Basic Geometry Terms
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:57 PM on 10/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
Point
Undefined term in Euclidean Geometry. A location in space. No measure (length, width, depth). Zero dimension. Name a point with one upper case letter.

2
New cards
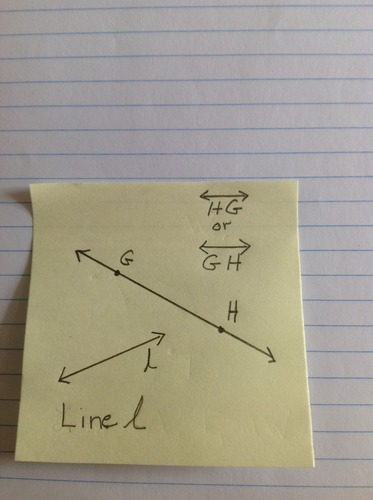
Line
Undefined term in Euclidean Geometry. The straight path of a point as it travels in space. No width or depth. Infinite length. One dimension. Name a line with two points or one lower case script letter.
3
New cards
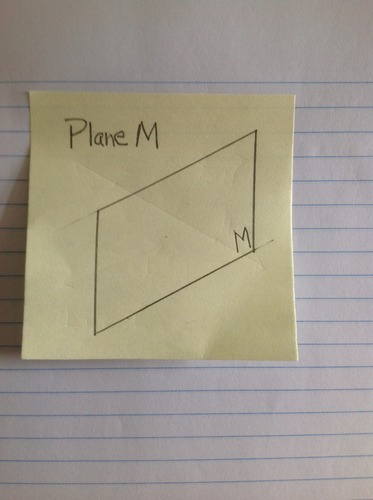
Plane
Undefined term in Euclidean Geometry. The straight path of a line as it travels in space. No depth. Infinite length and infinite width. Two dimensions. Name a plane with a capital letter.
4
New cards
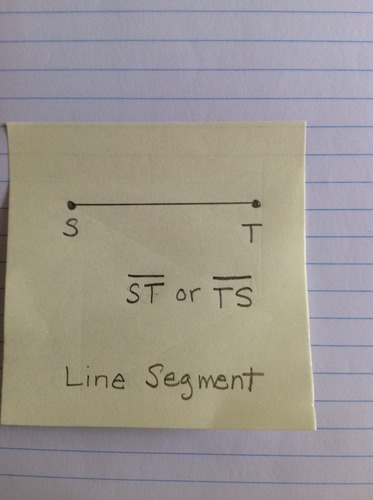
Line Segment
A portion of a line that has definite length, and two endpoints. Name the line segment by its two endpoints in any order.
5
New cards
Measure of a line segment
The length of a line segment, usually given in mm, cm, in, ft, or some other linear unit of measure.
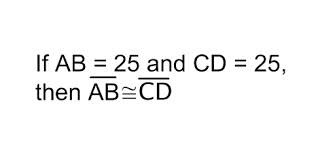
6
New cards
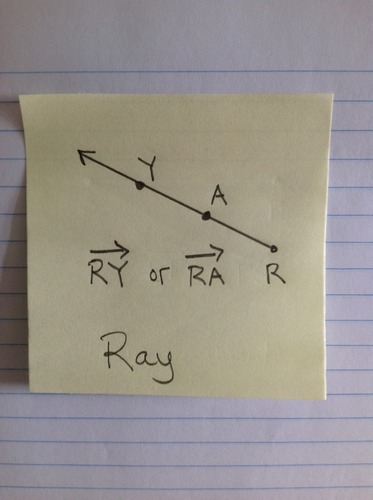
Ray
A portion of a line that has only one endpoint and infinite length. Name the ray with the endpoint first and another point second that shows the direction the ray extends.
7
New cards
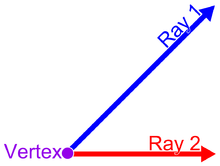
Vertex
A point that is the intersection of two segments, or two rays, at their endpoints.
