Earthquakes & Structures
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
What are Earthquakes
Seismic events caused by the sudden release of strain energy in the Earth's crust, resulting in ground shaking.
Divergent Plates
Resulting in shallow earthquakes
Converget
Wide zone of shallow, intermediate, and deep earthquakes
Transform
Shallow to intermediate earthquakes
Elasticity
The ability for rocks to bend/stretch & return to original shape
Stress
The force per unit applied to a rock (pulling on a rubber band).
Ductile
Rocks that bend/flow like soft metal, happens deep underground.
Brittle
Rocks that break/frature; Happens near surface
Normal (Extensional)
Stress type: Tension (pulling apart)
Movement: Hanging wall moves down in relations to foot wall
Pulling apart a noodle, it goes down the more it’s pulled
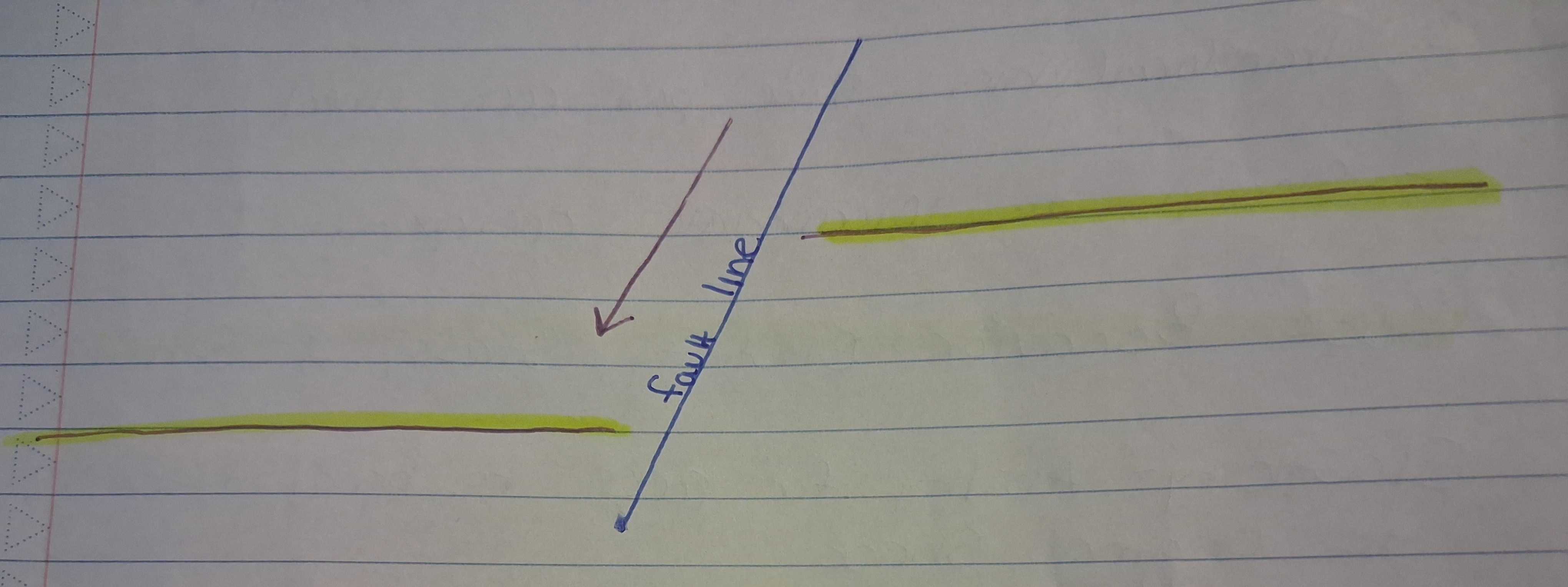

Thrust/Reverse Fault (Compressional)
Stress type: Compression (pushing together)
Movement: Hanging wall moves up
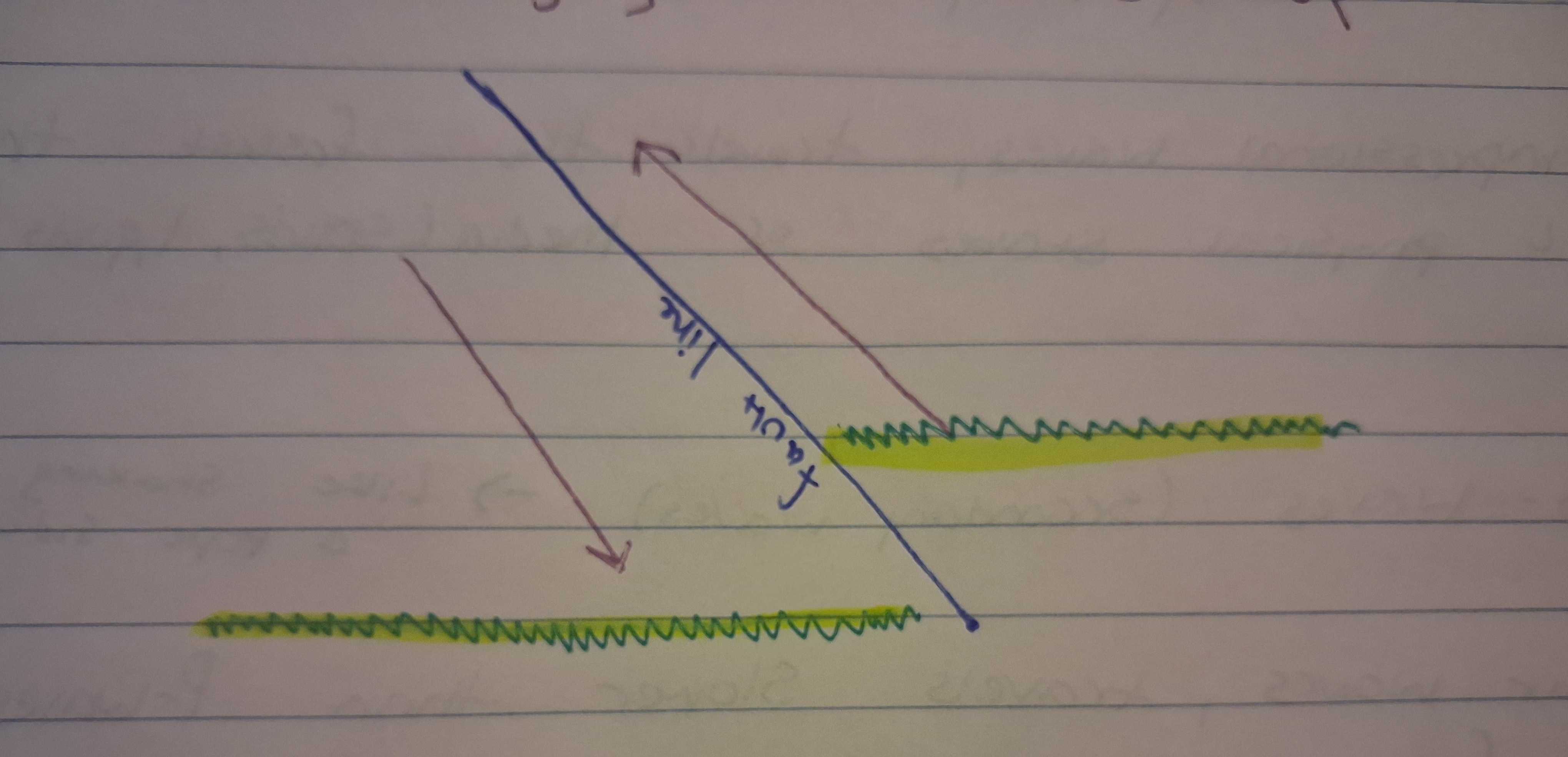
Transform (Sliding)
Stress type: Shear (sliding)
Movement: Left or right laterual fault
Seisim Waves
When rocks break, energy is released as waves moving through Earth
P-Wave (Primary waves)
Compressional waves, travels the fastest through ALL physical states of media (solids, liquids, & gas)
S-Waves (Secondary)
Shear waves, travels slower, only travels through solids.
Surface Waves
Moves along the Earth’s surface, travels the slowest but causes the most damage to buildings.
