(3) Lab 6: Muscles
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
# = Function, * = Origin and insertion
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
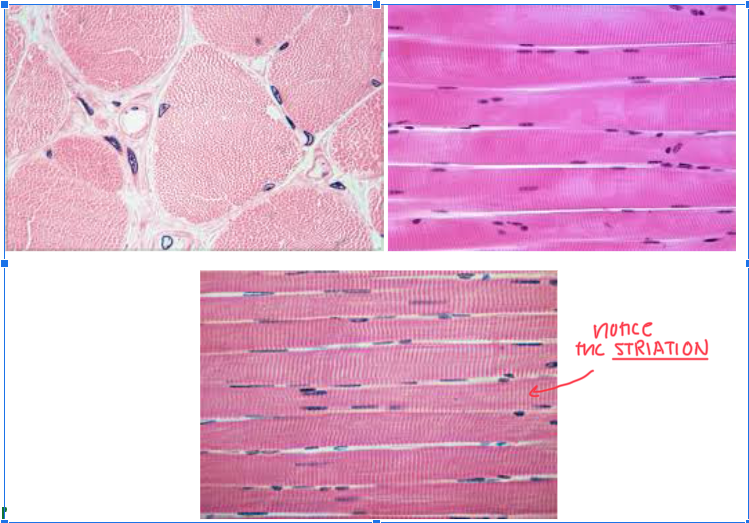
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Characteristic:
VOLUNTARY
MAKES LONG FIBERS
MULTINUCLEATE
Location: ATTACH TO BONES
Function:
CONTROL BREATHING
MAINTAIN BODY TEMP
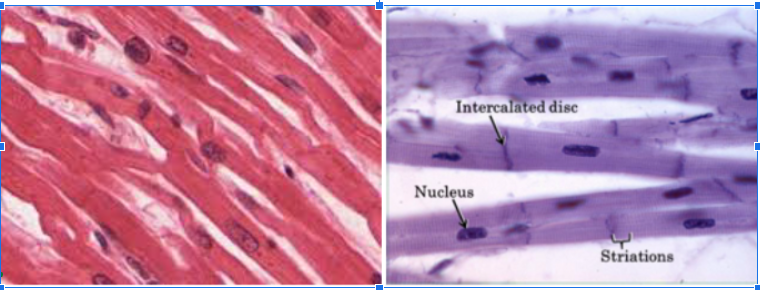
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Characteristic:
LOOKS BRANCHY
Has INTERCALATED DISCS
INVOLUNTARY
FAINT STRIATIONS
UNINUCLEATE
Location: HEART
Function: PUMP BLOOD THROUGHOUT BODY
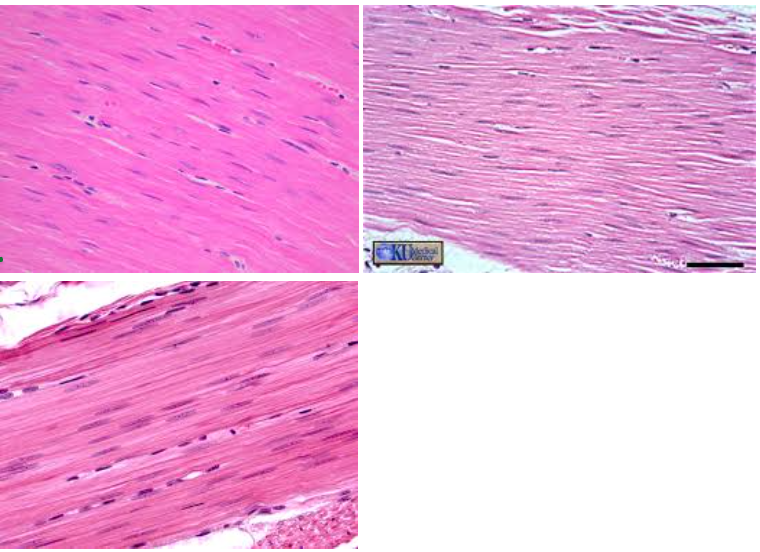
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Characteristic:
INVOLUNTARY
NO STRIATIONS
NOT WAVE-LOOKING
Location: INTERNAL ORGANS (DIGESTIVE TRACT)
Function: CONSTRICT BLOOD VESSELS/AIRWAYS
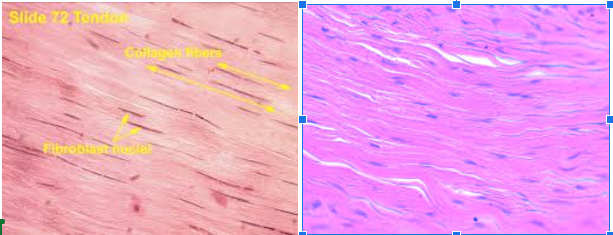
Dense Regular Connective Muscle
Characteristic:
WAVE-LOOKING
Made by FIBROBLASTS
Tightly packed collagen Fibers
Location: TENDONS AND LIGAMENTS
Tendons: Skeletal Muscle to Bones
Ligaments: Bone to Bone
Function: MOVEMENT AND STABILITY
Voluntary VS Involuntary
Under CONSCIOUS CONTROL (you can do these things willingly)
Actions that YOU CAN’T CONTROL; HAPPENS NATURALLY
Striations
THIN LINES PERPENDICULAR to any muscle tissue
