ANS3043 Exam2 - Bone + Tissue
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
epiblast
the outermost layer of an embryo before it differentiates into ectoderm and mesoderm.
2
New cards
hypoblast
forms the extraembryonic membranes
3
New cards
primitive streak
A groove on the surface of an early embryo along the future long axis of the body
-covers caudal 2/3 of embryo
-establishes bilateral symmetry
-covers caudal 2/3 of embryo
-establishes bilateral symmetry
4
New cards
Gastrulation
In animal development, a series of cell and tissue movements in which the blastula-stage embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo, the gastrula. (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
5
New cards
ectoderm
outermost germ layer that forms:
-CNS
-sense organs
-mammary glands
-sweat glands
-skin
-hair
-hooves
-CNS
-sense organs
-mammary glands
-sweat glands
-skin
-hair
-hooves
6
New cards
Mesoderm
middle germ layer that forms:
-circulatory system
-repro system
-kidneys
-urinary ducts
-muscle
-fat
-connective tissue
-bone
-circulatory system
-repro system
-kidneys
-urinary ducts
-muscle
-fat
-connective tissue
-bone
7
New cards
endoderm
inner germ layer that forms:
-digestive system
-liver
-lungs
-pancreas
-thyroid gland
-most other glands
-digestive system
-liver
-lungs
-pancreas
-thyroid gland
-most other glands
8
New cards
Neurulation
results in formation of precursors of spinal cord, brain, and peripheral nervous system
9
New cards
neurulation process
1. ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to form neural plate
2. neural folds come together to complete fusion of neural tube
3. neural plate folds to form neural tube, which will become spinal cord and brain
4. neural tube closes; neural crest cells delaminate & migrate to become peripheral nervous system and other cell types
5. closure of neural tube begins in cervical area and extends in both cranial/caudal directions
2. neural folds come together to complete fusion of neural tube
3. neural plate folds to form neural tube, which will become spinal cord and brain
4. neural tube closes; neural crest cells delaminate & migrate to become peripheral nervous system and other cell types
5. closure of neural tube begins in cervical area and extends in both cranial/caudal directions
10
New cards
spinal dysraphism
a group of neural tube defects that describe some manifestation of incomplete closure of the spine
11
New cards
spina bifida
a congenital defect that occurs during early pregnancy when the spinal canal fails to close completely around the spinal cord to protect it
12
New cards
somites
Paired blocks of mesoderm just lateral to the notochord of a vertebrate embryo. form along anterior-posterior axis of developing embryo
13
New cards
somitogenesis
-formation of paired cuboidal masses of mesoderm (somites), one on each side of neural tube
-occurs in a cranial to caudal manner
-occurs in a cranial to caudal manner
14
New cards
Dermamyotome
dorsolateral portion of the somite that forms dermatome and myotome (dermis and muscle)
15
New cards
Sclerotome
gives rise to the vertebrae (skeleton)
16
New cards
Embryogenesis
The process by which a single-celled zygote becomes a multicellular embryo. ends once species can be identified and can be called fetus
17
New cards
connective tissue functions
-support, surround and connect other tissues
-structural framework
-protect organs
-store energy reserves (in tissue called adipose)
-transport fluids within body
-structural framework
-protect organs
-store energy reserves (in tissue called adipose)
-transport fluids within body
18
New cards
connective tissue
extensive cellular matrix with relatively few cells (bone, cartilage, loose connective tissue)
19
New cards
connective tissues are classified by
-extracellular matrix
-mixture/arrangement of connective fibers
-type of cells present
-mixture/arrangement of connective fibers
-type of cells present
20
New cards
connective tissue proper
loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue
21
New cards
supportive connective tissue
-bone and cartilage
-strong protein fibers, thicker ground substance
-strong protein fibers, thicker ground substance
22
New cards
fluid connective tissue
blood and lymph, no fibers, mostly cells and ground substance
23
New cards
fibroblasts
In connective tissue, cells that
-secrete the proteins for extracellular fibers
-secrete hyaluronic acid which helps make grounding substance
-most abundant fixed cells in connective tissue
-secrete the proteins for extracellular fibers
-secrete hyaluronic acid which helps make grounding substance
-most abundant fixed cells in connective tissue
24
New cards
macrophages
-immune cells
-can be fixed or wandering
-can be fixed or wandering
25
New cards
mesenchymal cells
stem cells that respond to injury or infection
26
New cards
Adipocytes
fat cells that make up most of the subcutaneous layer