Epicenter
The point on the surface above where the Earthquake starts
Hypocenter Focus
Actual underground location where the rock breaks
Stage 1: Stress building along fault
Deep inside the Earth, tectonic plates constantly move. At the plate boundaries or along faults (cracks in crust), stress builds because of rocks pushing, pulling, or sliding against each other.
Stage 2: Elastic Deformation (strain)
As stress increases, rocks start to deform, bend & stretch without breaking
Stage 3: Rupture/Earthquake
The stress becomes too great for the rocks so they break/slip a long the fault line. The stored energy is realsed as seismic waves.
Stage 4: Aftershake
Smaller quakes can happen as rocks adjust & find a stable position. Can last days, to weeks to months.
Natural Earthquake
When there is a sudden release of strain energy caused by rock rupture (faulting)
Human activities
Induced earthquakes like reservior-induced, deep waste disposal, nuclear explosions, & magnitude.
Structual Geology
The study of how the Earth’s crust is shaped & deformed. Helps understand how rocks bend, break, & move
Deformation
All changes in the original form and/or size of the rockbody.
Where it happens: Mostly along the plate boundaries where the Earth’s plates collide, move apart, or slide past.
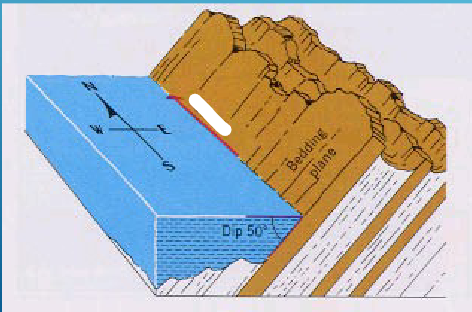
Strike (Trend)
The compass direction of a line made by the intersection of an inclined rock later or fault with a horizontal plane.
