earth and space
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Solar wind
stream of high energy particles sent into spaces causes the light displays AURORA BOREALIS (if seen from northern hemisphere and AURORA AUSTRALIS (southern hemisphere
prominences
storms that look klike a huge arches may last several days
solar flares
much more intense than prominences: lasts only about 15 minutes
sunspots
cool black storm areas
Sun
Average size and temperature energy comes from nuclear fusion of hydrogen and helium. More than 100x larger than earth
Mercury
Rocky
Venus
Morning star,, rocky, hottest, Brightest beefore sunrise and after sunset, rotates from east to west
Moon
Same period of rotation as period of revolution, causes tides
Mars
Red panet
asteroids
minor planets
Jupiter
gaseous
Saturn
gaseous
Uranus
Icy, rotates counter clockwise
Neptune
Icy
Pluto
Coldest, tilted and elongated orbit,
Last quarter
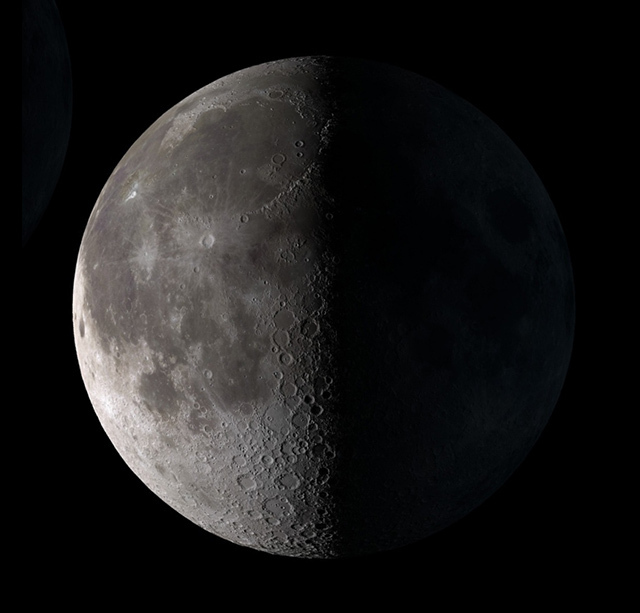

waning gibbous
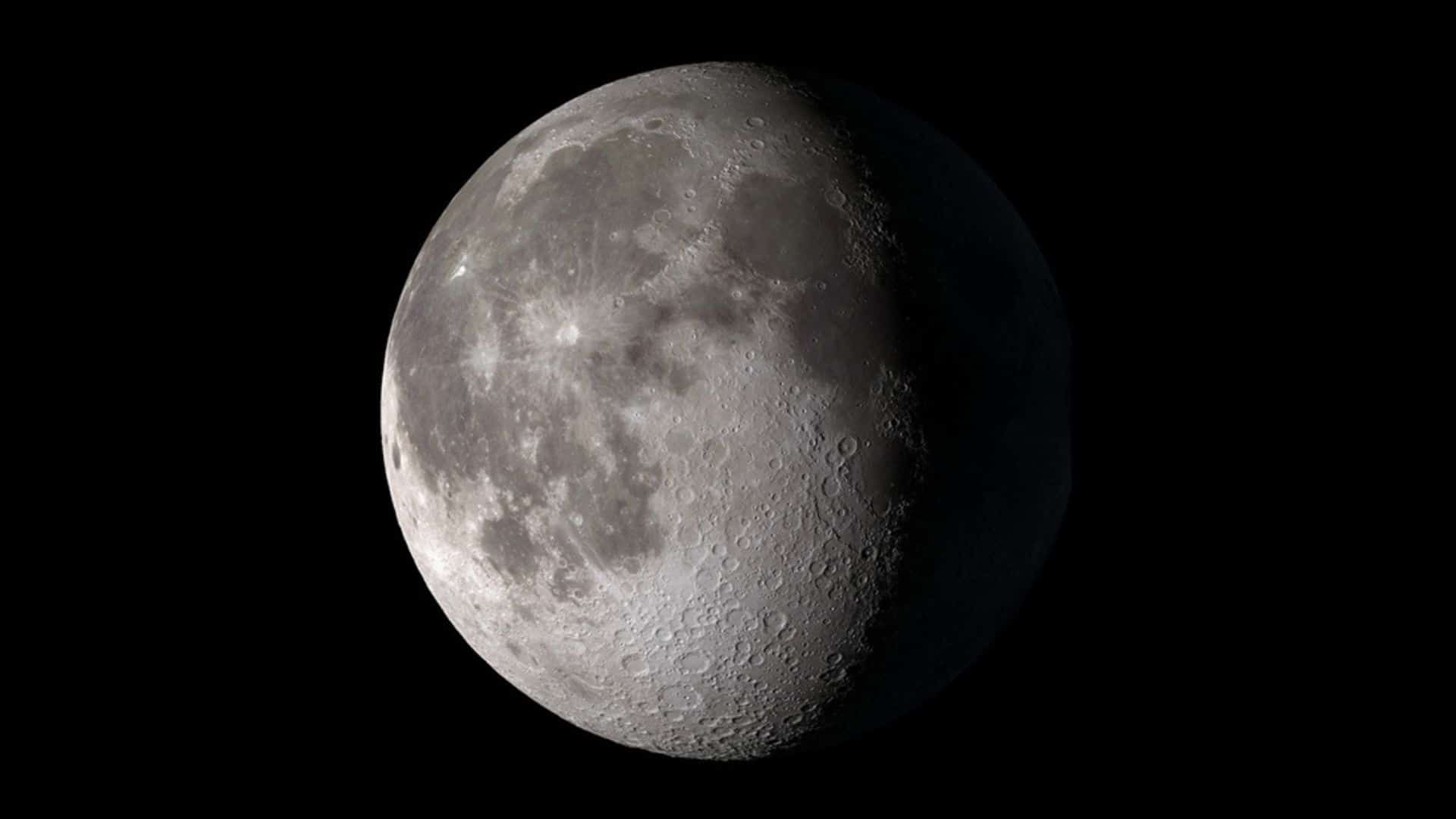

Full moon

Waxing gibbous
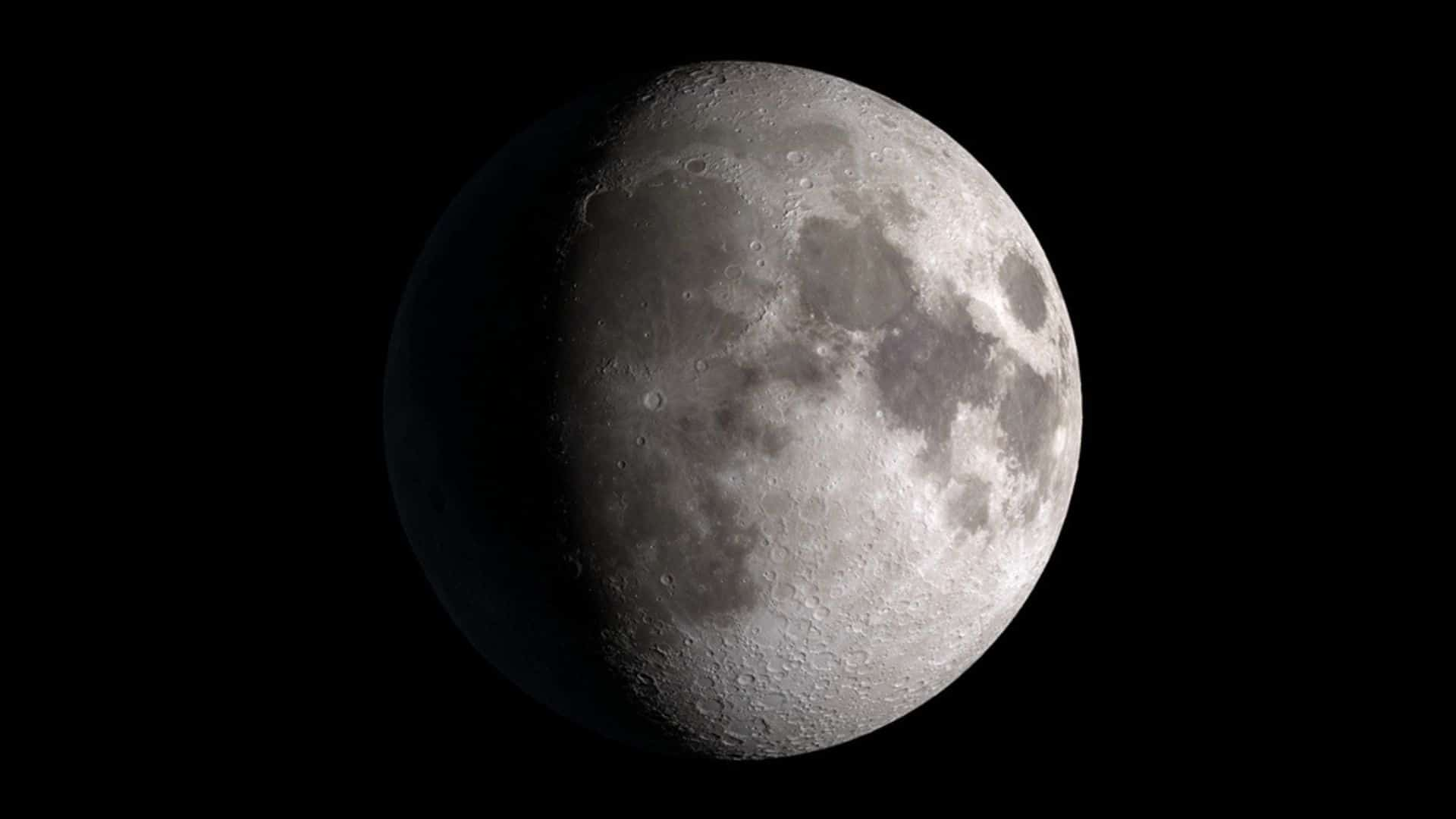

First quarter
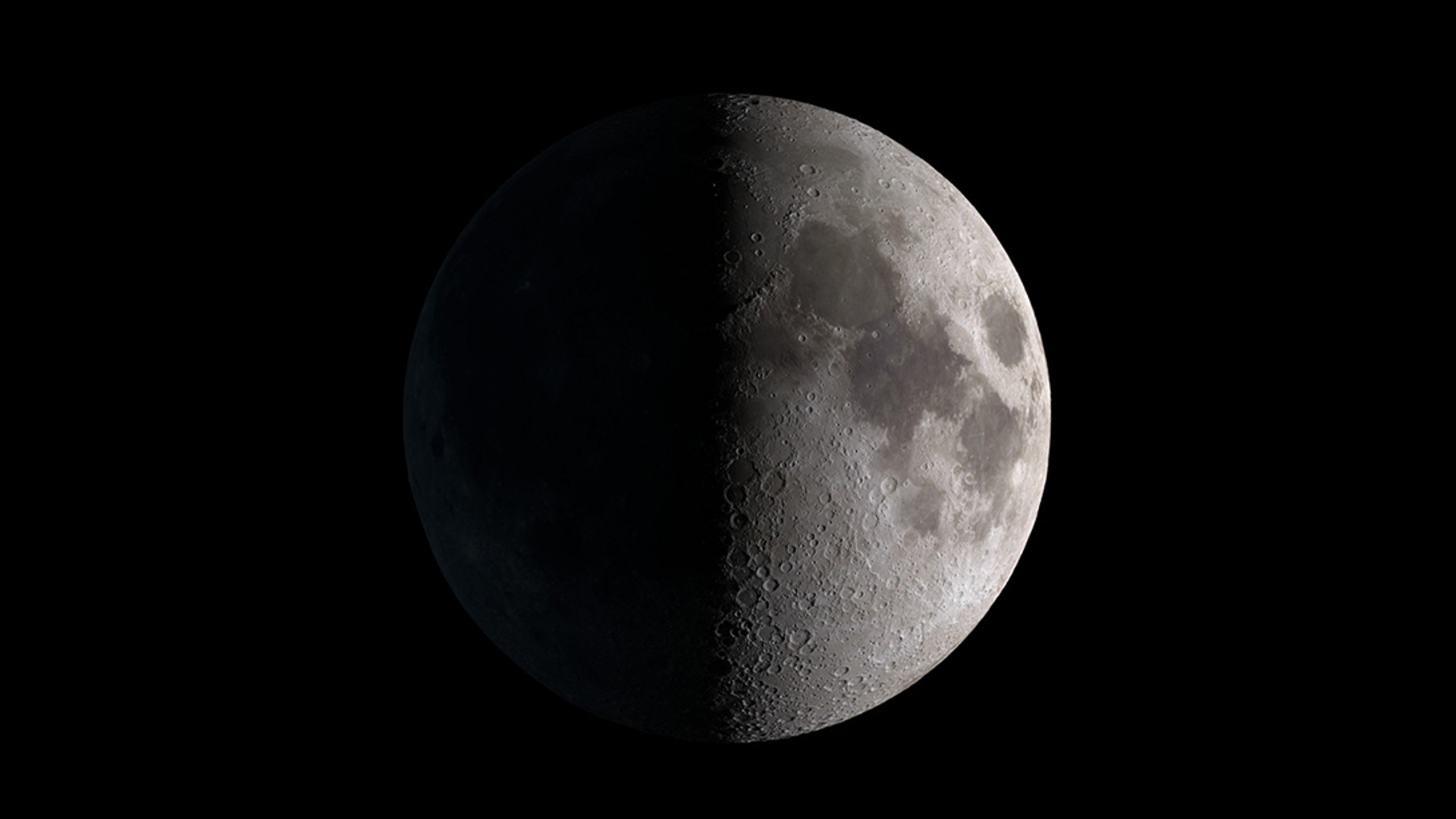

Waxing cresent

new moon

waning crescent

comets
known as dirty snowballs, heads of ice and rock tails of dujst and gases forced from the head by solar radiation, tail always poijnts away from the sun
Meteoroid
chunk of rock or metal smaller than an asteroid, not entering and not still burning in the earths atmosphere
