Biology: Reproductive System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Asexual Reproduction = No gametes, identical offspring
Binary fission
Budding
Regeneration
Parthenogenesis
Binary fission
DNA replicates, cell splits (prokaryotes, bacteria)
Budding
New organism forms from outgrowth (yeast, hydra)
Regeneration
Fragment regrows (planaria, fungi)
Parthenogenesis
Unfertilized egg becomes organism (honeybees: males haploid, females diploid)
Spermatogenesis (Sperm Formation)
Location: Seminiferous tubules in testes
Process: Spermatogonia → sperm (haploid) via meiosis
Structure:
Head: nucleus + acrosome (enzymes)
Midpiece: mitochondria (ATP)
Tail: flagellum (movement)
Pathway of sperm (SEVEn UP)
Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra → Penis
Seminiferous tubules
Site sertoli (spermatogenesis)
Epididymis
Sperm maturation
Vas deferens
Move sperms
Ejaculatory duct
Propels
Male: FSH
Stimulates sperm and Sertoli cells (support, inhibin)
Male: LH
Stimulates Leydig cells → testosterone
Male: Testosterone
Maturation and male traits
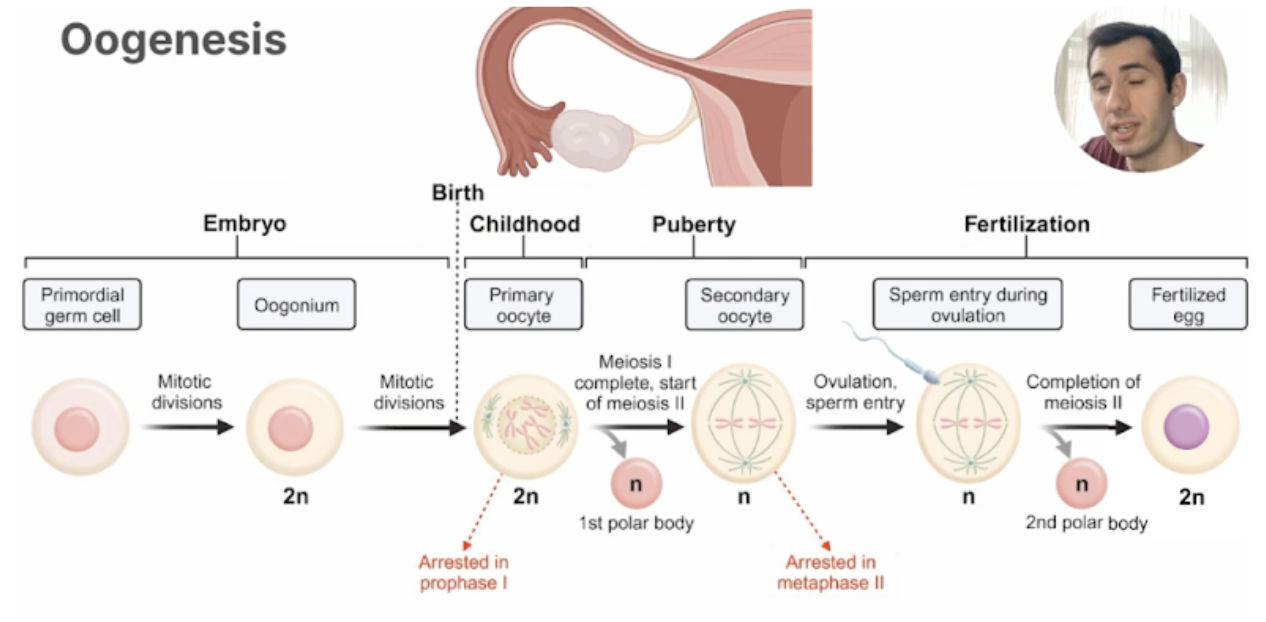
Oogenesis (Egg Formation)
Ovary: Produces egg (ovum)