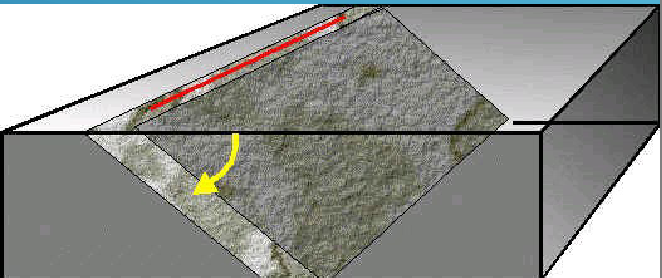
Dip
The highest angle of inclination of the surface from a horizontal plane. Includes both angle direction toward which rock is inclined
Anticline
Upfolded or arched rock layers; Oldest rocks in center
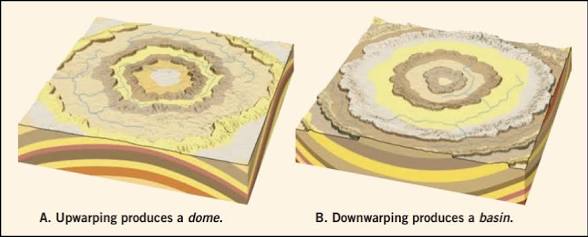
Syncline
Downfolded or throughs of rock layers; Youngest rocks in the center
Recumbent (Overturned)
Fold tipped on its side
Plunging
Fold dips into the ground
How is soil formed?
From parent material (the rock it came from) & changes over time due to:
Climate - Temperature & rainfall
Topography - Slope/elevation
Biological activity- Plants, animals, microbes
Time - The older = more developed
Laterite (soil type)
Warm and wet climate
Rich in aluminum & iron. Was formed in a high/wet tropical areas. High weathered soil that is nutrient poor.

Pedocal
Dry climate. Soil that forms in grassland regions. The climate is drier with less rain. When there's less rain, there's less chemical weathering, less organic material, & soil is more fertile.

Pedalfer
Cool and wet climate. Very fertile, dark brown or black soil. Rich in aluminum and iron oxides .

Flat slopes
Soil can be thicker & more developed. Rainwater moves slowly, allowing infiltration & plant growth. More organic matter builds up
Steep slopes
Soil is thin and easily eroded. Water runs off quickly, carrying away sediment. Less time for soil to form
Relative Dating
The process of determining the chronological order of events in Earth’s history w/o knowing the exact ages in years.
Law of Superposition
In an underformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, oldest rocks are on the bottom

Principle of Original Horizontality
Sediments are deposited horiontally. If layers are tilted/folded, that was after it was deposited.

Principle Lateral Continuty
Sediment layers extend in all directions until they thin out or encounter a barrier or “valley”
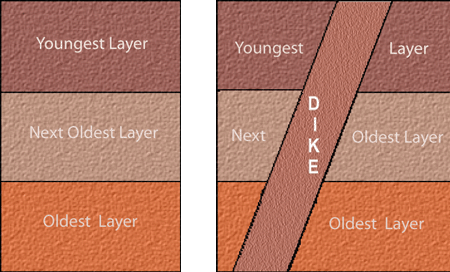
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
If 1 geologic feature cuts across another, it’s the youngest of what is cut
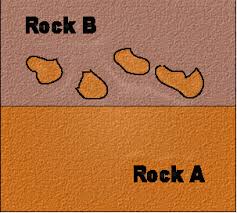
Inclusions
Fragments within a rock that are older than the rock itself
Unconformities
Gaps in the rock record that represent missing time.
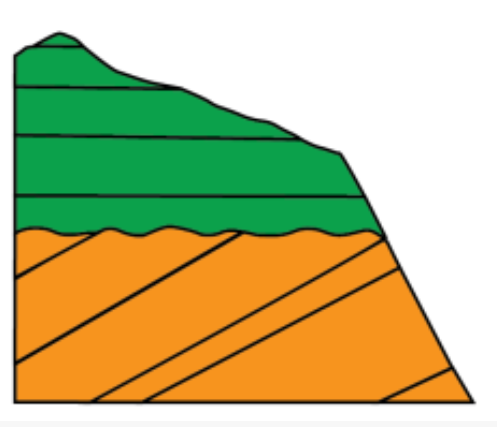
Angular uncomformity
Tilted rocks + flat rocks = ?
Older layers were deposited & tilted by tectonic forces. It eroded the top off and new horizontal layers deposited on top.
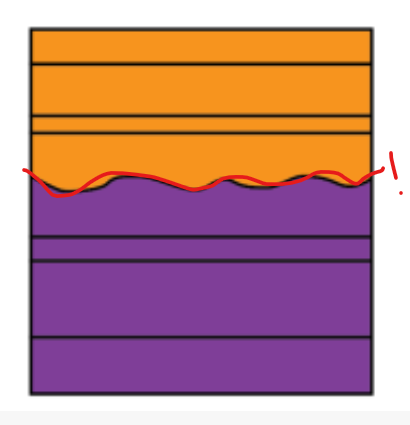
Disconformity
Parallel layers + erosion gap = ?