27
New cards
ground substance
fluid-like or gel-like substance that fills the space between cells and fibers, contains proteoglycans
28
New cards
Proteoglycans
A glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of animal cells, rich in carbohydrate
-linear core protein with glycosaminoglycans
(chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid are GAGs)
-linear core protein with glycosaminoglycans
(chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid are GAGs)
29
New cards
Major types of protein fibers in connective tissue
1. collagenous
2. reticular
3. elastic
2. reticular
3. elastic
30
New cards
Collagen
-main protein in tendons, bone cartilage
-strong, flexible but inelastic
-difference in AA sequence affects strength/functionality
-strong, flexible but inelastic
-difference in AA sequence affects strength/functionality
31
New cards
collagen synthesis and maturation
1. alpha chains
- hydroxylation of lysine and proline by enzymes
2. pre-procollagen
- helix formation
3. procollagen
-exported from fibroblast to extracellular matrix
-ends romoved
4. tropocollagen
- tropocollagen molecules align
- lysyl oxidase contributes to cross-link formation (stability and strength)
5. collagen fibril
-maturation of cross-links increase stability (insoluble)
6. collagen fiber (multiple fibrils)
- hydroxylation of lysine and proline by enzymes
2. pre-procollagen
- helix formation
3. procollagen
-exported from fibroblast to extracellular matrix
-ends romoved
4. tropocollagen
- tropocollagen molecules align
- lysyl oxidase contributes to cross-link formation (stability and strength)
5. collagen fibril
-maturation of cross-links increase stability (insoluble)
6. collagen fiber (multiple fibrils)
32
New cards
Osteolathyrism
-deficiency in collagen cross-linking caused by reduced lysyl oxidase activity
-caused by eating grass pea or sweet pea
-symptoms: weakness, spinal deformities, joint degeneration
-caused by eating grass pea or sweet pea
-symptoms: weakness, spinal deformities, joint degeneration
33
New cards
scurvy
-defective collagen formation caused by deficiency in prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase activity
-caused by vitamin c deficiency, needed as co-factor for activity of enzymes
-symptoms: weakness, fatigue, impaired wound healing, osteopenia (weak bones)
-caused by vitamin c deficiency, needed as co-factor for activity of enzymes
-symptoms: weakness, fatigue, impaired wound healing, osteopenia (weak bones)
34
New cards
reticular fibers
-contains type III collagen
-branching, interwoven network
-small, fine, delicate
-framework in glands, lymphs and connective tissue surrounding soft organs
-branching, interwoven network
-small, fine, delicate
-framework in glands, lymphs and connective tissue surrounding soft organs
35
New cards
elastin
-protein
-can be reversibly stretched to nearly 2x length
-cross-links indicate elastin fiber maturation
-high non-polar AA content
-insoluble in water
-in ligaments
-can be reversibly stretched to nearly 2x length
-cross-links indicate elastin fiber maturation
-high non-polar AA content
-insoluble in water
-in ligaments
36
New cards
loose connective tissue
-fills in space between organs and provides cushioning
-high proportion ground substance
-relatively few collagen and elastin fibers
-can distort and stretch w/o damage
-cushions shock
-vascularized w/ numerous cells
-separates skin from deeper structures
-surrounds/supports blood vessels/nerves
-route for diffusion
-high proportion ground substance
-relatively few collagen and elastin fibers
-can distort and stretch w/o damage
-cushions shock
-vascularized w/ numerous cells
-separates skin from deeper structures
-surrounds/supports blood vessels/nerves
-route for diffusion
37
New cards
dense connective tissue
-structure provides more strength but less flexibility
-numerous fibers, few cells
-dense regular and dense irregular
-numerous fibers, few cells
-dense regular and dense irregular
38
New cards
dense regular connective tissue
-mixture of collagen, elastin and reticular fibers
-fibers align in one direction
-aligned with forces applied to tissue (tendons, aponeuroses, ligaments, elastic tissue)
-fibers align in one direction
-aligned with forces applied to tissue (tendons, aponeuroses, ligaments, elastic tissue)
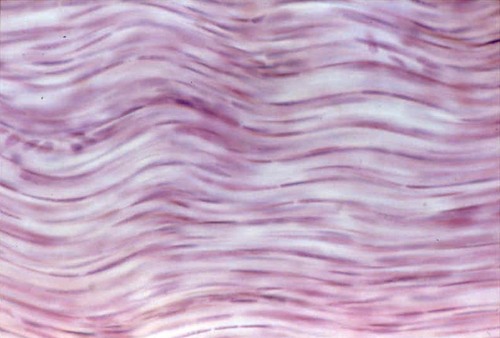
39
New cards
dense irregular connective tissue
- high amount of collagen
-dense, interwoven randomly arranged fibers
-supports stresses from different directions
-capsules around visceral organs
-dermis of skin
-nerve and muscle sheaths
-dense, interwoven randomly arranged fibers
-supports stresses from different directions
-capsules around visceral organs
-dermis of skin
-nerve and muscle sheaths
40
New cards
subcutanous injection
A subcutaneous injection or shot is one into the fatty tissues just beneath the skin.
