Chapter 45 (Cardiology Procedures)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Amplifier
A device on an electrocardiogram that enlarges the ECG impulses. (def.)
Arrhythmia
Without rhythm; Irregularity (def.)
Artifacts
Something extraneous to what is being looked for. Activity that causes interferences on EKG's/ (def.)
Atrial Depolarization
The excitement and contraction caused by the SA node at the beginning of the cardiac cycle. (def.)
Augmented
Refers to leads 4, 5, and 6 of the standard 12-lead ECG tracing; these leads are of different voltage. (def.)
Cardiology
The study of the heart and its action and diseases. (def.)
Countershock
a high intensity, short duration, electric shock applied to the area of the heart, resulting in total cardiac depolarization. (def.)
Defibrillator
a device designed to deliver an electric shock to a patient, in an effort to stop pulseless ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. (def.)
Echocardiography
Ultra high frequency sound waves to form an image of the inside of the heart. (def.)
Echoes
Reflection of sound waves. (def.)
Electrocardiogram
A graphic record of the electric currents generated by the heart; a tracing of the heart's action
Electrode
A instrument with a point or a surface that transmits current to the patient's body.
Galvanometer
An instrument that measures current by electromagnetic action.
Holter Monitor
a device that attaches electrodes to a patient's chest for the purpose of obtaining a 24-hour ECG tracing in an accessory tape recorder. (def.)
Impulse
A charged transmitted through certain tissue, especially nerve fibers and muscles.
Interference
Confusion of desired signals caused by undesired signals.