Both rocks were deposited horizontally, BUT the upper surface eroded after some time before a new sediment was deposited. There’s missing rock record (time gap!)
Line is wavy b/c of eroded surface
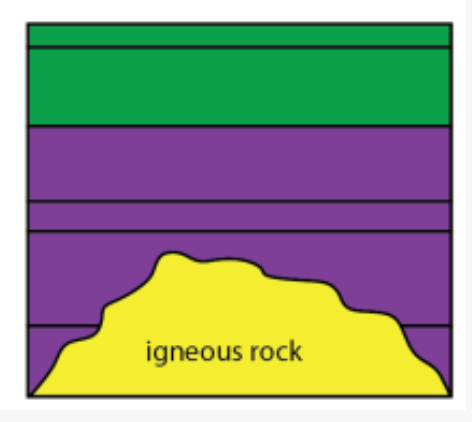
Nonconformity
When sedimentary layers are in contact with igneous or metamorphic rocks
Sedimentary rocks marks a huge time gap.
What are fossils?
Traces or remains of ancient life preserved in rocks, usually sedimentary.
Protons
Positively charged particles (found in nucleus_
Neutrons
Neutral particles (no charge, found in nucleus)
Electrons
Negatively charged particles (orbits the nucleus)
Atomic Number
Number of protons (defines the element)
Ex: Carbon = 6
Atomic Mass
Number of protons + neutrons (determines isotope type)
Isotopes
Versions of the SAME element that have the same # of protons BUT different # of neutrons
Radioactive Decay
When an unstable atom’s nucleu changes on its own (spontanous decay)
Alpha Decay
The atoms emits 2 protons + 2 neutrons
The mass decreases by 4, atomic # decreases by 2
Beta Decay
A neutron splits into an electron & proton
The electron is emitted
Atomic mass stays the same & atomic # increases by 1
Electron Capture
The electron combines with a proton to form a nucleus
Atomic mass stays the same, atomic # decreases by 1
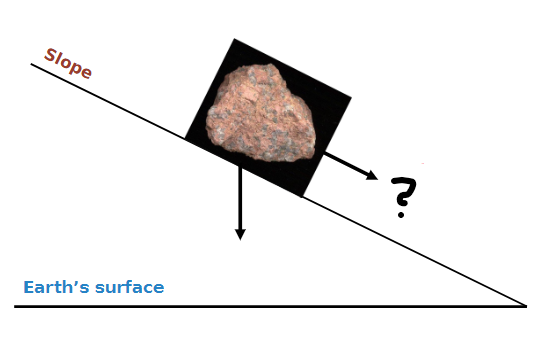
Mass Wasting?
The downhill movement of soil, rock, and debris caused by gravity
Driving Force (gravity)
Pulls downhill, the steeper the slope, the stronger the pull
Resisting Forces (friction & strength)
Keeps materials in place & depends on:
Friction between particles
Cohesion (how well the materials stick together)
Vegetation (roots help hold still)
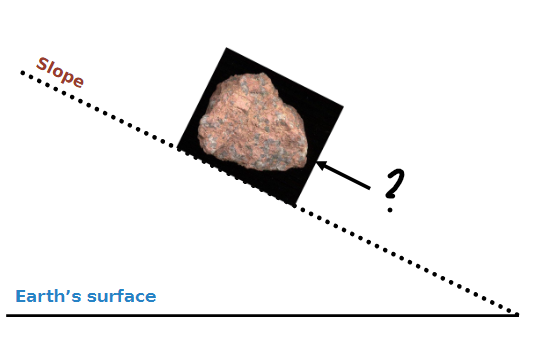
Angle of Response
The momentum angle at when a pile of material remains stable
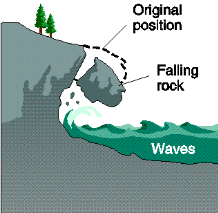
Rock fall
Loose rock fragments fall straight down through air (cliffs or mountain areas)
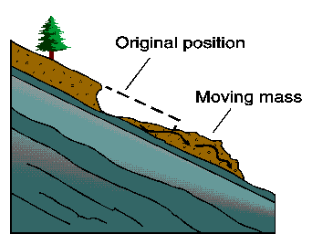
Slide
Material moves quickly downhill along a flat or curved surface (landslides)
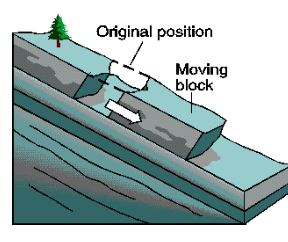
Slump
Loose material moves down a curved surface
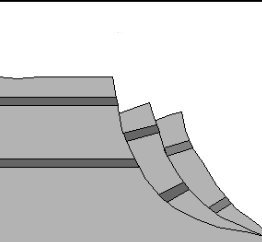
Flow
A mix of soil, water, and rock moves through thick liquid (mudflows)
Creep
Very slow downslope movement, happens gradually
Hydrology