8
New cards
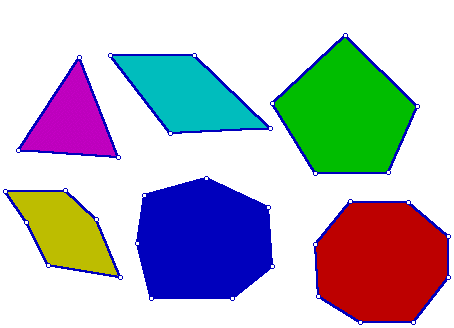
Polygon
A closed plane figure whose sides are line segments that intersect only at their endpoints. Name a polygon by its vertices in clockwise or counter-clockwise order, starting at any vertex.
9
New cards
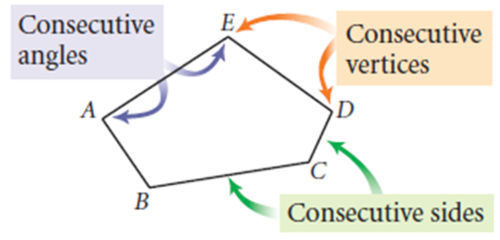
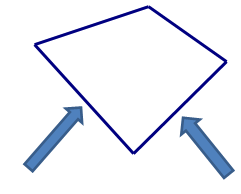
Consecutive Vertices
Two vertices of a polygon that are endpoints of the same side.
10
New cards
Consecutive Sides
Two sides of a polygon that share the same endpoint (vertex.)
11
New cards
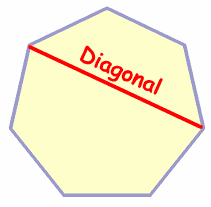
Diagonal
A segment that joins two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon.
12
New cards
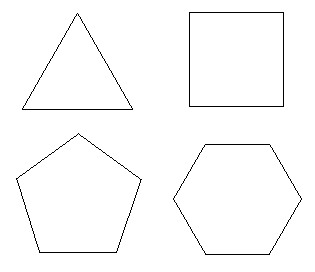
Convex Polygon
A polygon that has no diagonals or parts of a diagonal in the exterior of the polygon.
13
New cards
Concave Polygon
A polygon that has at least a portion of a diagonal in the exterior of the polygon.
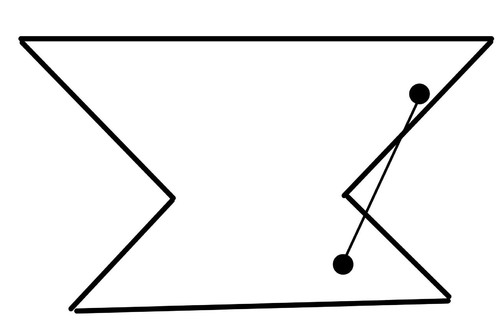
14
New cards
Collinear
Three or more points on the same line are collinear.
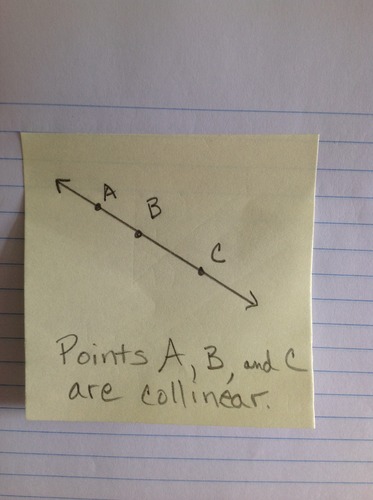
15
New cards
Coplanar
Three or more non-collinear points, or a line and non-collinear points, or two or more lines, that are on the same plane are coplanar.
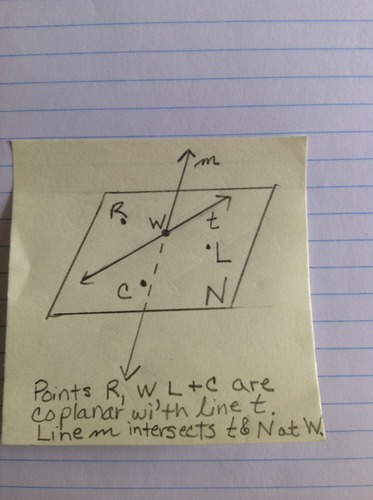
16
New cards
Angle
The union of two rays that intersect at their endpoints only. The measure of an angle is less than or equal to 180 degrees.
