
activator
Phosphofructokinase is allosterically _____ by high concentrations of _____.
I.activated; ATP
II.inhibited; ATP
III.inhibited; fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
IV.activated; fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
II, IV
Which of the following metabolic conversions is considered the major control point of glycolysis?
fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → dihydroxyacetone phosphate + glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
glucose → glucose-6-phosphate
2-phosphoglyerate → phosphoenolpyruvate
fructose-6-phosphate → fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate
fructose-6-phosphate → fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Which of the following is true regarding glycolysis?
I.There is a net oxidation of substrate carbon atoms.
II.There is no net release of free energy.
III.Pyruvate is generated only during aerobic glycolysis.
IV.There are 2 ATP formed for every 2 glucose molecules.
I only
The reaction catalyzed by the enzyme aldolase has a G˚' ≈ +23 kJ/mol. In muscle cells, the reaction proceeds in this same, forward direction. How can this occur?
This G˚' means it is thermodynamically favored.
The enzyme changes the ∆G of the reaction in cells to something favorable.
The concentration of reactant(s) must be significantly greater than product(s) in cells.
The concentration of product(s) must be significantly greater than reactant(s) in cells.
None of the above
The concentration of reactant(s) must be significantly greater than product(s) in cells.
Which of the following best describes the entry of mannose into glycolysis?
hydrolyzed into two glucose units, they enter normally
phosphorylated at C-1; UMP moiety transferred from UDP-glucose; epimerized at C-2; released from UMP moiety on next transfer as G1P
phosphorylated at C-1; UMP moiety transferred from UDP-glucose; epimerized at C-4; released from UMP moiety on next transfer as G1P
phosphorylated at C-6; epimerized at C-2 to produce G6P
phosphorylated at C-6; isomerized to produce F6P
phosphorylated at C-6; isomerized to produce F6P
What pathway is used to make glucose from other metabolites such as pyruvate or lactate?
glycogen synthesis
glycogen degradation
glycolysis
pentose phosphate pathway
gluconeogenesis
gluconeogenesis
How many equivalents of ATP are required to convert two molecules of pyruvate to glucose?
2
4
6
8
10
6
Gluconeogenesis is most active in the _____.
muscles
brain
heart
liver
kidneys
liver
Which of the following is true concerning the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase?
It is an oxidative decarboxylation.
It is activated by high concentrations of ATP.
The enzyme contains a pyridoxal phosphate prosthetic group.
The reaction is an anaplerotic reaction because it can replace citric acid intermediates that are removed for other pathways.
The enzyme contains two different types of subunits.
It is an oxidative decarboxylation.
Which of the following is an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
CoA
pyruvate
FADH2
NADH
CO2
NADH
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to _____ by pyruvate dehydrogenase.
oxaloacetate
ethanol
lactate
glucose
acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA
What cellular location contains pyruvate dehydrogenase and most of the citric acid cycle enzymes?
cytosol
mitochondrial matrix
inner mitochondrial membrane
mitochondrial intermembrane space
outer mitochondrial membrane
mitochondrial matrix
Under anaerobic conditions in skeletal muscle, pyruvate is converted into _____.
ethanol and CO2
propionate
acetyl-CoA
lactate
alanine
lactate
Glycolysis forms ___ under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions.
ATP
In skeletal muscle cells, oxidation of NADH generated from anaerobic glycolysis occurs during which of the following reactions?
acetaldehyde → ethanol
lactate → pyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate
pyruvate → lactate
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
pyruvate → lactate