The study of water on Earth- it’s sources, cycle, & effects on land
Hydrologic Cycle
The circulation of Earth’s water supply. Constantly moes through the cycle, changing between liquid, gas, & solid states as it circulates the atmosphere, oceans & lands
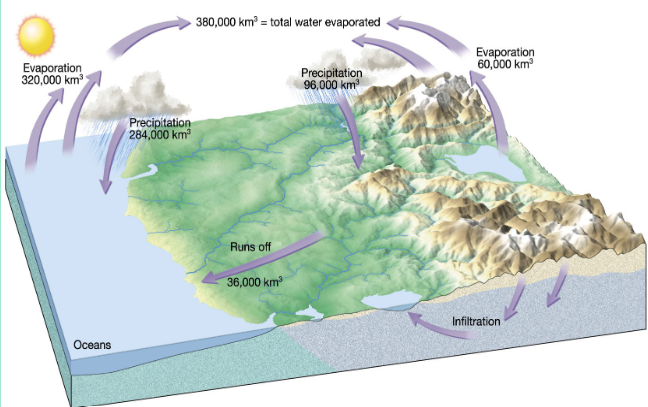
Reservior
A place where water is stored (oceans, lakes, groundwater, atmosphere)
Residence Time
Reservior capacity/influx or outflux
(How long water stays in reservior)
Preciptation process
Rain, snow, sleet, hail
Evaportation process
Water changes from liquid to vapor
Infiltration process
Water soaks into the ground. It’s capacity/amount is controlled by:
Intensity/duration of rainfall, prior wetted condition of soil, soil texture (sand, clay, etc.), slope of land (steeper = more runoff), & nature of vegetation cover (plants increase this process)
Running water - Surface water
Streams that transports sediments through erosion & depositon
Dissolved Load
A river's sediment that is carried in solution, consisting of ions and small molecules from minerals and organic matter.
How it works: These materials are invisible & traveled within the water itself as a chemical solution
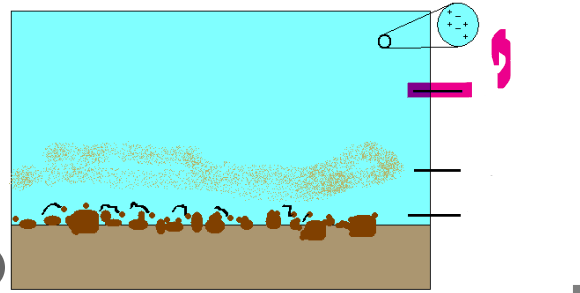
Suspended load
A river's sediment that is carried within the water column, consisting of larger particles like silt and clay
How it works: It remains above the ground due to turbulence
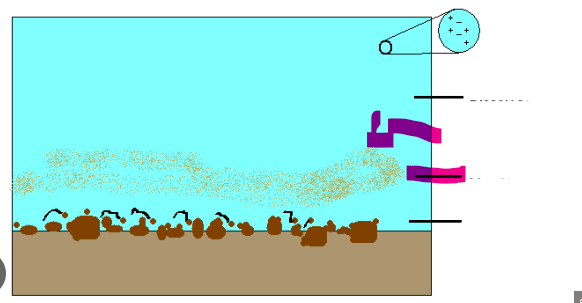
Bed load
Sediment that is transported along the bottom of a river or stream by the force of flowing water. This type of sediment transport includes larger particles, such as gravel and sand, which are moved through processes like rolling, sliding, and saltation.
Stream competence & Capacity
Streams differ in what & how they can carry depending on speed & volume
Competence
The largest particle size a stream can transport
Controlled by: Stream velocity (speed)
Ex: Fast mountain streams can carry boulders but slow rivers, only silt and clay
Capacity
The total amount (mass or volume) of sediment a stream can transport at once
Controlled by: Stream discharge
Ex: A wide, deep river has a greater ____ than small creek, even at the same velocity
Base level
The LOWEST part of erosion. This is the lowest elevation a stream can erode its channel to.
Ultimate base level
Sea level. The limit for most rivers.