Formed because of thick and thin protein filaments
Multinucleate
MANY NUCLEUS along the length of fibers
Uninucleate
ONE NUCLEUS
Intercalated Discs
DARK STRUCTURES in the muscle that SEPARATE THE CELLS
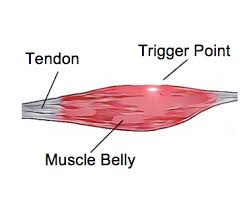
Origin (attachment point)
These are the END OF MUSCLE that ANCHORS TO THE BONE
Wont move during contraction
Insertion
Part of the muscle that ATTACHES TO THE BONE THAT MOVES DURING CONTRACTION
Action
MOVEMENT A MUSCLE CONTRACTION CAUSES
e.g: flexing the elbow
When you bend your elbow, the biceps muscle on the front of your upper arm contracts and shortens, while the triceps muscle on the back of your upper arm extends. This coordinated action is a type of muscle contraction known as flexion, where the angle between two bones (in this case, the humerus and radius/ulna) decreases.
Belly
PORTION OF MUSCLE BETWEEN ORIGIN AND INSERTION
Agonist/Primer Mover
The muscle that’s RESPONSIBLE FOR MAKING SPECIFIC MOVEMENT AT A JOINT
Antagonist
This is a muscle that OPPOSES ACTION OF AGONIST
This is the muscle that RELAXES while the other CONTRACTS to create a movement
Synergist
MUSCLES WORK TOGETHER to PERFORM SIMILAR ACTION
e.g: the brachialis and brachioradialis are synergistic muscles that HELP IN FOREARM FLEXION
-
Fixator