Intermittent
Stopping and starting at irregular intervals. (def.)
Interpretive
Computerized analysis of ECG tracings
Interval
Time between events; space (def.)
Limbs
Arms and legs (def.)
Mechanical
Pertaining to machinery (def.)
Multichannel
Refers to the capability of ECG equipment of processing impulses from multiple leads. (def.)
Precordial
Pertaining to the area of the chest wall over the heart for the placement of ECG chest leads. (def.)
Repolarization
Establishment of a polarized state in a muscle or nerve fiber following contraction of conduction of a nerve impulse (heart muscle). (def.)
Sedentary
Pertaining to sitting; inactivity (def.)
Segment
A part or section of an organ or a body. (def.)
Simultaneous
Occurring at the same time. (def.)
Somatic
relating to or affecting the body, corporeal. (def.)
Standardization
The process in which a test is administered to a large group of people whose performance then serves as a standard or norm against which any individual's score can be measured. (def.)
Stylus
The ECG writer. (def.)
Trace
The production of a sketch by a stylus (electrocardiogram). (def.)
Voltage
A measure of electromotive force. (def).
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Heart rhythm originating in the sinoatrial node with a rate in patients at rest of 60 to 100 beats per minute
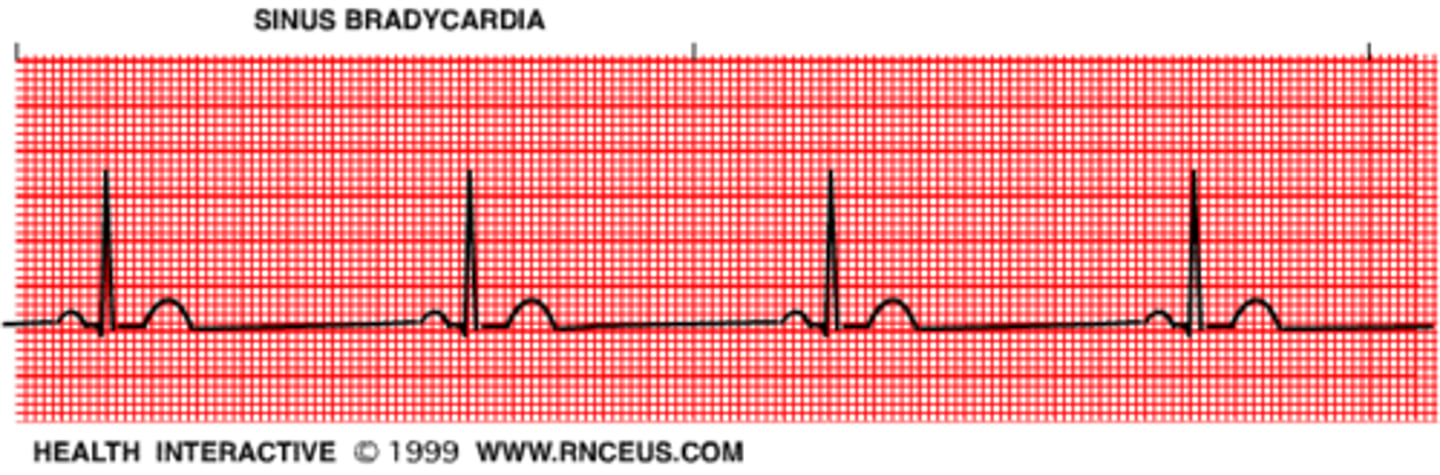
Sinus Bradycardia
<60 normal sinus rhythm
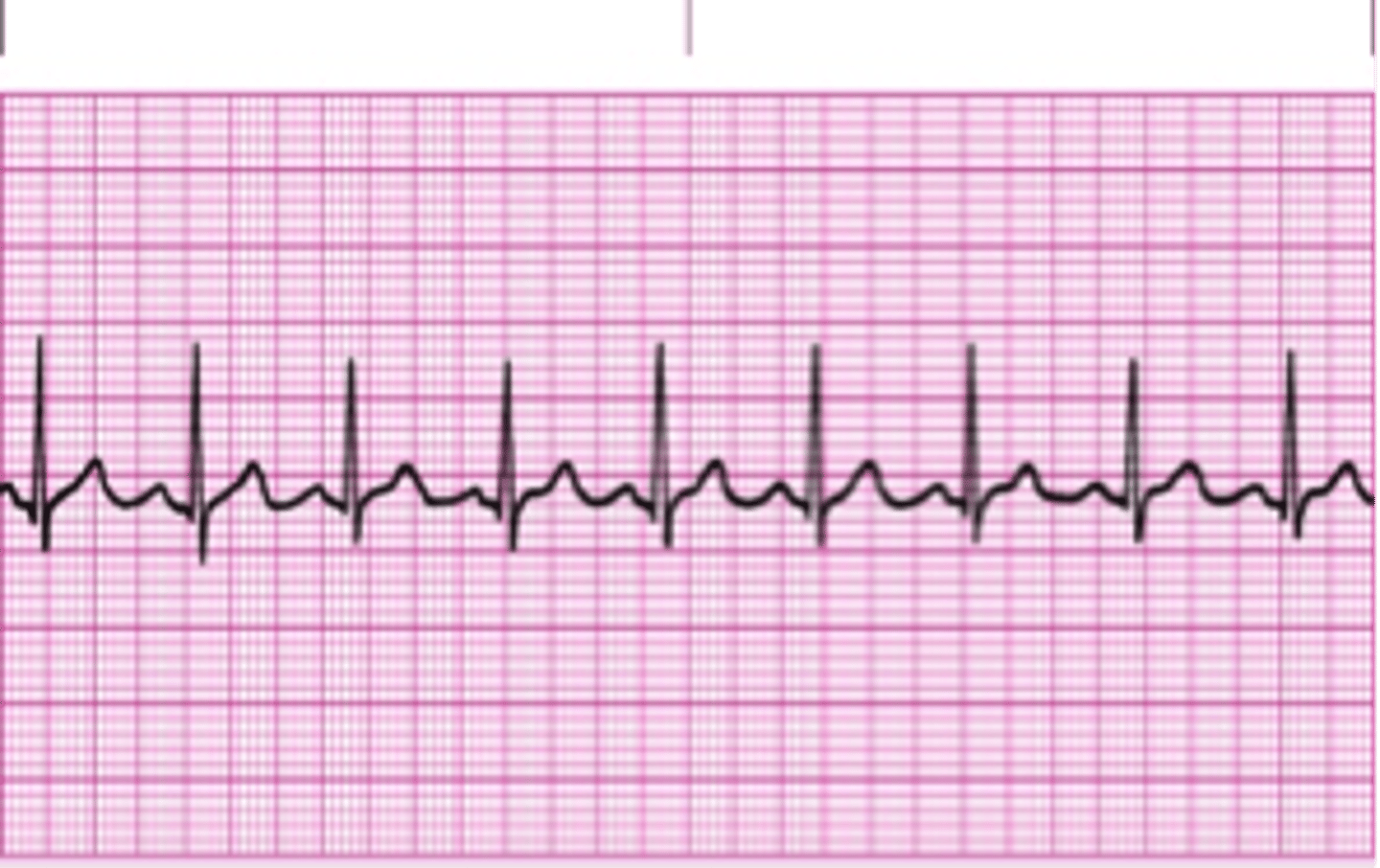
Sinus Tachycardia
>100 normal sinus rhythm
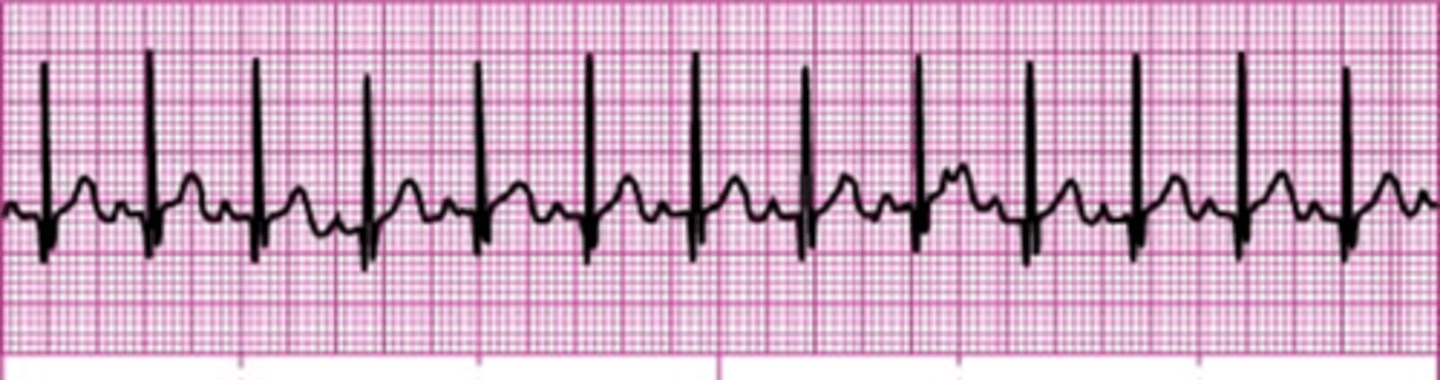
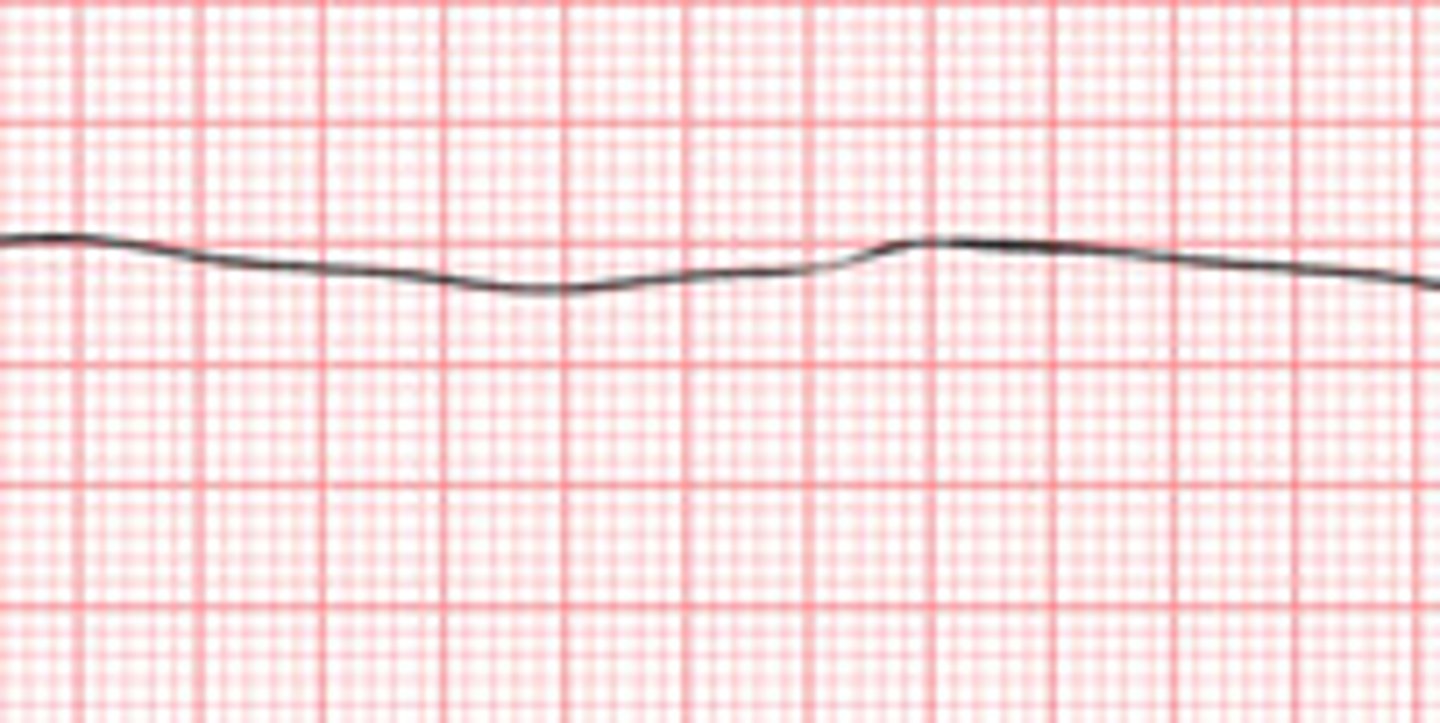
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
An irregular and often very fast heart rate originating from abnormal conduction in the atria.