Meteor
A meteoroid as it burns up in the atmosphere “shooting star”
Meteorite
A meteoroid that does not completely burn up
Spring tides
Strongest tides; when the sun, earth and moon are in a straight line the suns and the moons gravities add up highest and lowest tides
neap tides
weakest tides; whjen the sun, earth, and moon gravities cancel out one another; moderate tides
Polaris
North star; tip of little dipperds “handle”
Sirius
Brightest star in the night sky; “dog star'‘
Ursa major
Big bear; contains the big dipper
ursa minor
Little bear; contains the little dipper
canis major
big dog; contains sirius
canis minor
Little dog
orion
The hunter
Proxima centauri
Closest star to earth but is too small to be seen in the night sky
proxima centauri
closest star to earth but is too small to be seen in the night sky
pegasus
The winged horse
Light year
The distance that light travels in one year
Milky way
The galaxy where the solar system is
Supernova
The explosion of a big star
black hole
remains of a supernova explosion with very strong gravity from which notjhing can escape
litosphere
from the crust down to the rigid upper mantle
Divergent
Plate move away from one another forming mid ocean ridges
Convergent
Plates move toward each other
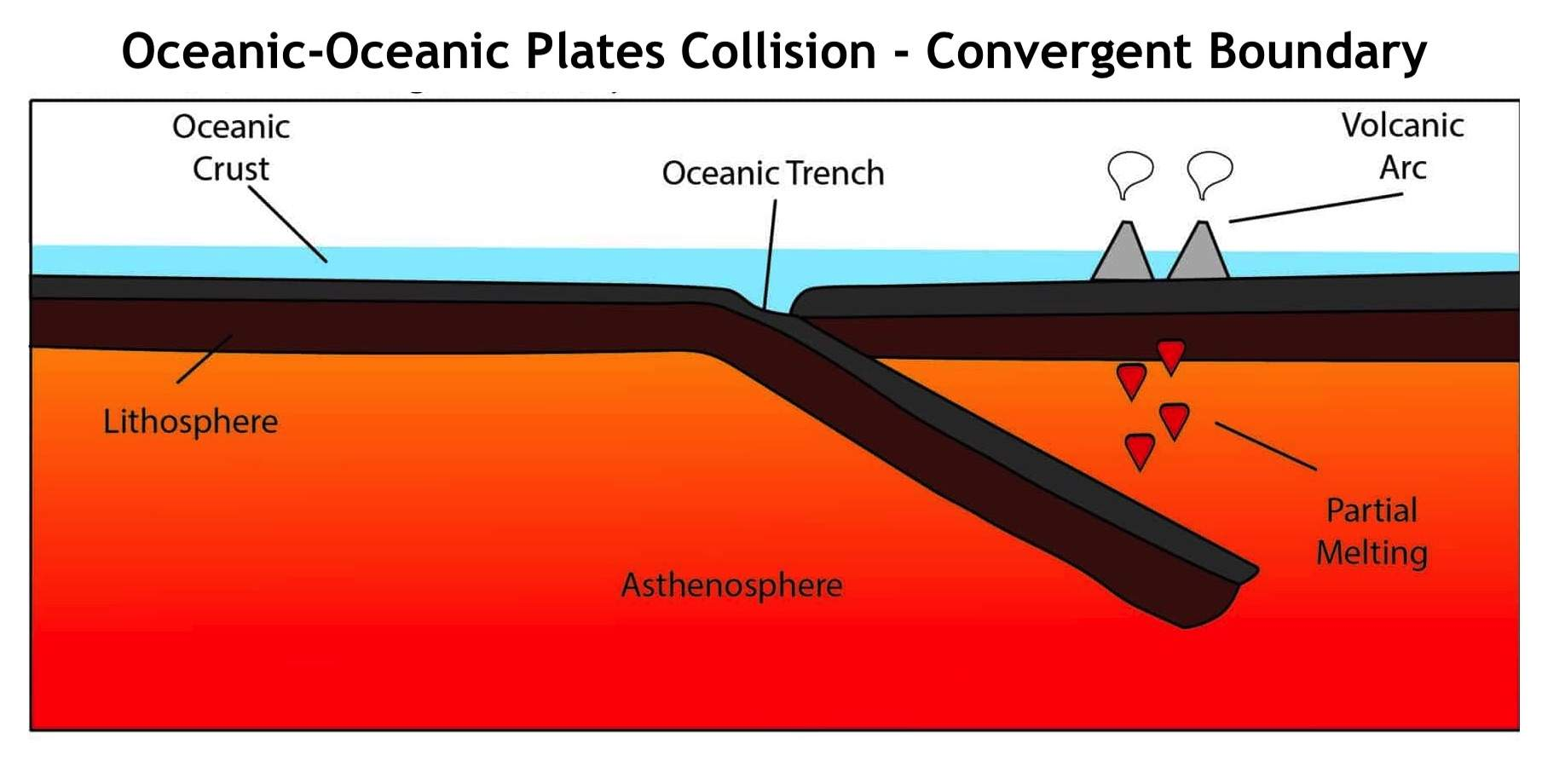
oceanic - oceanic (con)
one of the two oceanic plates is subducted into the mantle, magma rises, forming volcanoes; also creates trenches