Local or temporary
A lake, resistent rock layer or another river
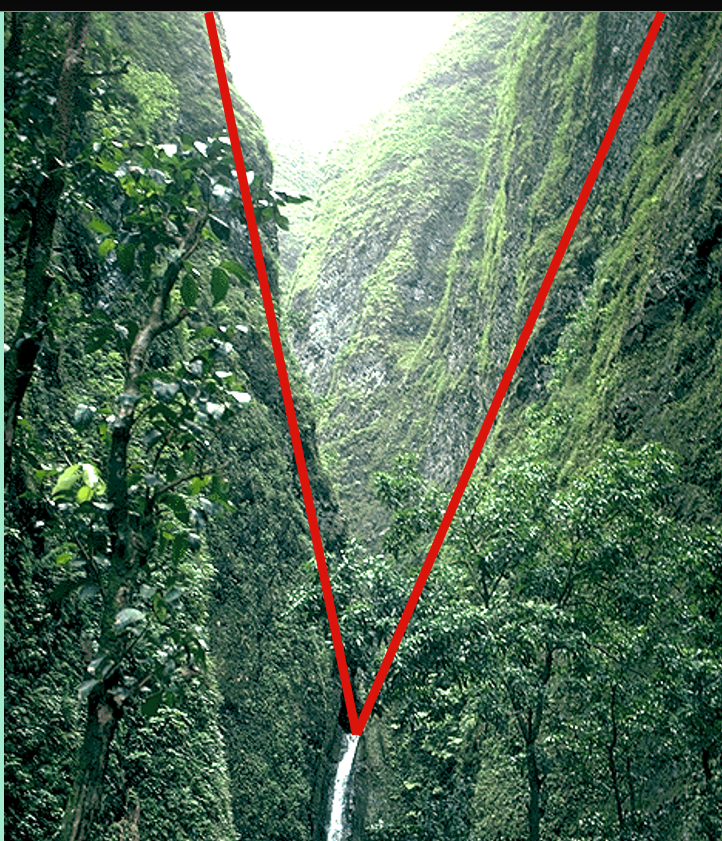
Channel
The path in which the stream normally flows (usually V-shaped)

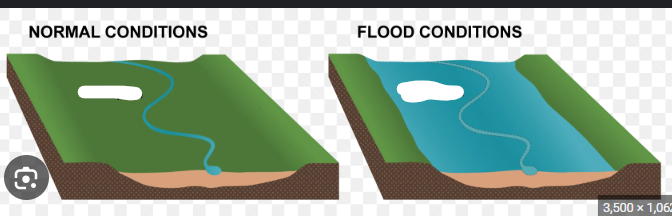
Floodplain
Flat area that floods when water overflows
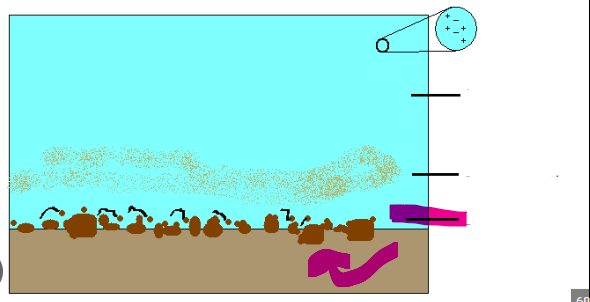
Thalweg
Fastest flowing part of stream
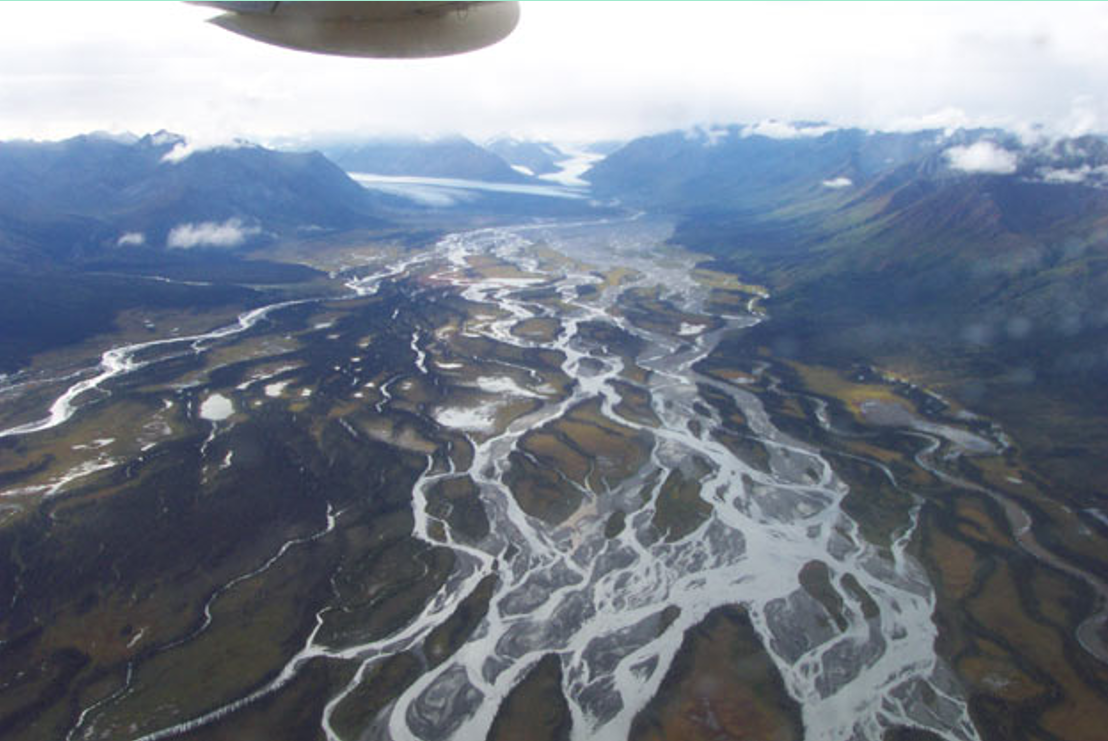
Braided stream
Multi channeled
High slope/steep gradient
Usually fairly shallow & wide
High velocity