Muscle that SURROUNDS JOINT to give STRENGTH AND STABILITY
Sprain
Injury where the LIGAMENT IS OVERSTRETCHED
Causes swelling
Strain
INJURY TO MUSCLE OR TENDON
Muscle Tear
When the MUSCLE FIBERS ARE TORN; HUGE INJURY
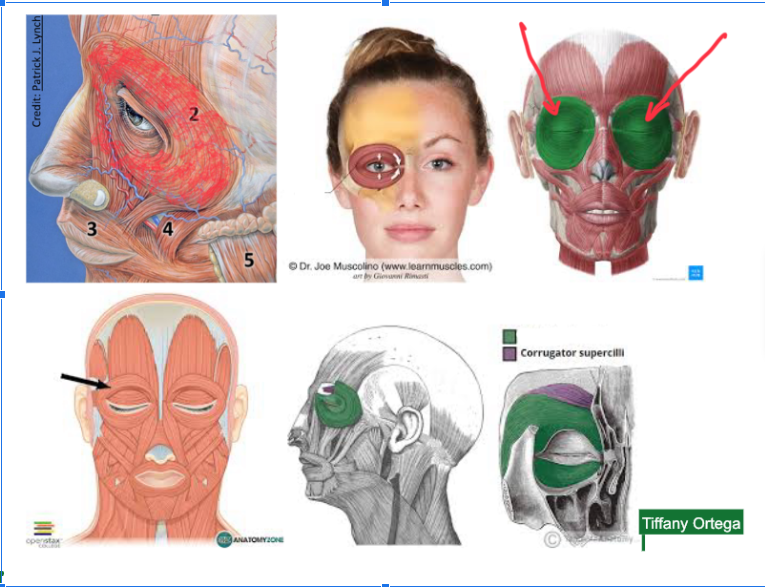
Orbicularis oculi (L/R) #
Function: RESPONSIBLE FOR CLOSING EYELIDS
Plays role in facial expressions (especially squinting or smiling)
**This ORBITS the EYES
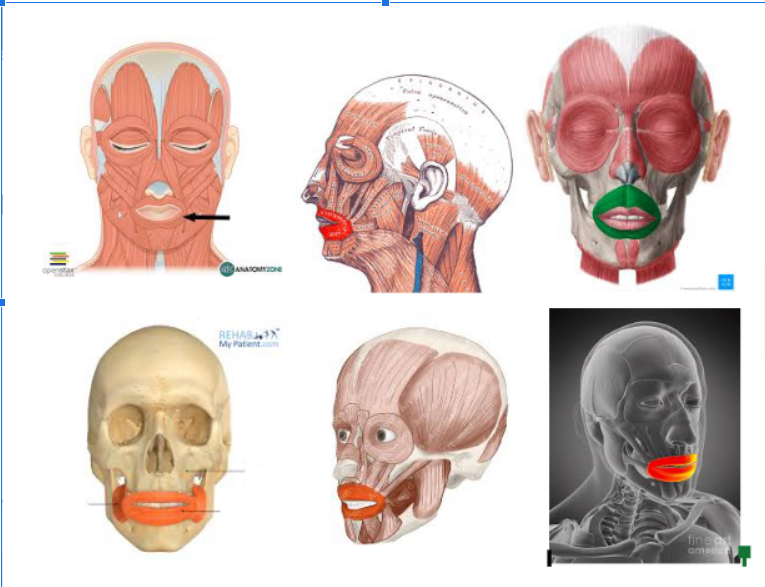
Orbicularis Oris
Surrounds the mouth
Zygomaticus Major (L/R)
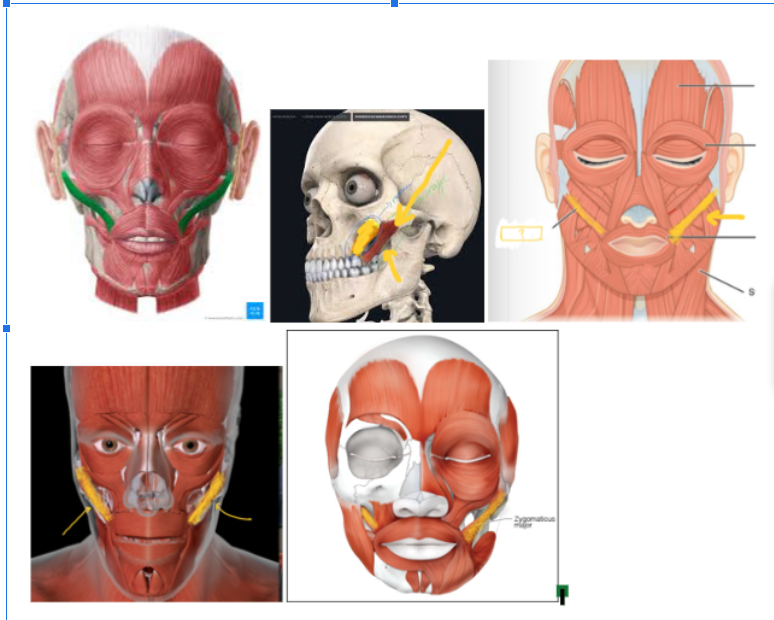
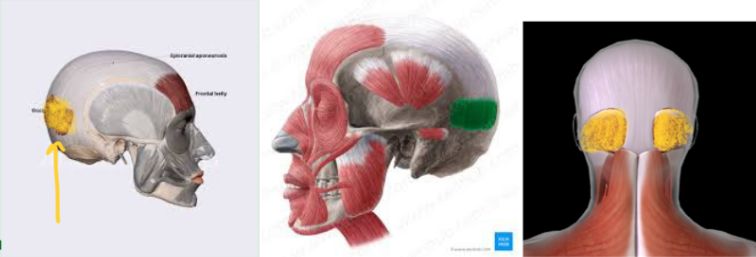
Occipitofrontalis (Frontal Section — L/R)
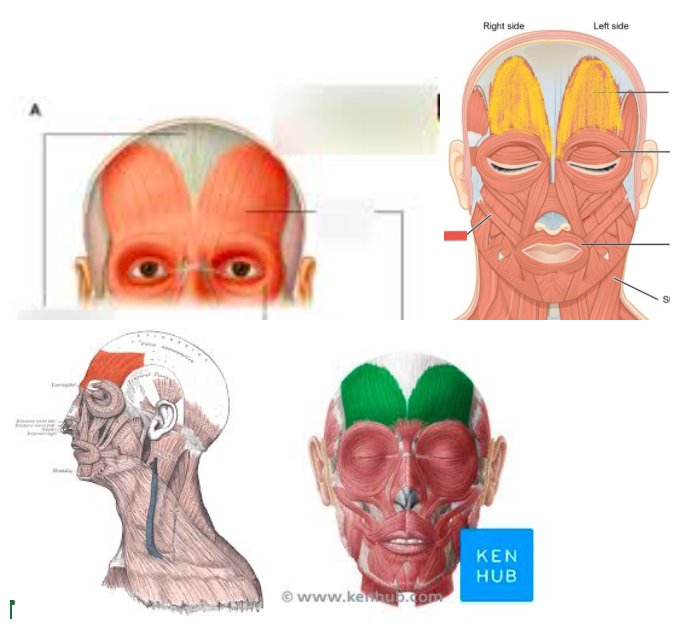
Occipitofrontalis (Occipital Section — L/R)
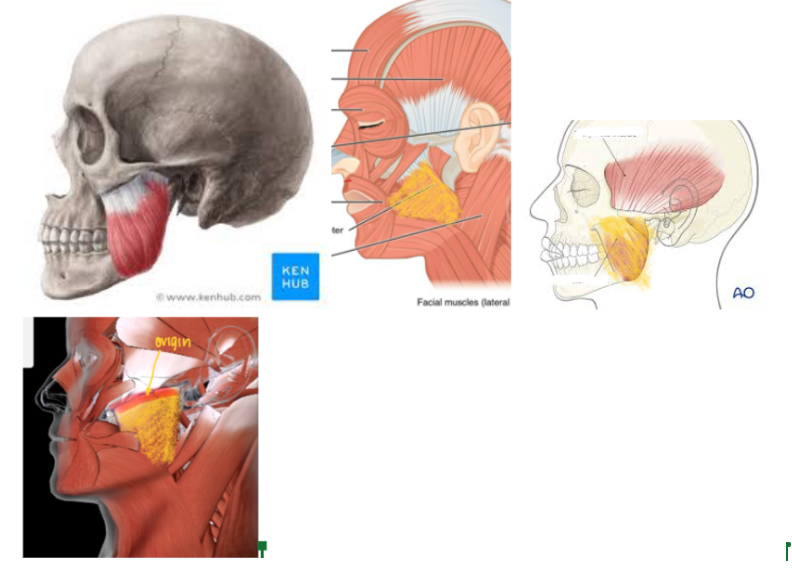
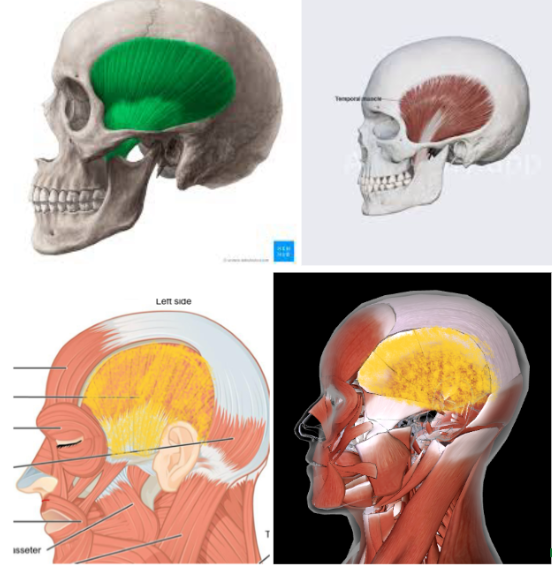
Masseter (L/R) #*
Function: Responsible for CHEWING (ELEVATE MANDIBLE AT THE JAW)
Origin: Zygomatic Bone
This is part of the muscle that just ATTACHES to the bone WITHOUT MOVEMENT
Insertion: Mandibular ramus and angle
This is the part of the muscle that MOVES when there’s a contraction
Temporalis (L/R)
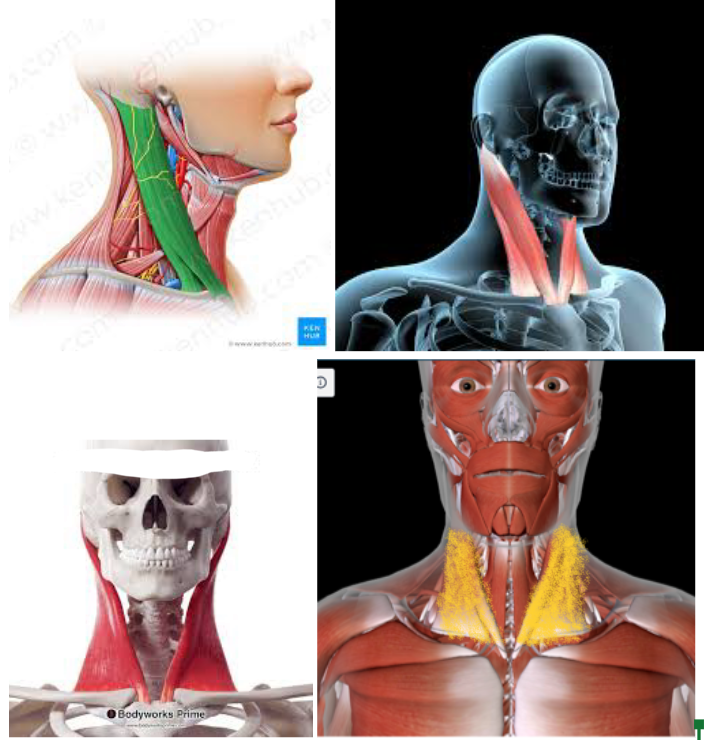
Sternocleidomastoid (L/R) #*
Function: ROTATE HEAD/FLEX NECK
Origin: MANUBRIUM of STERNUM MEDIAL CLAVICLE
Insertion: MASTOID PROCESS of the TEMPORAL BONE
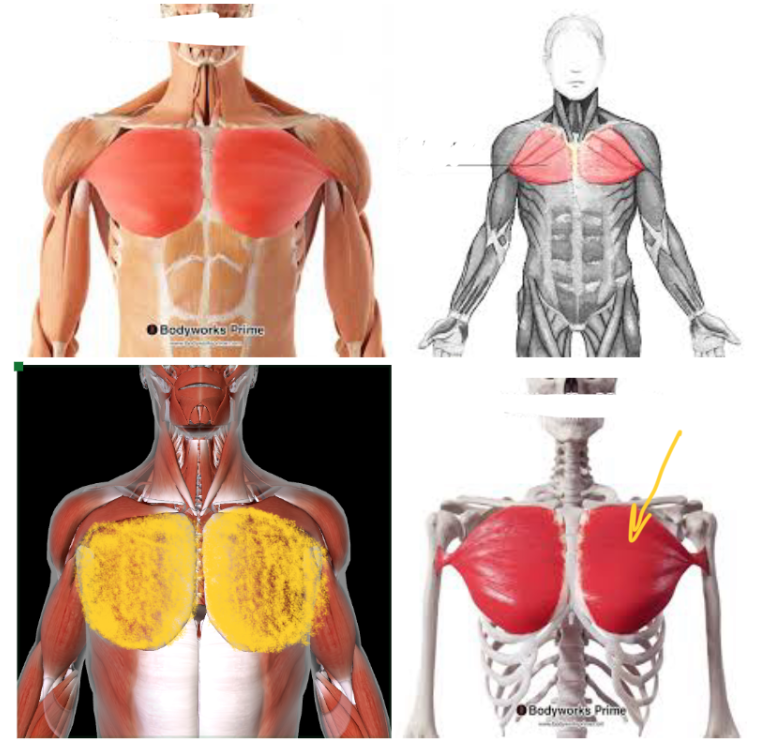