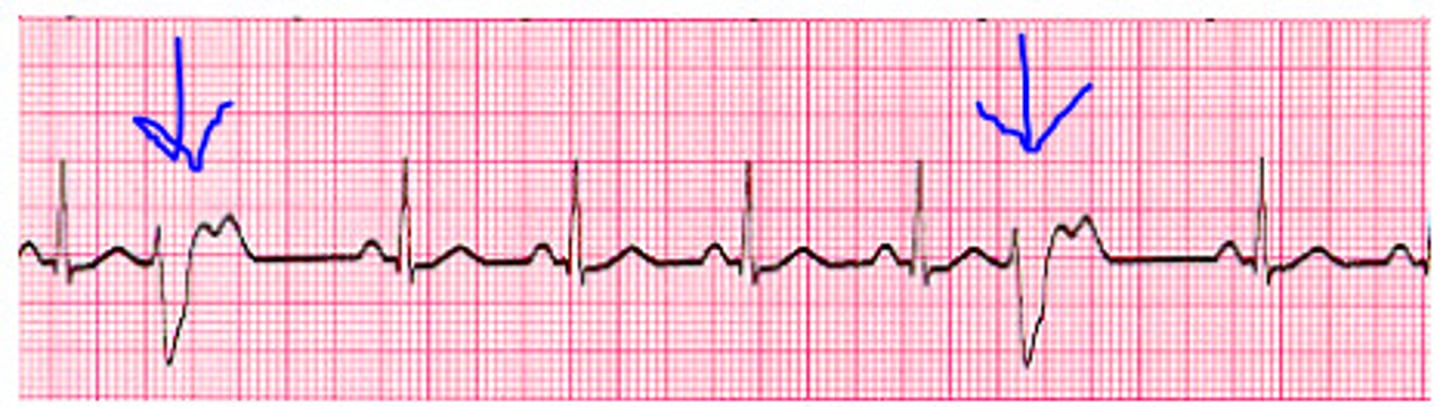
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
A common cardiac arrhythmia that results in the feeling of skipped or extra beats caused by impulses originating outside the SA node
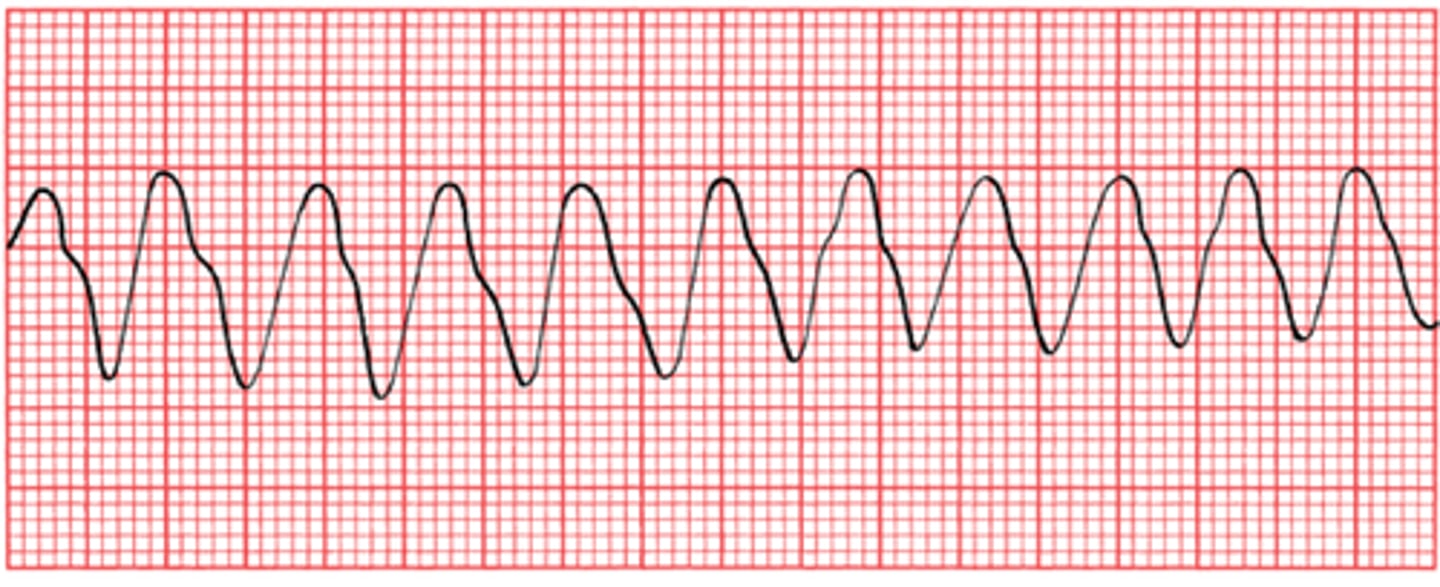
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)
Disorganized, ineffective twitching of the ventricles, resulting in no blood flow and a state of cardiac arrest.
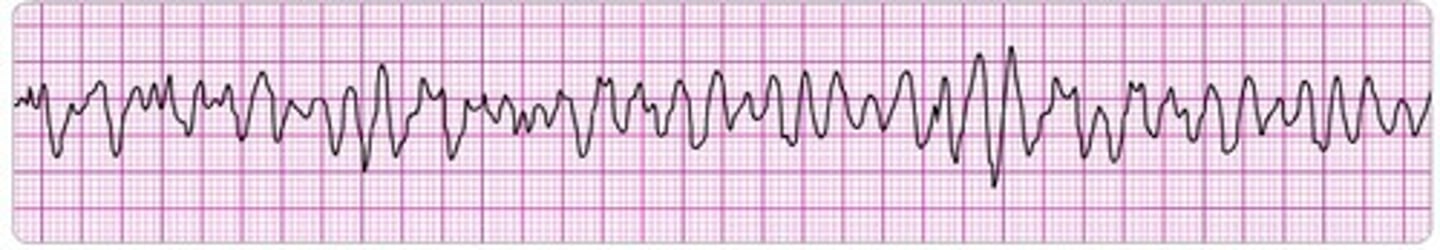
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Rate usually above 100 bpm. rhythm usually regular. no P wave or it appears after QRS complex with retrograde conduction. requires immediate medical attention. common causes: post MI, rheumatic heart disease, CAD and cardiomyopathy
Asystole
Absence of contractions of the heart