Typical of moutain regions

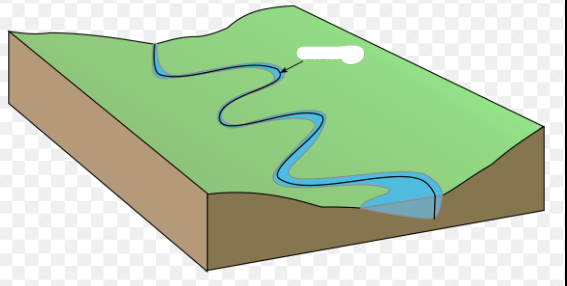
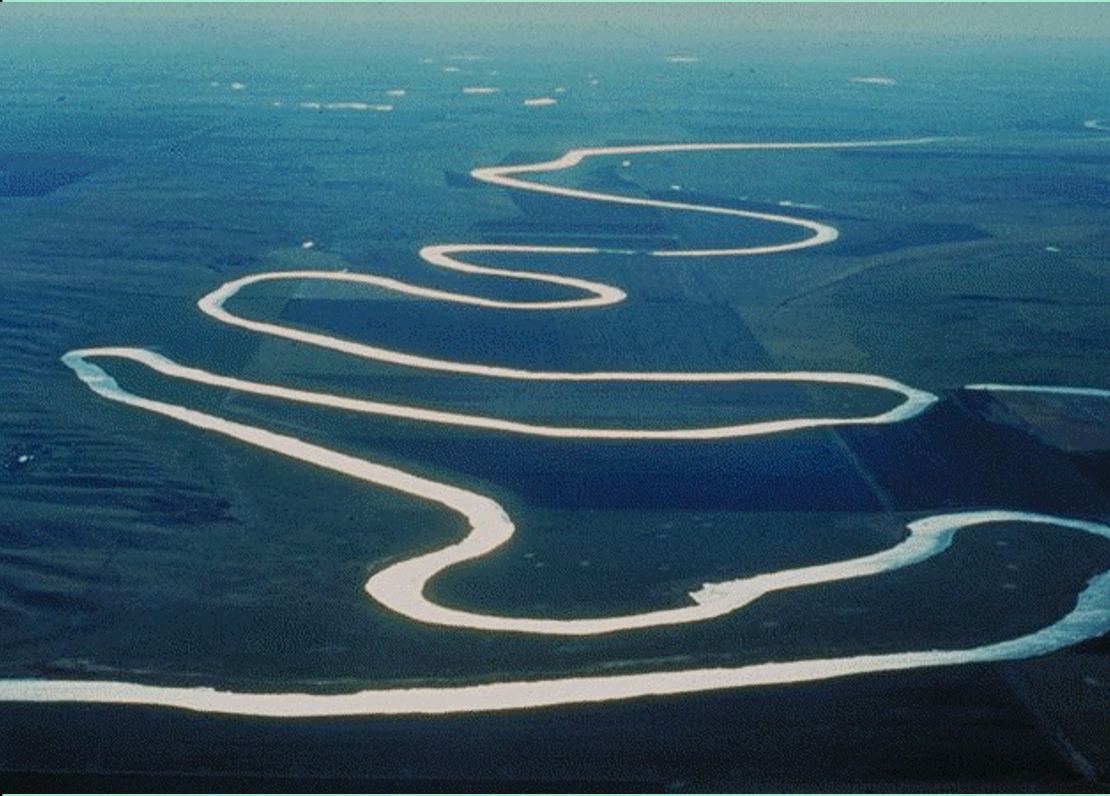
Meandering Stream
Single channeled
Low slope/shallow gradient
Slower flow
Found in plains

Drainage networks
Land area that contributes water to the stream is the drainage basin
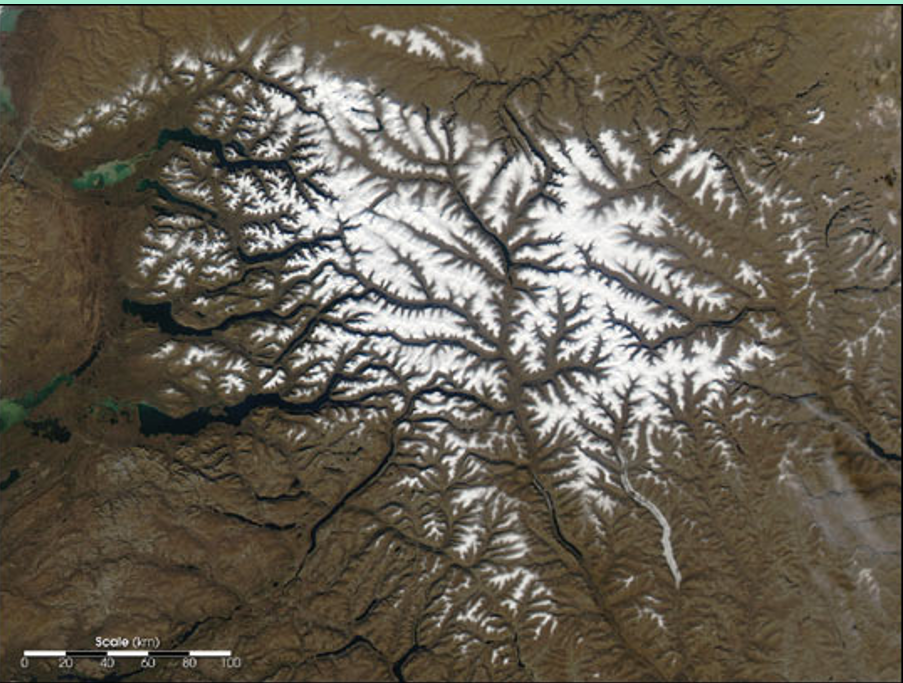
Dendritic
Formed by small streams (twigs) that join together to form larger streams (branches), which ultimately converge into a single, main river (the trunk).