Pectoralis Major (L/R) #
Function: FLEX SHOULDERS + ROTATE ARM at shoulders
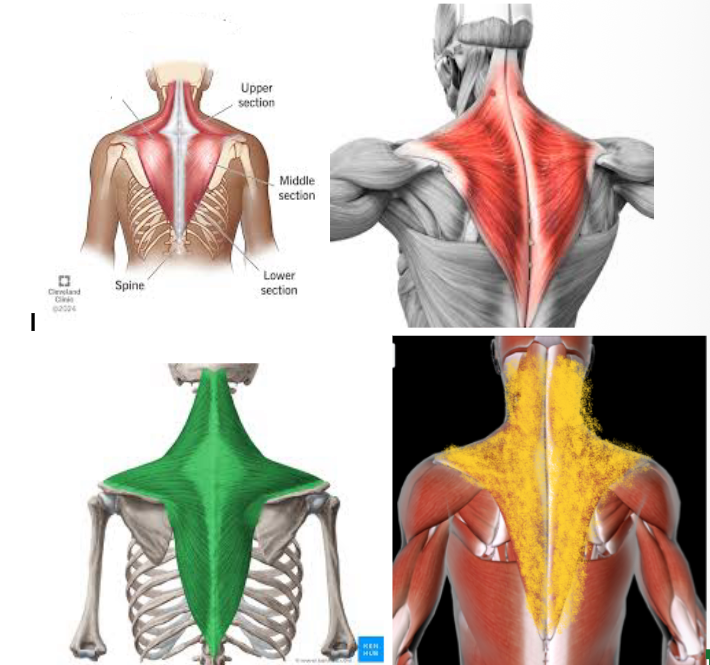
Trapezius (L/R)
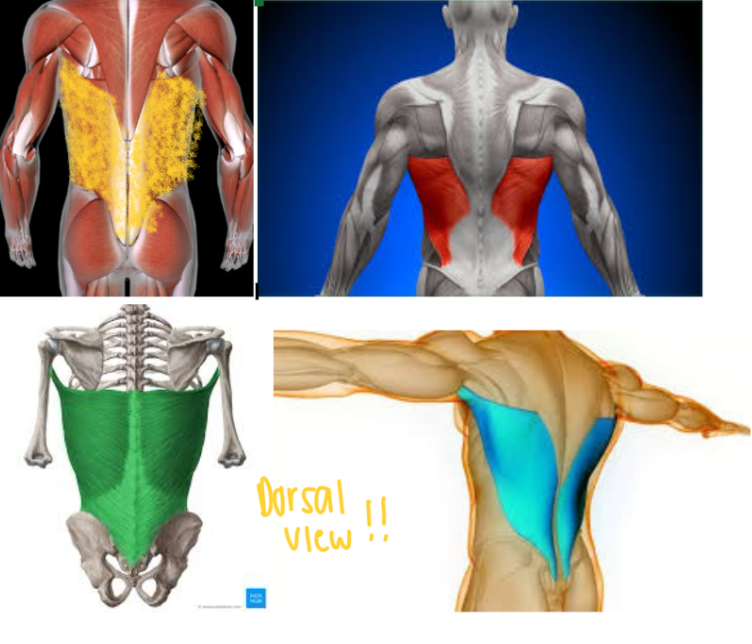
Latissimus Dorsi (L/R) #
Function: ADDUCT/ROTATE ARM at shoulder
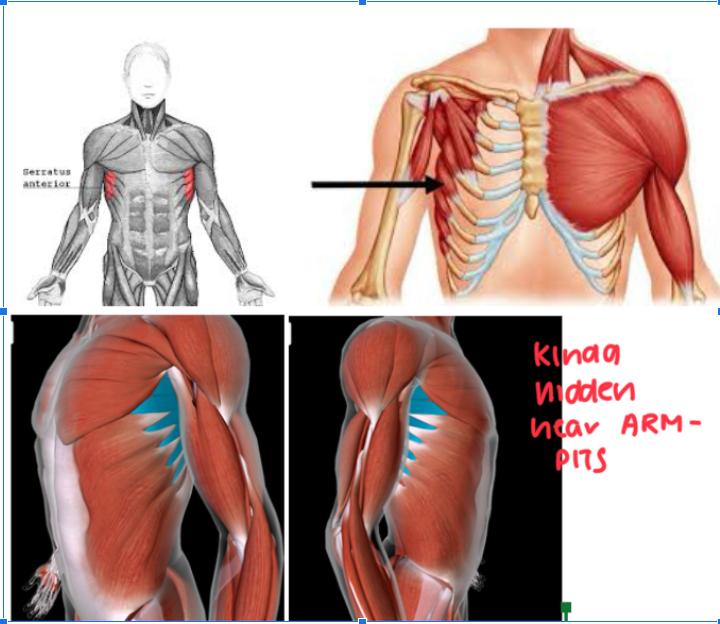
Serratus Anterior (L/R) #
Function: ROTATE SCAPULA + ELEVATE RIBS
Kinda near the armpit and pectoral area
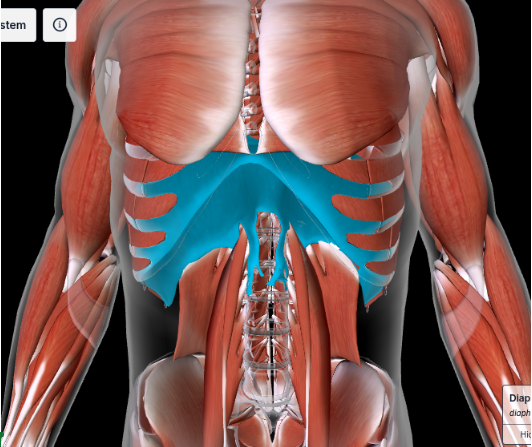
Diaphragm #
EXPANDS THORACIC CAVITY
Below the external, internal, transverse obliques and the rectus abdominis
Intercostal Muscles (internal) — L/R
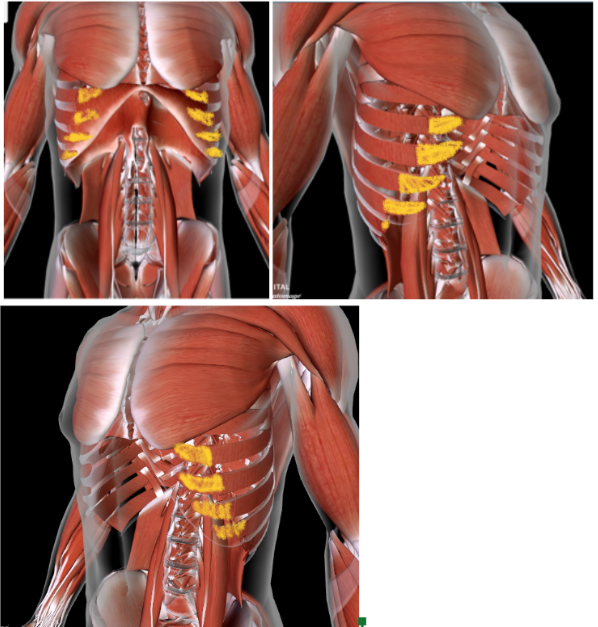
Intercostal Muscles (external) — L/R
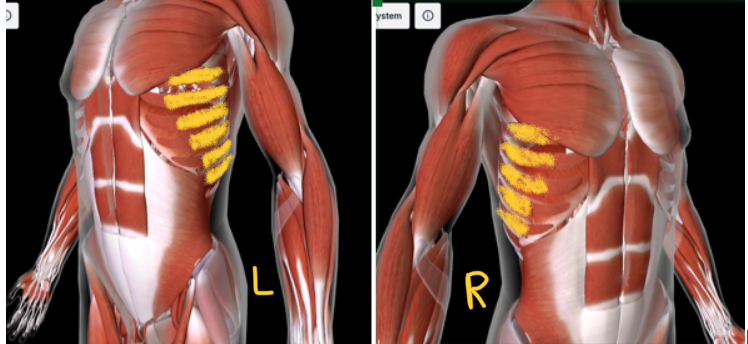
Rectus ABdominis (L/R) #
Function: FLEX/ROTATE TORSO
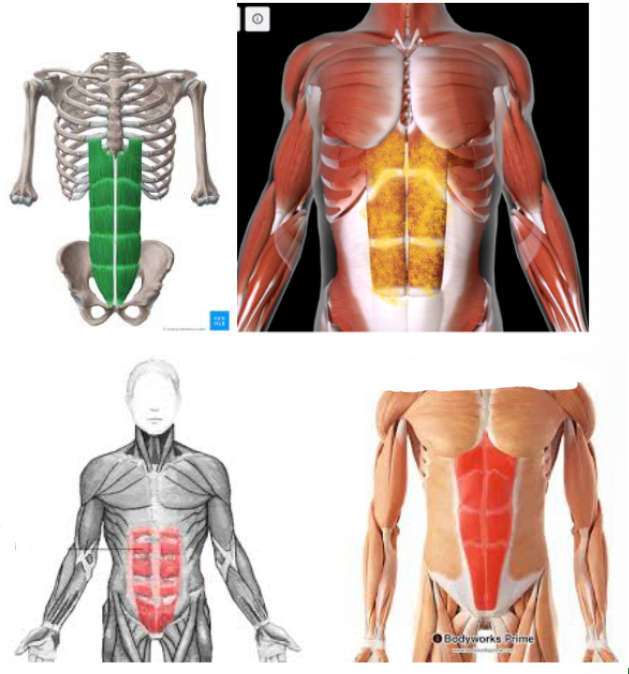
External Oblique #
Function: FLEX/ROTATE TORSO
This is SUPERIOR to the RECTUS ABDOMINIS and the other obliques
FIRST LAYER
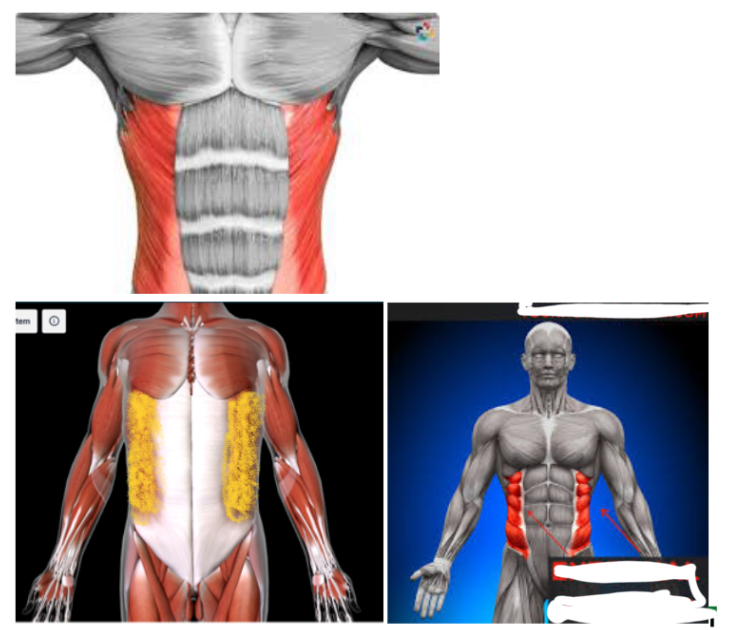
Internal Oblique #
Function: FLEX/ROTATE TORSO
SECOND LAYER
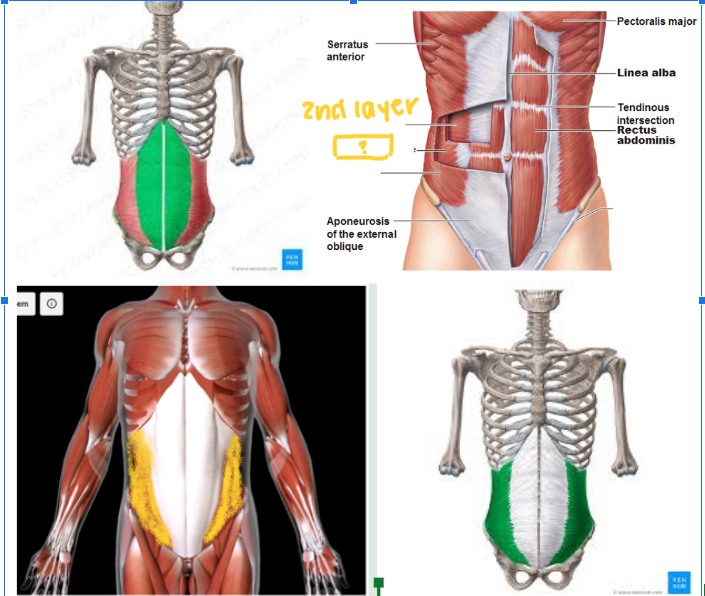
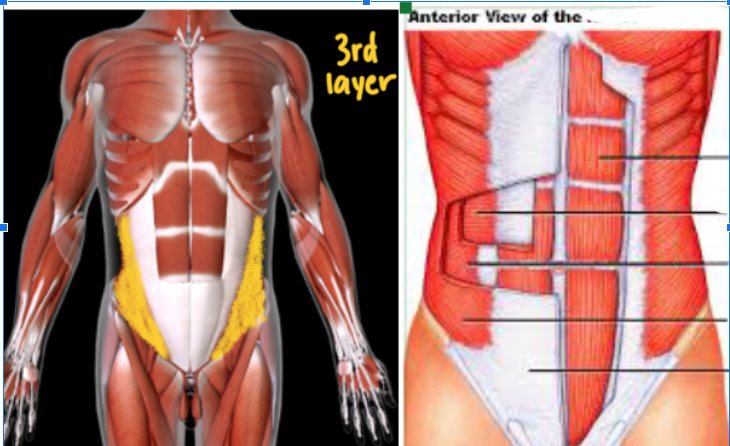
Transversus Abdominis #
Function: FLEX/ROTATE TORSO
THIRD LAYER (Most DEEP) layer
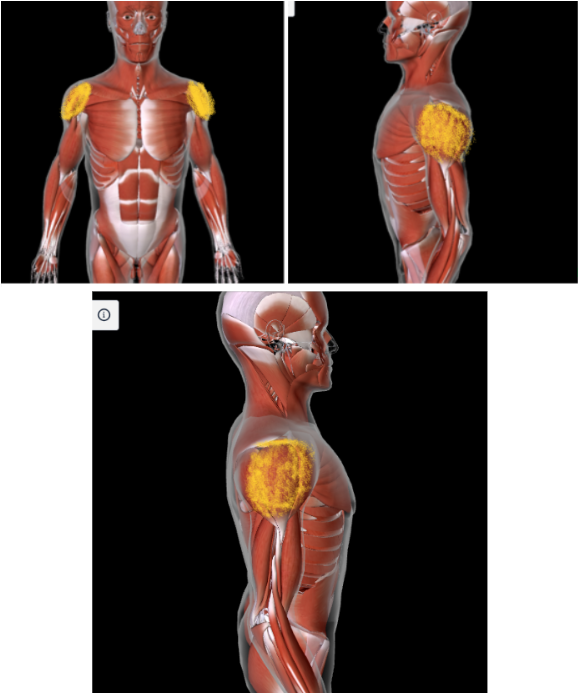
Deltoid (L/R) #*
Function: ABDUCT, FLEX, EXTEND, AND ROTATE ARM at the shoulder
Origin: ACROMION OF SCAPULA