CT circulatory supply and loose structure provides route for drug diffusion
CT circulatory supply and loose structure provides route for drug diffusion
41
New cards
epidermis
epithelial tissue
42
New cards
dermis (true skin)
dense irregular CT, nerve endings, capillaries, sweat glands, vessels
43
New cards
Scarring occurs when too much ______________ is produced during wound healing.
collagen; collagen fibers become more aligned rather than random
44
New cards
keloids
abnormal response to trauma, fibroblast proliferation, over-production of collagen
45
New cards
compared to bone, cartilage is
-lighter
-half as dense
-more flexible
-half as dense
-more flexible
46
New cards
Ground substance in cartilage is much more _________ than loose or dense connective tissue
rigid
47
New cards
Ground substance in cartilage is made of _________________ __________________
chondroiton sulfates
48
New cards
lacuna
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes in bone or chondrocytes in cartilage
49
New cards
chondrocyte
mature cartilage cell
50
New cards
types of cartilage
elastic, hyaline, fibrocartilage
51
New cards
elastic cartilage
-mostly elastic fibers
-least tough
-very flexible
-yellowish in color
-least tough
-very flexible
-yellowish in color
52
New cards
hyaline cartilage
-mostly densely packed fine collagen fibers
-ends of bones
-tough, resistant to pressure and friction
-somewhat flexible
-bluish-white, glassy
-most abundant cartilage type
-may become bone by ossification
-ends of bones
-tough, resistant to pressure and friction
-somewhat flexible
-bluish-white, glassy
-most abundant cartilage type
-may become bone by ossification
53
New cards
fibrocartilage
-almost all collagen fibers
-little ground substance
-most tough type of cartilage
-little ground substance
-most tough type of cartilage
54
New cards
cartilage characteristics
-highly specialized ECM
-avascular, nutrients supplied by diffusion
-limited healing ability
-limited proliferative capacity of chondrocytes
-chondrocytes are immoble
-avascular, nutrients supplied by diffusion
-limited healing ability
-limited proliferative capacity of chondrocytes
-chondrocytes are immoble
55
New cards
bone characteristics
-most rigid connective tissue
-made of inorganic matrix & collagen fibers
-few cells
-rich vascular supply
-considerable metabolic activity
-made of inorganic matrix & collagen fibers
-few cells
-rich vascular supply
-considerable metabolic activity
56
New cards
Inorganic matrix of bone is composed of _____ and ____. This makes up majority of bone (45%)
calcium and phosphorus
57
New cards
Organic component (30%) of bone is made up of
collagen, proteoglycans and non-collagenous proteins
58
New cards
25% of bone is made up of _____________
water
59
New cards
functions of bone
-protection
-support
-locomotion
-mineral/lipid storage
-hematopoiesis (blood formation)
-support
-locomotion
-mineral/lipid storage
-hematopoiesis (blood formation)
60
New cards
Matrix of bone is made up of
hydroxyapatite crystals and collagen fibers
61
New cards
hydroxyapatite crystals
-Ca5(PO4)3OH
-fluoride can replace OH to make stronger crystal
-inflexible
-brittle
-resists compression
-fluoride can replace OH to make stronger crystal
-inflexible
-brittle
-resists compression
62
New cards
collagen fibers
-provides flexibility and strength
-gives framework for formation of crystals
-gives framework for formation of crystals
63
New cards
flat and irregular bones
-ribs
-skull
-pelvis
-vertebrae
-scapula
-skull
-pelvis
-vertebrae
-scapula
64
New cards
long bones
-femur
-tibia
-fibula
-tibia
-fibula
65
New cards
long bone structure
diaphysis (shaft) and epiphysis (enlarged ends)
66
New cards
preiosteum
dense, vascularized membrane surrounding bone
67
New cards
growth plate
-the area just below the head of a long bone in which growth in bone length occurs; the epiphyseal plate.