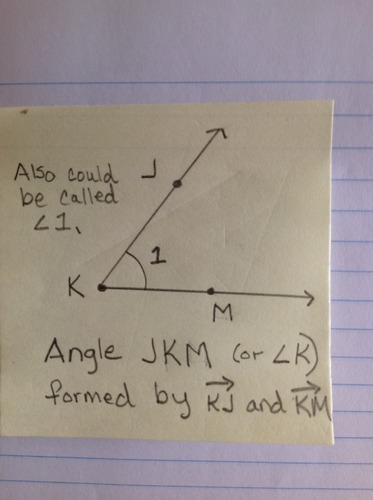
17
New cards
Side of an Angle
One of the rays that form an angle.
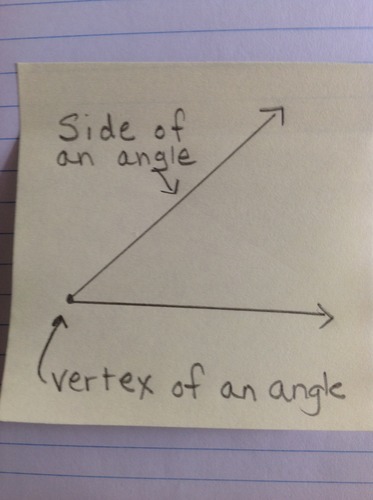
18
New cards
Vertex of an Angle
The common endpoint of the two rays that form the angle.
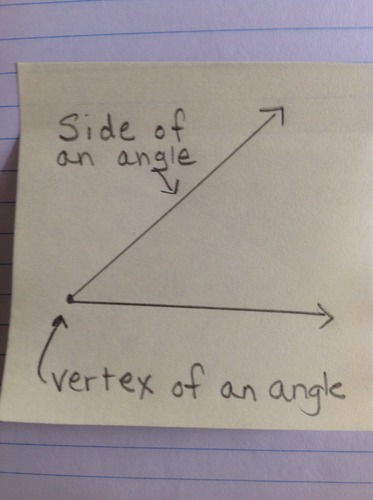
19
New cards
Congruent
Geometric shapes that are the same shape and have the same measure are congruent.
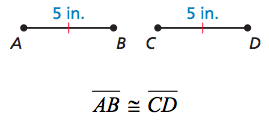
20
New cards
Measure of an angle
The amount of turning about the vertex from one side to the other. The measure of an angle is given in degrees or radians.
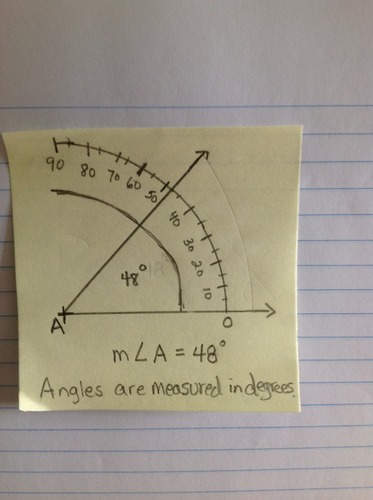
21
New cards
Acute Angle
An angle whose measure is more than zero degrees and less than 90 degrees.

22
New cards
Right Angle
An angle whose measure is exactly 90 degrees.
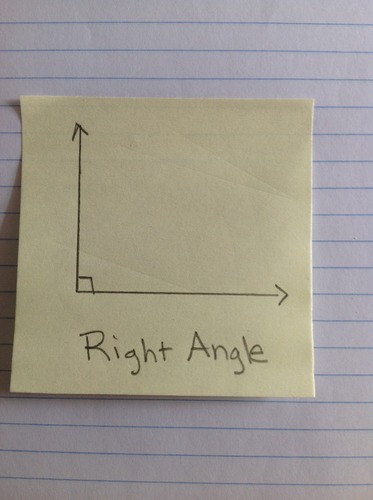
23
New cards
Obtuse Angle
An angle whose measure is more than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees.
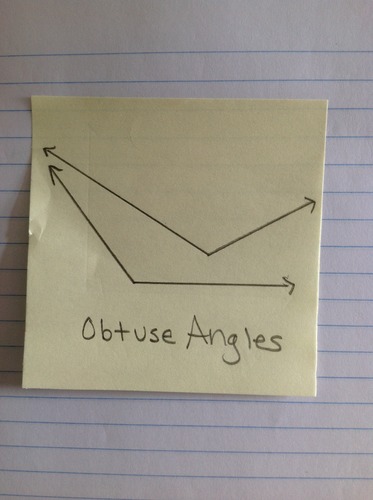
24
New cards
Straight Angle
An angle whose measure is exactly 180 degrees.