Insertion: DELTOID TUBEROSITY of HUMERUS
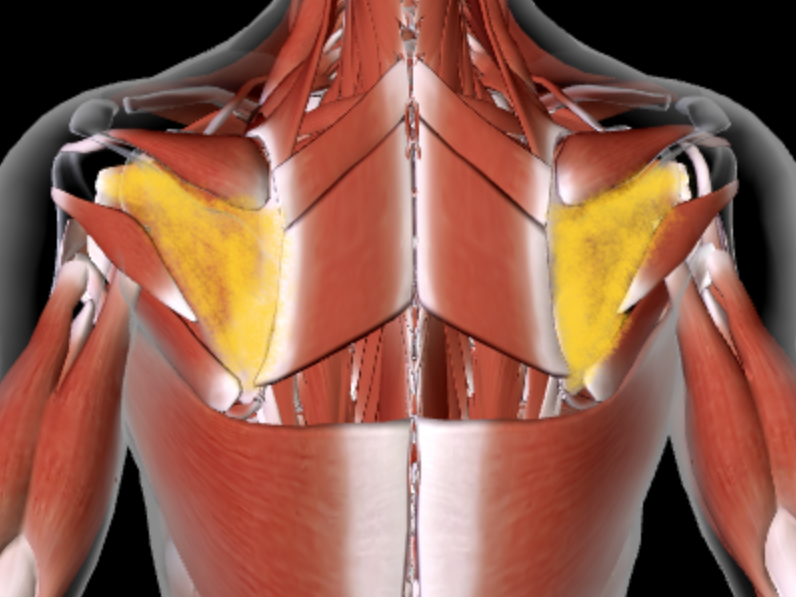
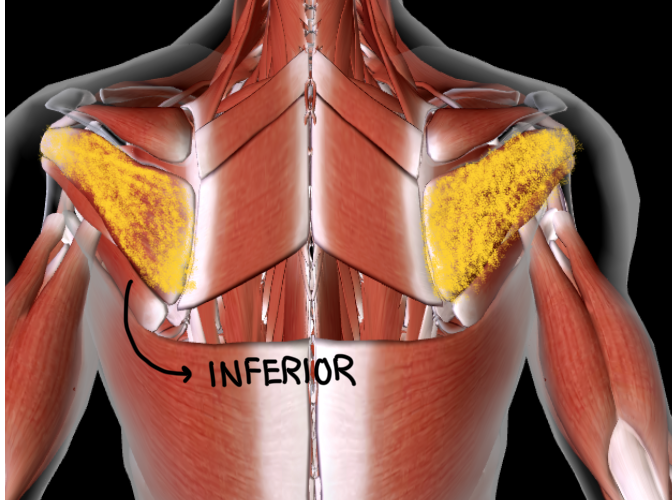
Rotator Cuff Muscles (L/R) #*
Function: ROTATE ARM IN ALL DIRECTIONS at shoulder
Origin: SCAPULA
Insertion: HUMERUS
Subscapularis (L/R) #
Function: ROTATE ARM IN ALL DIRECTIONS at shoulder
UNDERNEATH the INFRASPINATUS
Infraspinatus (L/R) #
Function: ROTATE ARM IN ALL DIRECTIONS at shoulder
NEXT to the RHOMBOID MAJOR
Supraspinatus (L/R) #
Function: ROTATE ARM IN ALL DIRECTIONS at shoulder
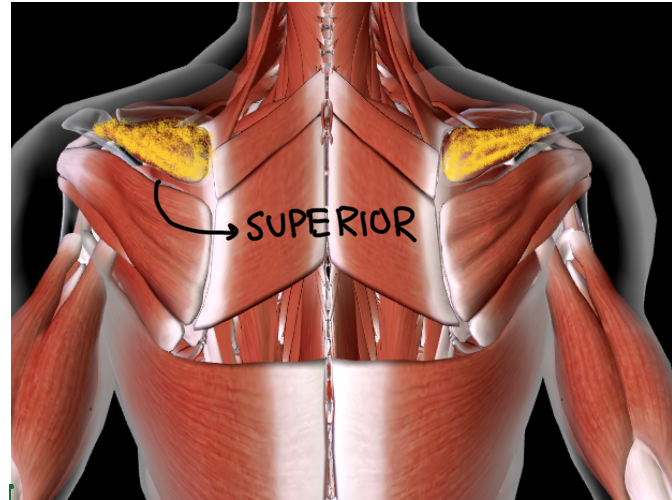
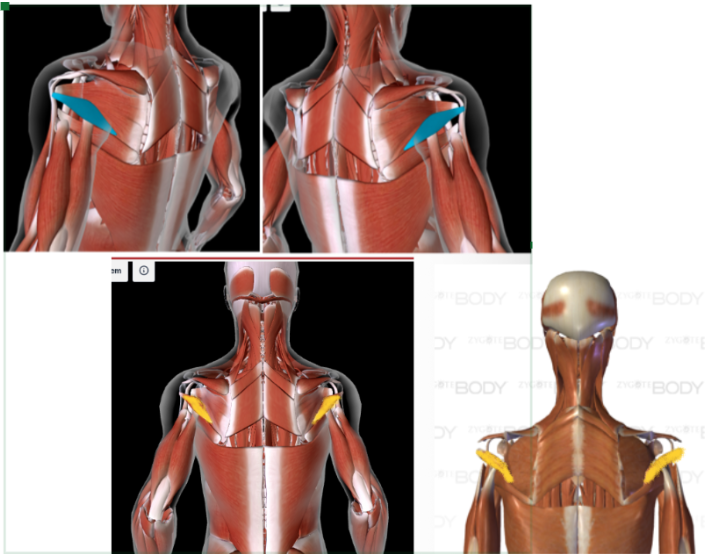
Teres MINOR (L/R) #
Function: ROTATE ARM IN ALL DIRECTIONS at shoulder
Kinda looks like mini wings
Below infraspinatus
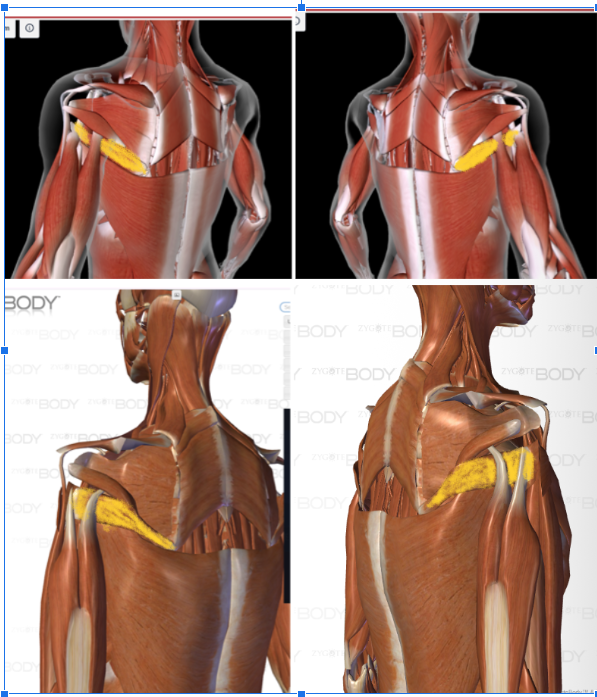
Teres MAJOR (L/R)
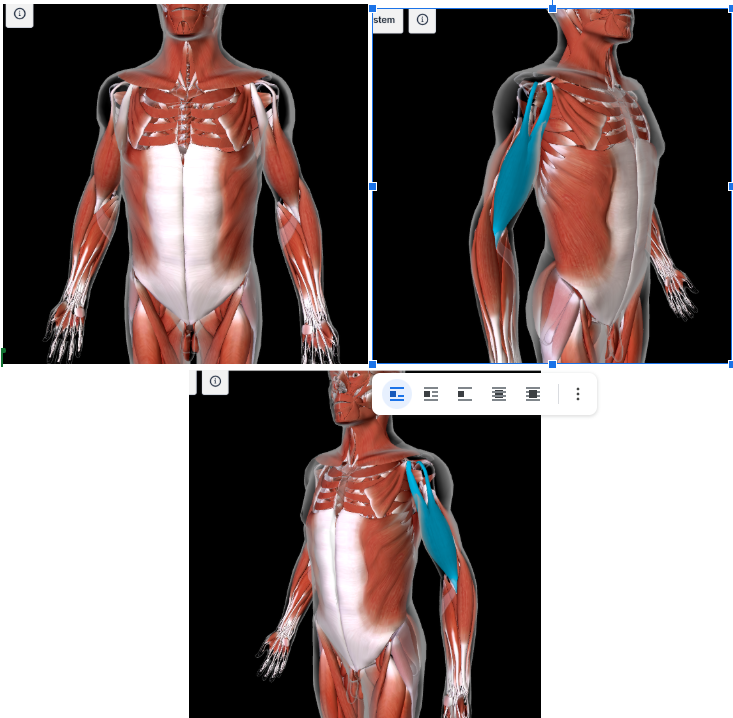
Biceps Brachii Muscle (L/R) #*
Function: FLEX FOREARM at the elbow, SUPINATE ARM at shoulder
Origin: Supraglenoid tubercle and coracoid process of scapula
Insertion: Radial tuberosity of radius
Brachialis (L/R) #
Function: Synergist to biceps brachii
BETWEEN BICEP AND TRICEP BRACHII
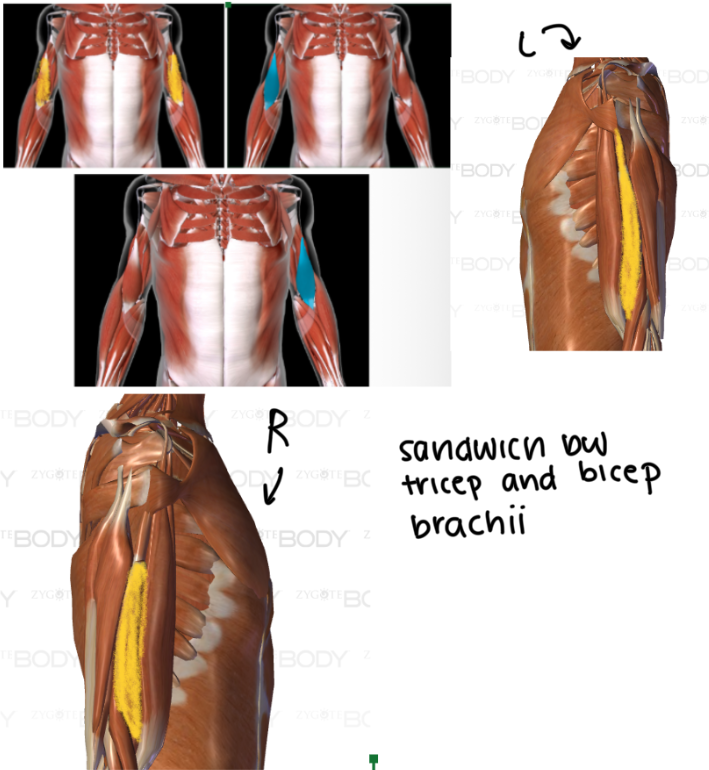
Triceps Brachii (L/R) #*
Function: EXTEND FOREARM AT ELBOW
Origin: INFRAGLENOID TUBERCLE of scapula
Insertion: OLECRANON PROCESS of ULNA
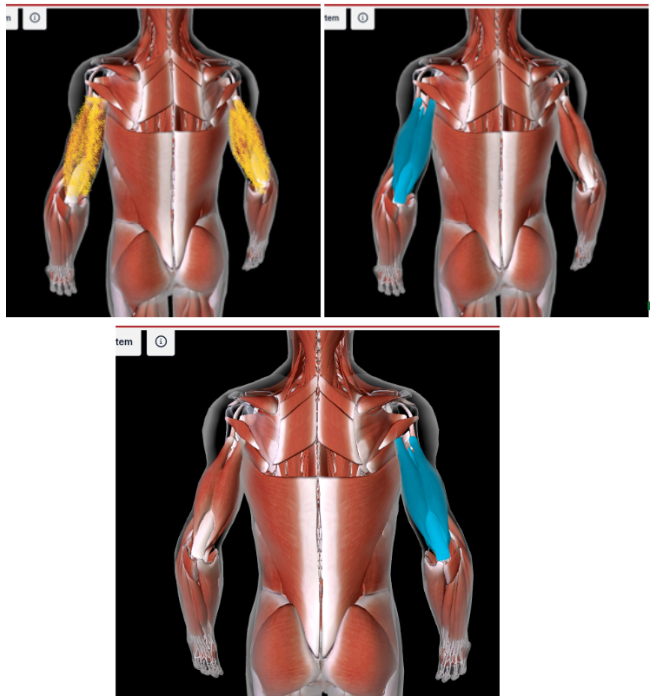