-made up of cartilage, once maturity is reached growth plate closes
-made up of cartilage, once maturity is reached growth plate closes
68
New cards
medullary cavity
cavity within the shaft of the long bones filled with bone marrow
69
New cards
articular cartilage
covers the surfaces of bones where they come together to form joints
70
New cards
compact bone
-aka cortical bone
-dense structure
-found at periphery of bones
-Ca not readily available
-dense structure
-found at periphery of bones
-Ca not readily available
71
New cards
spongy bone
-aka trabecular bone
-network of struts/thick netting
-Ca more readily available
-larger surface area
-vertebrae, flat bones, shafts/ends of long bones
-network of struts/thick netting
-Ca more readily available
-larger surface area
-vertebrae, flat bones, shafts/ends of long bones
72
New cards
bone tissue
-highly organized
-composed of osteons
-canals surrounded by lamellae
-osteocytes locked within lacunae and linked together through canaculus
-composed of osteons
-canals surrounded by lamellae
-osteocytes locked within lacunae and linked together through canaculus
73
New cards
osteon
structural unit of compact bone (aka haversian system)
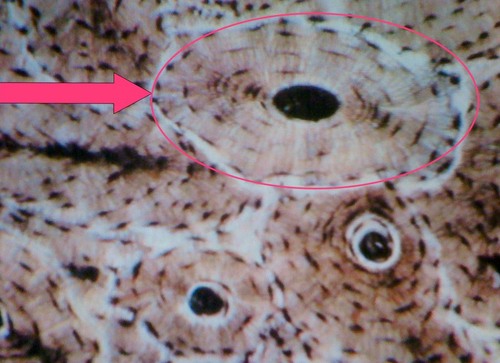
74
New cards
lamellae
Concentric rings made up of groups of hollow tubes of bone matrix
75
New cards
canaculi
passageways forming a branching network for the exchange of materials between blood vessels and osteocytes
76
New cards
osteoblast
cell that will produce new bone (osteo = bone, blast = immature)
77
New cards
osteocyte
mature bone cell within mineralized matrix
78
New cards
osteoclast
-involved in bone resorption and remodeling
-multinucleated, cannot replicate
-multinucleated, cannot replicate
79
New cards
bone lining cells
inactive cells on bone surface, can be activated if needed for repair
80
New cards
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
81
New cards
cartilage requires relatively ________ amounts of oxygen, while bone requires relatively ________ amounts of oxygen
low, high
82
New cards
osteogenesis
process of bone formation
83
New cards
endochondrial ossification
bone formation from a cartilage template
84
New cards
intramembranous ossification
bone formation as a replacement of connective tissue in the absence of cartilage
85
New cards
During fetal development, most bones have a _________ ____________, which is gradually replaced by bone
cartilage template
86
New cards
endochondrial ossification process
1. mesenchyme condenses during embryogenesis
2. committed mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes to form model for bone
3. remaining mesenchymal cells surround cartilage core to form perichondrium
4. centrally located chondrocytes undergo hypertrophy, then apoptosis
5. blood vessels fill space left by dead chondrocytes and deliver osteoblasts
6. osteoblasts deposit bone matrix, perichondrium converted to periosteum, bone layer formed around diaphysis
7. primary ossification center established in center of diaphysis, bone formed until diaphysis is filled, osteoclasts hollow out marrow cavity
8. secondary ossification centers from as blood vessels enter near tips of bone
9. osteoblasts produce spongy bone that replace epiphyseal cartilage, articular cartilage and growth plate cartilage left
2. committed mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondrocytes to form model for bone
3. remaining mesenchymal cells surround cartilage core to form perichondrium
4. centrally located chondrocytes undergo hypertrophy, then apoptosis
5. blood vessels fill space left by dead chondrocytes and deliver osteoblasts
6. osteoblasts deposit bone matrix, perichondrium converted to periosteum, bone layer formed around diaphysis