Pathway: Ovary → fimbriae → fallopian tube → uterus
Female: FSH
Matures follicle, increases estrogen
Female: LH
Triggers ovulation, forms corpus luteum
Female: Estrogen/Progesterone
Maintain endometrium and cycle
Egg Arrest
Arrested Before puberty: Prophase I
Primary oocytes: Prophase 1: resume puberty
Arrested After ovulation: Metaphase II
Secondary oocytes: Metaphase 2: resume: fertilization
Follicles release : estrogen and progesterone
Menstrual Cycle
Follicular Phase
Ovulation
Luteal Phase
Fertilization
No fertilization
Follicular Phase
FSH stimulates follicle growth → estrogen thickens endometrium
Ovulation
LH spike → egg released
Luteal Phase
Corpus luteum → estrogen & progesterone thickening(maintains lining FSH & LH)
Fertilization
hCG maintains corpus luteum → progesterone stays high → no menstruation
No fertilization
Hormones drop → menstruation
Positive and Negative Feedback Loops
Positive: Prolactin (milk), oxytocin (release & birth)
Negative: Estrogen/progesterone inhibit FSH/LH
Fertilization
Capacitation
Acrosomal Reaction
Blocks to Polyspermy:
Fast block: Na⁺ influx (depolarization)
Slow block: Cortical reaction (hard shell)