Most common type of drainage system

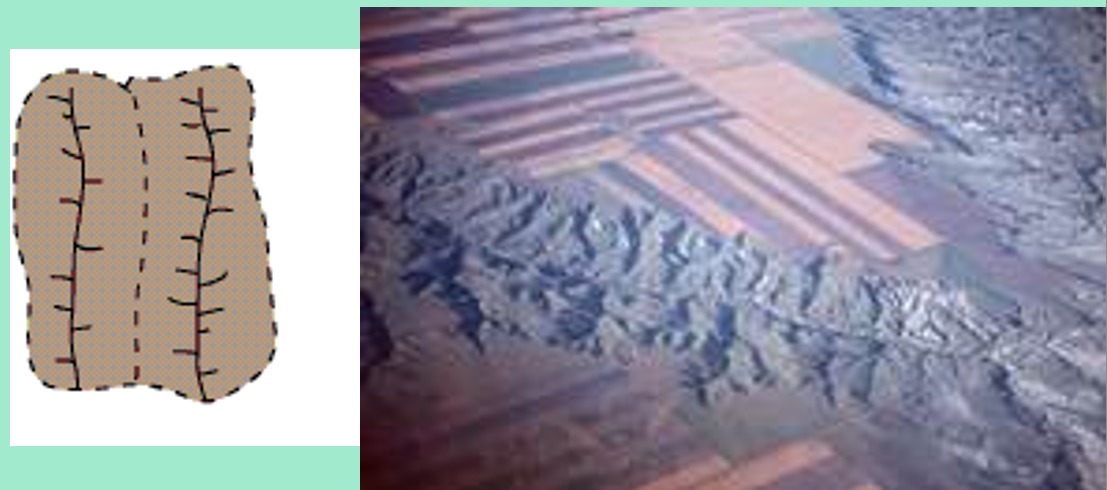
Rectangular
Type of river system where streams and tributaries bend at right angles, forming a grid-like network
Controlled by faults/fractures
Trells
Drainage pattern which develops in folded mountain belts (syncline & anticline) with alternating layers of hard and soft rock.

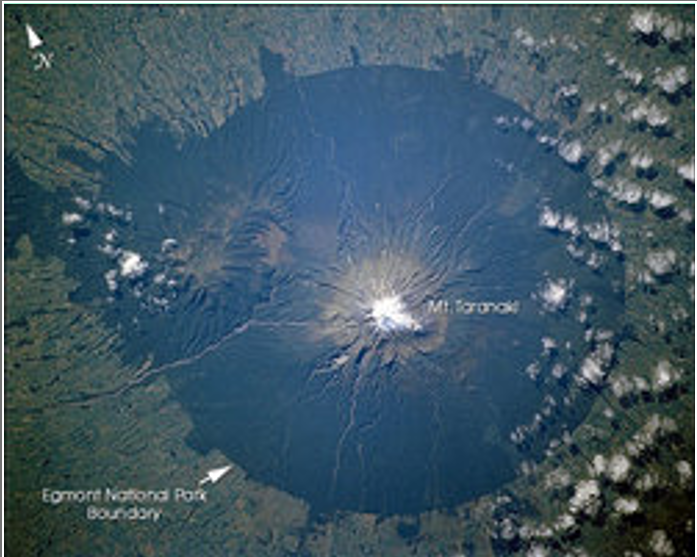
Radical
Formed by running water flowing down mountain peak
(Like a volcano is acne and the water is going down it)

Groundwater
Fills the pores of soils & cracks in rock beneath the surface. Largest reservior of freshwater.
Zone of saturation
Area in soil/below surface in which all pores are filled with water. Where underground water exists
Water table
Boundary between saturated/unsaturated zones. Shape usually mimics the land’s surface. Varies seasonably & it’s depth depends on rainfall, season, & soil type
Capillary Fringe
Extends upwards from the water table. Water is held by small pores by surface tension
Zone of aeration/vadose zone
Area above the water table in which the pores are not filled with water. Can’t pump water from here.
Gaining Stream
Water from groundwater seeping into streambed