7. primary ossification center established in center of diaphysis, bone formed until diaphysis is filled, osteoclasts hollow out marrow cavity
8. secondary ossification centers from as blood vessels enter near tips of bone
9. osteoblasts produce spongy bone that replace epiphyseal cartilage, articular cartilage and growth plate cartilage left
87
New cards
long bone lengthening
1. growth of cartilage on epiphyseal side of growth plate
2. ossification of cartilage on diaphyseal side of growth plate
2. ossification of cartilage on diaphyseal side of growth plate
88
New cards
zones of growth plate
-reserve (resting) zone
-proliferating zone
-prehypertrophic zone
-hypertrophic zone
-ossification zone
-proliferating zone
-prehypertrophic zone
-hypertrophic zone
-ossification zone
89
New cards
reserve (resting) zone
-chondrocytes closest to epiphysis
-source of chondrocytes forming proliferation zone
-source of chondrocytes forming proliferation zone
90
New cards
proliferating zone
-chondrocytes proliferate and flatten
-chondrocytes lay down a cartilage ECM that later serve as scaffold for bone formation
-pushes epiphysis away from diaphysis
-chondrocytes lay down a cartilage ECM that later serve as scaffold for bone formation
-pushes epiphysis away from diaphysis
91
New cards
prehypertrophic zone
-chondrocytes enter maturation zone, differentiate and enlarge
-cells produce additional molecules for ECM and collagen fibers, builds cartilage
-cells produce additional molecules for ECM and collagen fibers, builds cartilage
92
New cards
hypertrophic zone
-chondrocytes and lacuncae become 5-12x bigger
-chondrocytes die and leave behind calcified cartilage matrix that is invaded by capillaries + osteoblasts
-chondrocytes die and leave behind calcified cartilage matrix that is invaded by capillaries + osteoblasts
93
New cards
ossification zone
-development of new bone
-osteoblasts deposit organic matrix
-connection of adjacent osteocytes by cytoplasmic threads
-osteoblasts deposit organic matrix
-connection of adjacent osteocytes by cytoplasmic threads
94
New cards
osteoid + osteoblast differentiation =
ossification
95
New cards
chondrodysplasia
-defective formation of cartilage
-FGF3 involved in arrest of bone growth
-restricts proliferation of cartilage at growth plate, expressed in resting and proliferative chondrocytes
-SNP in FGFR3 gene results in AA substitution and enhanced proliferation of pre-hypertrophic chondrocytes
-FGF3 involved in arrest of bone growth
-restricts proliferation of cartilage at growth plate, expressed in resting and proliferative chondrocytes
-SNP in FGFR3 gene results in AA substitution and enhanced proliferation of pre-hypertrophic chondrocytes
96
New cards
break joint
denotes the point on a lamb carcass where the foot and pastern are removed at the cartilaginous junction of the front leg (young sheep)
97
New cards
Spool Joint
The joint where the foot and pastern are removed from the front leg of a sheep carcass. A carcass must have two spool joints to be classified as mutton (adult sheep)
98
New cards
long bone growth
-occurs as long as rate of cartilage growth > rate of bone formation within growth plate
-growth finished when cartilage of epiphyseal plate is eliminated and growth plate fused
-growth finished when cartilage of epiphyseal plate is eliminated and growth plate fused
99
New cards
long bone growth is influenced by
hormones, nutrition, minerals, chronological age
100
New cards
intramembranous bone formation
-direct laying down of bone into primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme)
-mesenchyme ---> osteoblast ---> osteocyte
-skull formed through this process
-mesenchyme ---> osteoblast ---> osteocyte
-skull formed through this process