Meiosis II completed after sperm entry
Capacitation
Sperm matures in uterus
Acrosomal Reaction
Sperm binds ZP3 on egg vitelline layer → enzymes digest egg coat
Twins
Monozygotic: One zygote → splits (identical)
Dizygotic: Two eggs fertilized 2 (fraternal)
Embryogenesis
Cleavage
Stages:
Meroblastic: uneven
Holoblastic: even
Zygote then goes through its process
Germ Layers
Cleavage: Rapid divisions, same total size
Radial: vertical (deuterostomes)
Spiral: spiral (protostomes)
Indeterminate (regulative) (totipotent: turn into anything)
Mosaic: Determinate (fixed fate)
Zygote: Morula
Solid ball blastomere
Zygote: Blastula
Hollow ball (fluid filled) blastocoel
Zygote: Gastrula
3 germ layers trilaminar embryo
Germ Layer: Ectoderm
Nervous system, skin, hair, enamel, adrenal medulla, mammary glands
Germ Layer: Mesoderm
Muscles, bones, heart, gonads, notochord
Germ Layer: Endoderm
Linings, pancreas, liver, thyroid
Stem cells
Undifferentiated cells with the potential (potency) to develop in many different ways
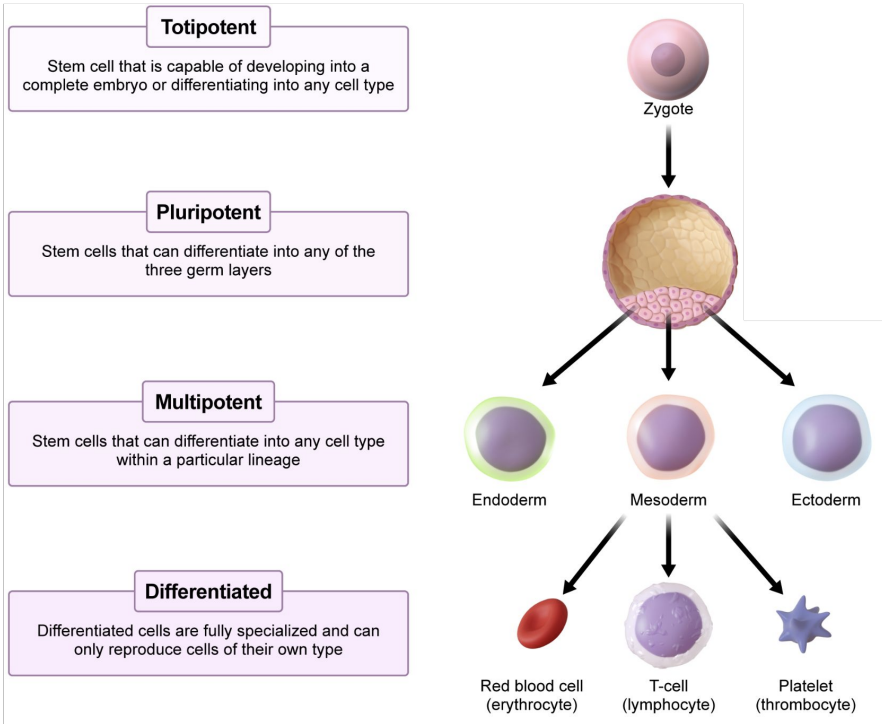
Totipotent
Stem cell that is capable of developing into a complete embryo or differentiating into any cell type