Brachioradialis (L/R) #
Function: FLEX FOREARM AT ELBOW
LATERAL and below the BICEP BRACHII
In the ANTEBRACHIAL area
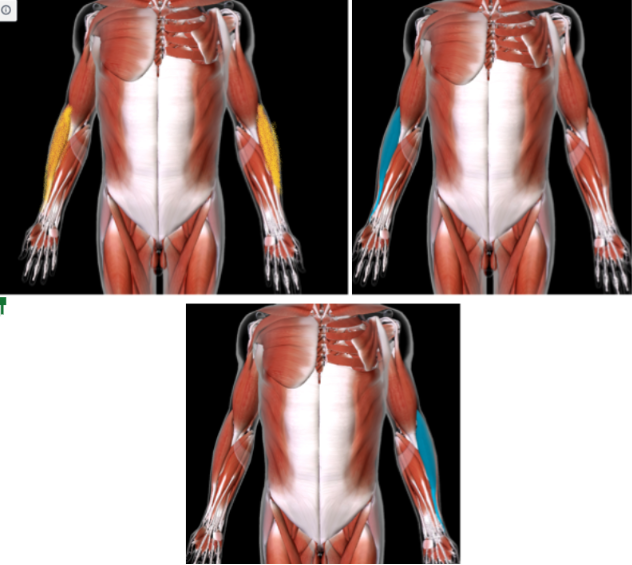
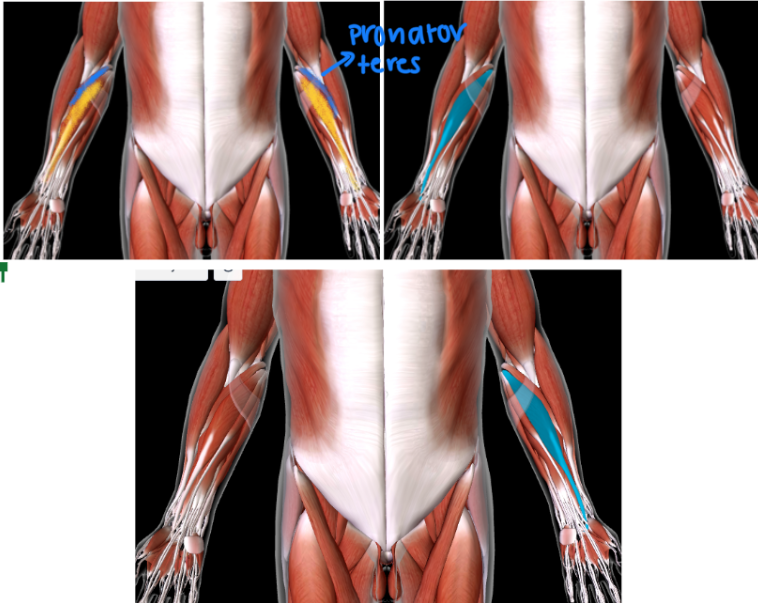
Pronator Teres (L/R) #
Function: PRONATE FOREARM
MEDIAL TO BRACHIORADIALIS
In the ANTEBRACHIAL area
Flexor Carpi Radialis (L/R) #*
Function: FLEX/ABDUCT WRISTS
Origin: MEDIAL EPICONDYLE of HUMERUS
Insertion: SECOND/THIRD METACARPALS
MEDIAL to the PRONATOR TERES
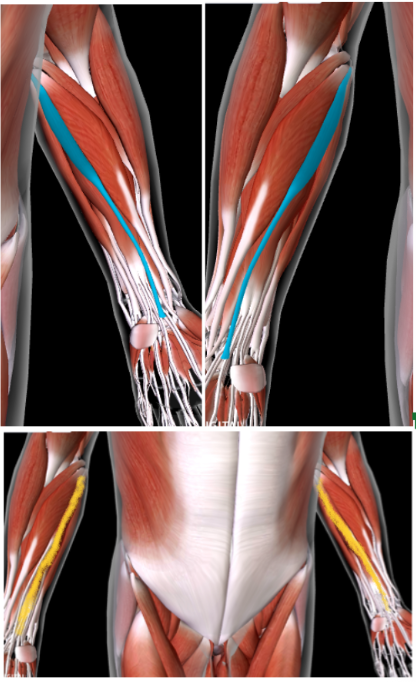
Palmaris Longus (L/R)
MEDIAL to the Flexor Carpi Radialis
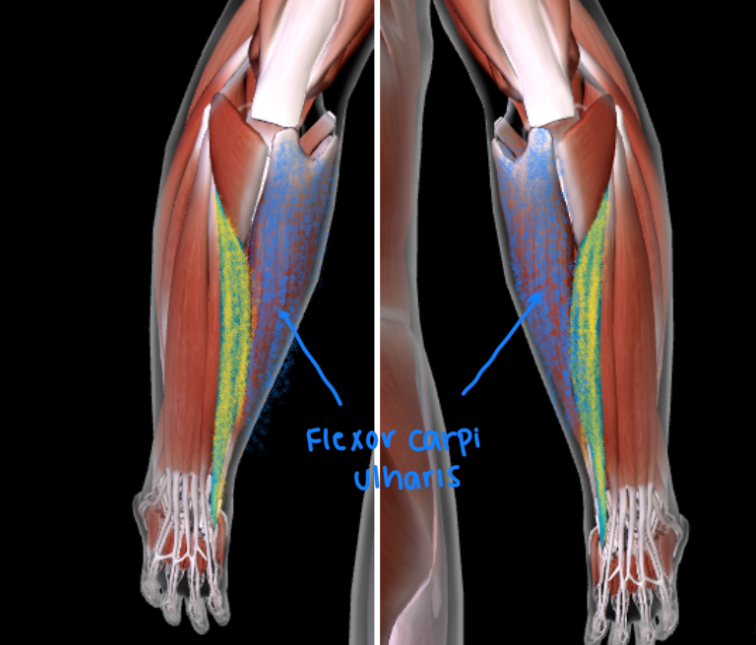
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris (L/R) #*
Function: ADDUCT and FLEX WRISTS
Origin: MEDIAL EPICONDYLE OF HUMERUS; OLECRANON PROCESS OF ULNA
Insertion: CARPAL BONES; 5TH METACARPAL
MOST MEDIAL from the brachioradialis (this is 4th AWAY from the brachioradialis)
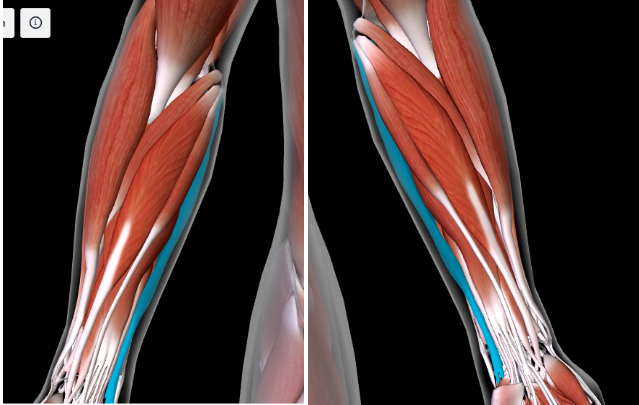
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND AND ADDUCT WRIST
POSTERIOR
Next to the FLEXOR CARPI ULNARIS
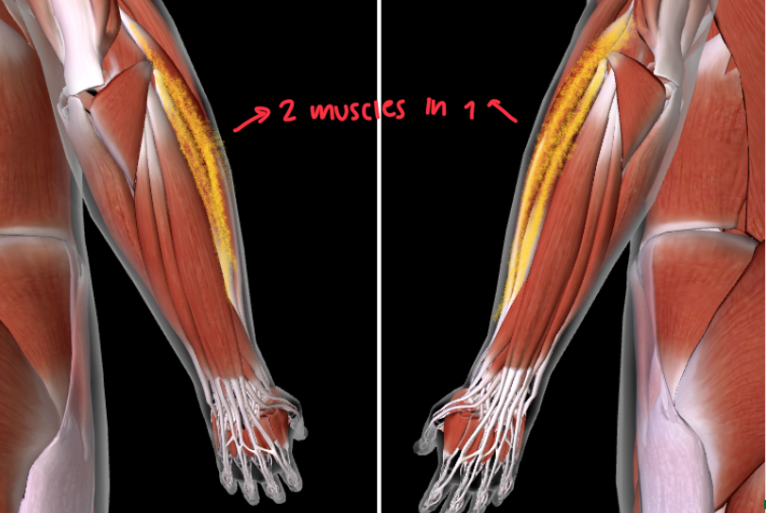
Extensor Digitorum (L/R) #
Function: EXTENDS DIGITS
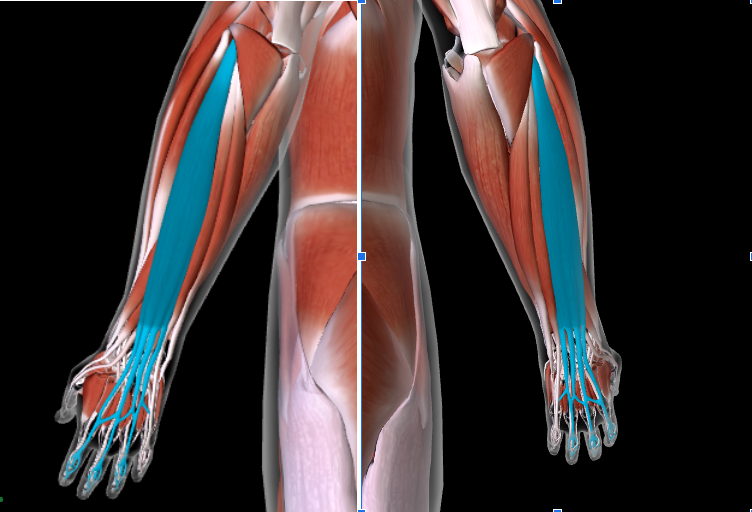
Extensor Carpi Radialis (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND and ABDUCT WRISTS
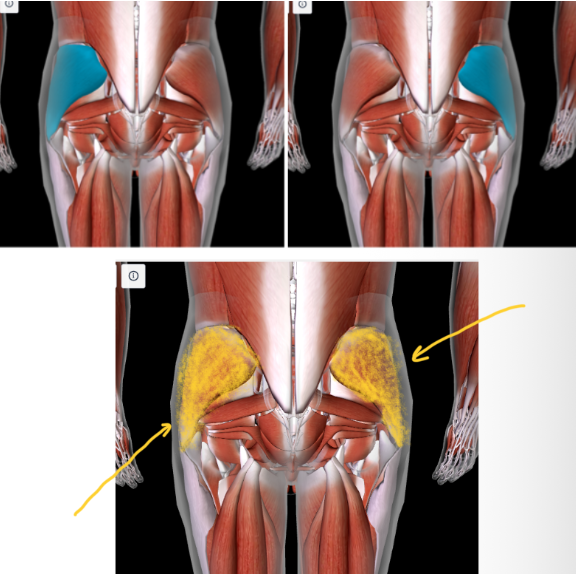