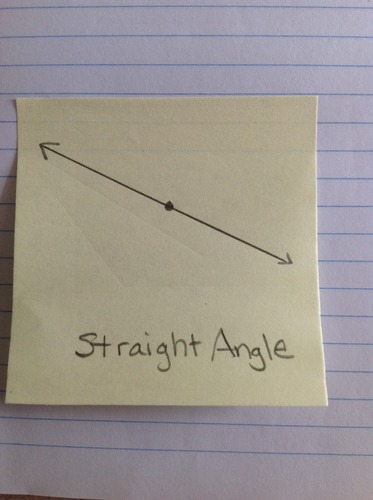
25
New cards
Complementary Angles
Two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. These two angles do not have to share any points.
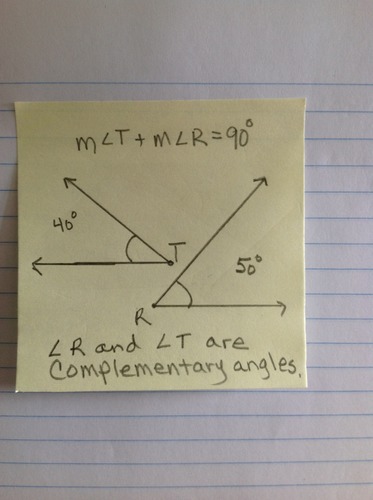
26
New cards
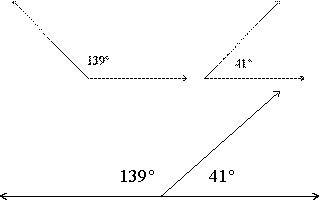
Supplementary Angles
Two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. These two angles do not have to share any points.
27
New cards
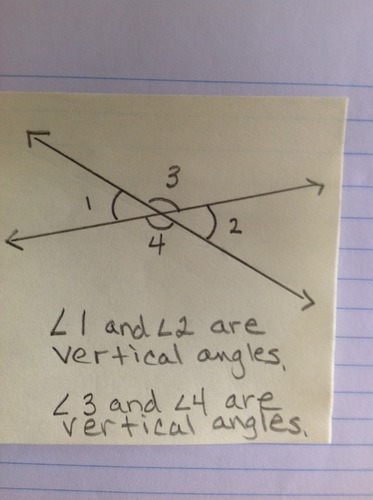
Vertical Angles
Two angles formed by intersecting lines that share only a vertex. A property of vertical angles is that they are congruent.
28
New cards
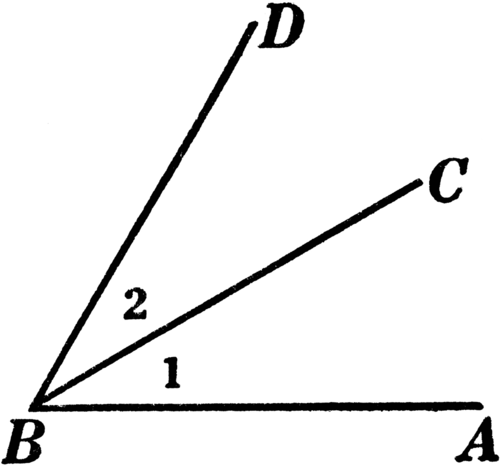
Adjacent Angles
Two angles that share a vertex and side and do not share any interior points.
29
New cards
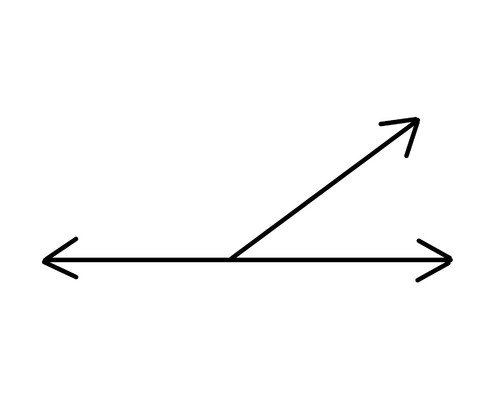
Linear Pair of Angles
Two adjacent angles whose unshared sides form a straight angle (or line.) A property of Linear Pairs is that the angles are supplementary. (Linear Pair Postulate)
30
New cards
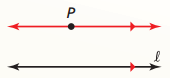
Parallel Lines
Two or more coplanar lines that do not intersect. They have the same slope.