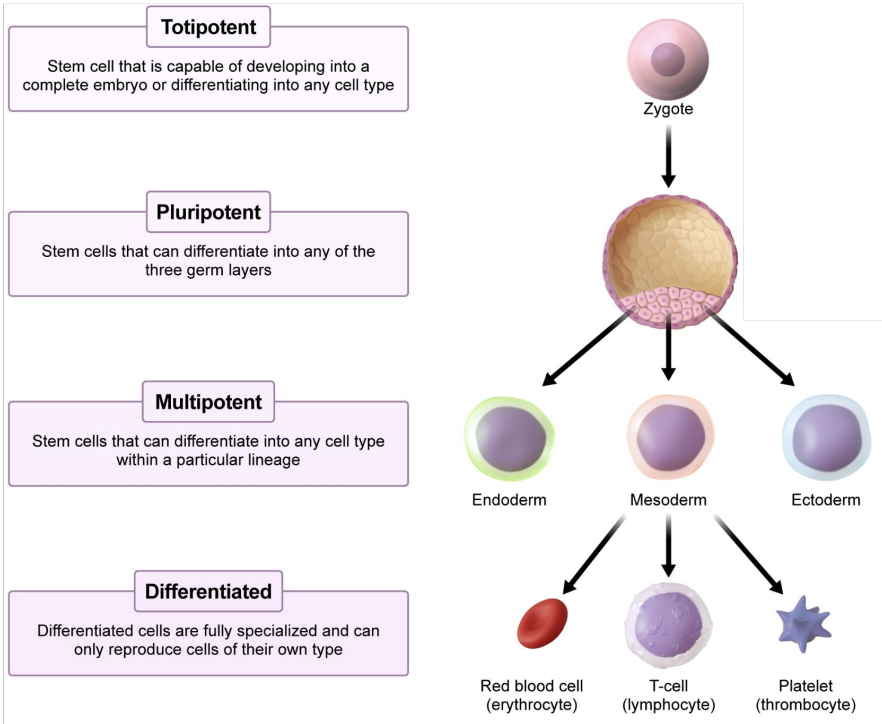
Pluripotent
Stem cells that can differentiate into any of the three germ layers
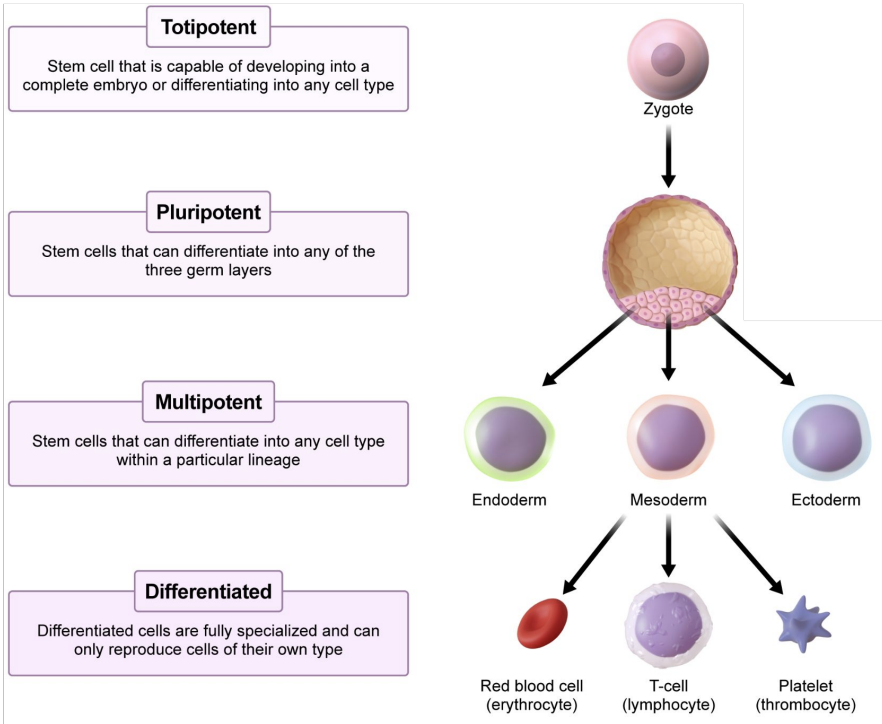
Multipotent
Stem cells that can differentiate into any cell type within a particular lineage
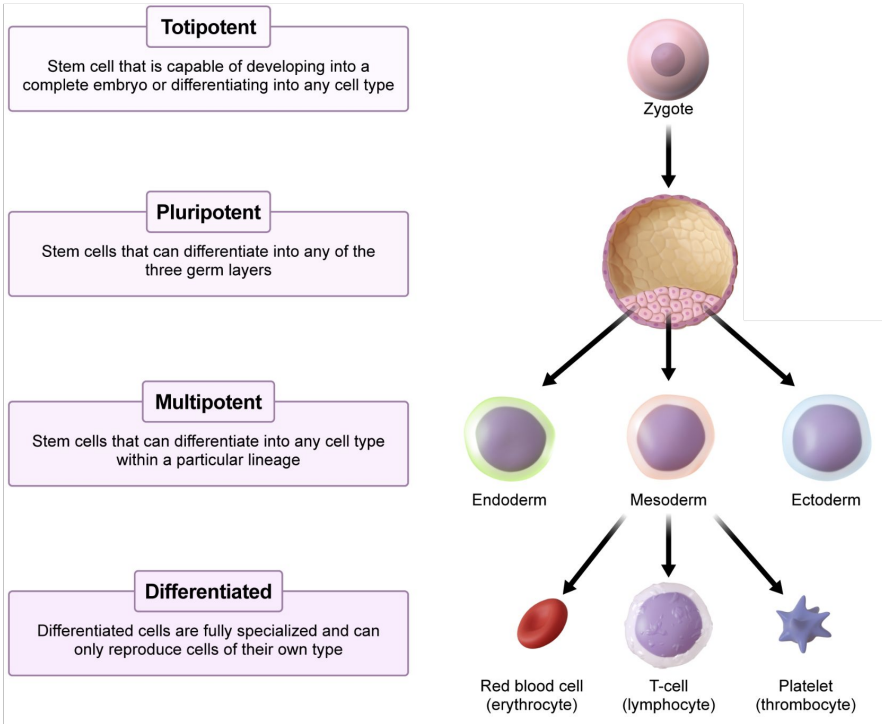
Differentiated
Differentiated cells are fully specialized and can only reproduce cells of their own type
Neurulation
Notochord (mesoderm) → induces neural plate (ectoderm)
Neural plate → neural tube → CNS
Extraembryonic Membranes
Amnion, Chorion, Allantois, Yolk sac
Amnion
Cushions embryo with fluid
Chorion
Forms placenta (in mammals)
Allantois
Waste transport, umbilical cord for mammals
Yolk sac
Early nutrients, blood formation
Embryonic induction
Organizers influence nearby cells
Homeotic genes (HOX)
Set body layout (head-tail)
Homeobox
DNA similar with different species with homeotic genes
Egg cytoplasm
Animal vs vegetal poles uneven guide cleavage
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death shapes development
Temperature-dependent sex
Turtles: warm = female
Crocodiles: medium = male
Oviparity
Egg
Viviparity
Inside
Ovoviviparity
Eggs inside and birth