Iliopsoas (L/R) #
Function: FLEX THIGH AND TRUNK
UNDERNEATH THE GLUTES (max and min and medius)
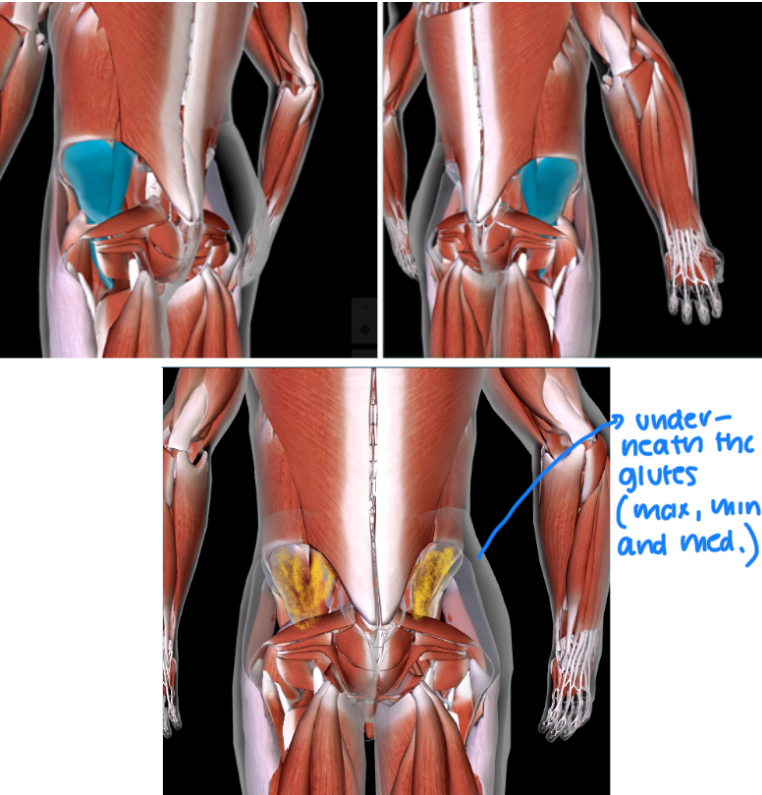
Gluteus Maximus (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND, ABDUCT, ROTATE THIGH AT HIP
BUTTCHEEKS
Gluteus Medius (L/R)
Quadriceps Femoris (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND LEG at KNEE
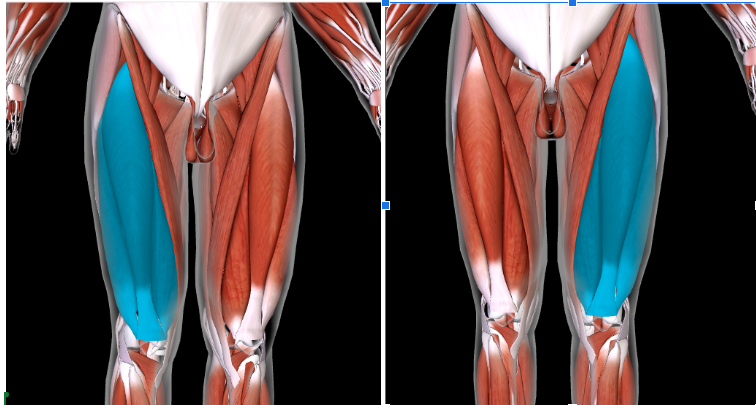
Rectus Femoris #*
Function: EXTEND LEG at KNEE
Origin: ANTERIOR INFERIOR ILIAC SPINE of ILIUM
Insertion: PATELLA TIBIAL TUBEROSITY of TIBIA
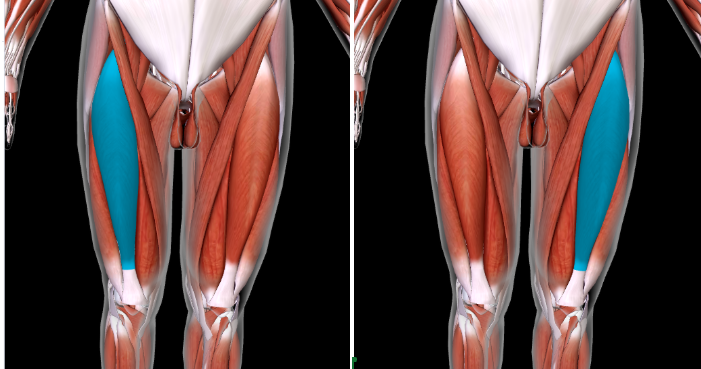
Vastus Lateralis (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND LEG at KNEE
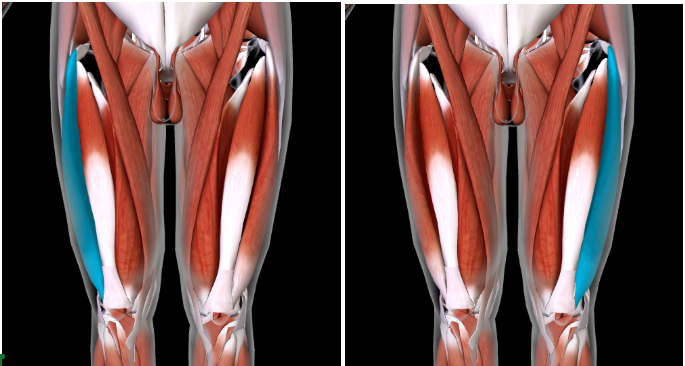
Vastus Intermedius (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND LEG at KNEE
This is DEEP of the RECTUS FEMORIS
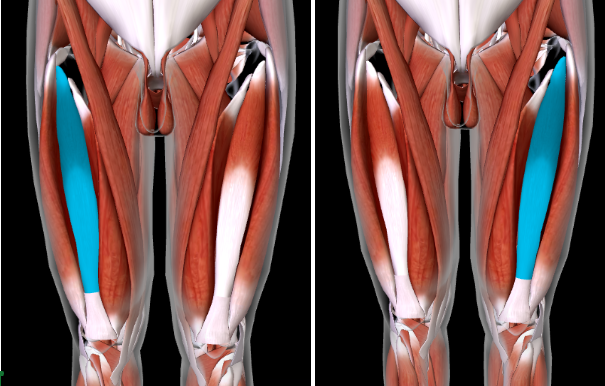
Vastus Medialis (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND LEG at KNEE
**Tip: Notice how the different vastus says the position of where it is in (e.g: LATERALIS = Lateral, MEDIUS = Medial, ETC)
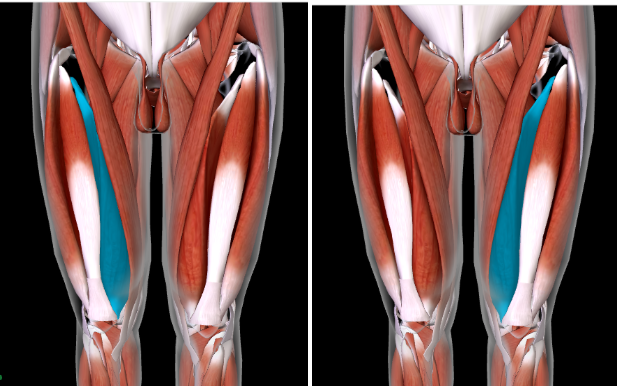
Gracilis (L/R)
INNER THIGH MUSCLE
Sartorius
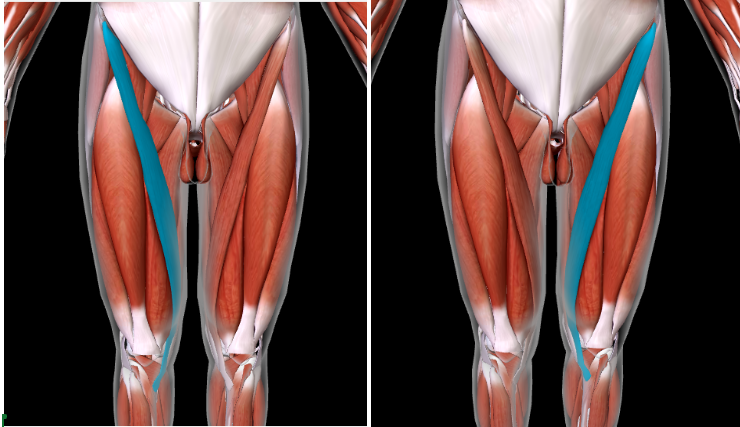
Adductor Longus #
Function: ADDUCT THIGH AT HIP
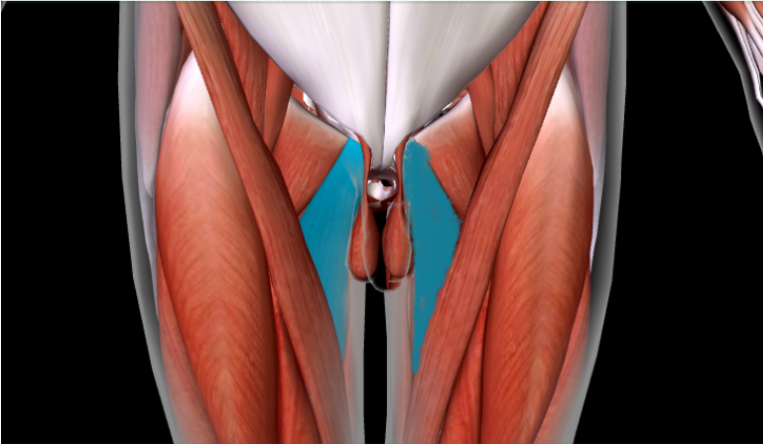