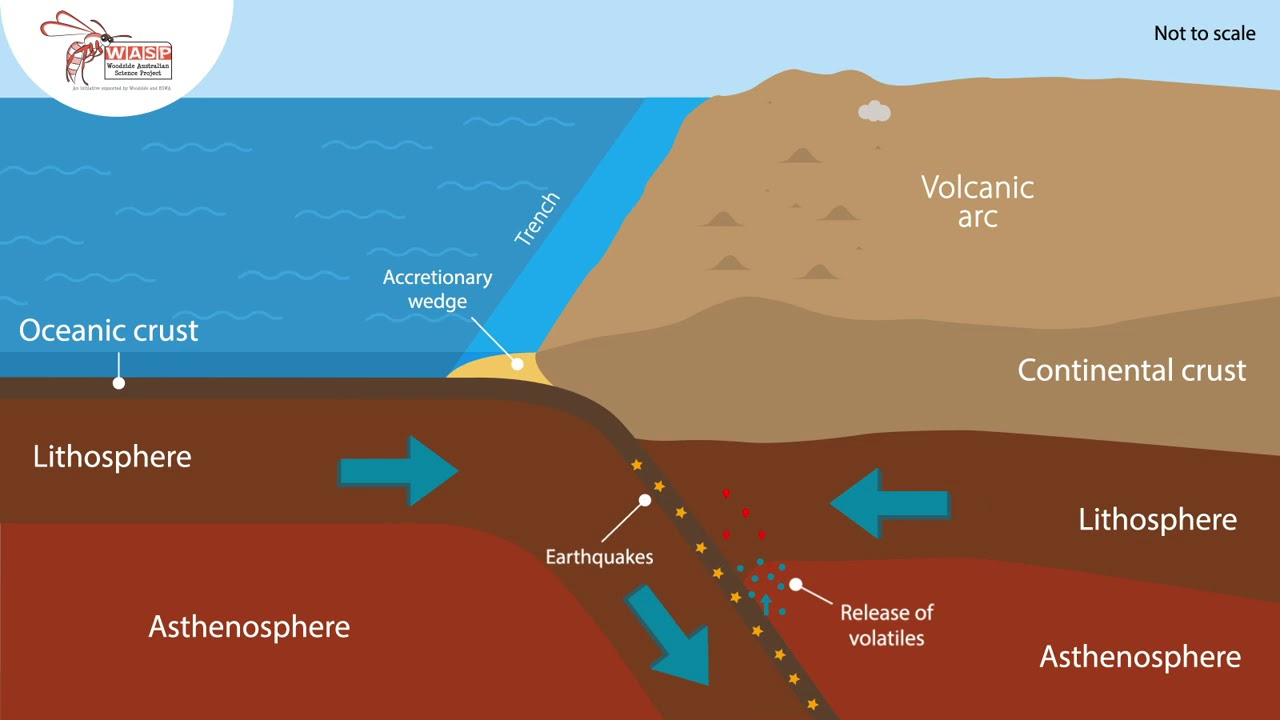
oceanic - continental (conv)
the oceanic plate is subducted into the mantle, magma rises, forming mountain ranges usually containing volcanoes
Continental - continental
Neither plate is fully subducted the plates are forced into one another, forming tall mountains
transform
plates slide past one another, causing earthquakes
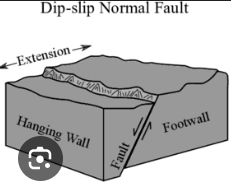
Normal dip slip
a type of fault where the rock above the fault plane (hanging wall) moves down relative to the rock below the fault plane (footwall). This movement is primarily vertical and occurs due to extensional stress, where the Earth's crust is being pulled apart.