31
New cards
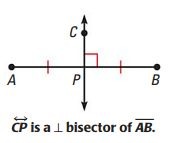
Perpendicular Lines
Two or more coplanar lines that intersect to form right angles. Their slopes are negative reciprocals of each other and their product equals -1.
32
New cards
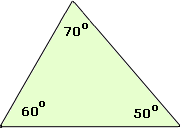
Triangle
A polygon with three sides.
33
New cards
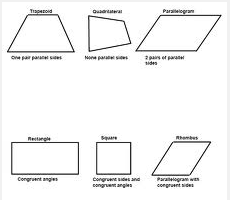
Quadrilateral
A polygon with four sides.
34
New cards
Pentagon
A polygon with five sides.
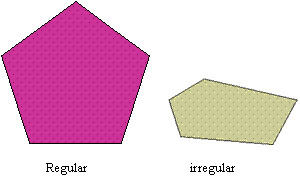
35
New cards
Hexagon
A polygon with six sides.
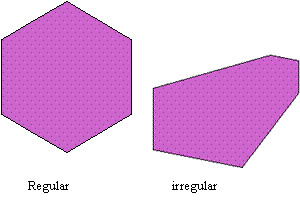
36
New cards
Heptagon
A polygon with seven sides.
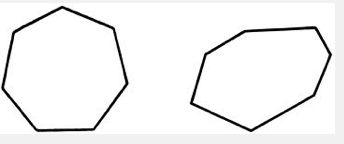
37
New cards
Octagon
A polygon with eight sides.
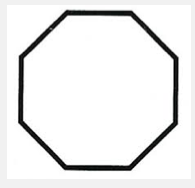
38
New cards
Nonagon
A polygon with nine sides.
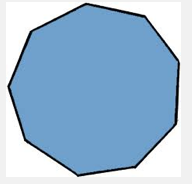
39
New cards
Decagon
A polygon with ten sides.
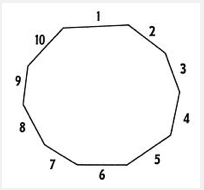
40
New cards
Scalene Triangle
A triangle whose sides are not congruent.
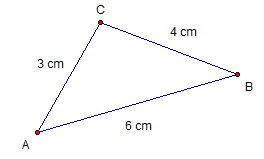
41
New cards
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle with at least two congruent sides.
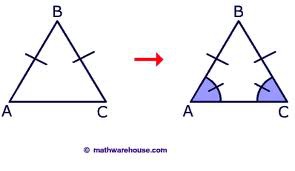
42
New cards
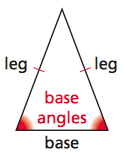
Base of an Isosceles Triangle
The non-congruent side (if there is one) of an isosceles triangle.
43
New cards
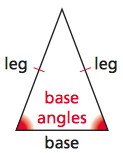
Base Angles of an Isosceles Triangle
Two angles that have one side that is the base of the isosceles triangle.
44
New cards
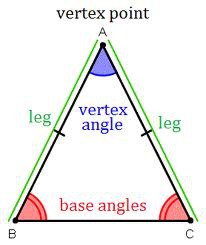
Vertex Angle of an Isosceles Triangle
The angle of an isosceles triangle formed by congruent sides.
45
New cards
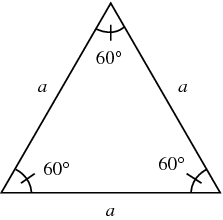
Equilateral Triangle
A triangle with all three sides congruent. (A regular triangle.)
46
New cards
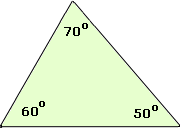
Acute Triangle
A triangle with three acute angles.
47
New cards
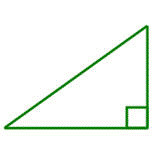
Right Triangle
A triangle with one right angle and two acute angles. The two acute angles are complementary.