Tensor Fasciae Latae (with Iliotibial band)
Red = T
Yellow = I
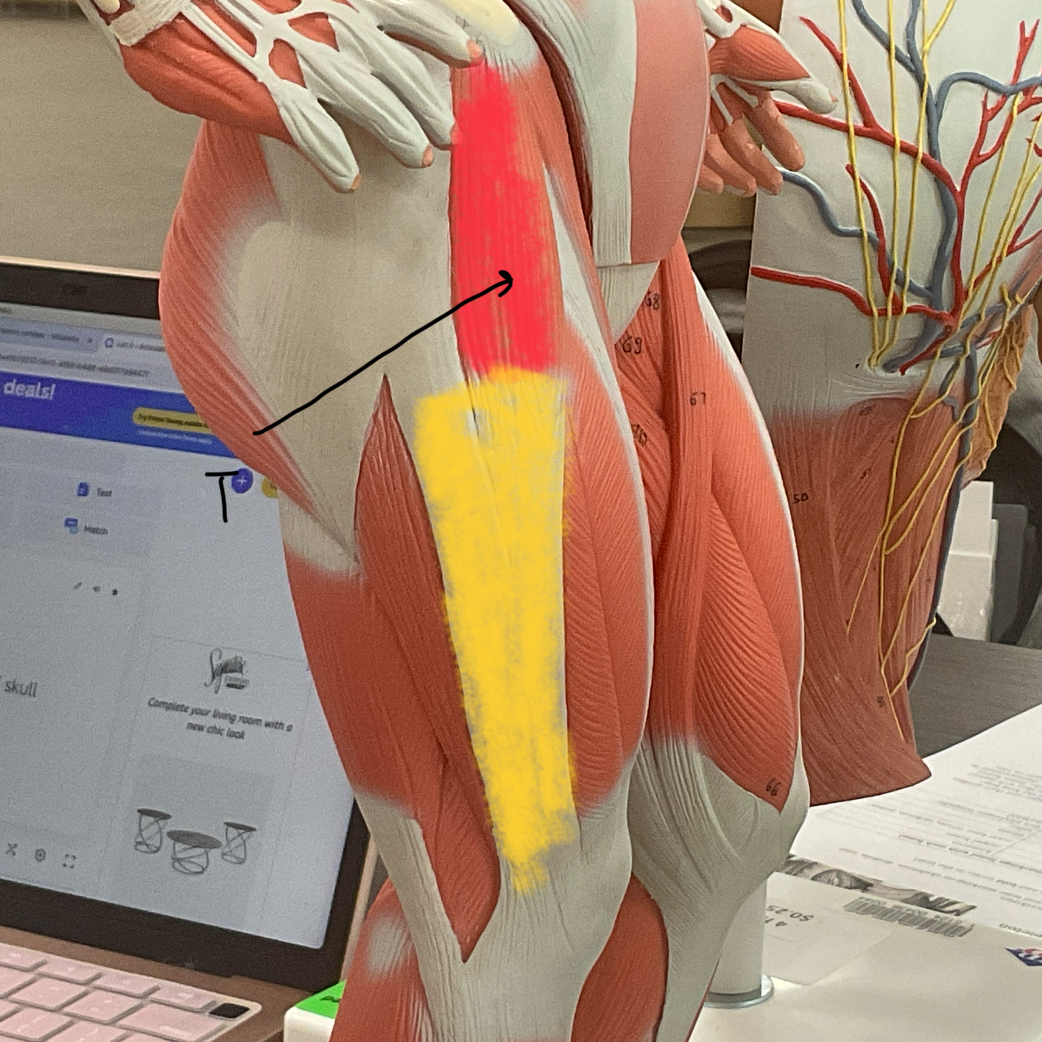
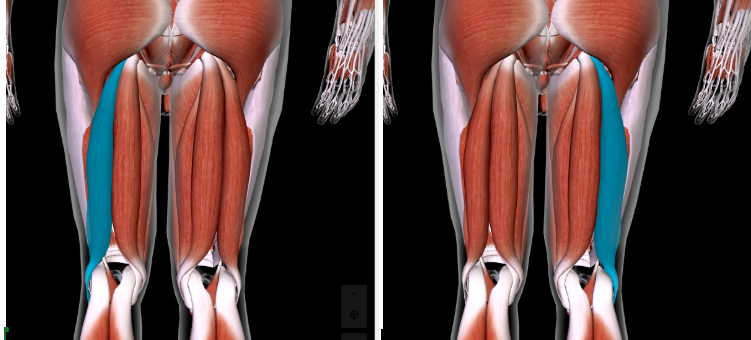
Biceps Femoris (L/R) #*
Function: FLEX LEG AT KNEE + ROTATE THIGH AT HIP
Origin: ISCHIAL TUBEROSITY OF ISCHIUM
Insertion: HEAD OF FIBULA
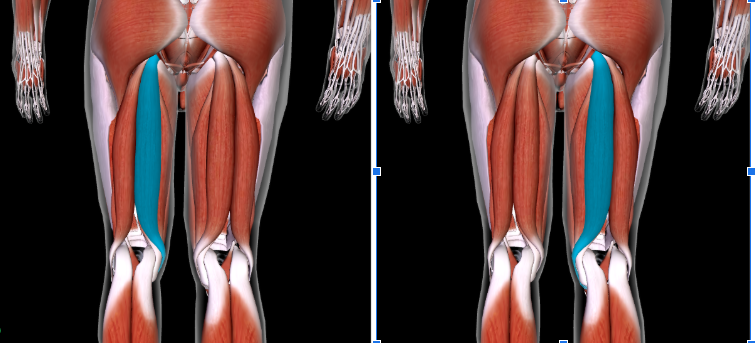
Semitendinosus (L/R) #
Function: FLEX LEG AT KNEE + ROTATE THIGH AT HIP
SANDWICHED between Semimembranosus and Biceps Femoris
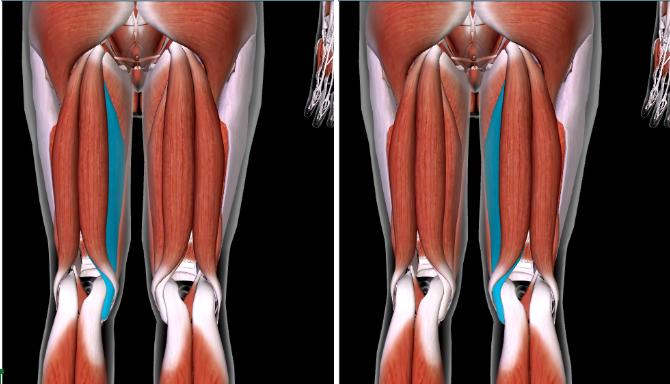
Semimembranosus (L/R) #
Function: FLEX LEG AT KNEE + ROTATE THIGH AT HIP
MOST MEDIAL towards the body
Tibialis Anterior (L/R) #*
Function: DORSIFLEX FOOT at ANKLE
Origin: LATERAL CONDYLE and TIBIAL DIAPHYSIS of TIBIA
Insertion: TARSAL BONE; FIRST METATARSAL
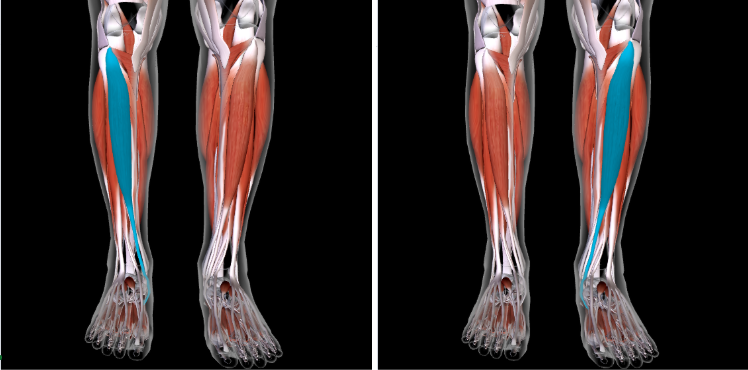
Extensor Digitorum Longus (L/R) #
Function: EXTEND AND DORSIFLEX TOES
LATERAL to the TIBIALIS ANTERIOR
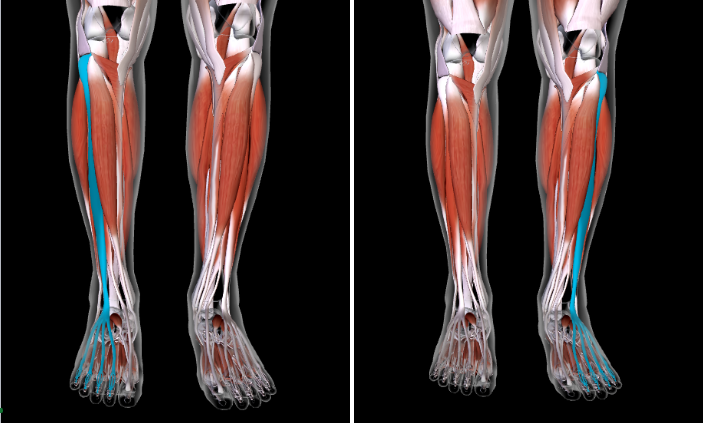
Fibularis Longus (L/R)
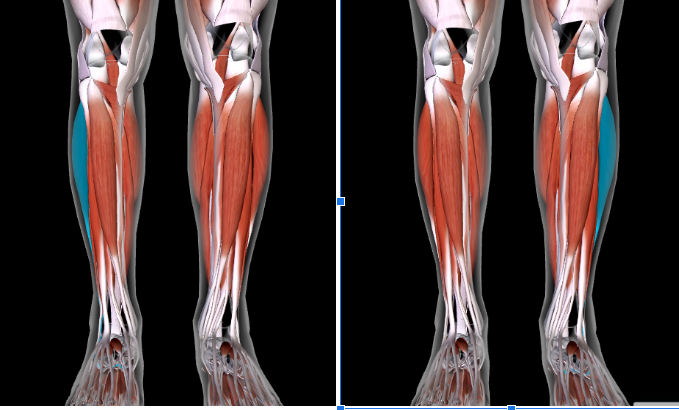
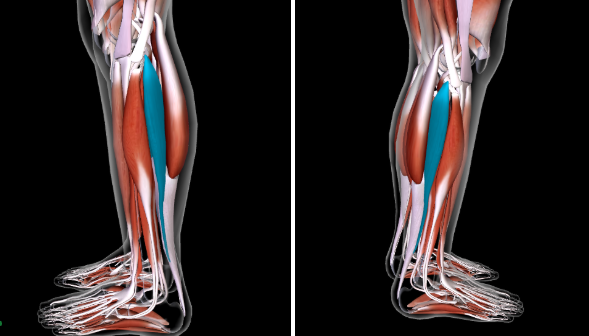
Gastrocnemius (L/R) #*
Function: PLANTAR FLEX FOOT AT ANKLE
Origin: LATERAL/MEDIAL CONDYLES OF FEMUR
Insertion: CALCANEUS
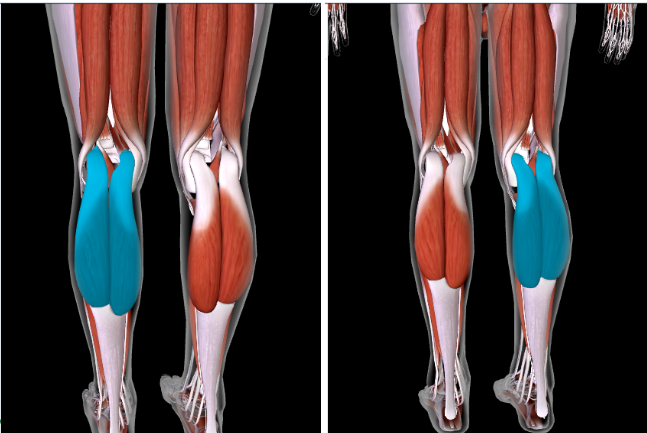
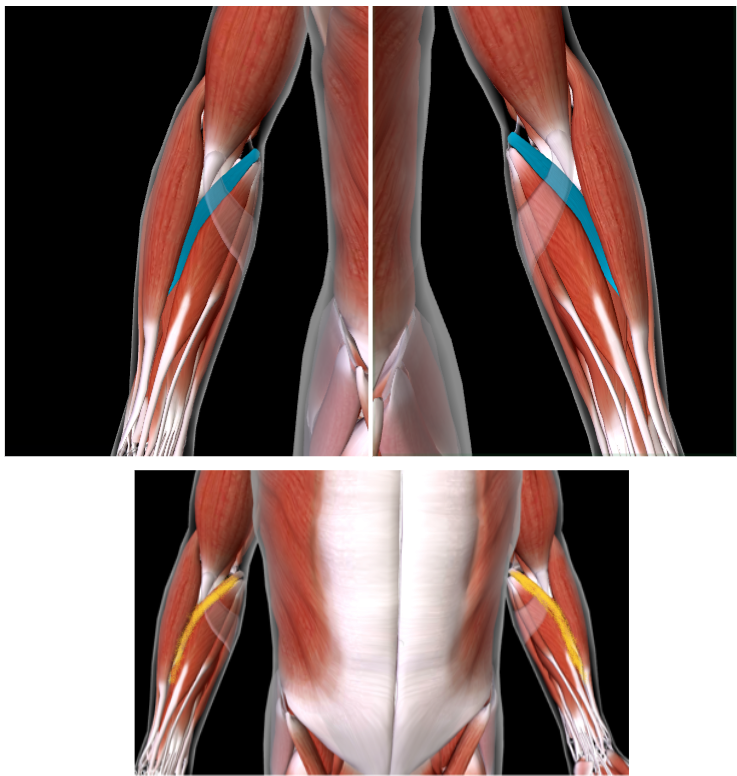
Soleus (L/R) #
Function: PLANTAR FLEX FOOT AT ANKLE
SANDWICH BW Gastrocnemius and Fibular Longus