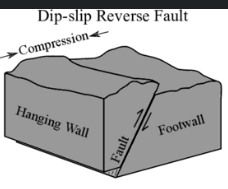
Reverse dip slip/thrust fault
hanging wall (the block of rock above the fault) moves up and over the footwall (the block below the fault).
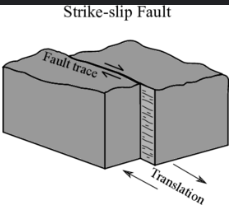
Strike slip
movement of the two blocks is horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault, meaning they slide past each other.
Magnitude
“size” of an earthquake, or energy realeased
Richter scale
measures the magnite where in magnitude 2 is ten times stronger than magnitude 1
Intensity
amount of damage, measured using the marcalli scale (1 to 12)
focus
earthquakes point of origin
Epicenter
the point on the earths surface directly above the focus
igneous
from lava, granite, basalt
formed from cooled and solidified molten rock, called magma or lava. Magma is molten rock found beneath the Earth's surface, while lava is molten rock that erupts onto the surface. The cooling and solidification process results in the formation of crystals within the rock.
metamorphic
from other rocks that were exchanged due to intense heat and preassure, marble slate
sedimentary
from sediments which were eroded to lower places; forms fossils; sandstone, shale
increasing particle size (decreasing water holding capacity)
clay-silt-sand-pebbles-gravel-
Theory of continental drift
Wegener 1912 the theory of the movement of the continents relative to each other
Evidences
Fossils in africa and south america
positions of mountain ranges
glacian striations scratches in rock caused by movement of glaciers
tillites glacial sediments buried in rock
Theory of plate tectonics
tectonic plates move explaints continentalk drift
Pangaea
Supercontinent that existed during Paleozoic and Mesozoic era; broke into Laurasia in the north and Gondwanaland in the south during Mesozoic era
Laurasia
Strated breaking up into asia, europe, and north america during the cenozoic era
Gondwanaland
started breaking upinto africa, australia, antarctica, and south america during the mesozoic era
renewable energy sources
will not run out due to continuous use
non renewable
in danger of running out
fossil fuels
energy sources that were formed by nature for hundreds of millions of years but which people are exploiting and may run out in just a few more years ( coal, natural gas, petroleum)
Global warming
the heating up of the earths surface due to a build up of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide) in the atmosphere
Melting of polar ice caps
Effect of global warming causing excessive flooding and even the loss of low lying land
Climate change
Effect of global warming increasing in the number and intensity of typhoons and a shortening of the wet season
Troposphere
Life forms, weather, densest layer
Stratosphere
ozone layer, airplanes
Mesosphere
Coldest, meteors burn up
thermosphere
Ionosphere, hottest
Exosphere
man made satellites
Summer solstice June 21
The suns direct rays fall on the northern hemisphere, marking the start of summer in the north
Fall equinox september 23
The suns direct rays fall on the equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night; marks the beginning of fall in the north
Winter solstice december 22
The suns direct rays fall on the south, marking the beginning of winter in the north
Spring equinox march 21
Sun rays fall on the equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night marks the beginning of spring in the north
Reason for seasons
Caused by the tilt of the earths axis as it orbits the sun, leading to varying direct sunlight on different parts of the earth