48
New cards
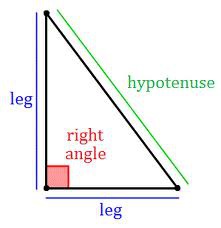
Hypotenuse
The longest side of a right triangle. It is opposite the right angle.
49
New cards
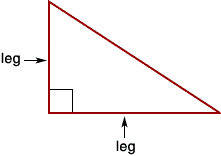
Legs of a Right Triangle
The two sides of the right triangle that form the right angle.
50
New cards
Obtuse Triangle
A triangle with one obtuse angle and two acute angles.
51
New cards
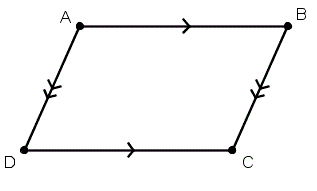
Parallelogram
A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
52
New cards
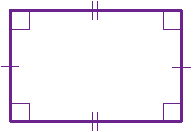
Rectangle
A parallelogram with four right angles (an equiangular parallelogram.)
53
New cards
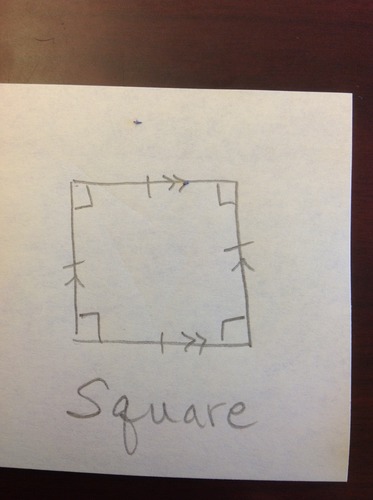
Square
A regular parallelogram. An equilateral rectangle. An equiangular rhombus.
54
New cards
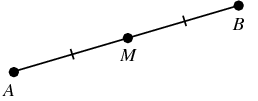
MIdpoint
The point of a segment that splits the segment into two congruent segments.
55
New cards
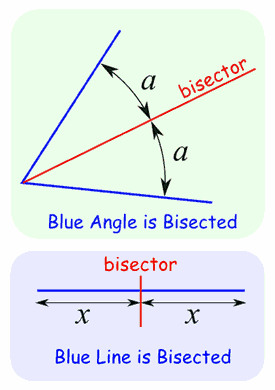
Bisect
To split into two congruent parts.
56
New cards
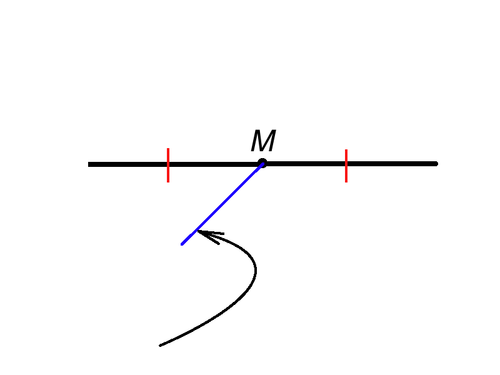
Segment Bisector
A line, ray, segment, or plane that passes through only the midpoint of a line segment. It creates two congruent segments that are half as long as the original segment.
57
New cards
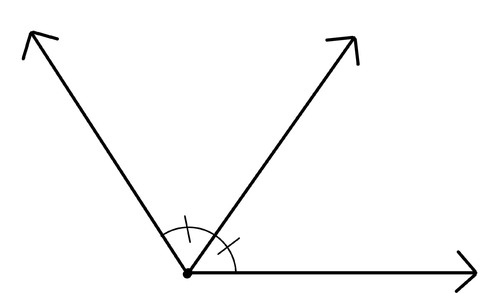
Angle Bisector
A ray or line that passes through the vertex of an angle and forms two congruent angles that are half the measure of the original angle.
58
New cards
Perimeter
The sum of the lengths of the sides of a polygon.
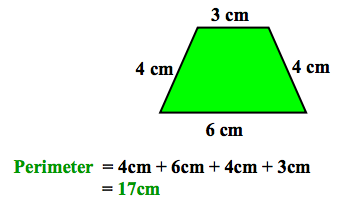
59
New cards
Area
The amount of two dimensional space within the borders of a plane figure. It is measured in square units.
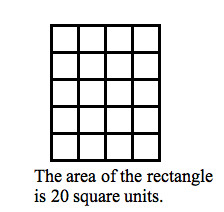
60
New cards
Area of a Triangle
A = (1/2)bh, where b = base, and h = height
(You will learn other area formulas for a triangle in subsequent chapters.)
(You will learn other area formulas for a triangle in subsequent chapters.)
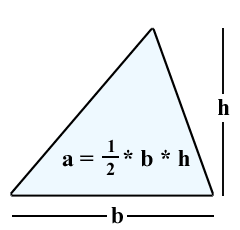
61
New cards
Area of a Parallelogram
A = bh, where b = base, and h = height
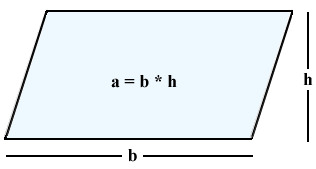
62
New cards
Area of a Rectangle
A = bh, where b = base, and h = height
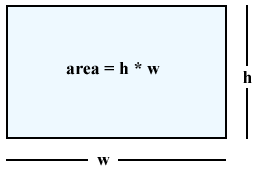
63
New cards
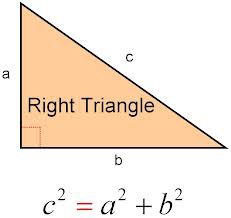
Pythagorean Theorem
In a right triangle, where a and b are legs, and c is the hypotenuse, a^2 + b^2 = c^2.
64
New cards
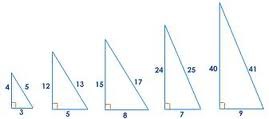
Pythagorean Triples
Three whole numbers that make the Pythagorean Theorem equation true.
65
New cards
Circles
The set of all points in a plane that are a given distance (radius) from a given point (center.)
66
New cards
Center of a circle
The point about which all points of a circle are equidistant. The circle is usually named by its center.
67
New cards
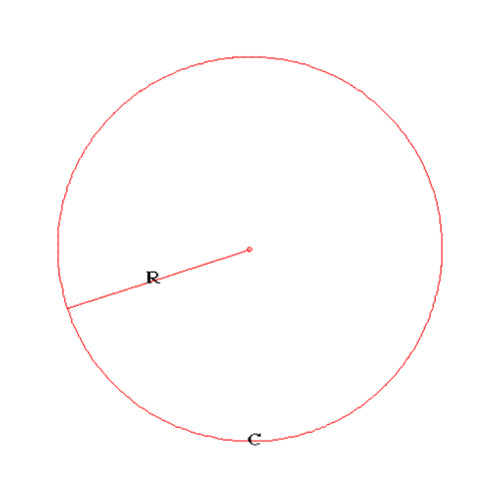
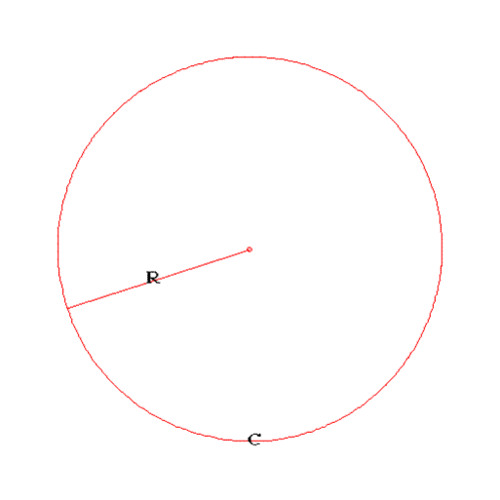
Radius
The distance from the center point to any point on the circle. OR The segment that joins the center point to any point on the circle.
68
New cards
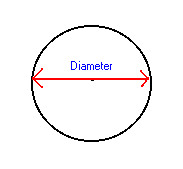
Diameter
The longest chord or a circle. OR The length of the chord that passes through the center of a circle.
69
New cards
Circumference of a Circle
The distance around a circle. C = d(pi), where d = diameter. OR C = 2r(pi), where r = radius
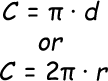
70
New cards
Area of a Circle
The two-dimensional space within the boundary of a circle. A = (r^2)(pi) where r = radius